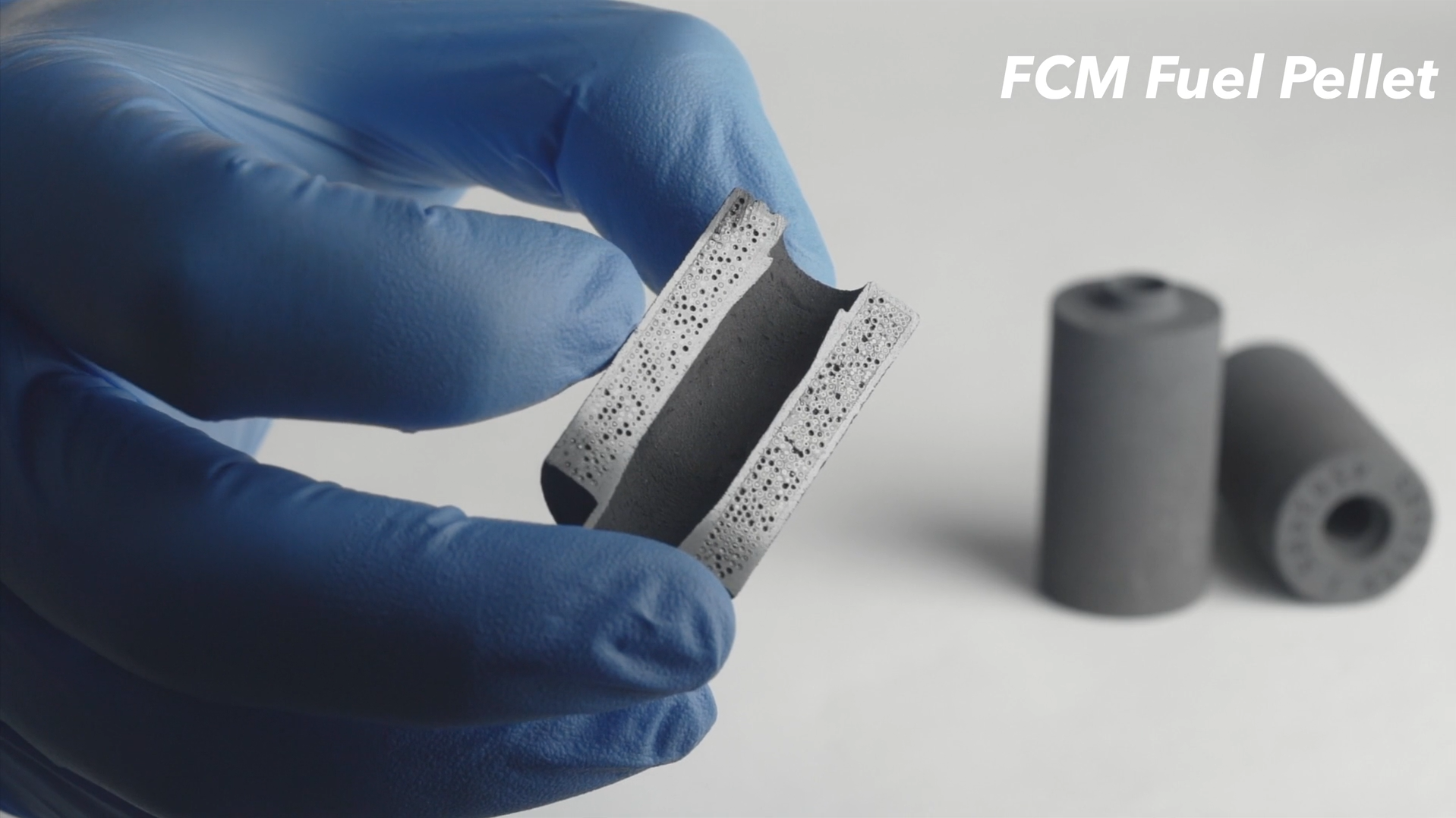
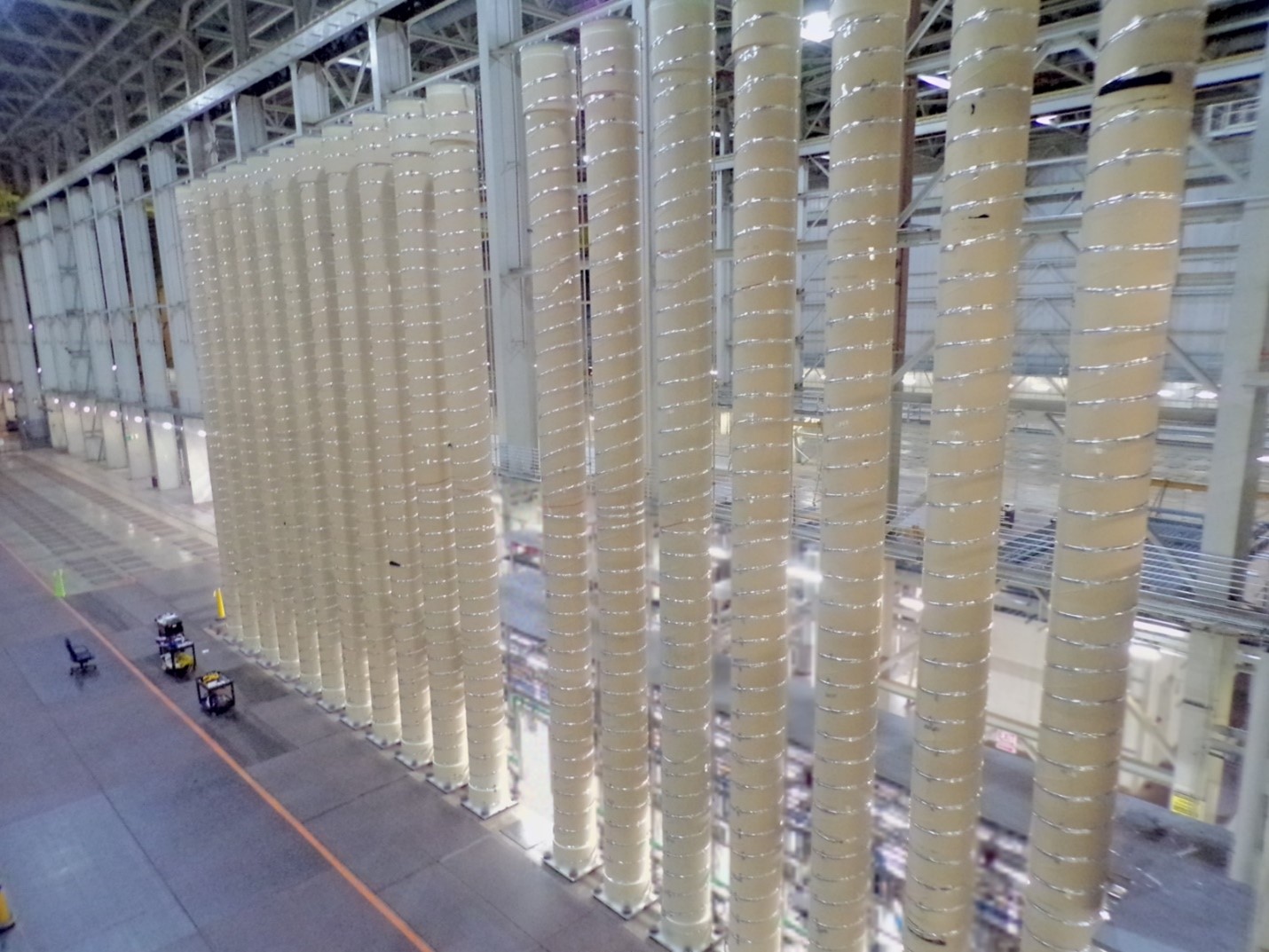
HALEU reguli fabricated from downblended high-enriched uranium recovered from legacy EBR-II fuel at Idaho National Laboratory. (Image: DOE)
The Department of Energy yesterday announced a draft environmental impact statement (EIS) on HALEU Availability Program plans to purchase high-assay low-enriched uranium under 10-year contracts to seed the development of a sustainable commercial HALEU supply chain.
Urenco UK’s Capenhurst enrichment site, which received a grant in July 2023 to prepare for HALEU enrichment. (Photo: Urenco UK)
The United Kingdom’s Department for Energy Security and Net Zero announced plans on January 7 to invest £300 million (about $383 million) to build a high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) enrichment facility in northwest England. The goal? To “end Russia’s reign as the only commercial producer of HALEU.” Britain is now the first European country to declare that it will begin HALEU enrichment in a bid for supply chain security.
The Irigaray central processing plant, in Wyoming’s Powder River Basin. (Photo: Uranium Energy)
TerraPower and Uranium Energy announced today that they have signed a memorandum of understanding to “explore the potential supply of uranium” for TerraPower’s demonstration reactor in Kemmerer, Wyo.
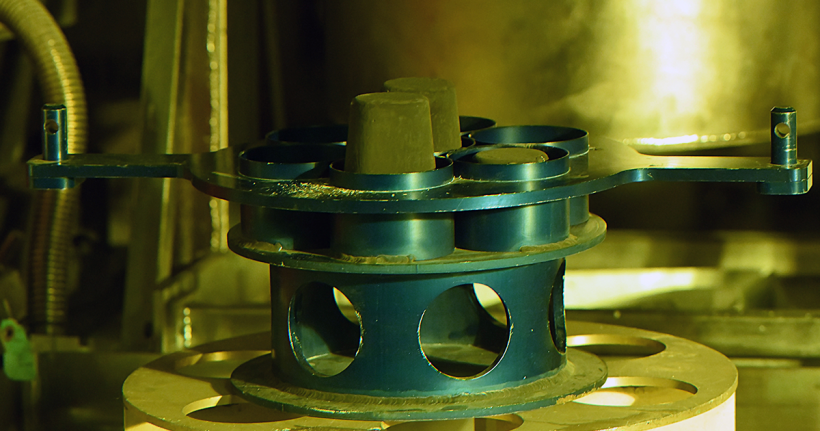
The project team included (from left to right) Jennifer Watkins, Seth Ashby, and Adrian Wagner. (Photo: INL)
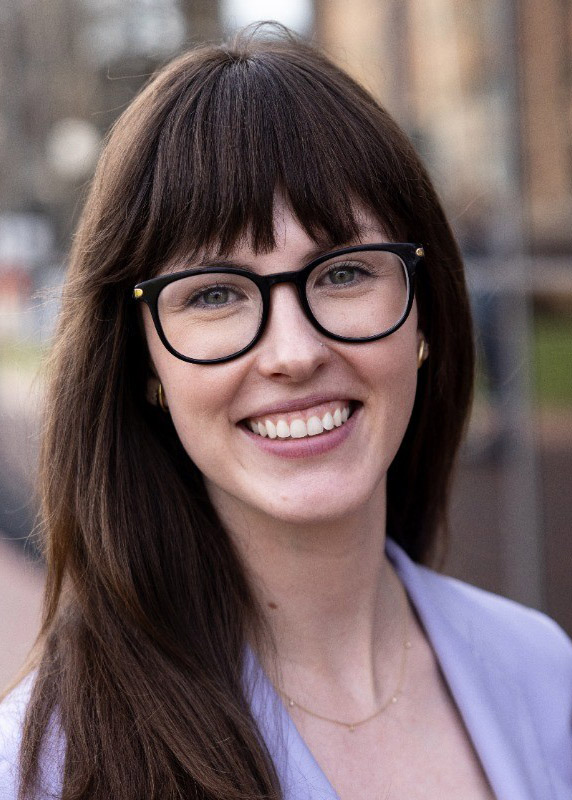
Researchers at Idaho National Laboratory in early 2023 manufactured commercial-grade high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) fuel pellets to the specifications of a General Electric accident tolerant fuel design, INL announced November 21. A team working at INL’s Experimental Fuels Facility at the Material and Fuels Complex fabricated about two dozen uranium dioxide pellets using HALEU enriched up to 15 percent U-235.
Centrus Energy staff posing in front of the American Centrifuge Plant. (Image: Centrus Energy)
Centrus Energy and the Department of Energy announced November 7 that Centrus has produced 20 kilograms of HALEU at the DOE-owned American Centrifuge Plant in Piketon, Ohio, satisfying Phase One of a DOE contract to stand up and operate 16 advanced centrifuges. Centrus will now move on to Phase Two of the contract, which requires a full year of HALEU production at a rate of 900 kilograms per year.
Idaho National Laboratory's TREAT reactor. (Photo: INL)
Researchers at Idaho National Laboratory have a new experimental tool to study nuclear fuel under simulated loss of coolant accident (LOCA) conditions in INL’s Transient Reactor Test (TREAT) Facility. A specialized experiment holder called a TWIST capsule holds a fuel sample surrounded by water, which can rapidly drain away during testing, simulating loss of coolant in a light water reactor environment.
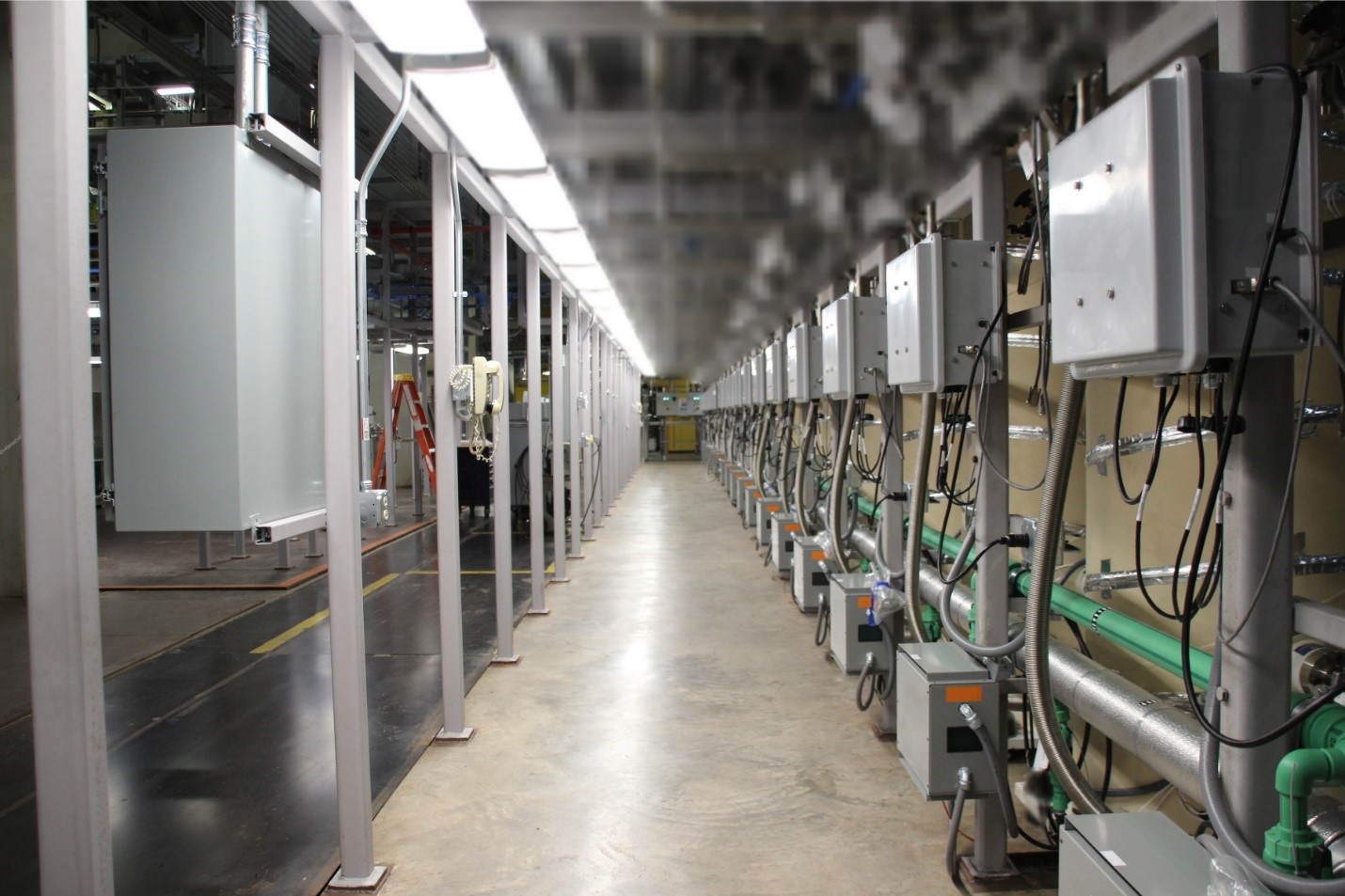
Upper-level view of Centrus’s HALEU cascade. (Photo: Centrus Energy)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is requesting comments on the regulatory basis for a proposed rule for light water reactor fuel designs featuring high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU), including accident tolerant fuel (ATF) designs, and on draft guidance for the environmental evaluation of ATFs containing uranium enriched up to 8 percent U-235. Some of the HALEU feedstock for those LWR fuels and for advanced reactor fuels could be produced within the first Category II fuel facility licensed by the NRC—Centrus Energy’s American Centrifuge Plant in Piketon, Ohio. On September 21, the NRC approved the start of enrichment operations in the plant’s modest 16-machine HALEU demonstration cascade.
View of the machine controls electronics of Centrus’s HALEU demonstration cascade. (Photo: Centrus)
TerraPower and Centrus Energy Corp. announced on July 17 that they have signed a memorandum of understanding to “significantly expand their collaboration aimed at establishing commercial-scale, domestic production capabilities for high-assay, low-enriched uranium (HALEU)” to supply fuel for TerraPower’s first Natrium reactor. Nearly three years ago, TerraPower first announced plans to work with Centrus to establish commercial-scale HALEU production facilities. The two companies signed a contract in 2021 for services to help expedite the commercialization of enrichment technology at Centrus’s Piketon, Ohio, facility.
A bank of Urenco centrifuges. (Photo: Urenco USA)
Urenco announced July 6 that it will expand enrichment capacity at its U.S. site in Eunice, N.M.—known as UUSA—by adding new centrifuge cascades to increase capacity by about 700 metric tons of separative work units per year, or a 15 percent increase, with the first new cascades coming on line in 2025.
Concept art of the planned Gadsden, Ala., MMR assembly plant. (Image: Ultra Safe Nuclear)
Ultra Safe Nuclear (USNC) announced on June 21 that it has selected the city of Gadsden, Ala., to host a $232 million MMR assembly plant. Modules for the company’s high-temperature, gas-cooled and TRISO-fueled microreactor, dubbed the Micro-Modular Reactor (MMR), would be manufactured, assembled, and tested at the “highly automated facility” once it is in operation.
Centrus’s HALEU demonstration cascade. (Photo: Centrus Energy)
Centrus Energy announced yesterday that it has received Nuclear Regulatory Commission approval to introduce uranium hexafluoride into its 16-machine centrifuge cascade in Piketon, Ohio, following operational readiness reviews by the NRC. Centrus says it “remains on track to begin production of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) by the end of 2023.” The announcement follows a series of inspections at the American Centrifuge site in April 2023.