NRC approves subsequent license renewal for Oconee
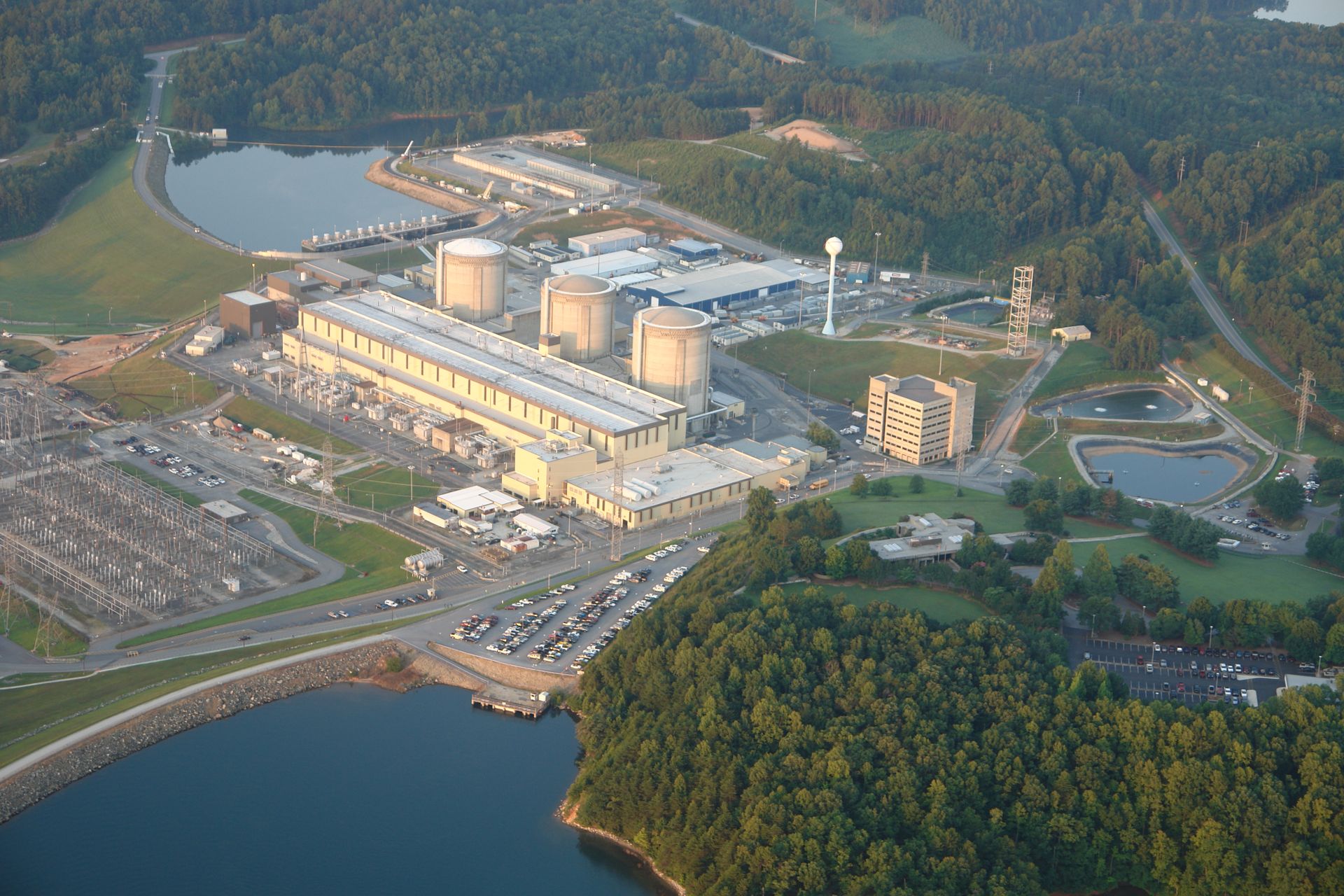

All three units at the Duke Energy’s Oconee nuclear power plant in South Carolina are now licensed to operate for an additional 20 years.

A message from Goodway Technologies
Optimizing Maintenance Strategies in Power Generation: Embracing Predictive and Preventive Approaches

All three units at the Duke Energy’s Oconee nuclear power plant in South Carolina are now licensed to operate for an additional 20 years.

The Department of Energy reissued a $900 million solicitation on March 24 designed to de-risk the deployment of “Gen-III+” light water small modular reactors. The same funding was previously offered in October 2024, with applications due January 17. Now, potential applicants have until April 23 to apply for a grant under a solicitation modified to “better align with President Trump's bold agenda to unleash American energy and AI dominance.”

The primary culprits behind contamination in a nuclear facility are fission products resulting from nuclear reactions and activated corrosion products like rust and metal. While these radioactive materials remain within the reactor system, the risk of contamination is minimal. However, the reality of a complex network of pipes and valves introduces vulnerabilities, leading to potential leaks and spills. The necessity for periodic system openings, required for sampling and maintenance, further heightens the risk of contamination. Once outside the system, radioactive materials can disperse, jeopardizing other plant components, areas, and even personnel.
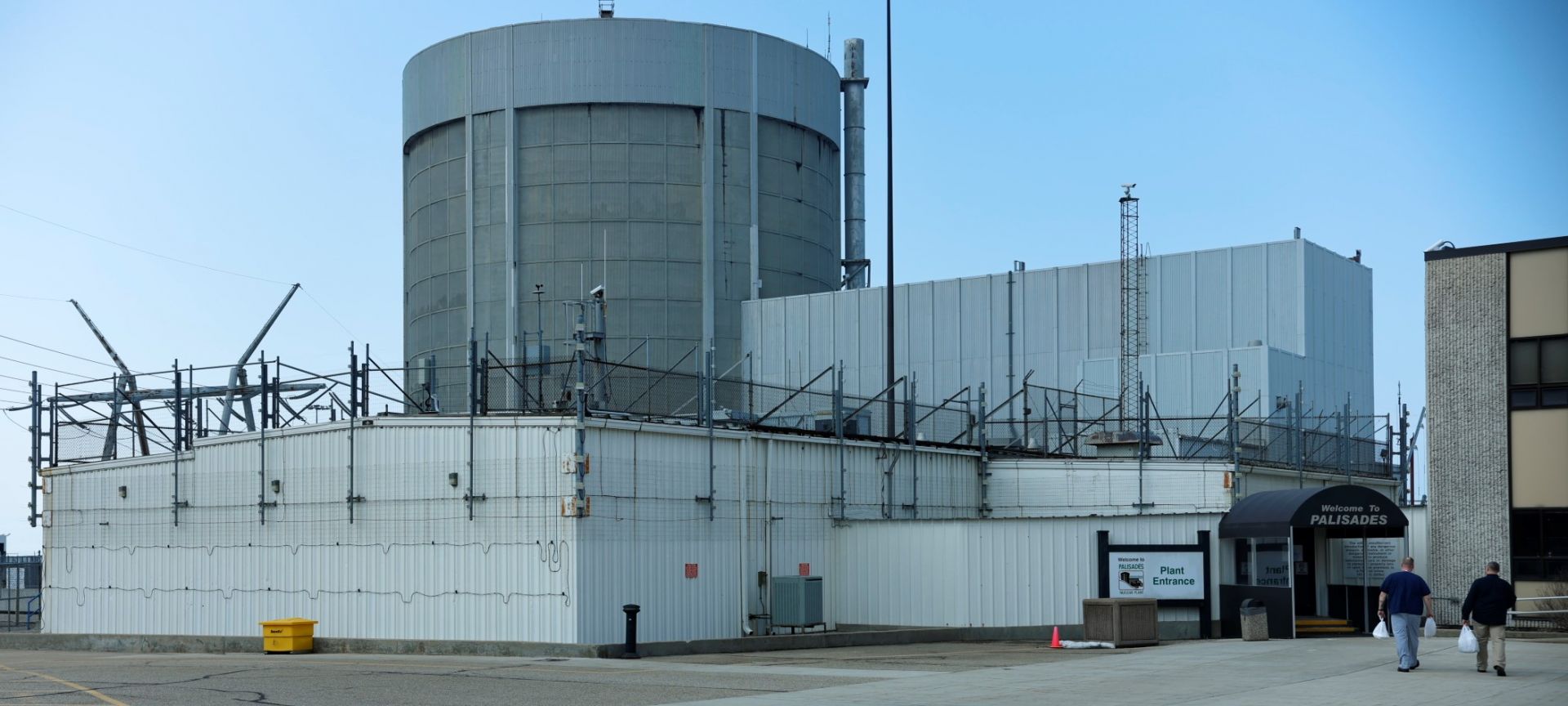

Energy Secretary Chris Wright announced this week the release of the second part of Holtec’s loan disbursement for the Palisades nuclear plant restart plans in Michigan.
Letters have been issued by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to the nation’s 94 operating commercial nuclear reactors regarding their performance in 2024, the agency reported yesterday. The assessment letters are issued annually.
Announcement from CERAWeek 2025 includes Amazon, Google, and Meta
Following in the steps of an international push to expand nuclear power capacity, a group of powerhouse corporations signed and announced a pledge today to support the goal of at least tripling global nuclear capacity by 2050.
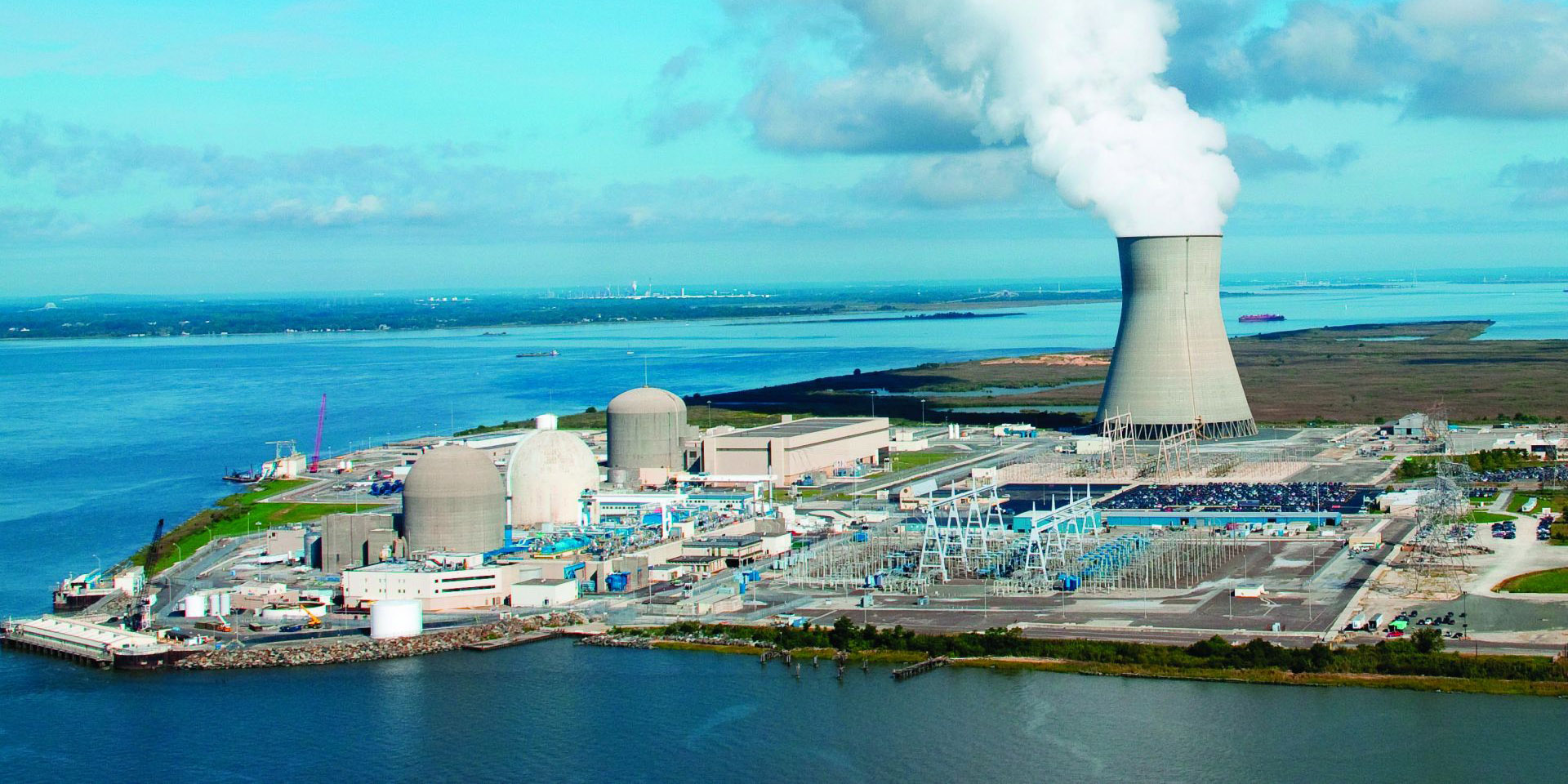

The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is conducting a special inspection at Hope Creek nuclear plant in New Jersey to investigate the cause of repeated inoperability of one of the plant’s emergency diesel generators, the agency announced in a February 25 news release.
.png)
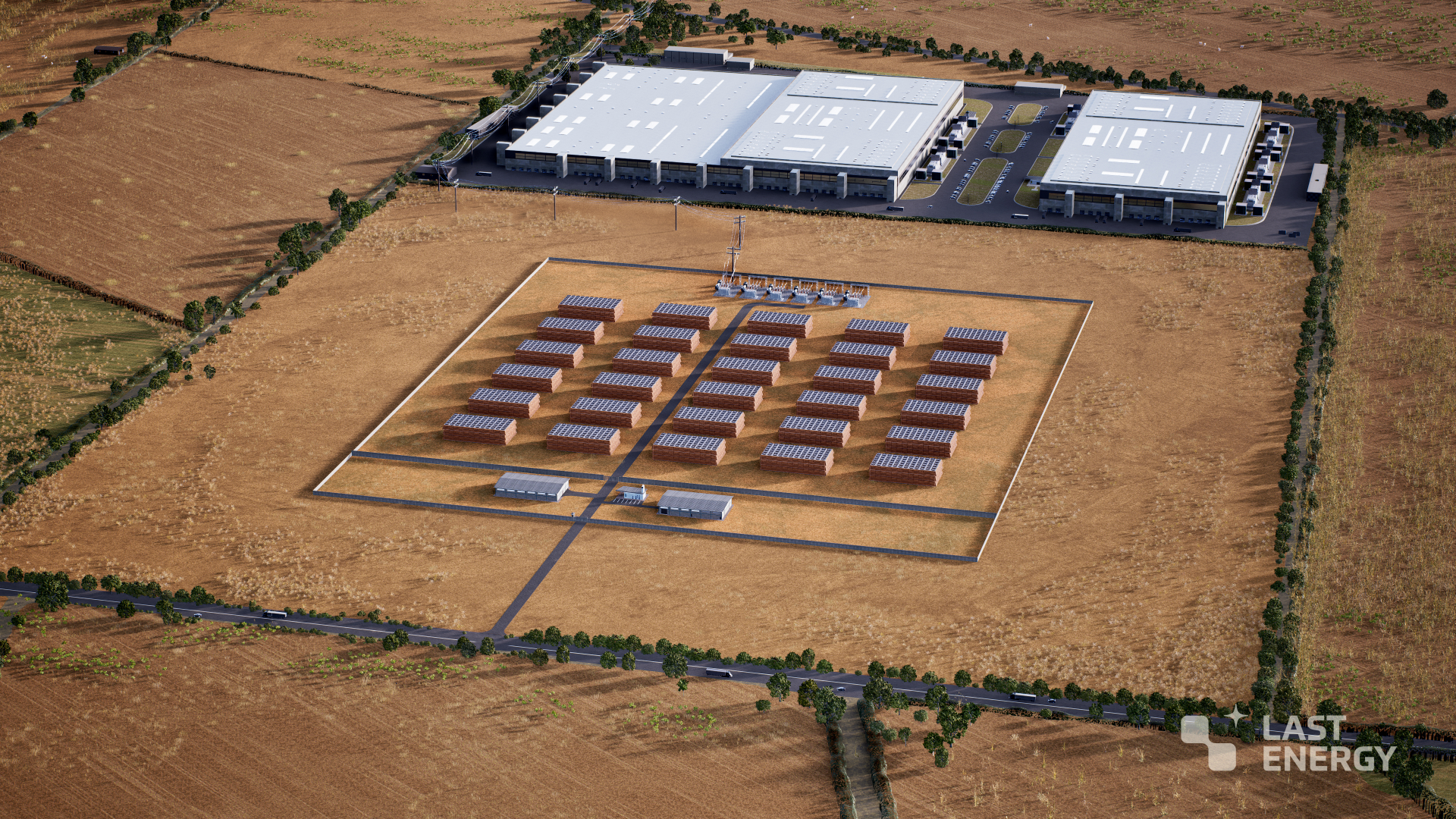
February has been big for nuclear in the state of Texas. On February 2, Governor Greg Abbott declared “It’s time for Texas to lead a nuclear power renaissance in the United States.” Two days later, Texas A&M University invited four advanced reactor developers—Aalo Atomics, Kairos Power, Natura Resources, and Terrestrial Energy—to build nuclear capacity on its RELLIS campus. On February 18 Natura announced plans for two 100-MWe molten salt reactors—one at TAMU RELLIS and the other in the Permian Basin—through a partnership with the Texas Produced Water Consortium and Texas Tech University. And today, Last Energy announced plans to site 30 microreactors—20-MWe pressurized water reactors—at a 200-acre site in northwestern Texas to power data centers.

The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has sent a February 26 letter to George Wilson, vice president of regulatory affairs for TerraPower, informing him that the agency’s draft safety evaluation (SE) has been completed on the company’s construction permit application for Kemmerer Power Station Unit 1. This advanced non–light water reactor design, dubbed Natrium, is slated for construction near a retiring coal plant in Wyoming as TerraPower’s first reactor.
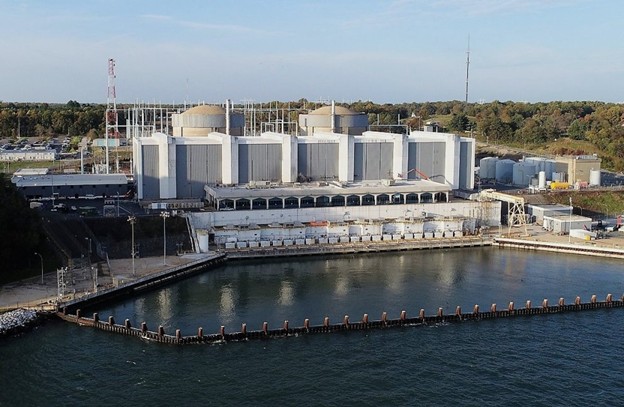

Nuclear powerhouse Constellation Energy announced Tuesday it will spend roughly $100 million to upgrade critical electrical systems and plant equipment at its Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, where the company may pursue license renewals.
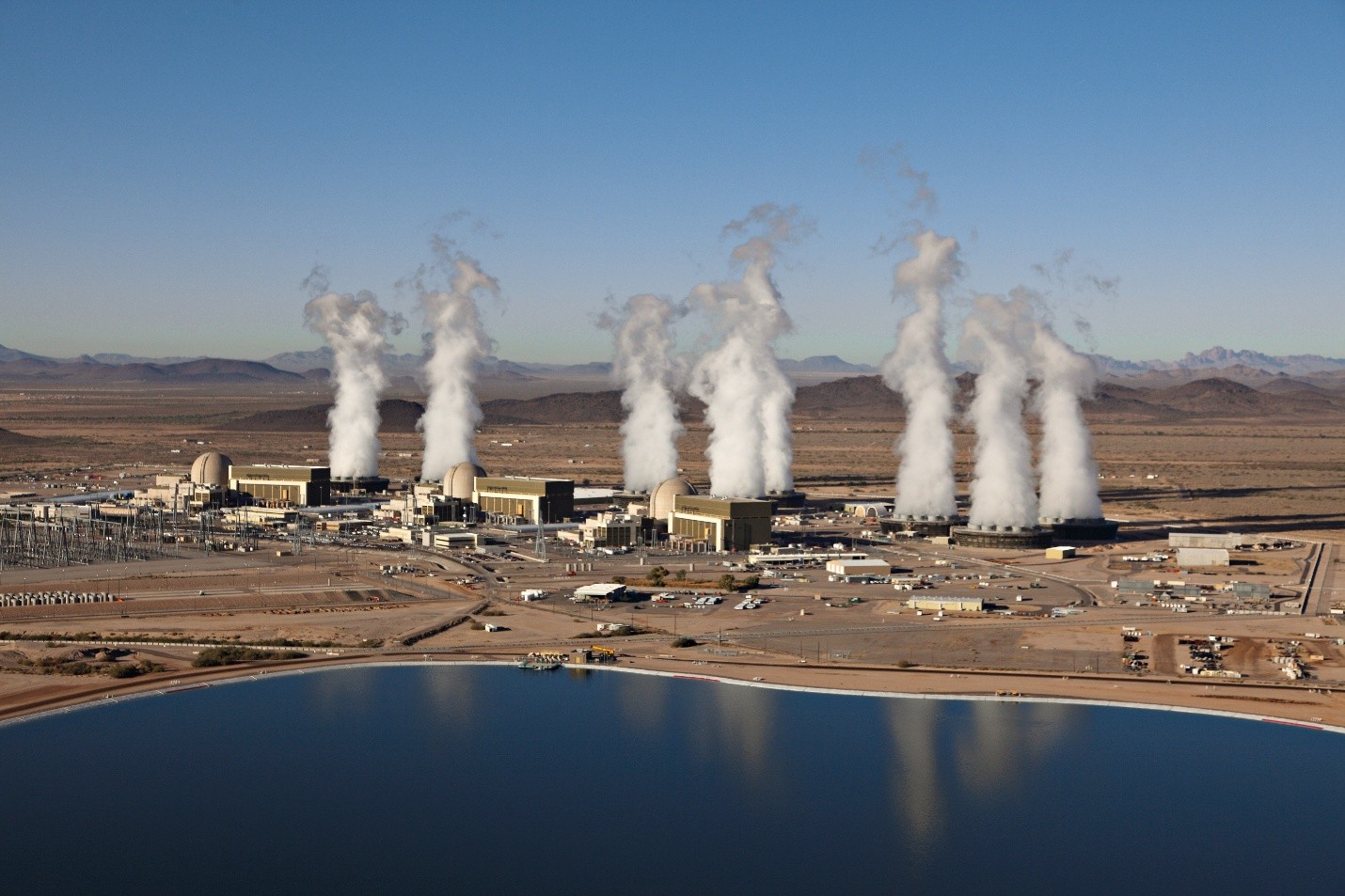

The top three utilities in Arizona are teaming up to explore opportunities to add nuclear generation facilities in the state.
Arizona Public Service (APS), Salt River Project (SRP), and Tucson Electric Power (TEP) announced in a February 5 news release that they are working together to assess possible sites, including retiring coal plants. The group is looking at possibilities for both small modular reactors—units generating 300 MW or less—and potential large reactor projects, which could generate nearly five times the power.
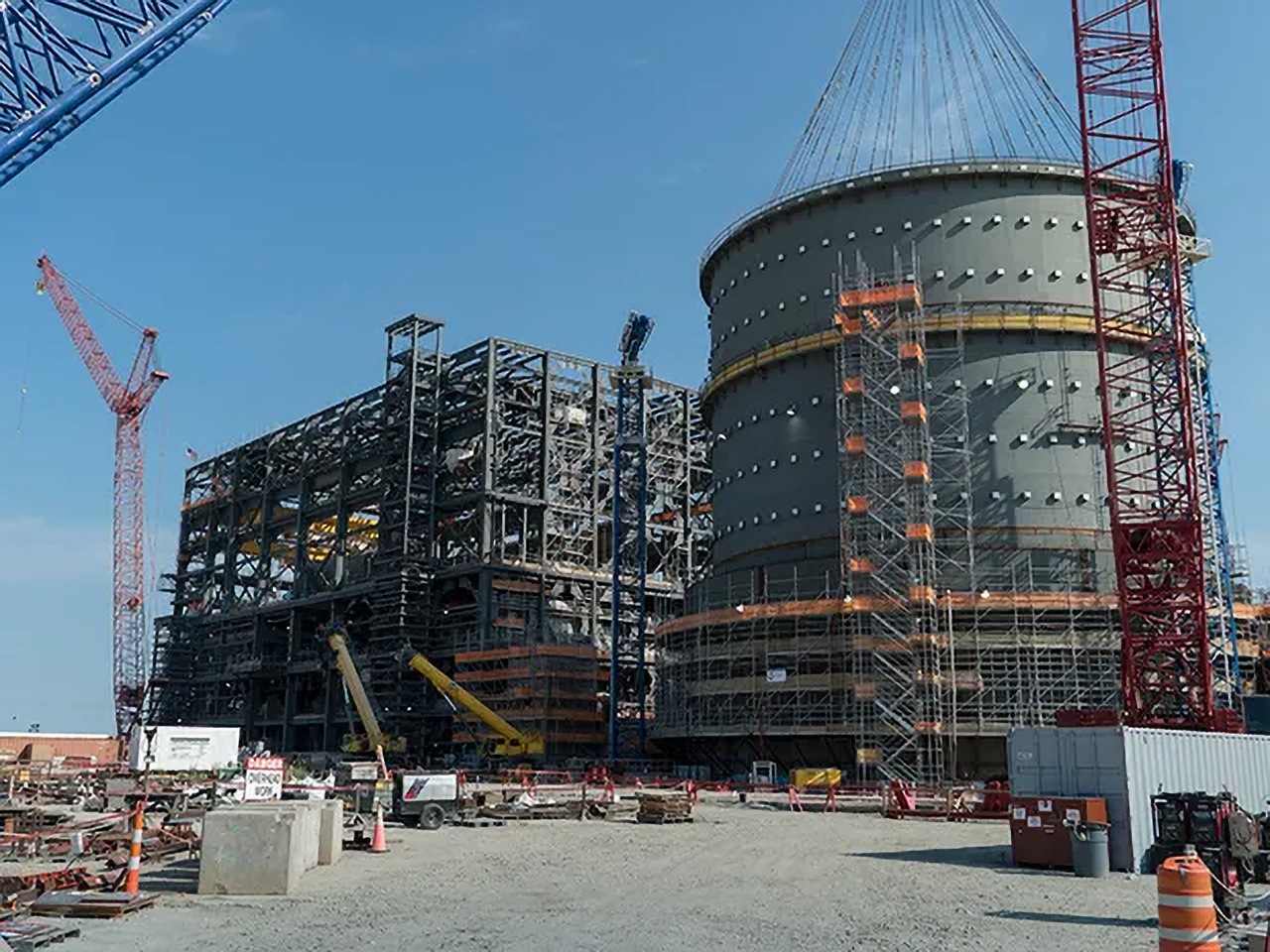

South Carolina public utility Santee Cooper and its partner South Carolina Electric & Gas (SCE&G) called a halt to the Summer-2 and -3 AP1000 construction project in July 2017, citing costly delays and the bankruptcy of Westinghouse. The well-chronicled legal fallout included indictments and settlements, and ultimately left Santee Cooper with the ownership of nonnuclear assets at the construction site in Jenkinsville, S.C.
Work will support Pickering life extension and Darlington SMRs

Ontario Power Generation announced this week new contracts with BWXT Canada worth more than C$1 billion ($695.4 million) for projects at the Pickering and Darlington nuclear power plants.
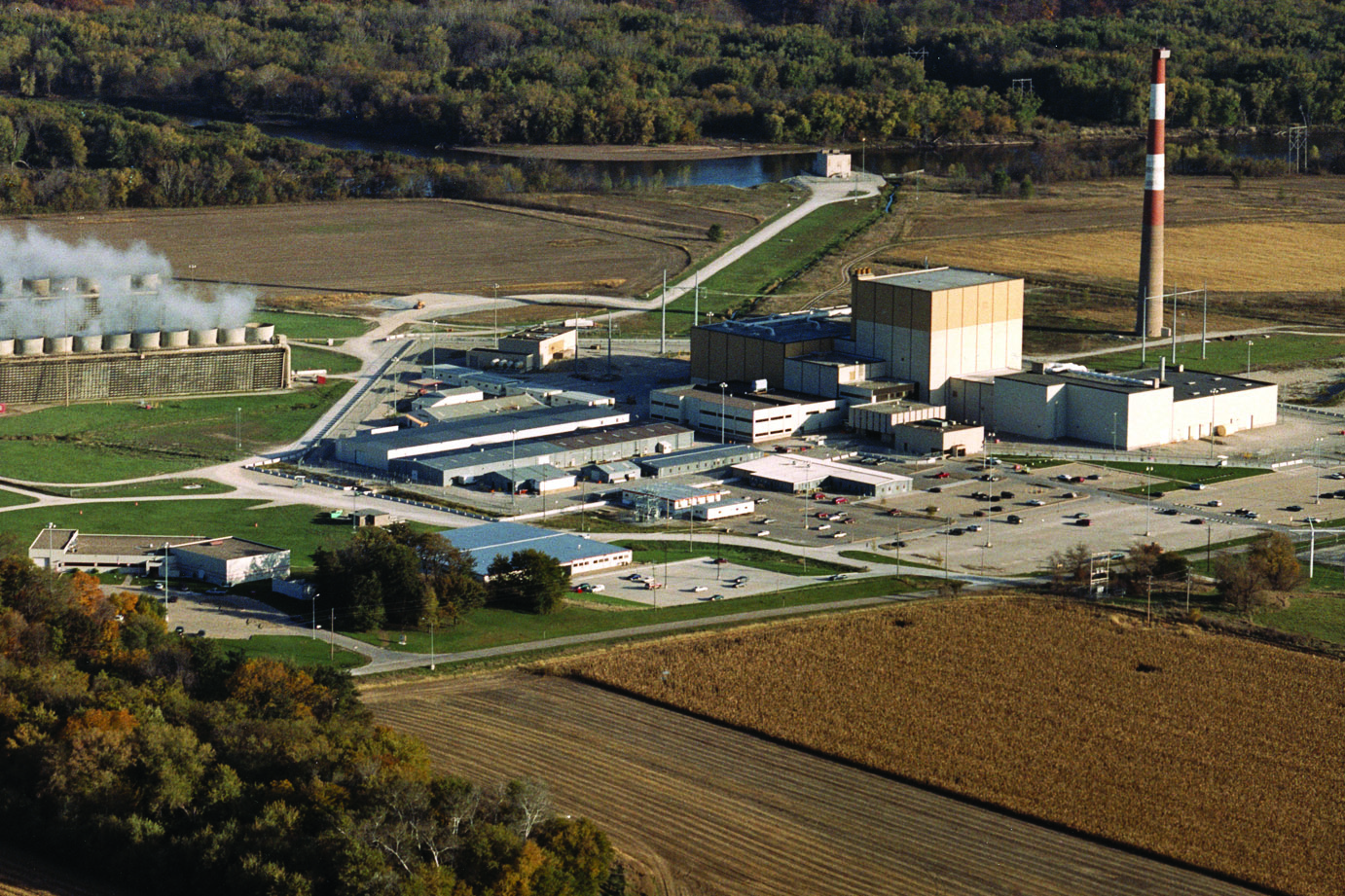

Iowa’s lone nuclear plant may soon see new life as NextEra Energy takes a step toward relicensing the Duane Arnold nuclear power plant.
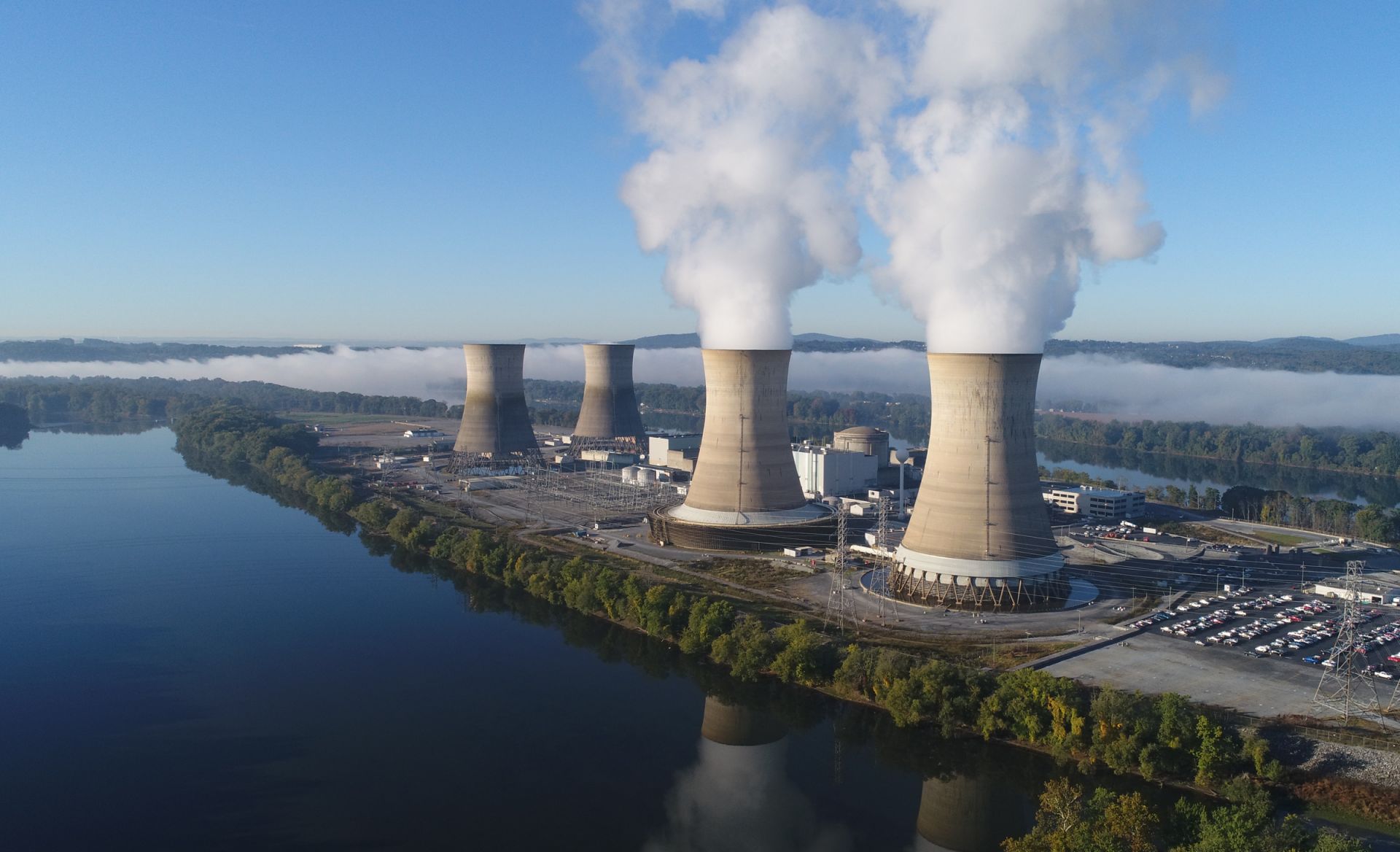

When Exelon Generation shut down Three Mile Island Unit 1 in September 2019, managers were so certain that the reactor would never run again that as soon as they could, they had workers drain the oil out of both the main transformer and a spare to eliminate the chance of leaks. The company was unable to find a buyer because of the transformers’ unusual design. “We couldn’t give them away,” said Trevor Orth, the plant manager. So they scrapped them.
Now they will pay $100 million for a replacement.
The turnaround at the reactor—now called the Crane Clean Energy Center—highlights two points: how smart Congress was to step in with help to prevent premature closures with the zero-emission nuclear power production credit of 0.3 cents per kilowatt-hour (only two years too late), and how expensive it is turning out to be to change course.

A Nuclear Regulatory Commission review board will hear oral arguments on February 12 on petitions concerning Holtec Palisades LLC.
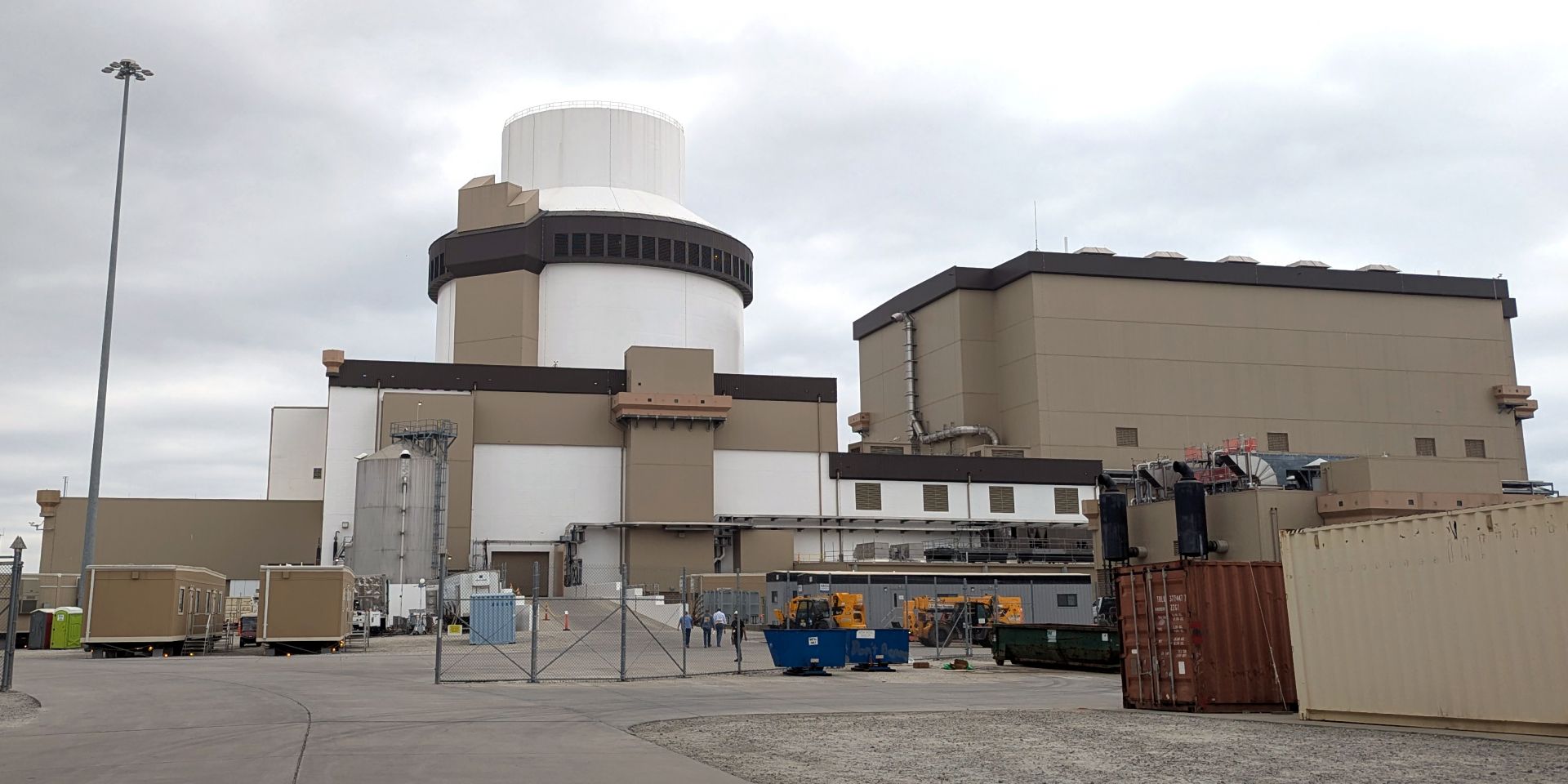

Southern Nuclear was first when no one wanted to be.
The nuclear subsidiary of the century-old utility Southern Company, based in Atlanta, Ga., joined a pack of nuclear companies in the early 2000s—during what was then dubbed a “nuclear renaissance”—bullish on plans for new large nuclear facilities and adding thousands of new carbon-free megawatts to the grid.
In 2008, Southern Nuclear applied for a combined construction and operating license (COL), positioning the company to receive the first such license from the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission in 2012. Also in 2008, Southern became the first U.S. company to sign an engineering, procurement, and construction contract for a Generation III+ reactor. Southern chose Westinghouse’s AP1000 pressurized water reactor, which was certified by the NRC in December 2011.
Fast forward a dozen years—which saw dozens of setbacks and hundreds of successes—and Southern Nuclear and its stakeholders celebrated the completion of Vogtle Units 3 and 4: the first new commercial nuclear power construction project completed in the U.S. in more than 30 years.

The media have gleefully resurrected the language of a past nuclear renaissance. Beyond the hype and PR, many people in the nuclear community are taking a more measured view of conditions that could lead to new construction: data center demand, the proliferation of new reactor designs and start-ups, and the sudden ascendance of nuclear energy as the power source everyone wants—or wants to talk about.
Once built, large nuclear reactors can provide clean power for at least 80 years—outlasting 10 to 20 presidential administrations. Smaller reactors can provide heat and power outputs tailored to an end user’s needs. With all the new attention, are we any closer to getting past persistent supply chain and workforce issues and building these new plants? And what will the election of Donald Trump to a second term as president mean for nuclear?
As usual, there are more questions than answers, and most come down to money. Several developers are engaging with the Nuclear Regulatory Commission or have already applied for a license, certification, or permit. But designs without paying customers won’t get built. So where are the customers, and what will it take for them to commit?
The potential application of artificial intelligence to the operation of nuclear power plants is explored in an article published in late December in the Washington Examiner. The article, written by energy and environment reporter Callie Patteson, presents the views of a number of experts, including Yavuz Arik, a strategic energy consultant.
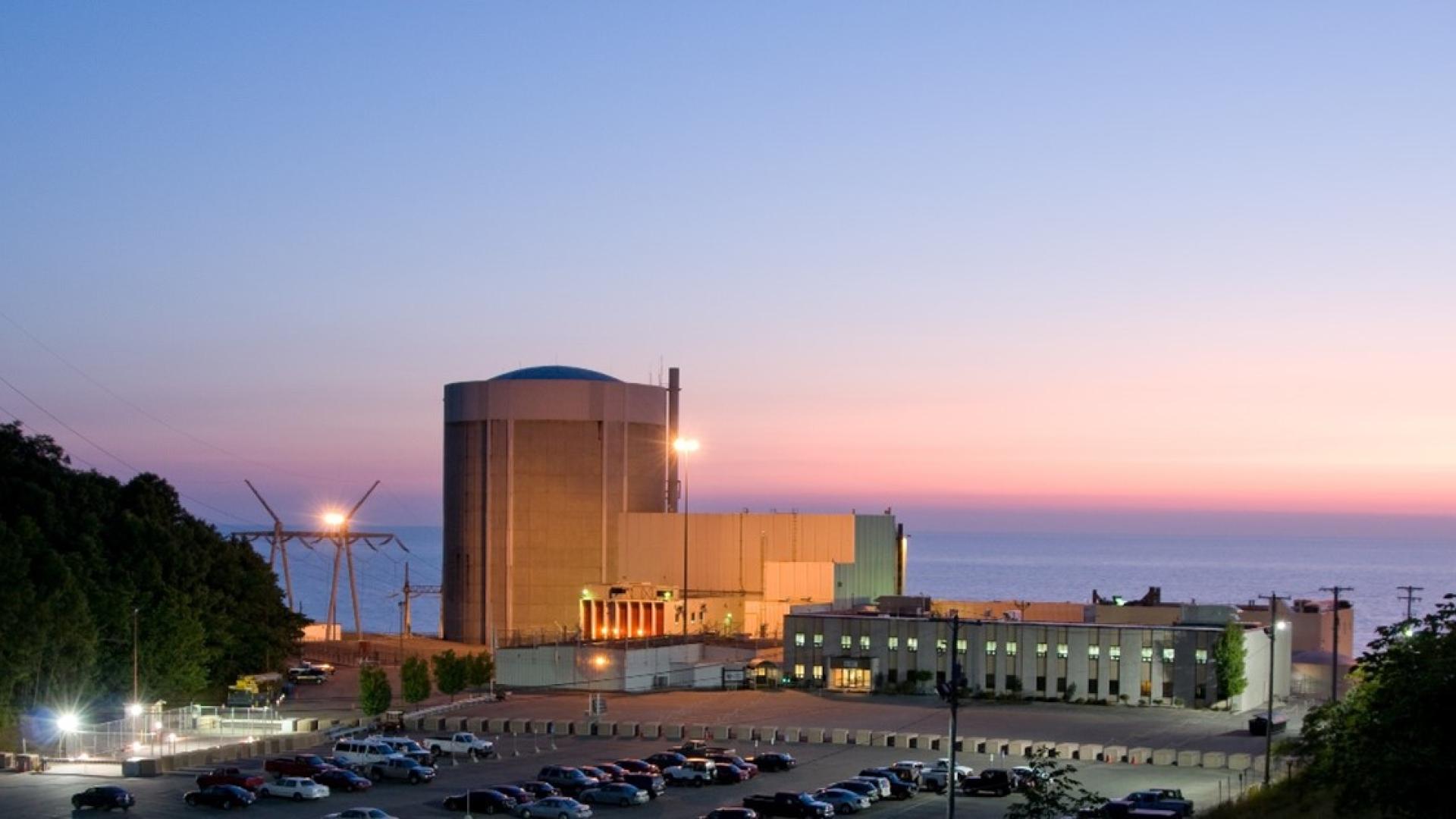

The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is hosting a hybrid public meeting with Holtec next week to discuss plans for needed repairs at Michigan’s Palisades nuclear plant before bringing the unit back on line.