The Prairie Island nuclear power plant. (Photo: Xcel Energy)
Clean energy technology firm Bloom Energy has announced plans to install a 240-kW electrolyzer at Xcel Energy’s Prairie Island plant in Red Wing, Minn., to demonstrate the benefits of producing hydrogen with nuclear power. (One of Xcel’s two nuclear plants, Prairie Island houses twin 550-MWe pressurized water reactors.)
Spain’s nuclear power plants are to use Holtec’s HI-STORM spent fuel storage technology. (Image: Holtec)
Holtec International announced that its flagship HI-STORM Multi-Purpose Canister (MPC) spent fuel storage technology was selected by Spain’s national company Enresa for a fleet of six nuclear power reactors at four plant sites in the country. Equipos Nucleares S.A. (ENSA), a Cantabria-based manufacturer of equipment for the Spanish nuclear fleet, was named a consortium partner with Holtec in the order, which was conducted under European Union procurement rules.
Highlights from Chairman Hanson’s visit with the ANS student section at UPRM. (Photos: NRC/Twitter)
The American Nuclear Society student section at the University of Puerto Rico—Mayagüez (UPRM) recently welcomed Christopher T. Hanson, chairman of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. While at UPRM, Hanson met with graduate students conducting nuclear-related research, as well as with deans, professors, and other university officials. He also delivered a speech, “Preparing to Regulate the Nuclear Technology of the Future.”
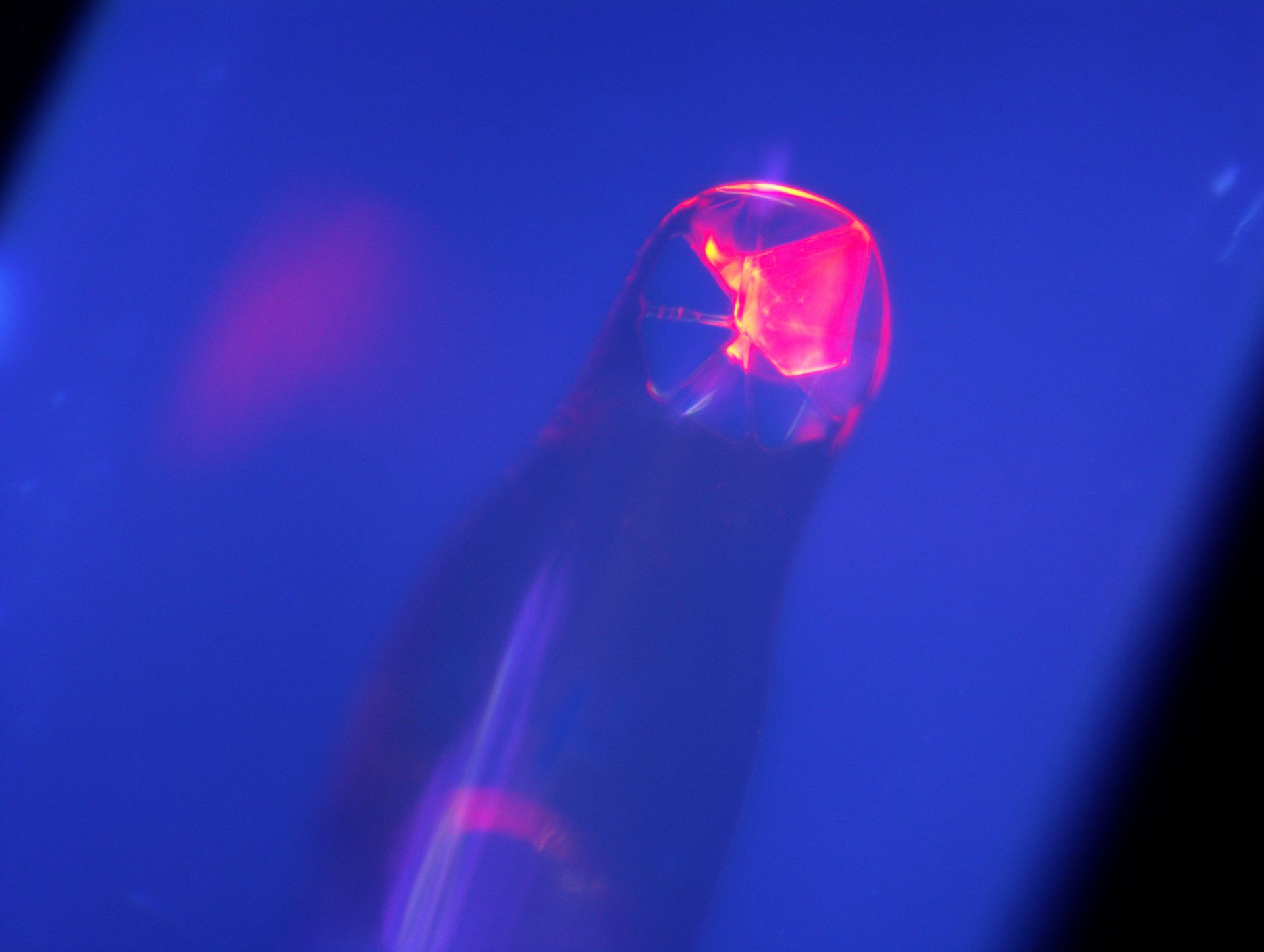
A new compound of curium photographed at LLNL during crystallography experiments. Crystals of this curium compound are uncolored under ambient light but glow an intense pink-red when exposed to ultraviolet light. (Image: LLNL/Deblonde)
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and Oregon State University (OSU) have developed a promising new method to isolate and study some of the rarest elements on Earth. Focused first on curium, they have identified three new complexes containing curium ions and revealed the molecules’ 3D structures, as well as previously unknown features.
How Kairos Power is applying rapid iterative development to the licensing process as part of its strategy to deliver on cost

Laufer
Developing a first-of-a-kind reactor is a daunting endeavor. To be successful, advanced reactor designers need to achieve cost certainty by delivering a safe and affordable product at the promised cost. To meet this goal, Kairos Power structured its approach around four key strategies: 1) achieving technology certainty through a rapid iterative approach; 2) achieving construction certainty by demonstrating the ability to build it; 3) achieving licensing certainty by proving Kairos can license it; and 4) achieving supply chain certainty by vertically integrating critical capabilities. By mitigating risk in these four key areas, Kairos Power is confident that it will get true cost certainty for our future products.
The third prong in Kairos’s strategy—achieving licensing certainty—was a key driver in the decision to build the Hermes low-power demonstration reactor, and it remains a major workstream as the company’s construction permit application (CPA) undergoes review by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Licensing a new nuclear technology is no small challenge, and there are multiple approaches companies can take. Here’s a look at how we at Kairos are approaching it.
Members of the Paragon Energy Solutions, Reuter-Stokes, and NuScale Power teams during a recent visit to Reuter-Stokes’ global headquarters in Twinsburg, Ohio. (Photo: Reuter-Stokes)
Paragon Energy Solutions and Reuter-Stokes have signed a contract to design and manufacture neutron monitoring detectors for small modular reactor developer NuScale Power.
Queen Elizabeth II visits Calder Hall for its ceremonial opening in 1956. (Photo: U.K. Nuclear Decommissioning Authority)
As citizens of the United Kingdom and others around the world mourn the death of Queen Elizabeth II, many have reflected on how the world has changed during the seven decades of the queen’s reign—the same decades that saw the rise of civilian nuclear power.
Calder Hall was already under construction at the Sellafield site in West Cumbria when Princess Elizabeth became queen in 1953. Queen Elizabeth traveled to the site in October 1956 and declared, in a televised ceremony, that “It is with pride that I now open Calder Hall, Britain’s first atomic power station.” Watch the fanfare in a historical clip uploaded to YouTube by Sellafield Ltd below.
The Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant.
The International Atomic Energy Agency’s board of governors has adopted a resolution calling for an immediate end to the Russian occupation of Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant. According to a report from Reuters, the 35-member board voted 26–2 yesterday in favor of the resolution, with seven abstentions. The two “no” votes were cast, unsurprisingly, by Russia and China, while abstentions came from Burundi, Egypt, India, Pakistan, Senegal, South Africa, and Vietnam.
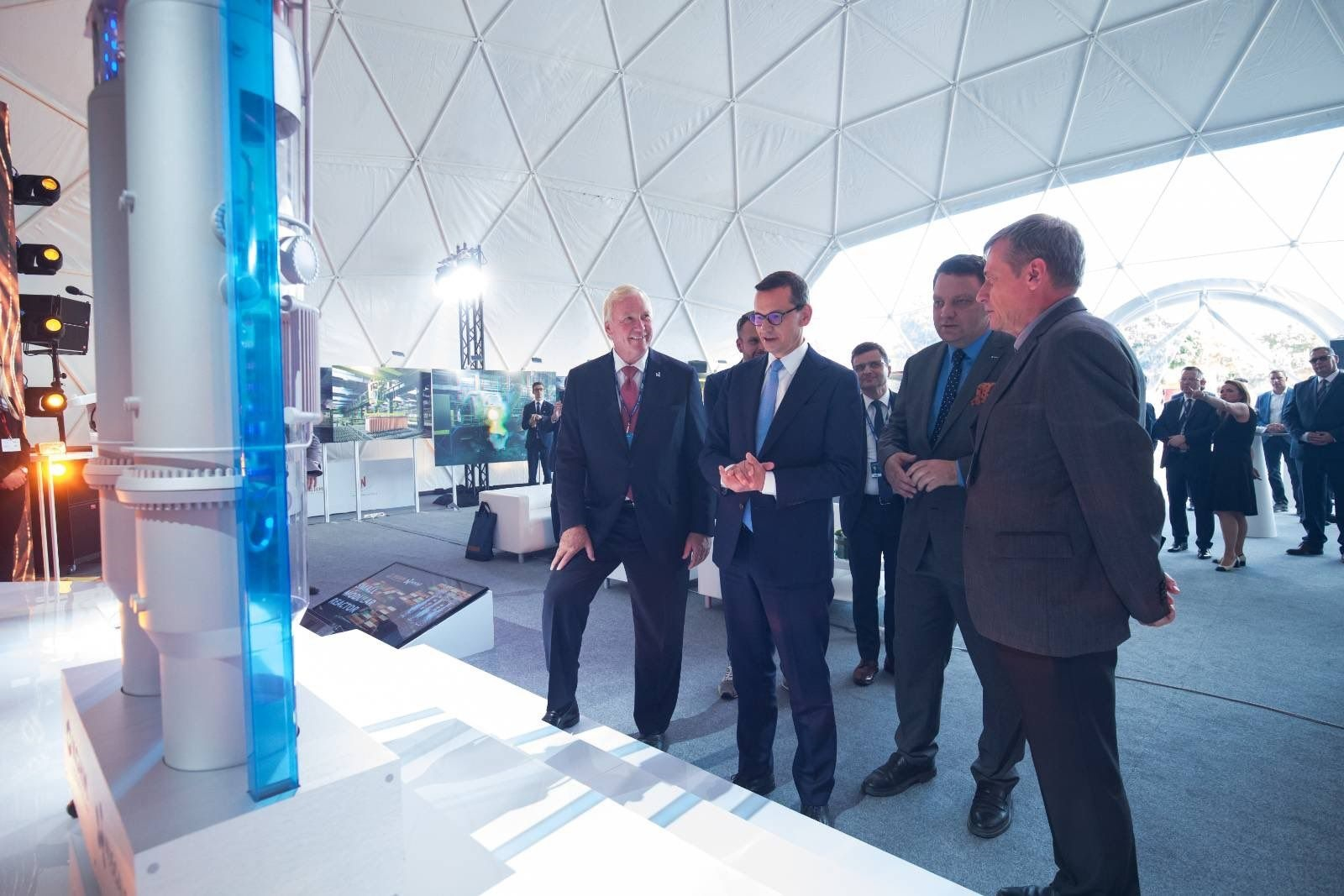
From left: NuScale president and CEO John Hopkins, Poland prime minister Mateusz Morawiecki, KGHM CEO Marcin Chludziński, and Ludwik Pieńkowski from AGH University of Science and Technology view a model of NuScale’s SMR technology. (Photo: Business Wire)
Portland, Ore.–based NuScale Power and KGHM Polska Miedź S.A. have signed the first task order and a statement of commencement to begin work under an agreement signed in February to initiate deployment in Poland of NuScale’s small modular reactor technology, the American firm announced this week. The task order was inked September 7 at the 31st Economic Forum, held September 6–8 in Karpacz, Poland.
Entergy’s Waterford nuclear plant, in Killona, La. (Photo: Entergy)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is increasing its oversight of the Waterford Steam Electric Station’s Unit 3 reactor due to a decade-long miscalibration of a radiation monitor.
In a September 13 letter to Entergy Operations, the NRC classified the issue at the Killona, La., facility as a “white finding”—agency parlance for a problem of low to moderate safety significance. (The NRC’s Reactor Oversight Process uses color-coded inspection findings and indicators to measure plant performance, starting at green and increasing to white, yellow, and red, commensurate with the safety significance of the issues involved.)





.png)