The 1958 Ford Nucleon concept car. (Photo: The Drive )
A car capable of traveling 5,000 miles between fueling stops? Sounds impossible, right? It turns out that, yes, it was impossible. But that didn’t stop the Ford Motor Company in 1958 from envisioning a car—the Nucleon—powered by a small nuclear reactor. The Drive took a close look at the fantastical idea in a July 5 article, “Inside the Impossible Dream of the Nuclear-Powered 1958 Ford Nucleon.”
Flags in front of the European Commission building in Brussels. (Image: Sébastien Bertrand)
The European Commission last week adopted the Euratom Work Programme 2021–2022, implementing the Euratom Research and Training Programme 2021–2025, a complement to Horizon Europe, the European Union’s key funding program for research and innovation.
Argonne marks its 75th anniversary on July 1. (Image: Argonne)
Seventy-five years ago today, on July 1, 1946, the first U.S. national laboratory was chartered with the singular mission of developing the peaceful uses of nuclear energy. Now, the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory is one of the nation’s largest science laboratories, working on diverse challenges in energy, climate, science, medicine, and national security.
A rendering of Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation’s micro modular reactor as proposed for construction on the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign campus. (Graphic: USNC)
The U.S. state with more nuclear power plants than any other—Illinois—has no operating university research reactors. A team at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) intends to reverse that situation and construct a high-temperature gas-cooled microreactor. If the team's plans go ahead, the first new U.S. university research reactor deployment in about 30 years could also support commercial advanced reactor deployment.
Left: An experimental setup showing a shielded detector. Right: A DT neutron source showing three disks of 6Li doped glass scintillator mounted on a photomultiplier tube. (Photos: MIT)
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) was developed by researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory to identify unknown materials inside a sealed object using a beam of neutrons from a laboratory-scale apparatus. Recognizing that the potential nuclear security applications of NRTA were limited by the size and location of the apparatus, Areg Danagoulian, an associate professor in the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering, began about five years ago to consider how NRTA could be made portable to examine materials on location.
ITER CS Module 1 (shown here at right with the General Atomics fabrication team) is being loaded onto a specialized heavy transport vehicle for shipment to Houston, Texas, where it will be placed on a ship for transit to France. (Photo: General Atomics)
After a decade of design and fabrication, General Atomics (GA) is preparing to ship the first module of the central solenoid—the largest of ITER’s magnets—to the site in southern France where 35 partner countries are collaborating to build the world’s largest tokamak and the first fusion device to produce net energy.
The Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics offers an interactive and informative 360-degree panoramic tour of Wendelstein 7-X. (Source: ipp.mpg.de)
U.S. scientists are getting funding to carry out seven research projects at two major stellarator fusion energy facilities located in Germany and Japan, the Department of Energy announced on June 8. A total of $6.4 million has been allocated for seven research projects with terms of up to three years.
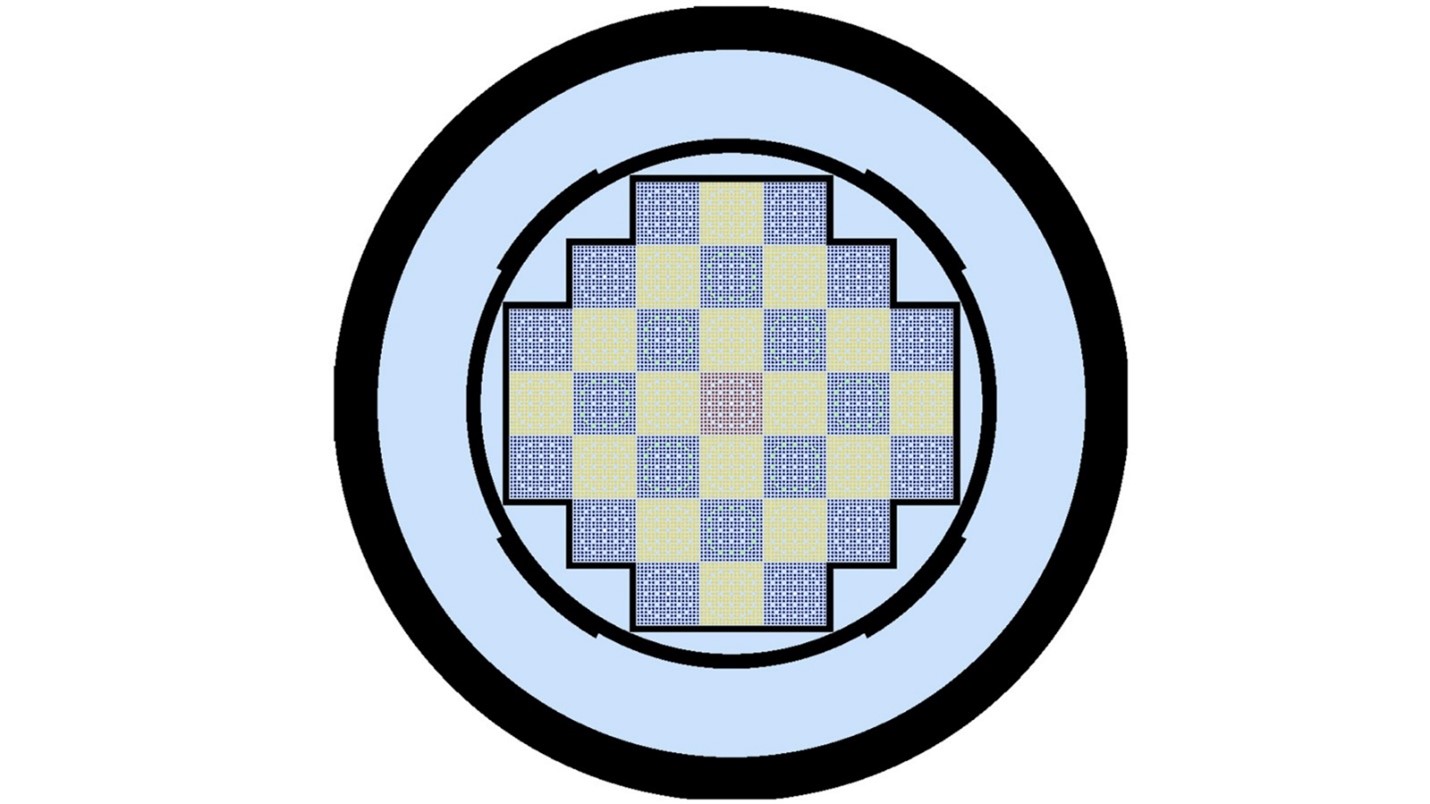
This image shows the individual pins in a full-core nuclear reactor simulation. (Image: ANL)
Coolant flow around the fuel pins in a light water reactor core plays a critical role in determining the reactor’s performance. For yet-to-be-built small modular reactors, a thorough understanding of coolant flow will be key to successfully designing, building, and licensing first-of-a-kind reactors.
ORNL associate laboratory director Kathy McCarthy at the prototype which led to the Material Plasma Exposure eXperiment (MPEX), a device that will support fusion materials research. Photo: ORNL
Oak Ridge National Laboratory has a long record of advancing fusion and fission science and technology. Today, the lab is focused more than ever on taking advantage of that spectrum of nuclear experience to accelerate a viable path to fusion energy and to speed efficient deployment of advanced nuclear technologies to today’s power plants and future fission systems.
The MARVEL reactor concept with Stirling engines. (Image: DOE)

-3 2x1.jpg)