Pictured, from left, are Steve Nesbit, Christina Leggett, John Kessler, Paul Dickman, John Mattingly, and Craig Hansen. Edwin Lyman, who joined the panel remotely, is not pictured.
Advanced reactors may be key to a clean energy future, but to prove it they’re going to need fuel—and that fuel will be derived from limited uranium resources and managed throughout the nuclear fuel cycle, whether that cycle is open (like the current fuel cycle) or closed (with reprocessing). Six panelists convened on June 12 during the Annual Meeting of the American Nuclear Society for the executive session “Merits and Viability of Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles: A Discussion with the National Academies.” They discussed those fuel cycles and the findings of a National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) consensus committee released as a draft report in November 2022 and published earlier this year.
Centrus’s HALEU demonstration cascade. (Photo: Centrus Energy)
Centrus Energy announced yesterday that it has received Nuclear Regulatory Commission approval to introduce uranium hexafluoride into its 16-machine centrifuge cascade in Piketon, Ohio, following operational readiness reviews by the NRC. Centrus says it “remains on track to begin production of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) by the end of 2023.” The announcement follows a series of inspections at the American Centrifuge site in April 2023.
An illustration of an IMSR plant. (Image: Terrestrial Energy)
Ontario–based Terrestrial Energy announced yesterday that its U.S. branch has been awarded a regulatory assistance grant from the Department of Energy to support the company’s Nuclear Regulatory Commission licensing program for the Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR) plant.
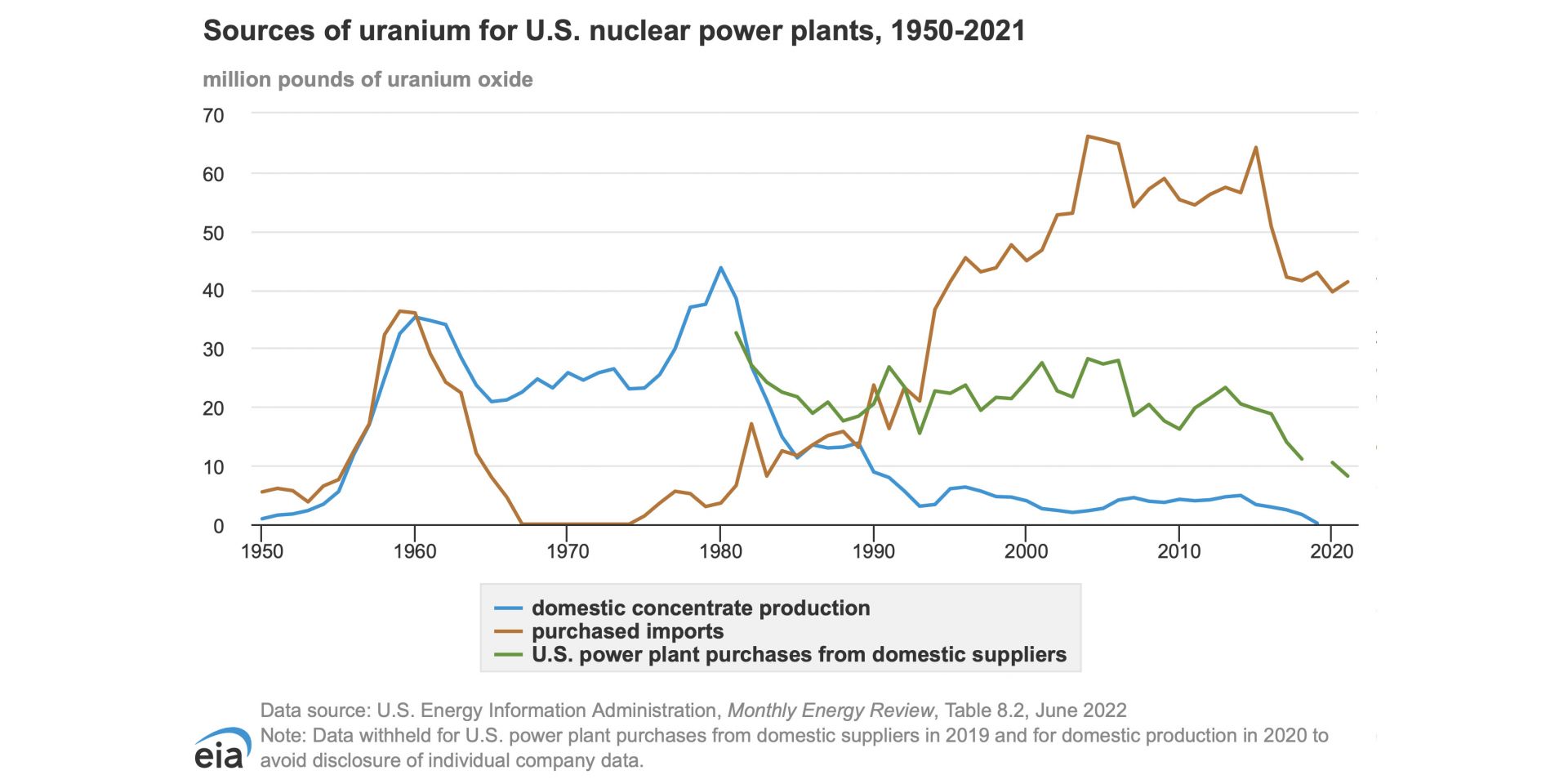
This chart from the EIA shows sources of uranium for U.S. nuclear power plants, 1950-2021. In 2020, according to the chart, 39.60 million pounds of uranium oxide was imported for the domestic nuclear power plant fleet. (Credit: Energy Information Agency)
The naturalist John Muir is widely quoted as saying, “When we try to pick out anything by itself, we find it hitched to everything else in the Universe.” While he was speaking of ecology, he might as well have been talking about nuclear fuel.
At the moment, by most accounts, nuclear fuel is in crisis for a lot of reasons that weave together like a Gordian knot. Today, despite decades of assertions from nuclear energy supporters that the supply of uranium is secure and will last much longer than fossil fuels, the West is in a blind alley. We find ourselves in conflict with Russia with ominous implications for uranium, for which Russia holds about a 14 percent share of the global market, and for two processes that prepare uranium for fabrication into reactor fuel: conversion (for which Russia has a 27 percent share) and enrichment (a 39 percent share).
March 14, 2023, 9:39AMEdited March 14, 2023, 9:38AMNuclear News In this screenshot from a video recording of the hearing, Huff, Wagner, and Dominguez answer a series of questions from Sen. Manchin
“Right now, our country is deficient in nearly every aspect of the fuel cycle. This must change and it must change quickly,” said Sen. Joe Manchin (D., W.V.), chairman of the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources (ENR), as he opened a Full Committee Hearing to Examine the Nuclear Fuel Cycle on March 9. “Whether it is uranium mining, milling, conversion, enrichment, nuclear fuel fabrication, power generation, or nuclear waste storage and disposal, there is much work to be done, starting with conversion and enrichment. Simply put, Russia dominates the global market, representing nearly half of the international capacity for both processes.”
Energy Fuels’ White Mesa Mill in southeastern Utah is the only operating conventional uranium mill in the United States. (Photo: Energy Fuels)
The bipartisan Nuclear Fuel Security Act (NFSA), introduced in the Senate last week, would authorize the Department of Energy to establish a Nuclear Fuel Security Program to “ensure a disruption in Russian uranium supply would not impact the development of advanced reactors or the operation of the United States’ light water reactor fleet.” The bill was introduced by Sen. Joe Manchin (D., W.V.), chairman of the Senate Energy and Natural Resources (ENR) Committee; Sen. John Barrasso (R., Wyo.), ranking member of the Senate ENR committee; and Sen. Jim Risch (R., Idaho).
A view of the completed demo cascade. (Photo: Centrus)
Centrus Energy announced February 9 that it has finished assembling a cascade of uranium enrichment centrifuges and most of the associated support systems ahead of its contracted demonstration of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) production by the end of 2023. When the 16-machine cascade begins operating inside the Piketon, Ohio, American Centrifuge Plant, which has room for 11,520 machines, it will be the first new U.S.-technology based enrichment plant to begin production in 70 years.
A rendering of the TRISO-X fuel fabrication facility. (Image: DOE)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission recently presented its proposed 30-month licensing review timeline of TRISO-X’s planned fuel fabrication facility at the project’s first-ever public meeting in Oak Ridge, Tenn.
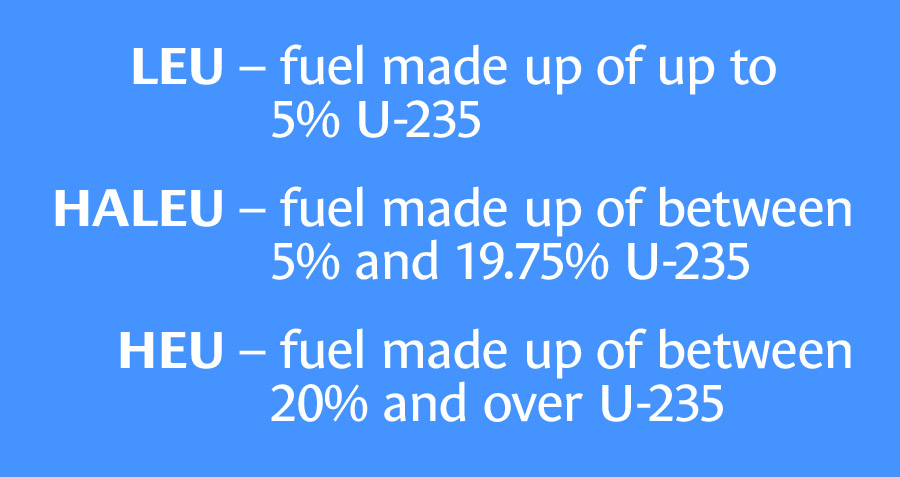
TRISO-X, a subsidiary of X-energy, has requested a 40-year license to possess and use special nuclear material to manufacture advanced fuel. The facility would be the first-ever commercial-scale fuel fabrication plant focused on using high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU).
Artist’s concept of the DRACO spacecraft, which will demonstrate a nuclear thermal rocket engine. (Image: DARPA)
NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) have announced they will collaborate on plans to launch and test DARPA’s Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations (DRACO). DARPA has already worked with private companies on the baseline design for a fission reactor and rocket engine—and the spacecraft that will serve as an in-orbit test stand—and has solicited proposals for the next phase of work. Now NASA is climbing on board, deepening its existing ties to DRACO’s work in nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) technology—an “enabling capability” required for NASA to meet its Moon to Mars Objectives and send crewed missions to Mars. NASA and DARPA representatives announced the development at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum in National Harbor, Md., on January 24.