Dongyu Qu, director general of the FAO (center left) with Rafael Mariano Grossi, director general of the IAEA and Najat Mokhtar, deputy director general and head of the IAEA Department of Nuclear Sciences and Applications (far right) on the sidelines of the World Food Forum. (Photo: D. Calma/IAEA)
The International Atomic Energy Agency and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations launched Atoms4Food on October 18 at the 2023 World Food Forum in Rome as a flagship initiative to help boost food security and tackle growing hunger around the world. Atoms4Food will support countries as they apply nuclear techniques to boost agricultural productivity, reduce food losses, ensure food safety, improve nutrition, and adapt to the challenges of climate change.
McMaster University’s Ousmane Hisseine is investigating how novel concrete materials can make SMRs safer. (Photo: McMaster University)
Ousmane Hisseine, an assistant professor of civil engineering at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, is using his expertise in concrete infrastructure in hopes of improving the safety of small modular reactors.
Concept art of a nuclear thermal propulsion system. (Image: USNC)
Ultra Safe Nuclear (USNC) announced on October 17 that it had been awarded a contract by NASA to develop and mature space nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) systems to advance the nation’s cislunar capabilities. Under the contract, USNC says it will manufacture and test proprietary fuel and simultaneously collaborate with its commercial partner, Blue Origin, to mature the design of an NTP engine optimized for near-term civil science and cislunar missions.
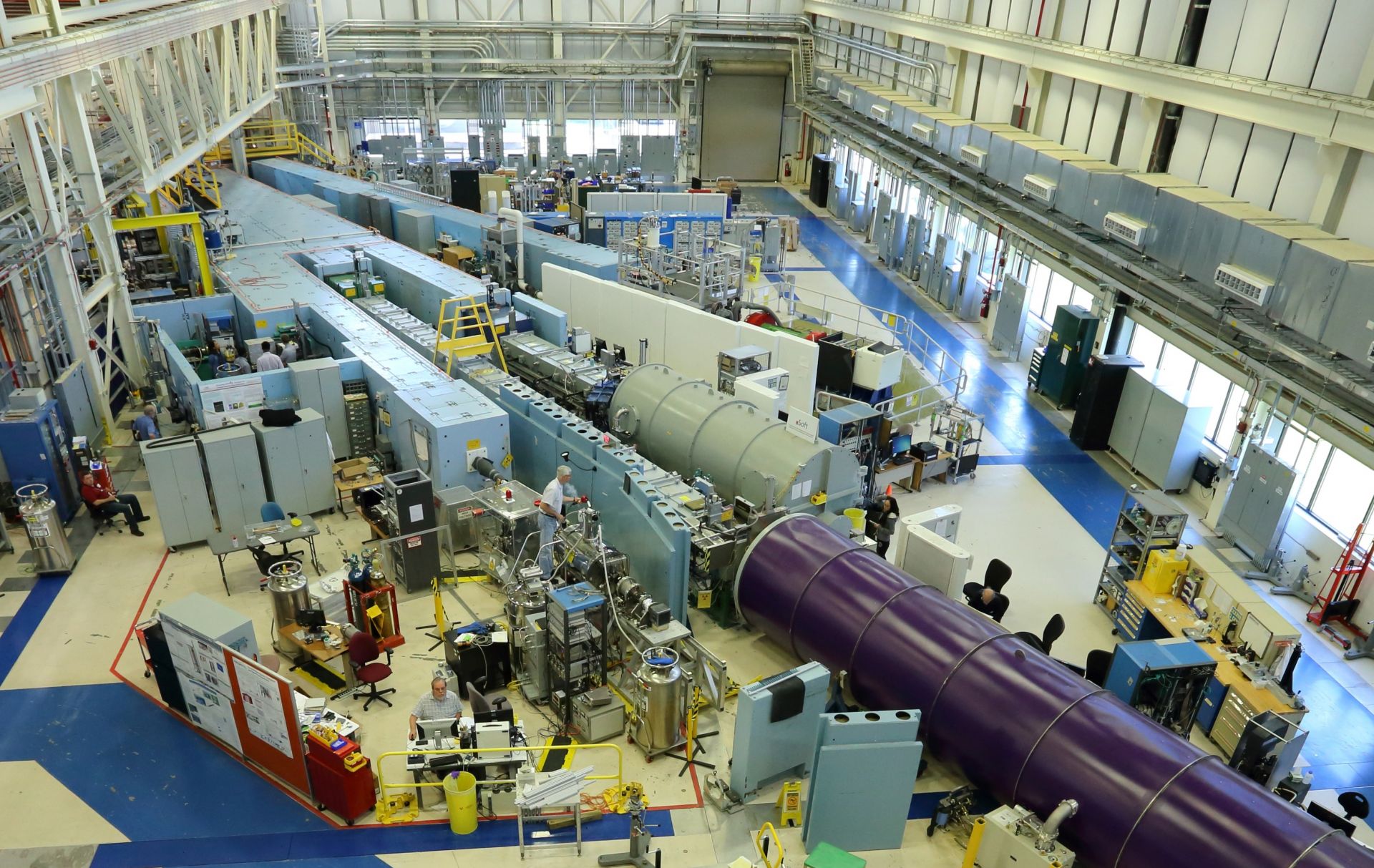
Idaho National Laboratory's TREAT reactor. (Photo: INL)
Researchers at Idaho National Laboratory have a new experimental tool to study nuclear fuel under simulated loss of coolant accident (LOCA) conditions in INL’s Transient Reactor Test (TREAT) Facility. A specialized experiment holder called a TWIST capsule holds a fuel sample surrounded by water, which can rapidly drain away during testing, simulating loss of coolant in a light water reactor environment.
A view of the NCNR guide hall, featuring the 30-meter Small Angle Neutron Scattering instrument. (Photo: NIST)
Following the February 2021 radiation release at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) resulting from a fuel failure in the 20-MWt NIST Center for Neutron Research (NCNR) research reactor, NIST investigated the root cause of the incident and developed corrective actions. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s probe of the incident found apparent violations and resulted in a confirmatory order issued in August 2022.
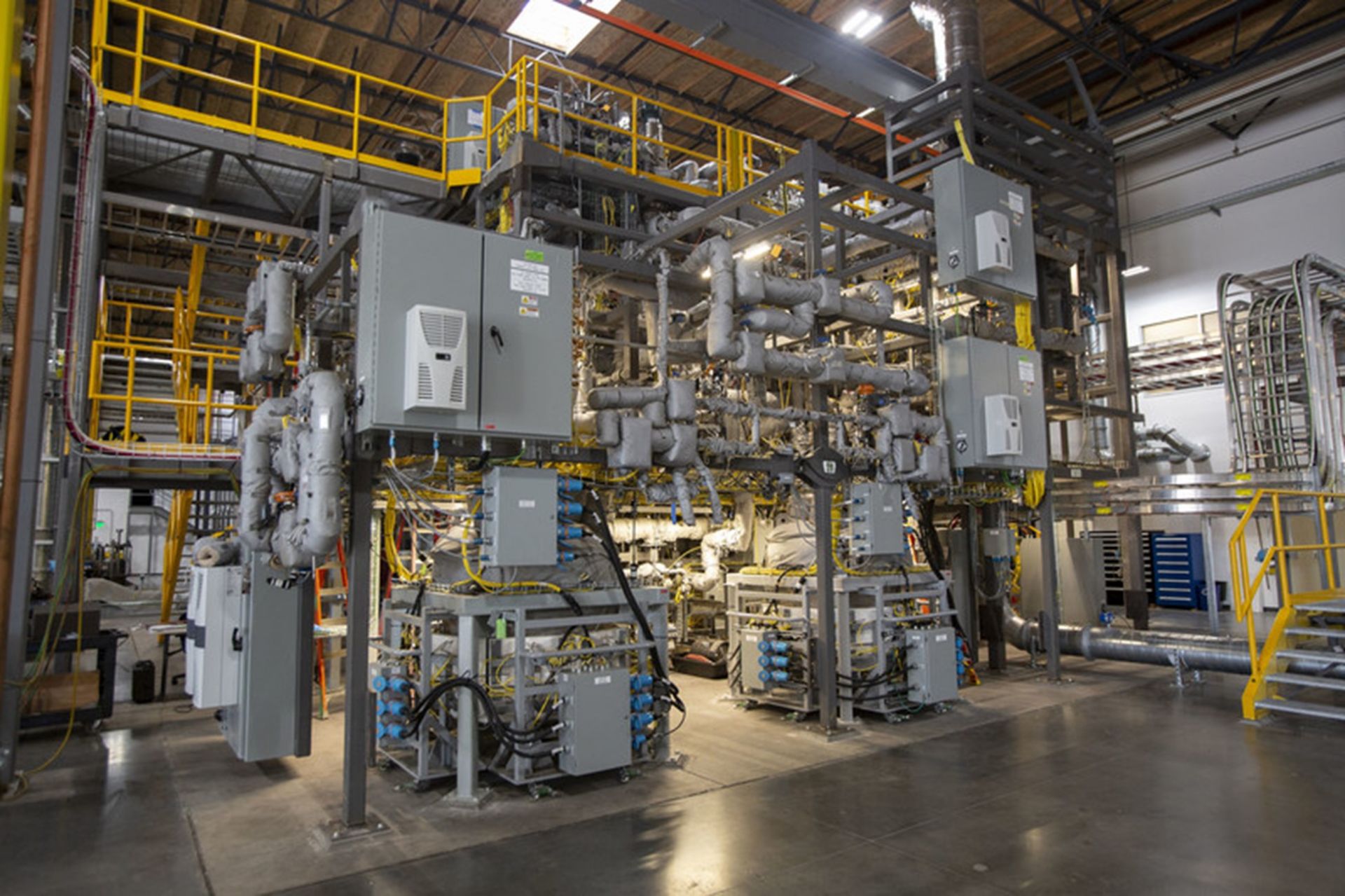
The Integrated Effects Test at TerraPower’s laboratory in Everett, Wash. (Photo: Southern Company/TerraPower)
Southern Company, TerraPower, and Core Power (a U.K.-based firm focused on developing nuclear technologies for the maritime sector) have commenced pumped-salt operations in the Integrated Effects Test (IET) facility, the Atlanta, Ga.-based utility announced Tuesday, marking another milestone in the development of TerraPower’s first-of-a-kind, Generation IV Molten Chloride Fast Reactor (MCFR).
The electrically heated PCAT replica of the MARVEL microreactor is installed and ready for testing at CEI’s facility in Pennsylvania. (Photo: DOE)
While initial operation of MARVEL, a tiny microreactor that will be installed and operated inside Idaho National Laboratory’s Transient Reactor Test (TREAT) Facility, might not occur until 2025, testing of a nonnuclear prototype is now under way at the New Freedom, Pa., manufacturing facility of Creative Engineers, Inc. (CEI). The Department of Energy announced the start of prototype testing on September 20.
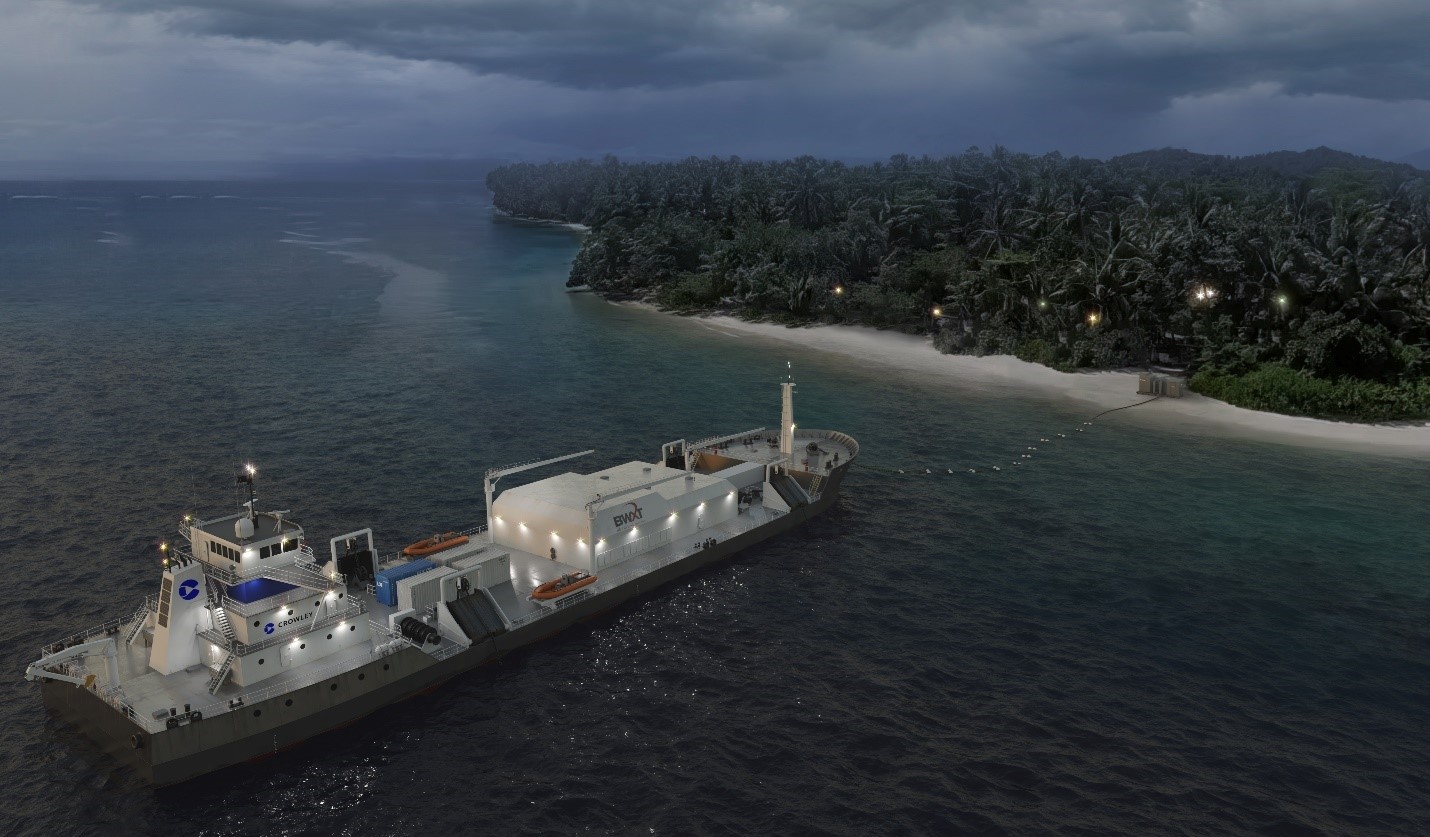
Conceptual art of the Crowley-designed ship with a BWXT microreactor onboard. (Image: BWXT)
BWX Technologies is teaming with Crowley, a global shipping and energy supply chain company, under a memorandum of understanding to develop a ship with an onboard microreactor that could deliver power to users on shore via buoyed power cables. The concept, announced by both companies on September 20, is envisioned as a zero-carbon energy option for defense and disaster needs.
Conceptual art of a direct air capture CO2 removal system. (Image: DOE)
Given how much carbon dioxide has been released into the atmosphere from fossil fuels, replacing those fuels with clean options like nuclear energy is urgent, but could be likened to shutting the barn door after the proverbial horse has bolted. But what if you could also round up excess CO2 already in the atmosphere? That’s the goal of direct air capture (DAC) and other so-called negative emission technologies—to capture climate warming CO2 for use in products or processes or for permanent storage.