HPR1000 passes U.K. design assessment

The Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) and the Environment Agency (EA) have found the UK HPR1000 reactor suitable for construction in the United Kingdom, the regulators jointly announced last week.

A message from Electrical Builders, Ind.
America’s Top Performing Nuclear Plants Rely on Electrical Builders, Industries to Expand and Extend the Life of Their Critical Electrical Assets

The Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) and the Environment Agency (EA) have found the UK HPR1000 reactor suitable for construction in the United Kingdom, the regulators jointly announced last week.

Citing “improving market sentiment,” Tim Gitzel, president and chief executive officer of the Canadian uranium mining company Cameco, announced on February 9 the planned restart of operations at the McArthur River mine in Saskatchewan.

Macron
As part of its drive for carbon neutrality by 2050, France will build at least six new nuclear reactors in the coming decades, according to a February 10 article from Reuters. "What our country needs, and the conditions are there, is the rebirth of France's nuclear industry," French president Emmanuel Macron said as he announced France’s new nuclear strategy.
Macron also said that he wanted to extend the life spans of France’s existing nuclear plants.
The price tag: The six new plants would be built and operated by state-controlled energy provider EDF, which has estimated the cost of those plants total at about 50 billion euros (about $57 billion), depending on financing conditions, according to the article.
The first new reactor, an evolution of the European Pressurized Reactor (EPR), would come on line by 2035, Macron said. The article added that the country would embark on a study to determine whether a further eight reactors beyond the initial six would be needed.

Regalbuto
High-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) is the power-dense feedstock of choice for a slew of advanced reactor designs. There’s just one problem: It isn’t available . . . yet. Downblending high-enriched uranium owned by the Department of Energy to between 5 and 19.75 percent fissile U-235 is a stopgap measure at best, and no U.S. facility can yet produce commercial quantities of uranium above the 5 percent U-235 limit for low-enriched uranium.
The problem is one not of technology, but of economics: Enrichment companies want to see clear market signals that advanced reactors will be deployed in quantity, leading to long-term purchase agreements that will justify investments made today.
ANS Fellow Monica Regalbuto is director of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Strategy at Idaho National Laboratory, tasked with leveraging her more than 30 years of fuel cycle experience to ensure an adequate domestic supply of HALEU. She was invited to speak about her work during the opening plenary session of the 2021 ANS Winter Meeting.

The Department of Energy’s Office Nuclear Energy has launched a $6 billion program aimed at preserving the existing U.S. fleet of nuclear power reactors. Established under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, the Civil Nuclear Credit Program will allow owners and operators of commercial nuclear power reactors at economic risk of shutting down to apply for credits via a sealed bid process.
.jpg)
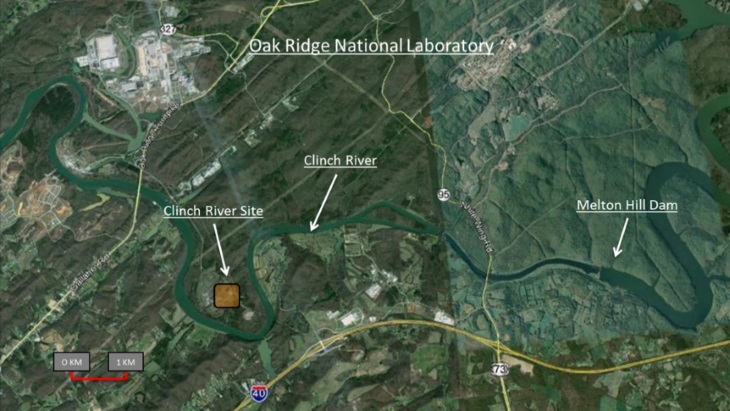
The Tennessee Valley Authority’s board of directors has given the go-ahead for a program that will explore the development and potential deployment of small modular reactors as part of the utility’s decarbonization strategy.
The way in which some New Mexico lawmakers are ganging up against Holtec International’s plans to build a consolidated interim storage site for spent nuclear fuel makes it seem that everyone in the state is against the project, no matter that the benefits would far outweigh any risks.
But, as a recent editorial in the Albuquerque Journal illustrates, the communities of southeastern New Mexico, where the facility would be located, are firmly behind the project. They are, after all, well versed in nuclear technology and cognizant of the economic and social benefits it would bring.

A new record has been set by the world’s largest operating tokamak, the Joint European Torus (JET). According to the EUROfusion scientists and engineers who work on JET at the U.K. Atomic Energy Authority’s Culham Centre for Fusion Energy, the landmark experiment, announced on February 9, which produced 59 megajoules of fusion energy over five seconds, is powerful proof of fusion’s potential as a clean energy source.
 Today’s #ThrowbackThursday post looks at the initial debate surrounding the conversion of research reactor fuel from high-enriched uranium to low-enriched uranium. An article published in the April 1984 issue of Nuclear News (available to all ANS members), titled “NRC studies HEU-to-LEU fuel conversion issue,” was written by the ANS Washington editor John Graham, and brings up several items of interest.
Today’s #ThrowbackThursday post looks at the initial debate surrounding the conversion of research reactor fuel from high-enriched uranium to low-enriched uranium. An article published in the April 1984 issue of Nuclear News (available to all ANS members), titled “NRC studies HEU-to-LEU fuel conversion issue,” was written by the ANS Washington editor John Graham, and brings up several items of interest.
The story: Graham introduces the readers to the growing security concerns around HEU and notes that the issue has its roots in the nonproliferation concerns from the Carter administration that forced the domestic nuclear industry to abandon certain projects—the subject of a #TBT post a couple of weeks ago.

Christina J. Leggett
I am so excited to be working in the nuclear industry right now! The U.S. nuclear industry includes dozens of advanced reactor companies that offer a variety of reactor designs, such as molten salt; sodium-cooled; and high-temperature, gas-cooled reactors. These reactors range in size from a few MWe for remote or mobile applications, to a few hundred MWe that could enable modular scale-up, to nearly 1 GWe, which is similar to existing light water reactors. These novel designs boast additional applications beyond traditional electricity generation, such as desalination to produce clean drinking water, district heating, hydrogen production, and process heat for industrial and chemical processes, opening up new possibilities to decarbonize industrial sectors and provide valuable resources to diverse stakeholders. The smaller footprint of microreactors and small modular reactors could also open new locations to reactor siting, further expanding advanced reactors’ market potential. Because of these possibilities, interest in advanced reactors comes from a variety of potential customers, including local communities, NASA, and the Department of Defense.

Justice
West Virginia Gov. Jim Justice signed a bill yesterday that repeals the state’s quarter-century-old ban on nuclear power plant construction. The legislation, S.B. 4, passed the West Virginia Senate and House of Delegates last month with no substantial opposition and will go into effect in May.
S.B. 4 rescinds article 27A of the West Virginia Code, which prohibited “the construction of any nuclear power plant, nuclear factory, or nuclear electric power generating plant until such time as the proponents of any such facility can adequately demonstrate that a functional and effective national facility, which safely, successfully, and permanently disposes of radioactive wastes, has been developed.” 27A also required nuclear facility construction to be economically feasible for West Virginia ratepayers and in compliance with all applicable environmental protection laws, rules, and requirements.
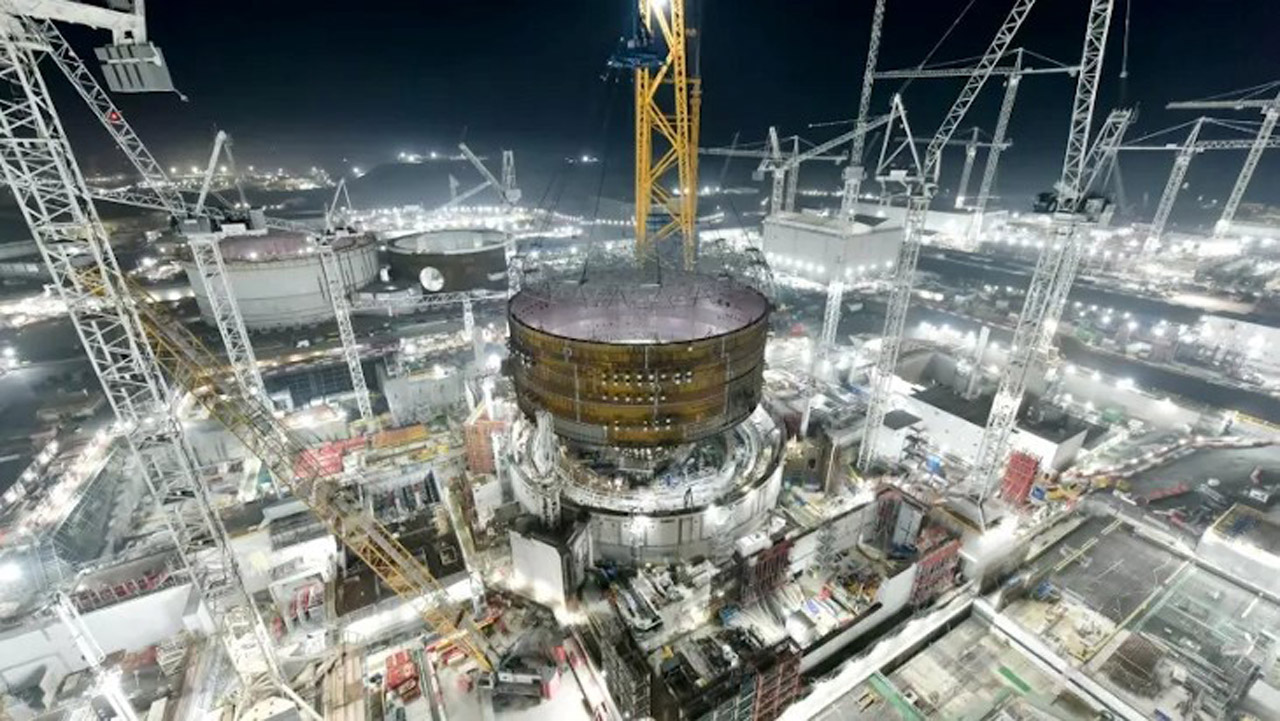

The United Kingdom’s Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) has granted permission for the start of bulk mechanical, electrical, and HVAC component installation work at the Hinkley Point C site in Somerset, England, where two 1,630-MWe EPRs are under construction. Thus far, most of the activity at Hinkley Point C has been in the field of civil construction.
This new phase, according to ONR, will require a workforce of up to 4,000 during peak times, including welders, pipe fitters, and electricians. The work is to be accomplished over a three-year period, with NNB Genco—the EDF Energy subsidiary set up in 2009 to build and operate Hinkley Point C—teaming up with four suppliers: Balfour Beatty Bailey, Doosan, Cavendish, and Altrad.
Two GOP lawmakers are calling on the Government Accountability Office to undertake an assessment of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s preparedness to review and approve advanced reactor applications.
In a February 4 letter to the GAO, Sen. Shelley Moore Capito (R., W.Va.), ranking member of the Senate Environment and Public Works Committee, and Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R., Wash.), ranking member of the House Energy and Commerce Committee, wrote, “Recent NRC actions concerning certain licensing activities raise questions about the agency’s capability to manage effectively first-mover applications for new, advanced technologies.”
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has denied a petition for rulemaking, filed in February 2019 by Gerard P. Van Noordennen on behalf of EnergySolutions, requesting that the agency revise its regulations to allow licensees access to a nuclear power plant’s decommissioning trust fund to pay for the disposal of major radioactive components before the plant permanently ceases operations and begins decommissioning.
“Major radioactive components” refers to the reactor vessel and internals, steam generators, pressurizers, large bore reactor coolant system piping, and other large components.
Small modular reactor developer NuScale Power has informed the Nuclear Regulatory Commission via letter that a combined license application (COLA) for the Carbon Free Power Project’s SMR plant is expected to be submitted to the agency in January 2024. The COLA will be for a six-unit 77-MWe plant.
The public power consortium Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems launched the Carbon Free Power Project in 2015 to develop, own, and operate the nation’s first SMR plant, to be located at Idaho National Laboratory, with reactor technology supplied by NuScale.

When I came to work at BWX Technologies immediately after getting my degree in chemical engineering from the University of Virginia, I was amazed to see how nuclear energy could be harnessed to both power and protect our country. Since then, I’ve come to see that nuclear energy can do even more. The nuclear industry’s next tasks are to address climate change, propel us to other bodies in the solar system, and provide power when we arrive. Recently developed coated fuels are an enabling technology for these tasks.

An article published on the Carlsbad Current-Argus news site on February 5 presents the wide gap between lawmakers in New Mexico on either side of the issue of temporary storage of spent nuclear fuel in the state.
The article noted that two identical bills—Senate Bill 54 and House Bill 127, which advanced in legislative committees last week—would block a spent fuel storage facility in New Mexico by prohibiting state agencies from issuing permits for such a facility.

The American Nuclear Society will host a one-hour webinar this Thursday, February 10, at 2:00 p.m. EST, celebrating “Black Excellence in the Nuclear Field.” The free webinar will be moderated by Lisa Marshall of North Carolina State University and will feature former U.S. assistant secretary for nuclear energy Warren “Pete” Miller, X-energy’s Jeff Harper, Idaho National Laboratory’s J’Tia Hart, and Booz Allen Hamilton’s Christina Leggett.

A full-scale, electrically heated prototype for the Department of Energy’s Microreactor Applications Research Validation and Evaluation (MARVEL) project was fabricated in just nine months, according to an article published by Idaho National Laboratory on January 31. The article explains in part how a team from the lab’s machine shop created the prototype.

The International Atomic Energy Agency has launched the Rays of Hope program to tackle a severe shortage of cancer care capacity in poorer countries. The program’s initial focus will be on Africa, where people often die from the disease because of the lack of access to potentially life-saving nuclear medicine and radiotherapy, according to the IAEA.
A video on the program is available on YouTube.