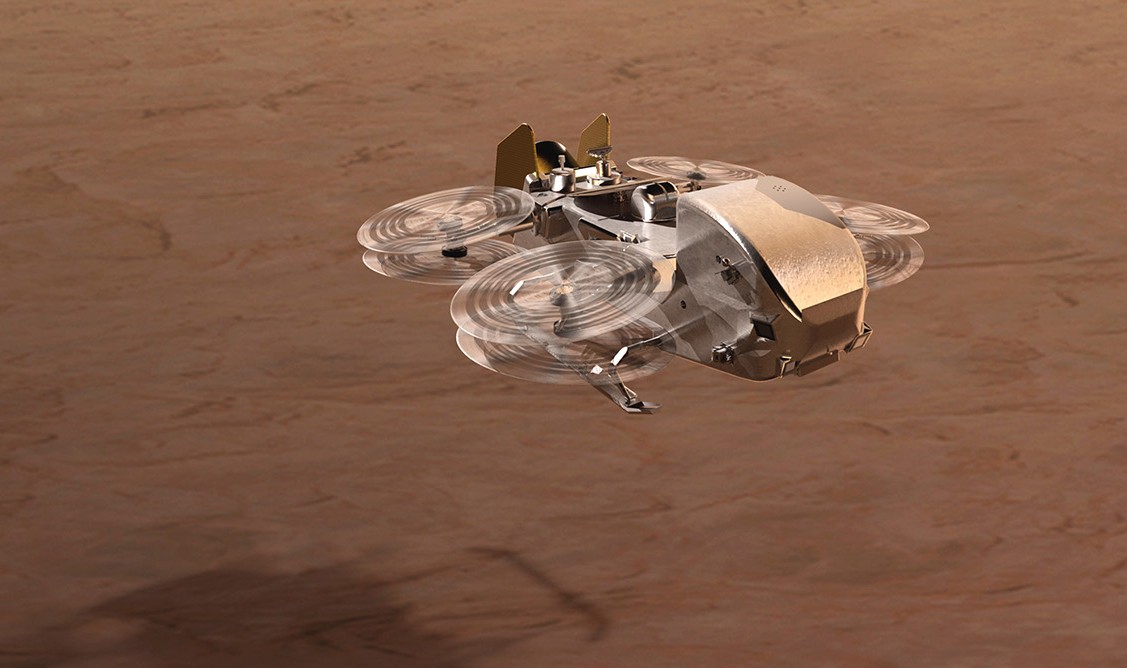
Artist’s impression of NASA’s Dragonfly approaching a landing site on Saturn’s moon Titan. Essentially a flying chemistry lab, along with cameras and other science instrumentation, Dragonfly will travel between dozens of landing sites on Titan’s surface to investigate the chemical origins of life. (Image: NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Steve Gribben)
Curiosity landed on Mars sporting a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) in 2012, and a second NASA rover, Perseverance, landed in 2021. Both are still rolling across the red planet in the name of science. Another exploratory craft with a similar plutonium-238–fueled RTG but a very different mission—to fly between multiple test sites on Titan, Saturn’s largest moon—recently got one step closer to deployment.
On April 25, NASA and the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) announced that the Dragonfly mission to Saturn’s icy moon passed its critical design review. “Passing this mission milestone means that Dragonfly’s mission design, fabrication, integration, and test plans are all approved, and the mission can now turn its attention to the construction of the spacecraft itself,” according to NASA.
The nuclear fuel reprocessing plant product store at Sellafield. (Photo: NDA)
The United Kingdom’s Nuclear Decommissioning Authority has announced that it will establish a Plutonium Ceramics Academic Hub with the Universities of Manchester and Sheffield. The announcement follows a decision by the U.K. government in January to immobilize the country’s inventory of civil separated plutonium at the Sellafield nuclear site, mitigating the material’s long-term safety and security risks.
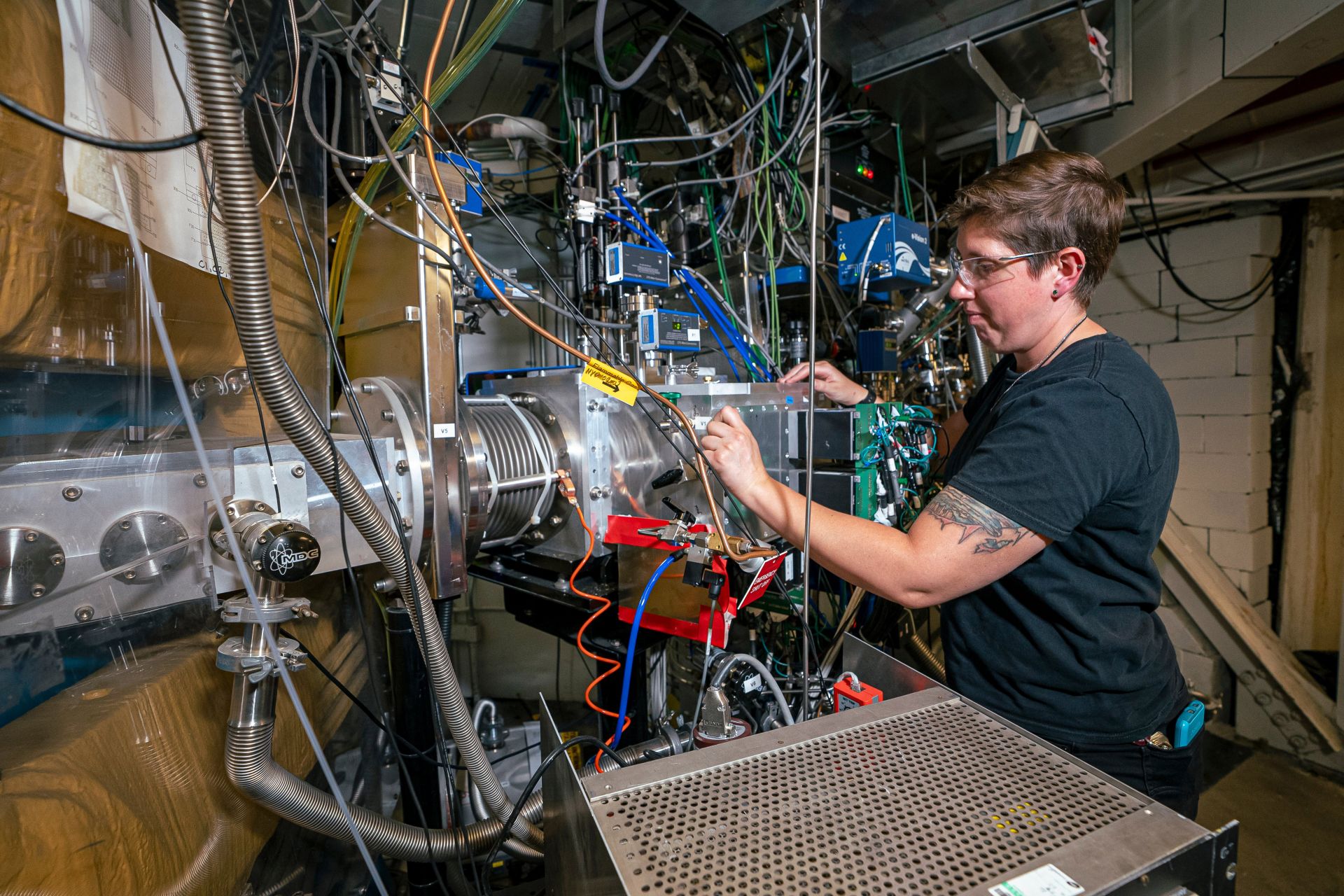
Scientist Jacklyn Gates at the Berkeley Gas-filled Separator used to separate atoms of element 116, livermorium. (Photo: Marilyn Sargent/Berkeley Lab)
A plutonium target bombarded with a beam of titanium-50 in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory’s 88-Inch Cyclotron for 22 days has yielded two atoms of the superheavy element 116, in a proof of concept that gives Berkeley Lab researchers a path to pursue the heaviest element yet—element 120. The result was announced July 23 at the Nuclear Structure 2024 conference; a paper has been submitted to the journal Physical Review Letters and published on arXiv.
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are investigating the details of plutonium chemistry with the goal of aiding the cleanup of the Hanford Site in Washington state. For more than 40 years, reactors located at Hanford produced plutonium for America’s defense program, resulting in millions of gallons of liquid radioactive and chemical waste.
The exterior of the Clementine nuclear reactor at Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. (Photo: LANL)
In March 1949—75 years ago this month—the 25-kilowatt reactor known as Clementine reached full power. As an experimental reactor, it had a rather long and successful run. It was the world’s first fast neutron (high-energy) reactor and operated from initial criticality in 1946 to final shutdown in 1952.
ORNL has developed an automated metrology system to produce Pu-238 pellets. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy recently shipped half a kilogram of plutonium oxide pellets from Oak Ridge National Laboratory to Los Alamos National Laboratory, the agency announced July 18, marking the largest such shipment since the DOE restarted domestic plutonium-238 production over a decade ago.
NETS participants are credited with helping relaunch the nation’s domestic production of Pu-238 to fuel the Mars Perseverance rover. (Photo: NASA)
Connecting nuclear engineers and scientists with space exploration missions has been a focus of the American Nuclear Society’s Aerospace Nuclear Science and Technology Division since its creation in 2008. One of the main ways those connections are made is through the Nuclear and Emerging Technologies for Space (NETS) conference, which the division supports in conjunction with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
ORNL’s Benjamin Manard places a swipe on the extraction stage of Advion’s Plate Express, a microextraction tool that has been paired with a mass spectrometer. (Photo: Carlos Jones/ORNL, DOE)
International nuclear safeguards verification relies on a precise count of isotope particles collected on swipes during International Atomic Energy Agency inspections of nuclear facilities and isolated through a series of lengthy chemical separations that can take about 30 days to complete. On October 15, Oak Ridge National Laboratory—a member of the IAEA’s Network of Analytical Laboratories (NWAL)—announced that analytical chemists at the site have developed a faster way to measure isotopic ratios of uranium and plutonium collected on swipes, which could help IAEA analysts detect the presence of undeclared nuclear activities or material.
The Plutonium Facility at Los Alamos National Laboratory. (Photo: LANL)
The Defense Nuclear Facility Safety Board, which provides independent federal oversight of Department of Energy weapons facilities, has reported that low-level radioactive and other combustible waste is accumulating in the basement of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s Plutonium Facility (PF-4), and that housekeeping and waste management in the PF-4 basement have been a continuing challenge.
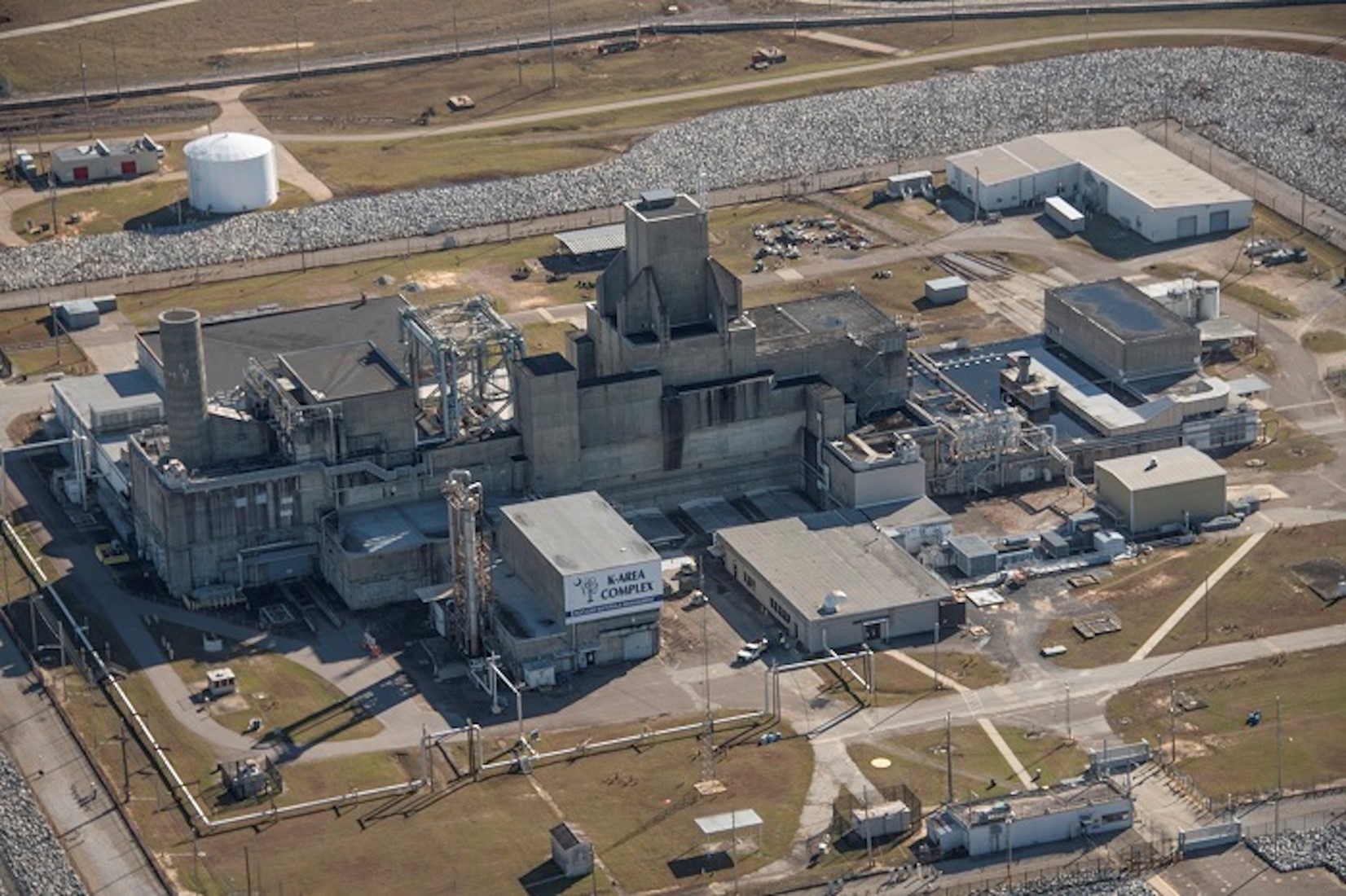
A view of Savannah River’s K Area Complex, where plutonium downblending operations take place. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management has doubled the number of work shifts for employees in glove box operations at its Savannah River Site in South Carolina. The increased work pace will help the department meet its commitment to South Carolina to remove surplus plutonium from the state, the DOE said.
A loaded waste container at the site of the former Plutonium Finishing Plant is surveyed to ensure that it is safe for transfer to Hanford’s on-site disposal facility. (Photo: DOE)
Final cleanup activities at the Hanford Site’s demolished Plutonium Finishing Plant have resumed following a pause in work prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the Department of Energy announced. Crews with the DOE’s Richland Operations Office and site contractor Central Plateau Cleanup Company will remove, package, and dispose of rubble remaining from the demolition of the plant’s plutonium reclamation facility, which was torn down in 2017.
Video still showing samples of red trinitite. (Source: University of Florence)
The world’s first atomic bomb test—code-named Trinity and conducted in New Mexico on July 16, 1945—had an unintended outcome that was only recently discovered.

-3 2x1.jpg)







 Research into the high-resolution detection of plutonium mixtures by Purdue University professor Rusi Taleyarkhan and his team was featured on the cover of the February issue of the Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectroscopy, published by the British Royal Society of Chemistry.
Research into the high-resolution detection of plutonium mixtures by Purdue University professor Rusi Taleyarkhan and his team was featured on the cover of the February issue of the Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectroscopy, published by the British Royal Society of Chemistry.





