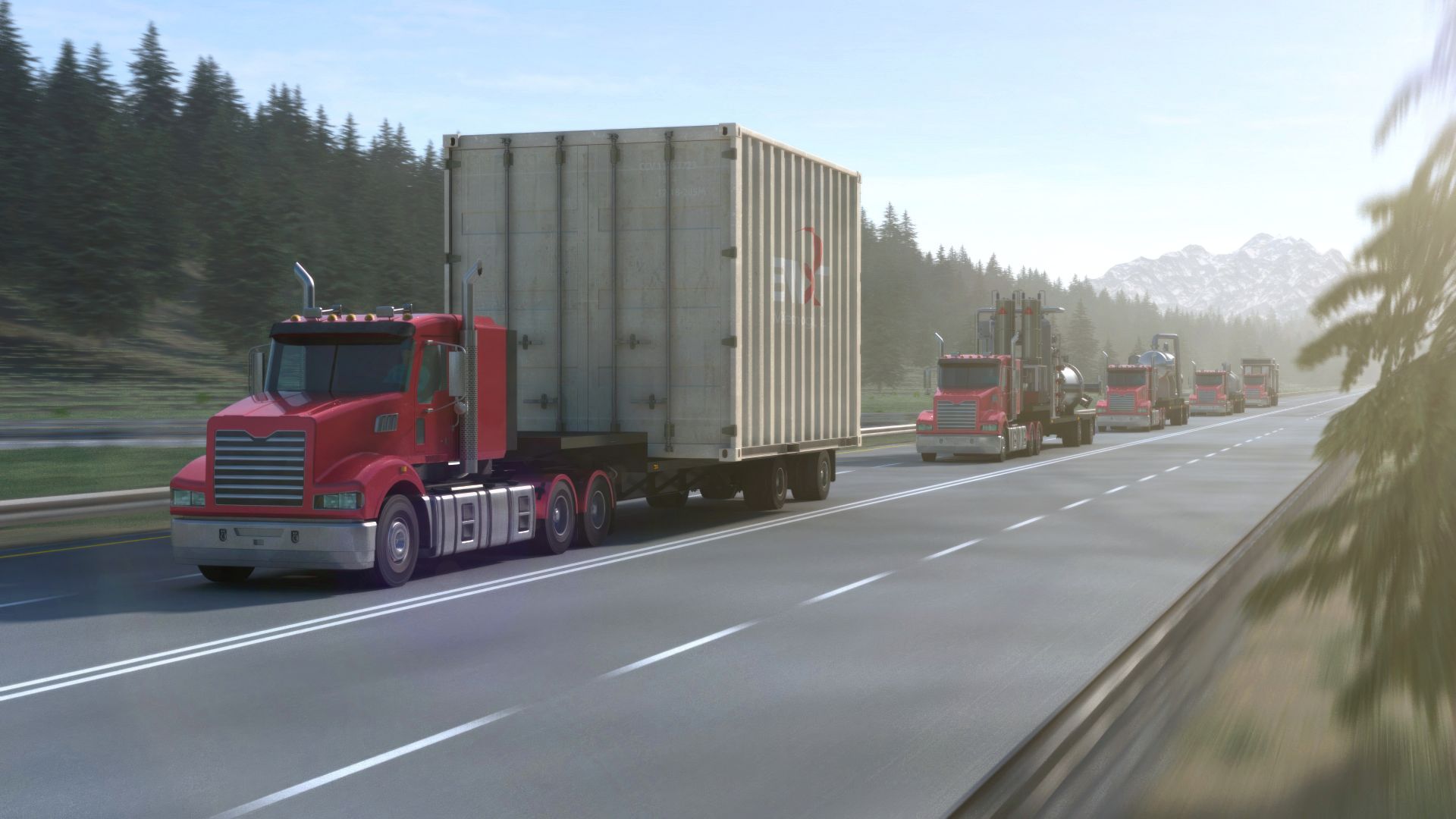
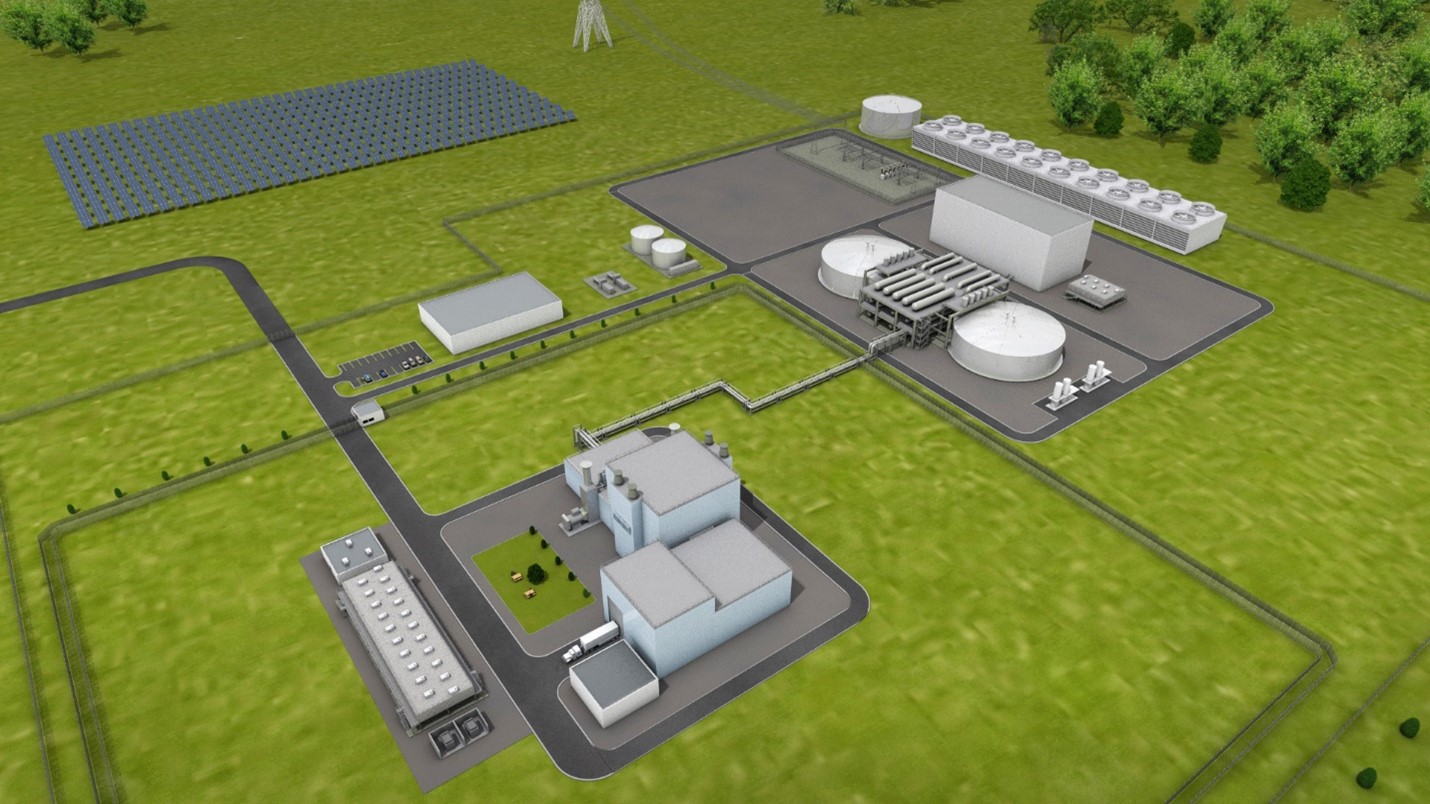
December 15, 2023, 4:56PMNuclear NewsDonna Kemp Spangler and Joel Hiller BWXT’s microreactor components would be designed to be transported directly from the factory to the deployment site. (Image: BWXT)
“The tools of the academic designer are a piece of paper and a pencil with an eraser. If a mistake is made, it can always be erased and changed. If the practical-reactor designer errs, he wears the mistake around his neck; it cannot be erased. Everyone sees it.”
Many in the nuclear community are familiar with this sentiment from Admiral Rickover. A generation of stagnation in the industry has underscored the truth of his words. But as economies around the world put a price on carbon emissions, there’s a renewed sense of urgency to deploy clean energy technologies. This shifts the global balance of economic competitiveness, and it’s clear that the best path forward for nuclear requires combining the agility of private innovators with the technology and capabilities of national laboratories.
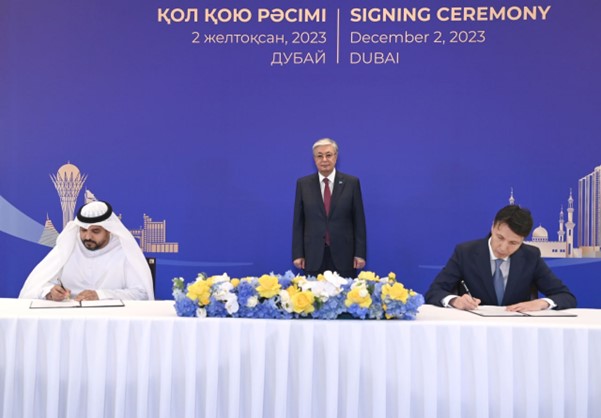
Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, president of Kazakhstan (standing), looks on as the commercial uranium fuel supply contract between ENEC and Kazatomprom is signed. (Photo: Kazatomprom)
On the margins of the COP28 climate conference in Dubai, UAE, this week, Barakah nuclear plant owner Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation (ENEC) signed its first commercial uranium fuel supply contract with Kazatomprom, in addition to memorandums of understanding with two U.S.-based advanced reactor developers—TerraPower and GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH).
The Irigaray central processing plant, in Wyoming’s Powder River Basin. (Photo: Uranium Energy)
TerraPower and Uranium Energy announced today that they have signed a memorandum of understanding to “explore the potential supply of uranium” for TerraPower’s demonstration reactor in Kemmerer, Wyo.
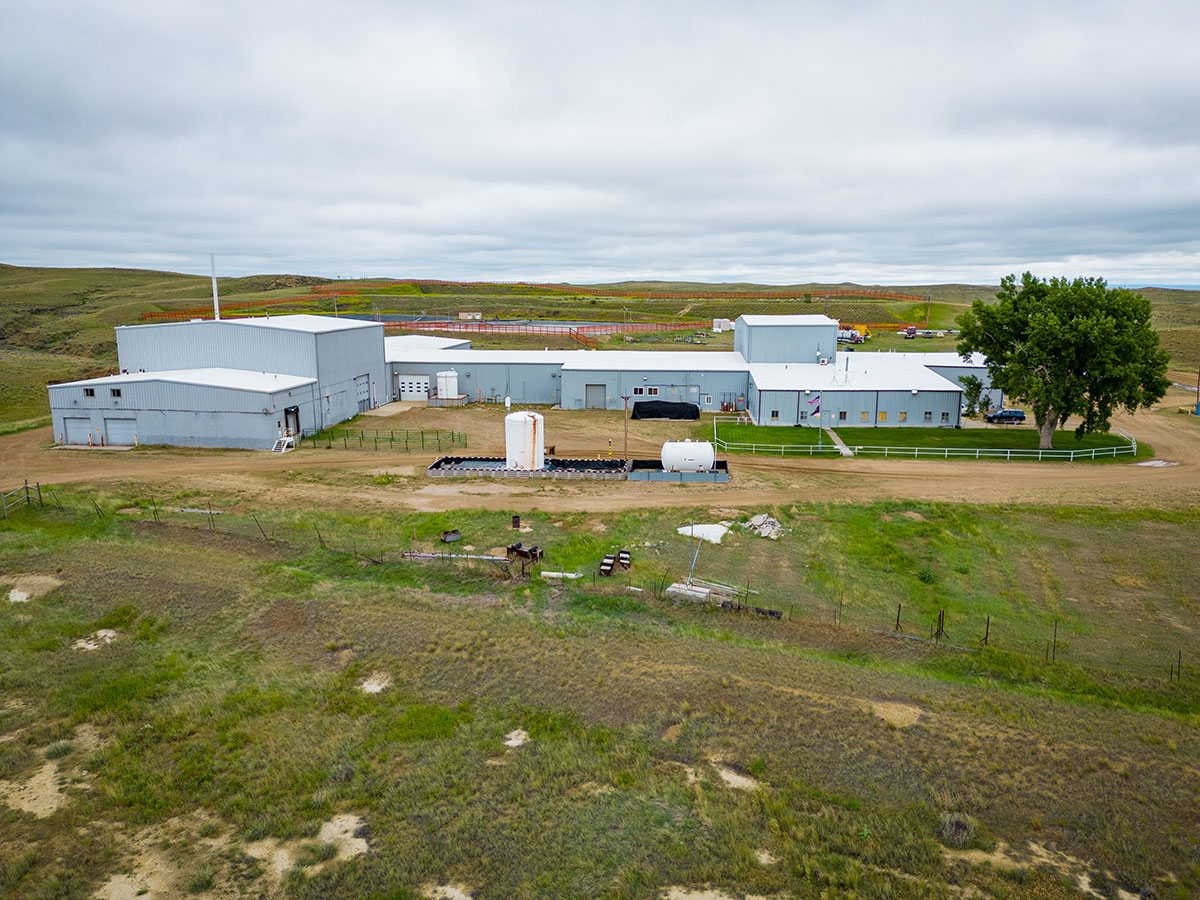
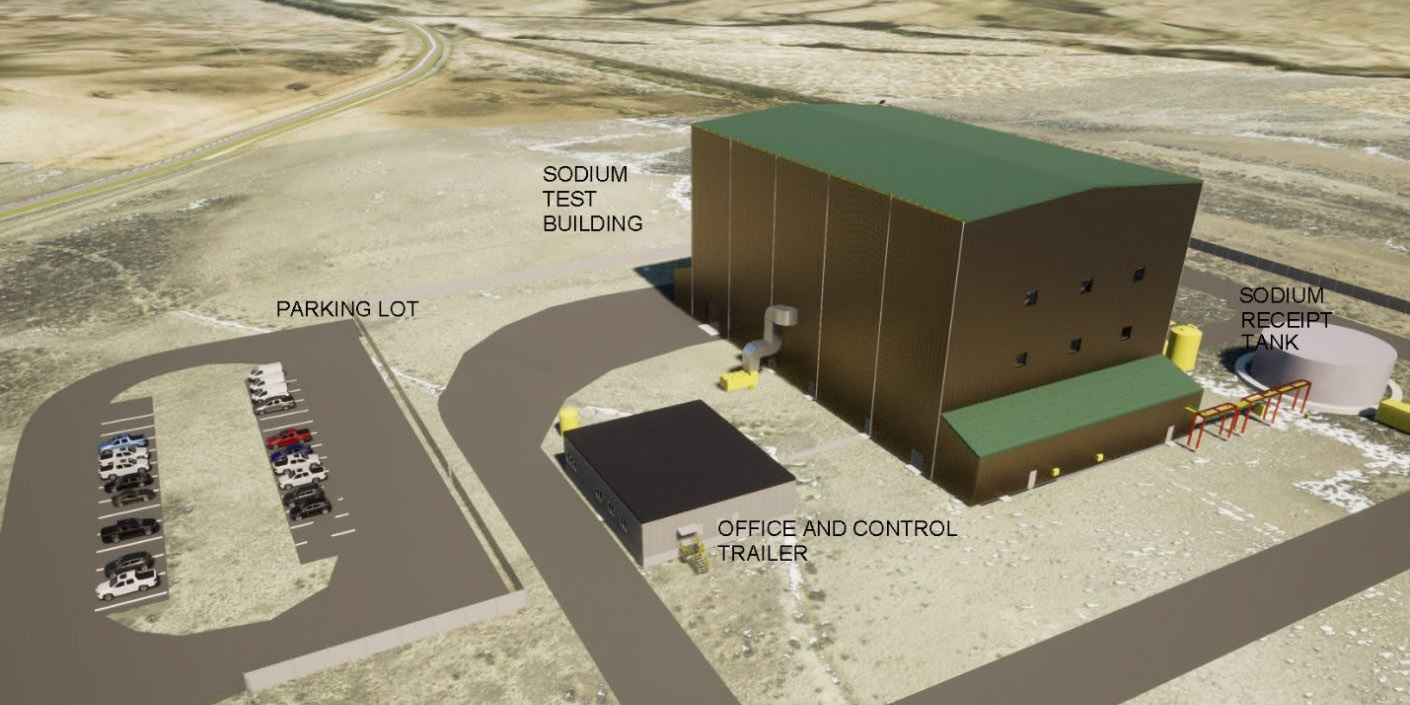
Image from the DOE’s draft EA showing a rendering of the TFF building. (Image: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations issued a draft environmental assessment (EA) in early November for a test and fill facility (TFF) that TerraPower plans to build in Kemmerer, Wyo.—the town selected two years ago to host the company’s first Natrium sodium fast reactor. The draft EA, open for comment through December 1, describes TerraPower’s plans to construct a nonnuclear facility that would safely store about 400,000 gallons of sodium to test coolant system designs and ultimately fill the planned reactor.
The Integrated Effects Test at TerraPower’s laboratory in Everett, Wash. (Photo: Southern Company/TerraPower)
Southern Company, TerraPower, and Core Power (a U.K.-based firm focused on developing nuclear technologies for the maritime sector) have commenced pumped-salt operations in the Integrated Effects Test (IET) facility, the Atlanta, Ga.-based utility announced Tuesday, marking another milestone in the development of TerraPower’s first-of-a-kind, Generation IV Molten Chloride Fast Reactor (MCFR).
An artist’s rendering of Natrium. (Image: TerraPower)
Advanced nuclear technology firm TerraPower announced today the selection of four suppliers to support its Natrium reactor demonstration project, in development near a retiring coal plant in Kemmerer, Wyo.
The former Zero-Power Physics Reactor cell at INL’s Materials and Fuels Center could be home to the MCRE. (Photo: INL)
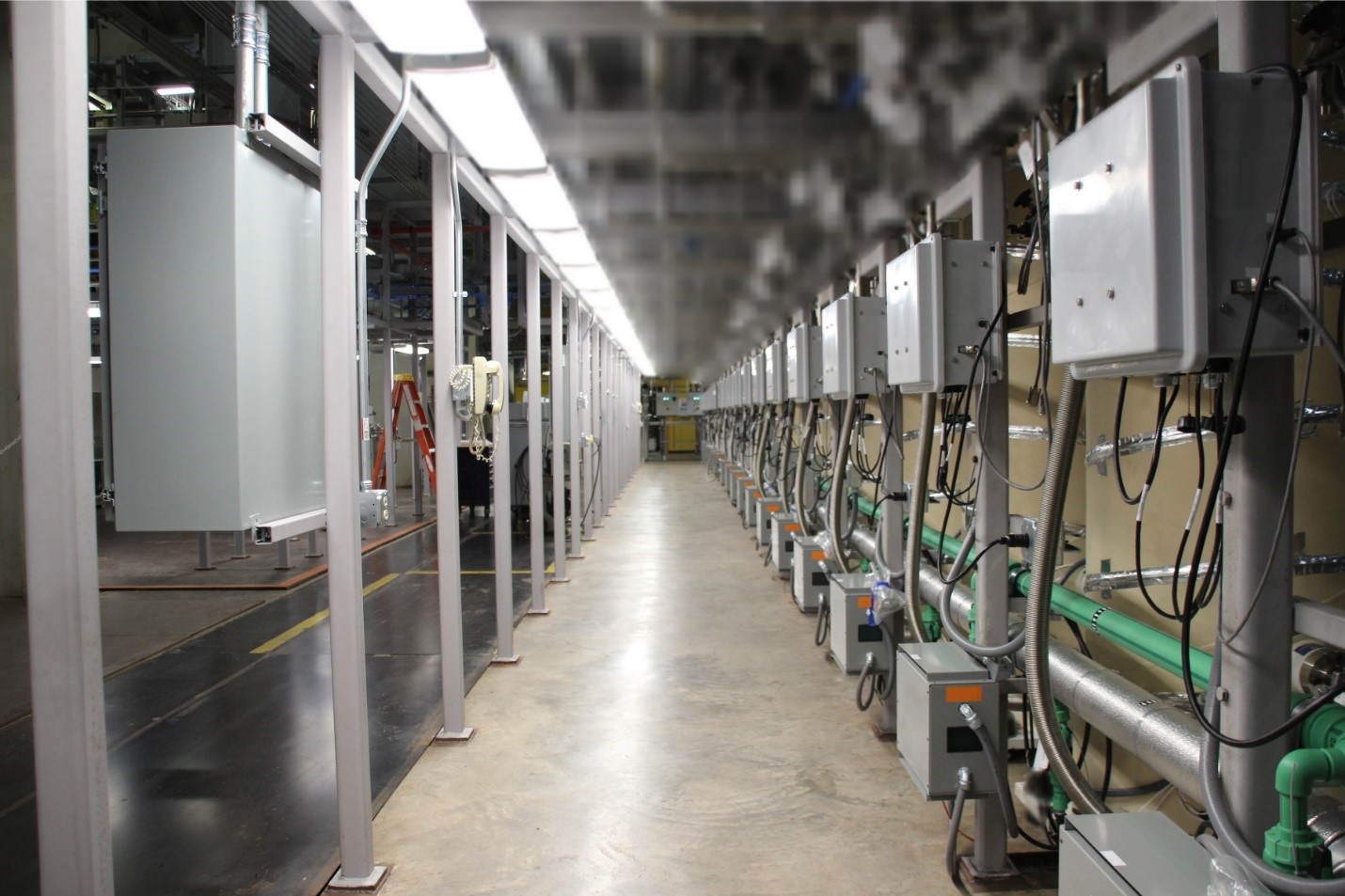
View of the machine controls electronics of Centrus’s HALEU demonstration cascade. (Photo: Centrus)
TerraPower and Centrus Energy Corp. announced on July 17 that they have signed a memorandum of understanding to “significantly expand their collaboration aimed at establishing commercial-scale, domestic production capabilities for high-assay, low-enriched uranium (HALEU)” to supply fuel for TerraPower’s first Natrium reactor. Nearly three years ago, TerraPower first announced plans to work with Centrus to establish commercial-scale HALEU production facilities. The two companies signed a contract in 2021 for services to help expedite the commercialization of enrichment technology at Centrus’s Piketon, Ohio, facility.
MCRE could be built inside the ZPPR cell (shown here) at INL’s Materials and Fuels Complex. (Photo: INL)
A tiny 200-kWt reactor the Department of Energy says would be the first critical fast-spectrum circulating fuel reactor and the first fast-spectrum molten salt reactor (MSR) could be built and operated inside the Zero Power Physics Reactor (ZPPR) cell at Idaho National Laboratory’s Materials and Fuels Center (MFC). Details included in the Molten Chloride Reactor Experiment (MCRE) draft environmental assessment (EA)—released on March 16 for two weeks of public comment (later extended to four weeks, through April 14)—covered the potential environmental impacts associated with the development, construction, operation, and decommissioning of MCRE at INL, facilitated by the National Reactor Innovation Center (NRIC).