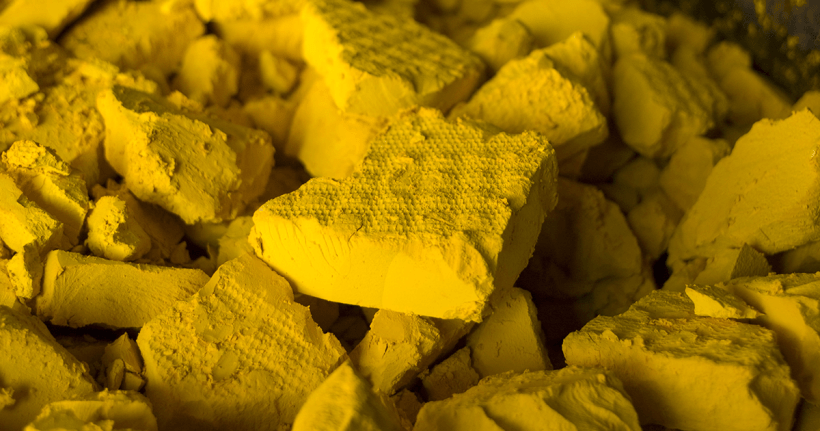
Uranium yellowcake is used in the preparation of uranium fuel that is used in nuclear reactors. (Photo: DOE)
On May 13, President Biden signed the Prohibiting Russian Uranium Imports Act, unlocking the $2.72 billion that Congress conditionally appropriated in March to increase production of low-enriched uranium (LEU) and high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU).
Bulgarian prime minister Dimitar Glavchev, left, and acting energy minister Vladimir Malinov visited Kozloduy nuclear power plant, where Westinghouse is lined up to build two new reactors. (Photo: gov.bg)
Bulgarian officials have approved the transition to Westinghouse fuel at the nation's Kozloduy nuclear power plant, as Bulgaria moves away from its reliance on Russian supplies. The fuel was recently delivered for use in Unit 5.
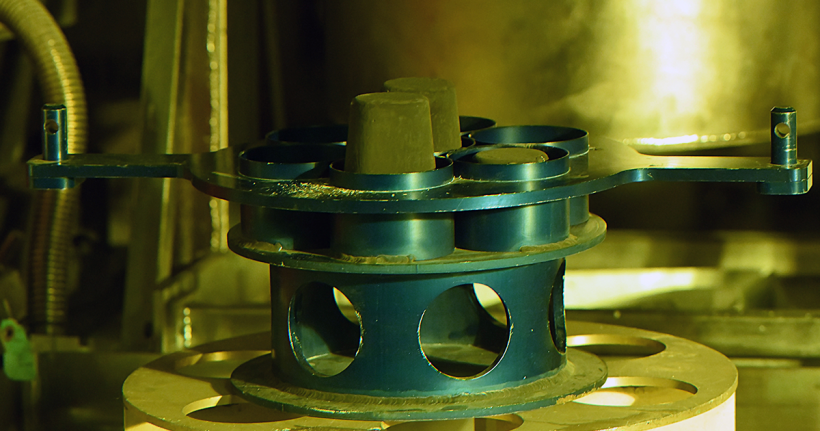
ANEEL fuel experiment capsules being staged at the ATR. (Photo: Clean Core)
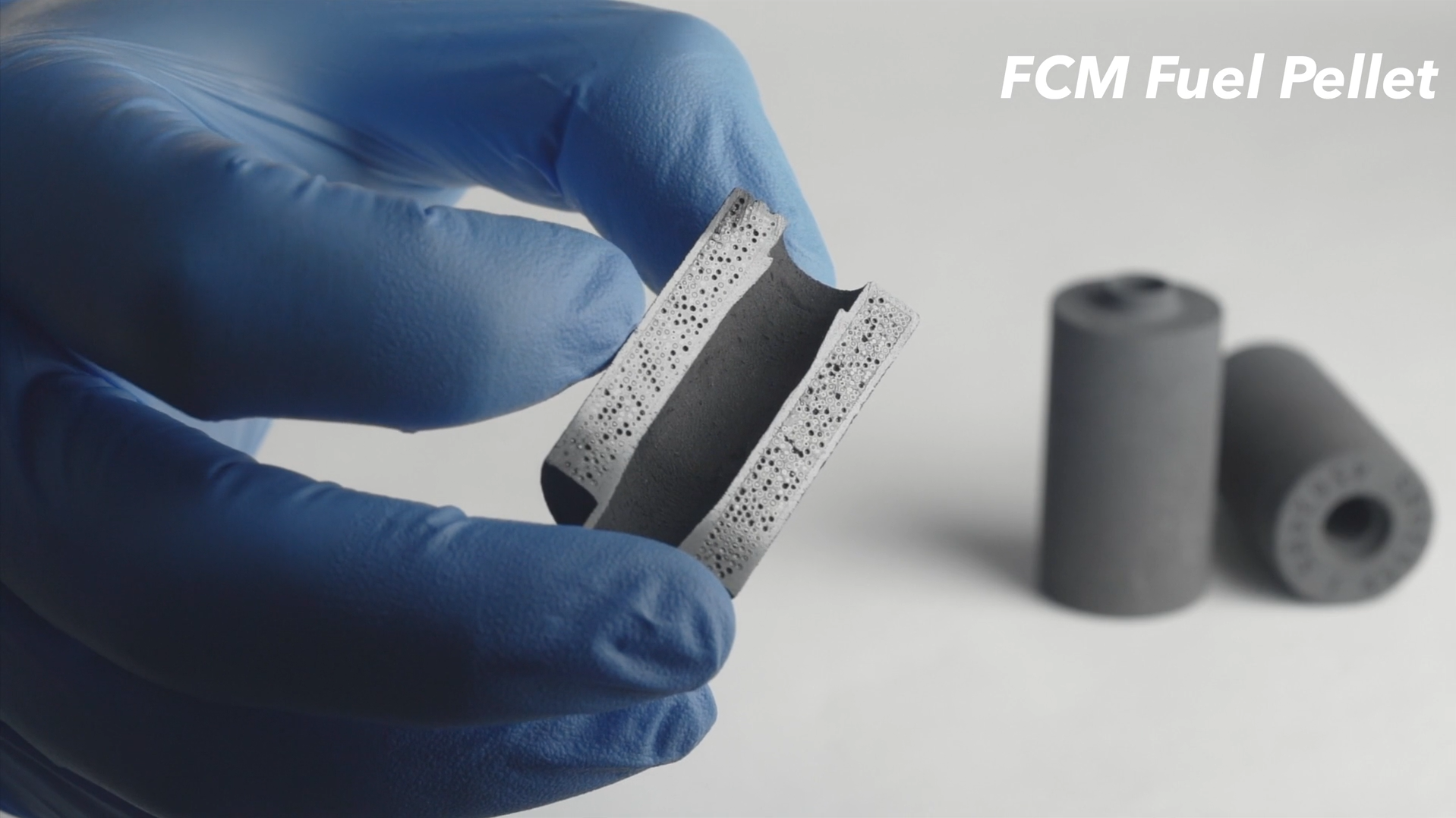
Clean Core Thorium Energy (Clean Core) has announced that its ANEEL fuel is ready to begin irradiation testing and qualification at Idaho National Laboratory. The fuel, made of thorium and HALEU, was developed by Clean Core for use in pressurized heavy water reactors, including CANDU (Canadian deuterium-uranium) reactors. Irradiation of the fuel samples in INL’s Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) is set to begin this month.
Irradiation of test fuel at SCK-CEN's BR2 reactor in Belgium. (Photos: KAERI)
The Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute has developed a high-density uranium silicide fuel designed to replace high-enriched uranium in research reactors. Recent irradiation tests appear to be successful, KAERI reports, which means the fuel could be commercialized to continue a key global nuclear nonproliferation effort—converting research reactors to run on low-enriched uranium fuel.
The extrusion in progress. (Photo: INL/Lightbridge)
Lightbridge Corporation announced today that it has reached “a critical milestone” in the development of its extruded solid fuel technology. Coupon samples using an alloy of zirconium and depleted uranium—not the high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) that Lightbridge plans to use to manufacture its fuel for the commercial market—were extruded at Idaho National Laboratory’s Materials and Fuels Complex.
HALEU reguli fabricated from downblended high-enriched uranium recovered from legacy EBR-II fuel at Idaho National Laboratory. (Image: DOE)
The Department of Energy yesterday announced a draft environmental impact statement (EIS) on HALEU Availability Program plans to purchase high-assay low-enriched uranium under 10-year contracts to seed the development of a sustainable commercial HALEU supply chain.
Urenco UK’s Capenhurst enrichment site, which received a grant in July 2023 to prepare for HALEU enrichment. (Photo: Urenco UK)
The United Kingdom’s Department for Energy Security and Net Zero announced plans on January 7 to invest £300 million (about $383 million) to build a high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) enrichment facility in northwest England. The goal? To “end Russia’s reign as the only commercial producer of HALEU.” Britain is now the first European country to declare that it will begin HALEU enrichment in a bid for supply chain security.
The Irigaray central processing plant, in Wyoming’s Powder River Basin. (Photo: Uranium Energy)
TerraPower and Uranium Energy announced today that they have signed a memorandum of understanding to “explore the potential supply of uranium” for TerraPower’s demonstration reactor in Kemmerer, Wyo.
The project team included (from left to right) Jennifer Watkins, Seth Ashby, and Adrian Wagner. (Photo: INL)
Researchers at Idaho National Laboratory in early 2023 manufactured commercial-grade high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) fuel pellets to the specifications of a General Electric accident tolerant fuel design, INL announced November 21. A team working at INL’s Experimental Fuels Facility at the Material and Fuels Complex fabricated about two dozen uranium dioxide pellets using HALEU enriched up to 15 percent U-235.
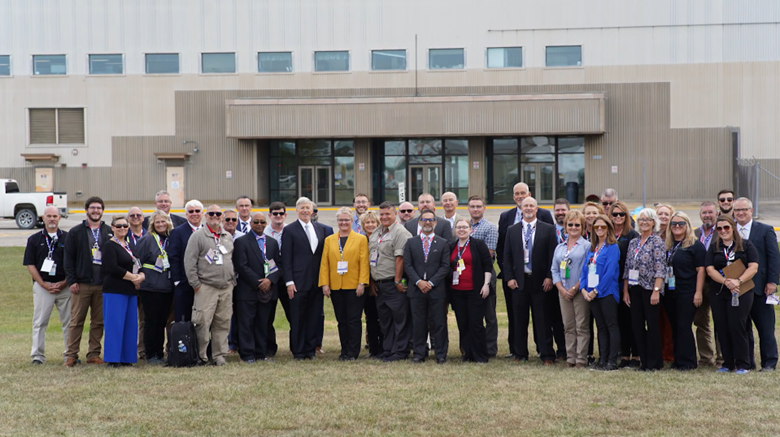
Centrus Energy staff posing in front of the American Centrifuge Plant. (Image: Centrus Energy)
Centrus Energy and the Department of Energy announced November 7 that Centrus has produced 20 kilograms of HALEU at the DOE-owned American Centrifuge Plant in Piketon, Ohio, satisfying Phase One of a DOE contract to stand up and operate 16 advanced centrifuges. Centrus will now move on to Phase Two of the contract, which requires a full year of HALEU production at a rate of 900 kilograms per year.