[CLICK TO VIEW FULL IMAGE] The diagram at left illustrates the experimental setup and the resulting zirconium oxide layer of varying thickness. The second diagram shows the circular zirconium alloy sample that is affected by the band of nickel alloy and radiation. Finally, the electron image at right shows a band of oxidation on the zirconium alloy sample. (Images: Peng Wang, Michigan Ion Beam Laboratory)
A longstanding issue in boiling water reactors—shadow corrosion on zirconium alloy fuel rods and fuel channels—has been reproduced in the Michigan Ion Beam Laboratory as part of an effort to understand and prevent the phenomenon. Research led by Peng Wang, a University of Michigan assistant research scientist in nuclear engineering and radiological sciences, was published in the January 2022 issue of the Journal of Nuclear Materials and described in a recent university news article.
INL scientists Matt Snow and Jessica Ward hold a natural vanadium solution that will be separated into the cancer-treating isotope scandium-47. (Photo: INL)
Idaho National Laboratory researchers have, for the first time, used a novel technique using high-energy photons to produce scandium-47 from the element vanadium. The project is a collaboration with Jon Stoner and John Longley from Idaho State University’s Idaho Accelerator Center and Tara Mastren from the University of Utah. The results are published in the journal Applied Radiation and Isotopes.
In 2021, the Fusarium wilt disease continued to spread in banana plantations across South America. (Photo: M.Dita/Biodiversity International, Colombia)
A lethal banana disease, known as the Fusarium wilt or Panama wilt, is spreading rapidly in South America and threatening global supplies of the Cavendish banana, the world’s most popular export variety. Working with experts in the Andean countries of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru, the IAEA and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) are using irradiation and nuclear-derived techniques to combat, manage, and prevent the spread of the disease. The IAEA describes the work in a December 24 news article.
July 2, 2021, 2:15PMUpdated December 30, 2021, 7:15AMNuclear NewsSusan Gallier A hot cell at Argonne National Laboratory was used to demonstrate a process for purifying molybdenum-99, an important diagnostic medical isotope. (Photo: Wes Agresta/ANL)
The biggest impact of radiation in our lives may come not from radiation itself, but from regulations and guidelines intended to control exposures to man-made sources that represent a small fraction of the natural radiation around us.
Decades of research have been unable to discern clear health impacts from low levels of ionizing radiation, leading to calls for a new research program—one with a strategic research agenda focused on how the scientific understanding of the health effects of low doses (below 100 millisievert) and low dose rates (less than 5 mSv per hour) can best be augmented, applied, and communicated.
Building instrumentation and control technologies into the design of the next generation of advanced nuclear reactors will help the industry meet zero-carbon-emissions goals.
December 23, 2021, 3:00PMNuclear NewsAlexander Heifetz, Matthew Weathered, Nathan Hoyt, Mark Anderson, Scott Sanders, Anthonie Cilliers Kairos Power’s Instrumentation Test Unit
As a source of carbon-free electricity, nuclear energy currently dominates in the United States. However, the light water reactors in the U.S. are approaching the end of their licensed service lives. Meanwhile, low-cost electricity generated by fossil fuel–based sources (such as natural gas) poses an ongoing challenge to the economic viability of commercial nuclear reactors. To enhance the competitiveness of the nuclear industry, we need to bring down the high operating and maintenance (O&M) costs through savings available from utilizing modern, efficient sensing and automation technologies.
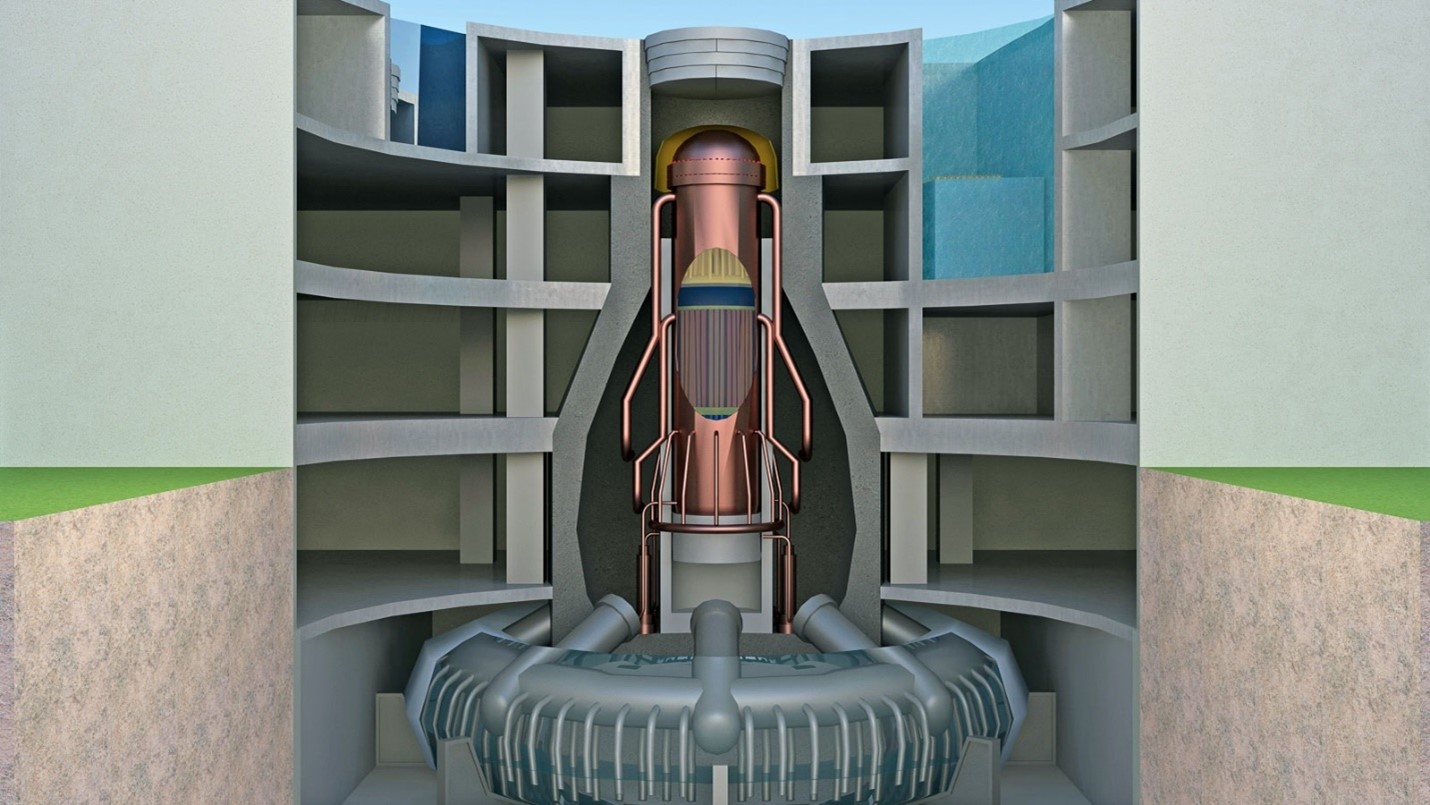
A cutaway view of a nuclear reactor. Its construction consists of two essential material types: fuel, which comprises the rods and cores that hold the fuel (center vertical bands); and structural, those parts of the reactor that house the fuel materials. (Graphic: Shutterstock/petrov-k)
Researchers from the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are developing a “tool kit” based on artificial intelligence that will help better determine the properties of materials used in building a nuclear reactor.
The Summit supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory began operations in 2018. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy has announced $9.25 million for research into the behavior and properties of structural materials under molten salt reactor conditions through collaborations using the DOE’s high-performance supercomputers.
Coated uranium fuel kernels, as viewed through a glovebox. (Photo: BWXT)
Nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) is one technology that could propel a spacecraft to Mars and back, using thermal energy from a reactor to heat an onboard hydrogen propellant. While NTP is not a new concept, fuels and reactor concepts that can withstand the extremely high temperatures and corrosive conditions experienced in the engine during spaceflight are being designed now.
BWX Technologies announced on December 13 that it has delivered coated reactor fuels to NASA for testing in support of the Space Technology Mission Directorate’s NTP project. BWXT is developing two fuel forms that could support a reactor ground demonstration by the late 2020s, as well as a third, more advanced and energy-dense fuel for potential future evaluation. BWXT has produced a videoof workers processing fuel kernels in a glovebox.
A screen shot from the “Research Reactors in Support of Advanced Reactor R&D” session at the 2021 ANS Winter Meeting and Technology Expo.
First-of-a-kind research reactors, demo reactors, and research facilities are being developed and sited on university campuses to support the broader deployment of advanced reactors. At the 2021 ANS Winter Meeting and Technology Expo, during a December 2 panel session titled “Research Reactors in Support of Advanced Reactor R&D,” several of these planned projects were discussed in detail—including a molten salt reactor in Texas and a high-temperature gas–cooled reactor in Illinois.
The session was sponsored by the Reactor Physics Division and organized and chaired by Pavel Tsvetkov, of Texas A&M University. A video of the session is available to registered Winter Meeting attendees.
Jamie Weaver with the neutron depth profiling instrument. (Photo: T. Barvitskie/NIST)
The newest generation of lithium-ion batteries now being developed uses thin-film, solid-state technology and could soon safely power cell phones, electric vehicles, laptops, and other devices. However, like all batteries, solid-state lithium-ion batteries have a drawback: Impedance—electrical resistance—can build up as batteries are discharged and recharged, limiting the flow of electric current.
Artist's rendition of the Versatile Test Reactor. (Source: DOE)
SwRI engineers used LIDAR point cloud data to reconstruct a high-resolution image of a facility that houses electric turbines at the nuclear power plant. 3D cubes, or voxels, on the left provide spatial information on the turbine facility. Point clouds were reconstructed to create the high-resolution image of the turbines on the right. SwRI specializes in data visualizations to identify damage and potential hazards following accidents at nuclear power plants and other hazardous facilities. (Graphic: SwRI)
During the EnRicH 2021 European Robotics Hackathon, Southwest Research Institute’s unmanned aircraft system (UAS or drone) explored and mapped the interior of a nuclear power plant, detecting radiation sources autonomously, without the aid of a human pilot.
SwRI’s UAS technology can potentially assist in life-saving search-and-rescue missions and hazardous inspections at industrial facilities and infrastructure following natural disasters and other incidents.