It’s Hydrogen Day—and yes, that has a lot to do with nuclear

If you’re hearing for the first time that October 8 is Hydrogen Day, you might be wondering, “Why October 8?” and “What’s the connection to nuclear?”
ANS Nuclear Newswire has the answers.


If you’re hearing for the first time that October 8 is Hydrogen Day, you might be wondering, “Why October 8?” and “What’s the connection to nuclear?”
ANS Nuclear Newswire has the answers.

Arizona Public Service is the latest nuclear utility with confirmed plans to install hydrogen production capacity, an investment decision that is based on analysis conducted under the Department of Energy’s H2@Scale program and backed by a $20 million DOE award.

The Hungarian office of Framatome this week signed a memorandum of understanding with Budapest-based research and economic development company Hunatom and the University of Dunaújváros to work together supporting nuclear education and training, research and development, and implementation of new technologies for Hungary and surrounding countries.
Representatives of the three organizations signed the MOU during a ceremony at Hungary’s University of Dunaújváros, about 40 miles south of Budapest.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is relinquishing its licensing authority for exports of deuterium for nonnuclear use to the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security. The NRC said that the change reflects the growing peaceful use of deuterium, including heavy water, as well as deuterium gas and deuterium or deuterated compounds, for nonnuclear industrial and research activities.

The U.K. government has just published Towards Fusion Energy: The UK Government’s Fusion Strategy, which sets out the goal of the United Kingdom's moving from “a fusion science superpower to a fusion industry superpower,” with a prototype fusion power plant being built in the country by 2040.
While a slightly ambitious plan, there are now about 20 startup companies working to achieve a Wright brothers’ moment in fusion sooner than that. This includes Commonwealth Fusion Systems, which is aiming for a working fusion power plant by 2030 and is the subject of Rivka Galchen’s October 4 New Yorker article, “Can Nuclear Fusion Put the Brakes on Climate Change?”

Therapeutic radiation is typically reserved for cancer treatment, but scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have applied radiation therapy to treat ventricular tachycardia, a life-threatening heart arrhythmia. A news release issued by the university says that the results of the study show that radiation therapy can “reprogram” heart muscle cells to “a younger and perhaps healthier state.” The findings were published in the journal Nature Communications on September 24.
Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL) last week issued a call for proposals for the third round of its Canadian Nuclear Research Initiative (CNRI) program.
More information about the program, including application details, can be found online.
Only a few of the more than 3,000 radioisotopes that scientists have synthesized in the laboratory are regularly used in diagnostic or therapeutic medicine. One significant barrier to the development of new medical radioisotopes is the difficulty of gaining access to radionuclides during the early stages of development and research. PRISMAP is a new medical radionuclide program designed to streamline that access for medical research in the European Union and the United Kingdom.

The fight against plastics pollution using nuclear technology will be bolstered by a $1 million contribution from the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration to the International Atomic Energy Agency.

By 2030, Kairos Power aims to demonstrate electricity production from a full-scale, 140-MWe fluoride salt–cooled high-temperature reactor, the KP-X. In service of that goal, Kairos plans to demonstrate Hermes, a scaled-down 35-MWth nonpower reactor, in Oak Ridge, Tenn.
Hermes is being built to “prove our ability to deliver affordable nuclear heat,” said Mike Laufer, Kairos Power chief executive officer and cofounder, as he explained Kairos’s plans to the local community during a September 28 webinar now available to view on demand. Laufer took questions, and Kairos took the opportunity to introduce a virtual open house that visitors can tour to view videos and interactive features and even submit comments.

Bruce Power has received approval from the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) to begin the production of lutetium-177, becoming the first power reactor globally to commercially produce the medical radioisotope. Isogen, a joint venture between Framatome and Kinectrics, will produce Lu-177 at Bruce’s eight-unit CANDU nuclear power plant in Ontario, Canada, using Isogen’s isotope production system (IPS).
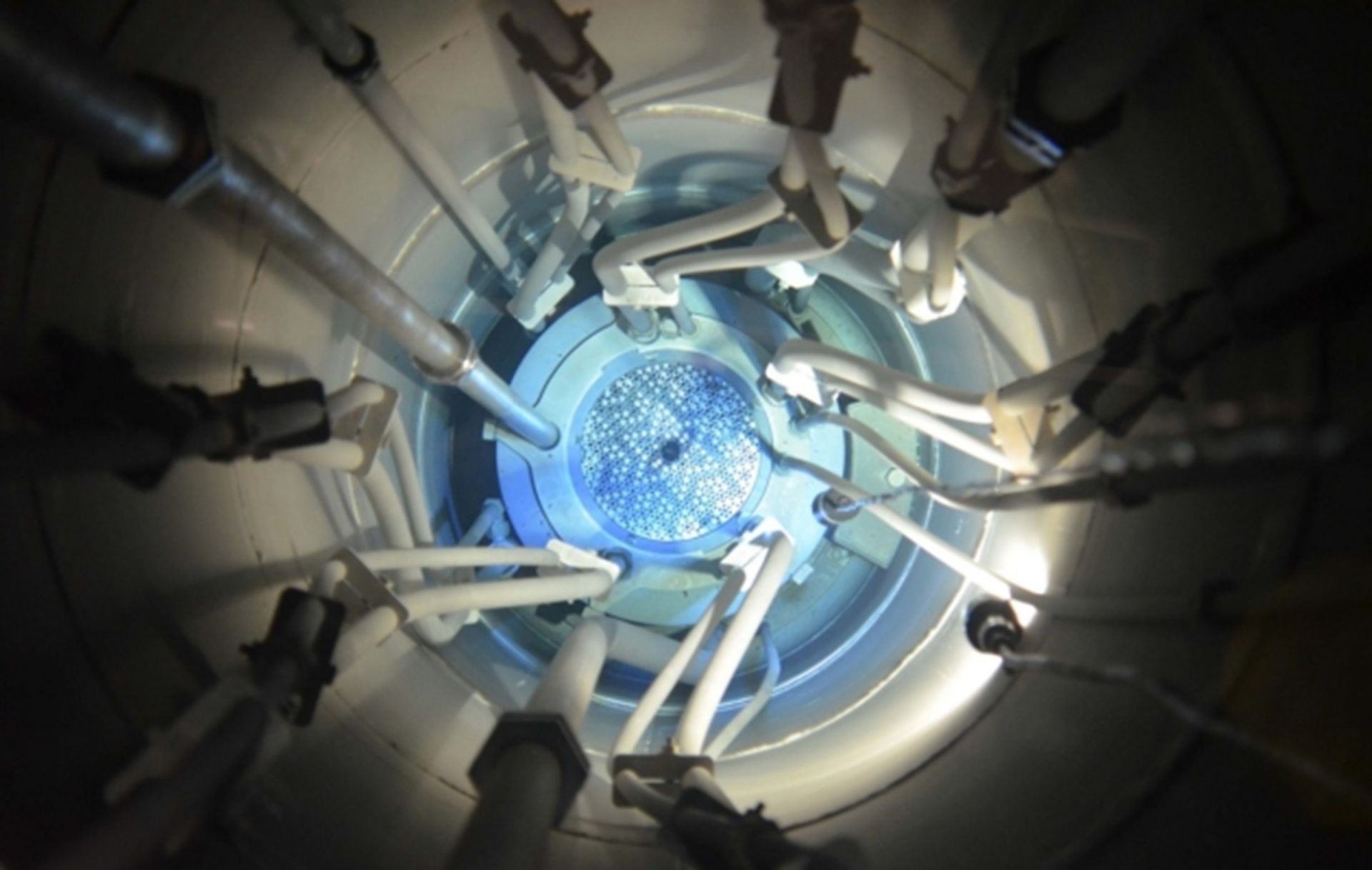

Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL) announced on September 23 that it had refueled the SLOWPOKE-2 research reactor at the Royal Military College of Canada (RMC) in Kingston, Ontario. The reactor was recommissioned on September 10 after a 22-day outage.
Plans to test a prototype mobile microreactor designed to military requirements moved ahead when the Department of Defense (DOD), acting through its Strategic Capabilities Office and with the Department of Energy serving as a cooperating agency, on September 16 announced the availability of a draft environmental impact statement for the construction and demonstration phase of Project Pele.
. of OPG, and Michael Lefebvre, of Laurentis Energy Partners, examine tew He-3 extraction tool installed at Darlington NPP.jpg)
Laurentis Energy Partners, a subsidiary of Ontario Power Generation (OPG), has launched a new program to produce helium-3. The He-3 will be obtained from tritium stored at OPG’s Darlington nuclear power plant, a four-unit CANDU station located about 100 kilometers east of Toronto.
Darlington houses one of the world’s largest reserves of tritium, which is a by-product of the heavy water used in CANDU reactors.
Paul Dabbar, former undersecretary for science at the Department of Energy and distinguished visiting fellow at Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy, is lauding the recent successful test of a 10-ton high-temperature superconducting magnet performed by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Commonwealth Fusion Systems. In an op-ed published on September 10 in The Hill, Dabbar calls for a new level of investment and support for the commercial fusion sector.

A high-temperature superconducting magnet reached and maintained a magnetic field of more than 20 tesla in steady state for about five hours on September 5 at MIT’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center. Not only is the magnet the strongest high-temperature superconducting (HTS) magnet in the world by far, it is also large enough—when assembled in a ring of 17 identical magnets and surrounding structures—to contain a plasma that MIT and Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS) hope will produce net energy in a compact tokamak device called SPARC in 2025, on track for commercial fusion energy in the early 2030s.

In the aftermath of a devastating explosion in the port of Beirut, Lebanon, in August 2020, an International Atomic Energy Agency team visited the country at the government’s request and found no evidence of artificial radionuclides and no increase in radiation levels. The powerful blast, which was caused by an explosion of improperly stored ammonium nitrate, killed more than 200 people and leveled numerous buildings while leaving other buildings standing with possible structural damage. The IAEA recently announced that a different team of experts has traveled to Lebanon with a new mission: to assist the nation in the use of non-destructive testing (NDT) to check the structural soundness of buildings that were impacted by the explosion.

The Center for Advanced Energy Studies (CAES) has announced the opening of the Small Modular Reactor Simulator Laboratory, featuring NuScale Power’s Energy Exploration Center, at its headquarters in Idaho Falls, Idaho. The new lab will increase CAES’s capabilities to train future scientists, engineers, and members of the energy workforce and will be used to educate the public about nuclear energy and reactor technology, according to an August 31 CAES press release.

Inside the ITER Assembly Hall, aided by a 20-meter-tall sector subassembly tool known as SSAT-2, the first of nine 40-degree wedge-shaped subassemblies that will make up the device’s tokamak is taking shape. On August 30, the ITER Organization announced that all the components of the first subassembly were in place on the SSAT-2. After the wings of the subassembly tool slowly close, locking two vertical coils in place around the outside of a vacuum vessel section that is already wrapped in thermal shielding, the completed subassembly will be ready for positioning in the ITER assembly pit in late October.

Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have been expanding MELCOR—the severe accident modeling computer code used by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to evaluate the safety of light water reactors—to study the small modular reactors and non-light-water advanced reactors that are under development. An article published in Sandia Lab News on August 27 describes in detail how MELCOR is being expanded to work with different reactor geometries, fuel types, and coolant systems.