Concept art of Oklo's Aurora Powerhouse in use. (Source: Oklo)
Next-generation reactor company Oklo Inc. is teaming up with Diamondback Energy Inc. to bring Oklo’s Aurora Powerhouse units to the American Southwest.
The companies signed a nonbinding letter of intent (LOI) this week to collaborate on a 20-year power purchase agreement that would provide 50 MW of electricity per unit to Diamondback’s Permian Basin operations area. The agreement lays out options to renew and extend the agreement for an additional 20-year term, since the units are designed to operate for 40 years without needing to refuel. Diamondback is an independent oil and gas company headquartered in Texas.
As part of its DUF6 conversion program, the DOE is shipping converted depleted uranium oxide to WCS for disposal.
The first major shipment of depleted uranium oxide for disposal departs the DOE’s Paducah Site in Kentucky in early 2023 for disposal at the WCS facility in Texas.
Last year in late August, 120 storage cylinders of depleted uranium oxide (DUOx) safely arrived by rail in West Texas, having been shipped from the Department of Energy’s Portsmouth Site in Ohio. It was the first such shipment of the stable crystalline powder from the Portsmouth Site and was another milestone in the DOE Office of Environmental Management’s (EM) efforts to ship DUOx for off-site disposal.
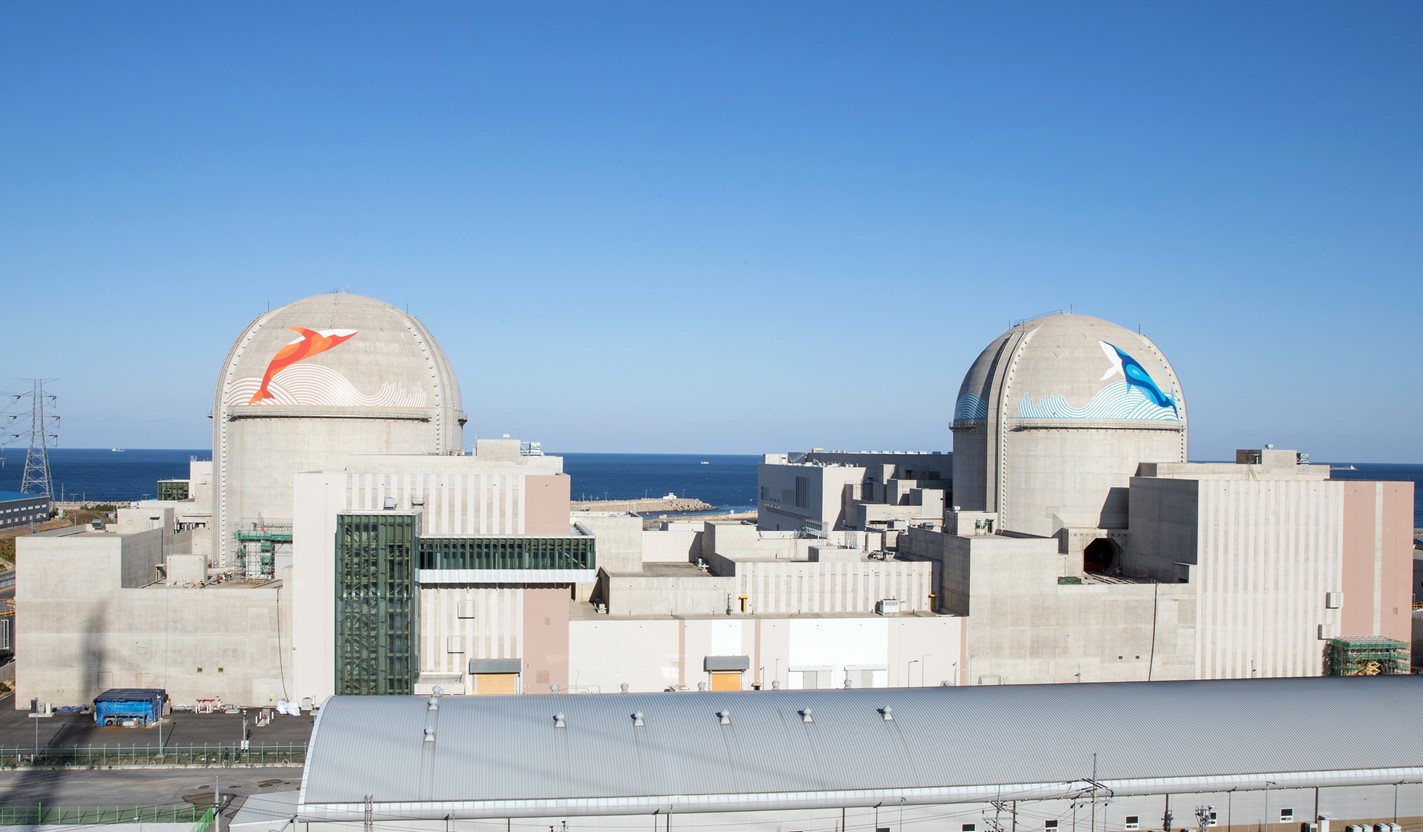
South Korea’s Shin-Hanul-2 is on the right, with Unit 1 to the left. (Photo: KHNP)
Unit 2 of South Korea’s Shin-Hanul nuclear power plant entered commercial operation on April 5, Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power announced. It is the nation’s 26th operating reactor, which continues the upward nuclear trend as South Korea reverses a previous phase-out plan for nuclear.
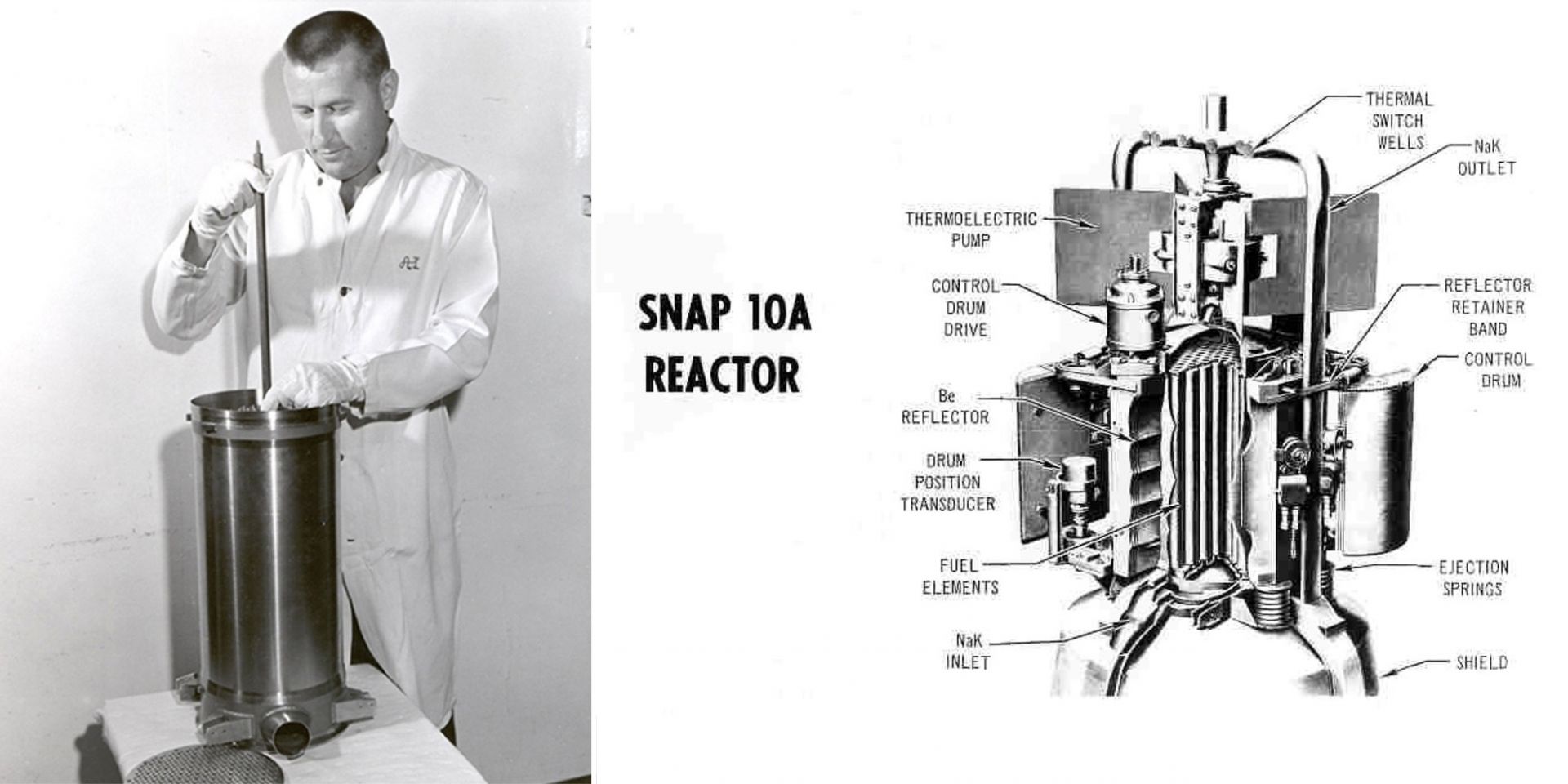
Left: A technician inserts a steel tube containing fuel into the SNAP-10A reactor core vessel. (Photo: DOE) Right: A cross-section view of the reactor. (Image: DOE)
Systems for Nuclear Auxiliary Power (SNAP) was an Atomic Energy Commission program with the goal of producing a portable and dependable power source centered around nuclear technology that could be utilized in land, sea, and space applications. The program aimed to provide a compact reactor—a necessity for space applications—and ran from 1955 until 1973, when it was discontinued.
In Curaçao, IAEA experts built national capacity through demonstrations, including practicing removing the Ra-226 source from the container, characterizing it, and placing it into a stainless-steel capsule. (Photo: IAEA)
Once used for applications in medicine, industry, and research, many countries now have legacy radium-226 sources, according to the International Atomic Energy Agency. With the support of the IAEA’s technical cooperation program, these disused sealed radioactive sources are being recovered, and countries are improving national capacities for their long-term management, including their potential reuse and recycling.
SRMC’s Dave Olson (left) presents a $10,000 check to Voorhees University president Ronnie Hopkins. (Photo: SRMS)
Savannah River Mission Completion (SRMC), the liquid waste contractor at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site, recently presented a $10,000 check to Voorhees University to fund science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) scholarships.
Upgrades are under way at the Hanford Site's 222-S Laboratory, including replacing the Cold War-era windows in the labs hot cells. Photo: DOE)
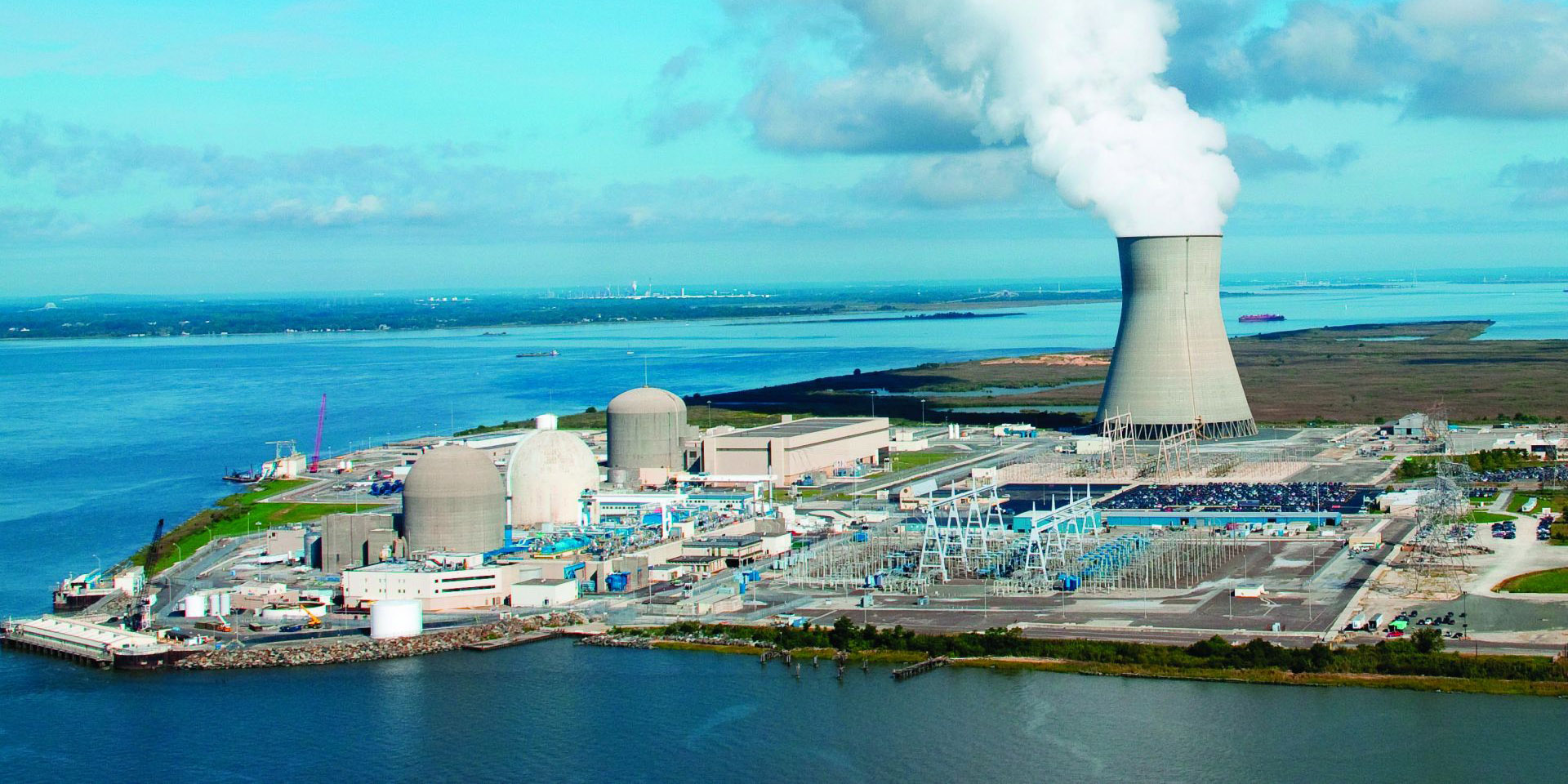
The Hope Creek and Salem nuclear power plants. (Photo: PSE&G)
PSEG Nuclear LLC announced this week it will pursue subsequent license extensions to keep the three reactors at its Hope Creek and Salem plants operating for an additional 20 years. Both plants had been granted initial life extensions years ago by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Salem-1 and -2 on June 30, 2011, and Hope Creek on July 20, 2011.