The NNSA's ERICA initiative aims to provide resources to develop resiliency against climate-related obstacles like the 2021 shuttering of the Pantex
Plant due to the polar vortex. (Image: NNSA)
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration is establishing an Energy Resilient Infrastructure and Climate Adaptation (ERICA) initiative, which will help position it to deal with climate issues. In a recent press release, the NNSA noted that ERICA will help it to meet the requirements of federal legislature and executive orders, along with the DOE’s climate adaptation, energy resilience, and sustainability goals in support of the agency’s national security missions.
The initiative was outlined in President Biden’s fiscal year 2023 budget request for the DOE.
Conceptual site layout for the VTR, as shown in the Final EIS. (Image: DOE-NE)
The Versatile Test Reactor, a custom-designed sodium-cooled fast neutron spectrum test reactor, is one step closer to its goal of providing data to accelerate research, development, and demonstration of diverse advanced reactor designs. The Department of Energy released the Final Versatile Test Reactor Environmental Impact Statement (Final VTR EIS) on May 13, and 30 days after its anticipated May 20 publication in the Federal Register, the DOE will issue a Record of Decision on the project.
PSFC director Dennis Whyte (left) and CFS chief executive officer Bob Mumgaard in the test hall at MIT’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center. (Photo: Gretchen Ertl, CFS/MIT-PSFC)
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC) recently announced it will expand its involvement in fusion energy research and education under a new five-year agreement with Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS), a fusion energy company that got its start at MIT and is now building what it says will be the world’s first net-energy fusion machine—the demo-scale SPARC.
“CFS will build SPARC and develop a commercial fusion product, while MIT PSFC will focus on its core mission of cutting-edge research and education,” said PSFC director Dennis Whyte in describing the collaboration.
Denmark’s Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy. The two cylindrical buildings outermost on the peninsula contained the two nuclear reactors DR-2 and DR-3. (Photo: DTU)
An independent review of Denmark’s radioactive waste management program by an International Atomic Energy Agency team found that the country has developed a robust and well-functioning system, but that the national program needs further refinement if it is to be effectively implemented.
The government of Denmark requested the review of its waste management program to fulfil its European Union obligations requiring an independent review of EU member states’ national radioactive waste management programs. The Danish parliament adopted a resolution outlining the policy goals and activities of its national program for safely managing radioactive waste and spent nuclear fuel in 2018.
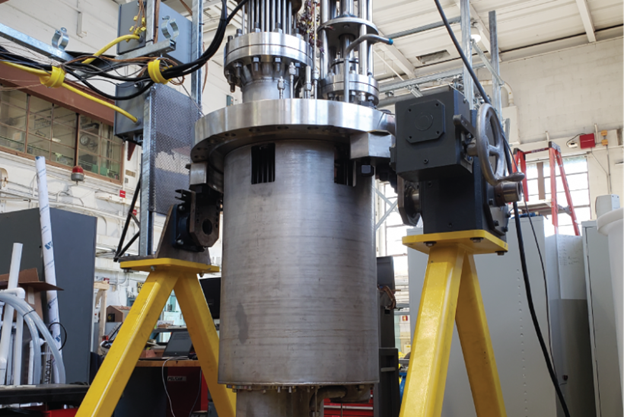
THETA pictured in Argonne National Laboratory’s METL lab. (Photo: ANL)
The Thermal Hydraulic Experimental Test Article (THETA) at Argonne National Laboratory is now operating and providing data that could support the licensing of liquid-metal fast reactor designs by validating thermal-hydraulic and safety analysis codes. The new equipment has been installed in Argonne’s Mechanisms Engineering Test Loop (METL), and its first experiments are supporting data validation needs of Oklo, Inc., by simulating normal operating conditions as well as protected and unprotected loss-of-flow accidents in a sodium-cooled fast reactor.
Energy Harbor’s Beaver Valley plant houses two reactors: Unit 1, a 939-MWe pressurized water reactor, and Unit 2, a 933-MWe PWR. (Photo: Energy Harbor)
Energy Harbor has signed a memorandum of understanding with blockchain company Standard Power to develop a large-scale carbon-free data infrastructure operation adjacent to the Beaver Valley nuclear plant, located in Shippingport, Pa.
In its May 9 announcement, Energy Harbor described Standard Power as “a leading infrastructure service provider for advanced data processing companies and a leading hosting provider for blockchain mining companies.”
Energy Harbor is based in Akron, Ohio.
Idaho National Laboratory nuclear engineer Yasir Arafat (Photo: INL)
From refugee in Bangladesh to top nuclear engineer at Idaho National Laboratory, ANS member Yasir Arafat has led quite an interesting life, as described in a recent online profile written by Donna Kemp Spangler for the INL website. Arafat is leading the development of the Department of Energy’s Microreactor Applications Research Validation and EvaLuation (MARVEL) project at INL. The profile notes that MARVEL, which Arafat envisioned soon after joining INL in 2019, is scheduled to be “built and demonstrated at INL’s Transient Reactor Test Facility and connected to the world’s first nuclear microgrid within two years.”






 ANS has recently published a new standard:
ANS has recently published a new standard: