Concept art showing Project Harmonia’s RSG for lunar surface missions. (Image: Zeno Power)
NASA has selected 11 companies, including Zeno Power, to develop technologies that could support long-term exploration on the moon and in space. The technologies range from lunar surface power systems to tools for in-space 3D printing, which will expand industry capabilities for a sustained human presence on the moon through the Artemis program, as well as other NASA, government, and commercial missions.
Upgrades to the particle accelerator enabling the record 1.7-MW beam operating power at the ORNL’s SNS included adding 28 high-power radio-frequency klystrons (red tubes) to provide higher power for the accelerator. (Photo: Genevieve Martin/ORNL)
The Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory set a world record when its particle accelerator beam operating power reached 1.7 MW, an improvement on the facility’s original design capability of 1.4 MW, ORNL announced on July 21. That higher power provides more neutrons for researchers who use the Office of Science user facility for materials science investigations.
ORNL has developed an automated metrology system to produce Pu-238 pellets. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy recently shipped half a kilogram of plutonium oxide pellets from Oak Ridge National Laboratory to Los Alamos National Laboratory, the agency announced July 18, marking the largest such shipment since the DOE restarted domestic plutonium-238 production over a decade ago.
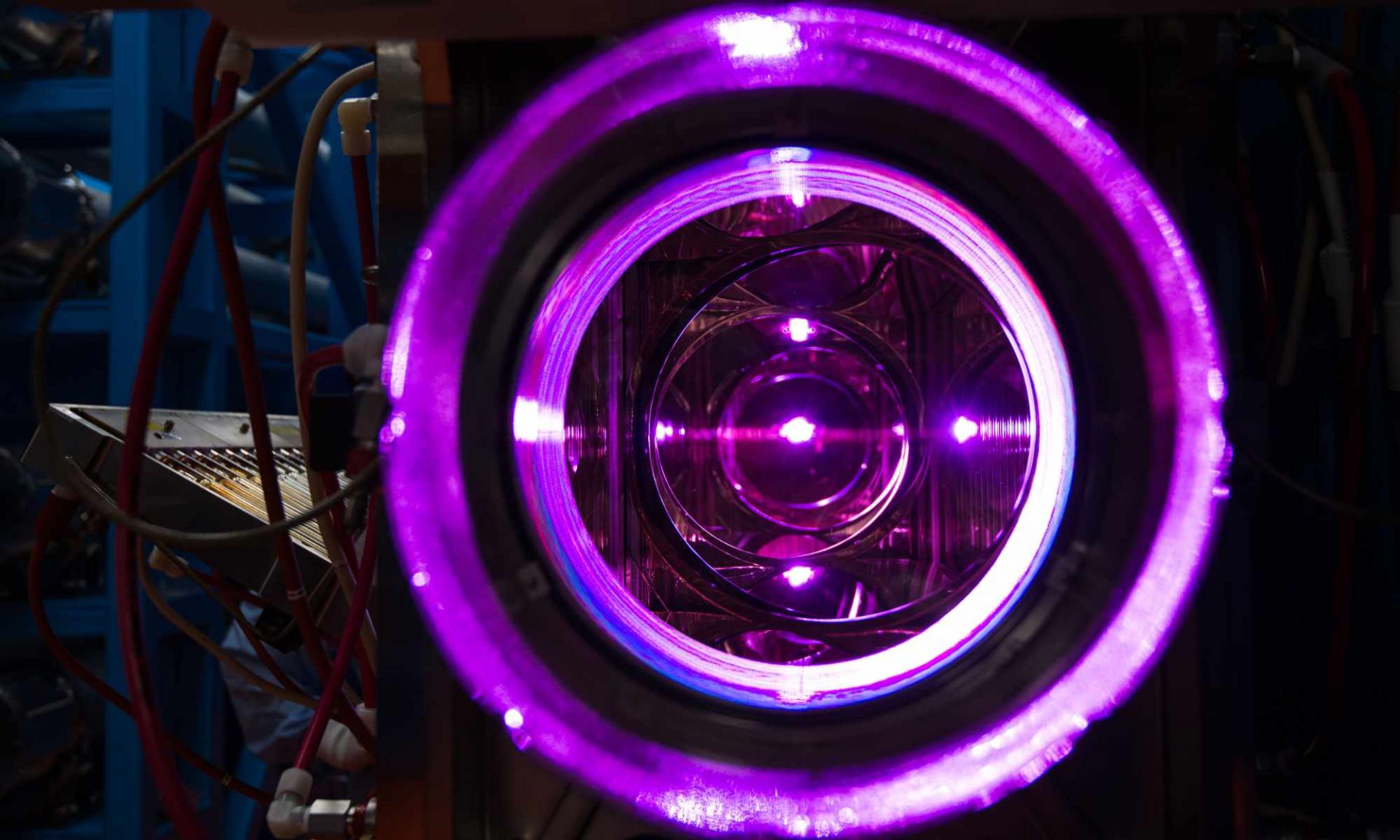
A view through the 20-cm disk amplifiers of the OMEGA laser at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics. (Photo: University of Rochester/J. Adam Fenster)
Proponents of inertial fusion energy celebrated in December 2022, when researchers at the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory achieved fusion ignition by subjecting a carefully crafted diamond cryogenic sphere containing frozen deuterium-tritium fuel to NIF’s laser energy. NIF has yet to repeat the feat, in part because that facility was not designed to produce fusion energy, and ignition requires near-perfect targets. For inertial fusion energy to serve as a reliable power source, it will require swift, reliable, and economic target production.
SHINE Technologies founder and CEO Greg Piefer shows the hot cell banks that will be used to produce Lu-177. (Image: SHINE)
Fusion tech company SHINE Technologies announced that it is opening the largest facility in North America dedicated to the production of non-carrier-added lutetium-177, a medical isotope used in targeted cancer therapies.
Representatives from the U.S., EU, and Japan announce the WAC at the 12th International Symposium for Targeted Alpha Therapy. (Photo: NIDC)
The World Astatine Community (WAC) was formed earlier this year during the 12th International Symposium for Targeted Alpha Therapy by representatives from the United States, Japan, and the European Union to share astatine production technology and advance science and health care. The National Isotope Development Center (NIDC), which is managed by the Department of Energy’s Isotope Program (DOE-IP), announced the news on June 15 and explained how the United States plans to help expand the global supply of astatine-211.
(Photo: Nielander/WikiCommons)
Westinghouse Electric Company says its eVinci microreactor technology is “100 percent factory built and assembled before it is shipped in a container to any location.” And “any location” is not restricted to planet Earth, given the company’s goal of sending a scaled-down version of eVinci to the lunar surface or on a mission to provide power in other space applications.
Announcing the funding for commercial fusion energy development were Asmeret Asefaw Berhe (top left), director of the DOE-OS; Jennifer Granholm, secretary of energy (top right); and Arati Prabhakar (bottom), director of the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy and science advisor to the president.
From a crowded field of would-be fusioneers, the Department of Energy has selected eight companies for the public-private Milestone-Based Fusion Development Program to develop fusion pilot plant designs and resolve related scientific and technological challenges within five to 10 years. The DOE announced awards totaling $46 million for an initial 18 months of work on May 31.
GA’s Magnet Technologies Center. (Photo: GA)
General Atomics (GA) and Tokamak Energy Ltd. are each independently developing magnetic confinement fusion power plant concepts that would use a tokamak and high-temperature superconducting (HTS) magnets to confine and shape a plasma heated to over 100 million degrees Celsius. On May 30, they announced a memorandum of understanding to collaborate on HTS magnet technology for fusion energy and other applications.






.jpg)









