Conceptual art of a direct air capture CO2 removal system. (Image: DOE)
Given how much carbon dioxide has been released into the atmosphere from fossil fuels, replacing those fuels with clean options like nuclear energy is urgent, but could be likened to shutting the barn door after the proverbial horse has bolted. But what if you could also round up excess CO2 already in the atmosphere? That’s the goal of direct air capture (DAC) and other so-called negative emission technologies—to capture climate warming CO2 for use in products or processes or for permanent storage.
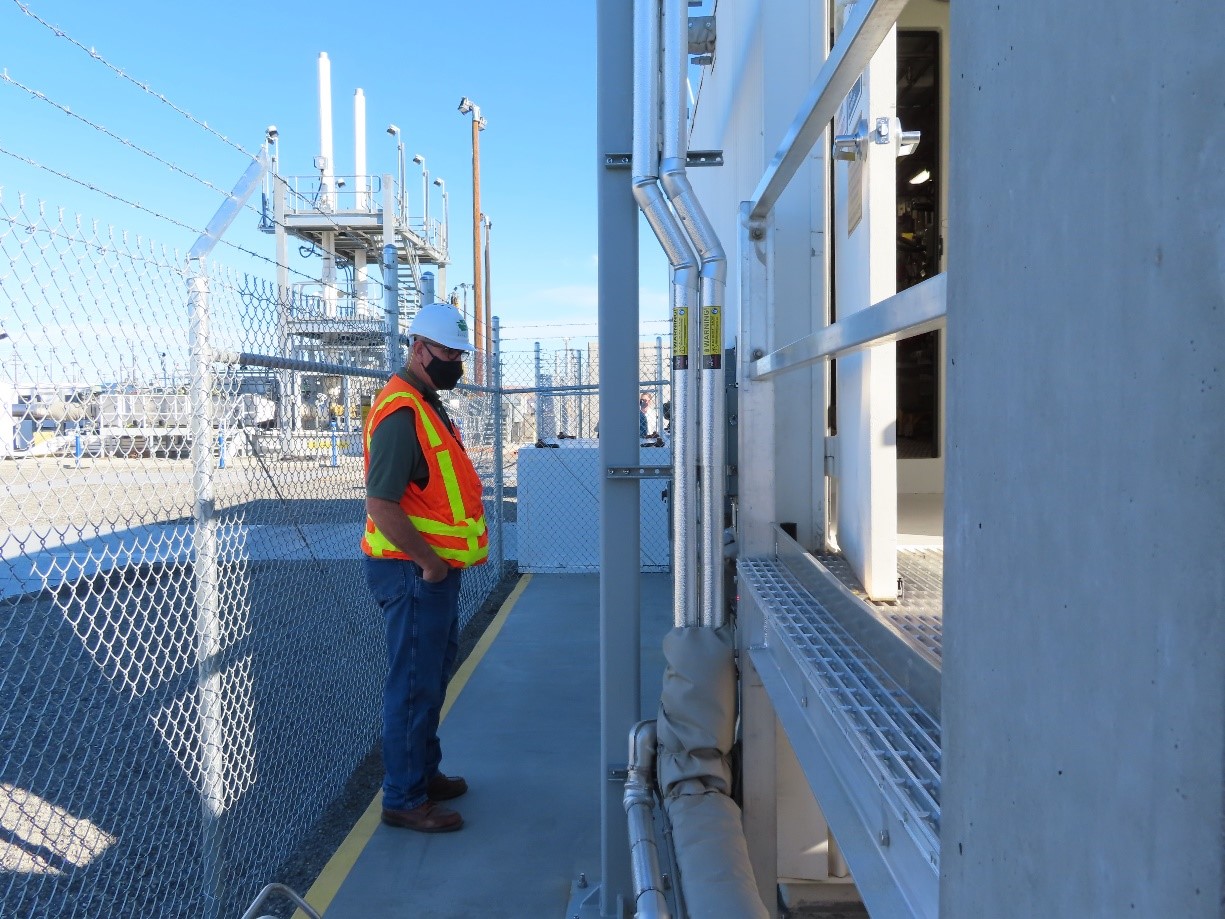
A Department of Ecology inspector at the Hanford Site. (Photo: Department of Ecology)
Washington state’s Department of Ecology said it has reached a settlement with the Department of Energy over access to data the state described as “critical” to the cleanup of the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash.
A startup heater is removed from a melter in the Vit Plant’s Low-Activity Waste Facility. (Photo: DOE)
Workers at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant, have begun removing the first three of 18 temporary startup heaters, the Department of Energy announced on September 12. The startup heaters were used to raise the first of two 300-ton glass melters in the plant’s Low-Activity Waste Facility to its operating temperature of 2,100°F.
DOE-EM senior advisor Ike White provided remarks to the audience during 7th International Forum on the Decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. (Photo: DOE)
Senior advisor Ike White and others with the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management traveled to Japan this week to attend the 7th International Forum on the Decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
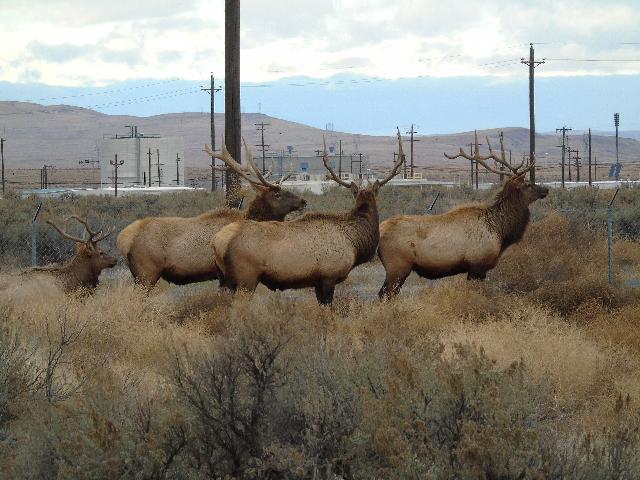
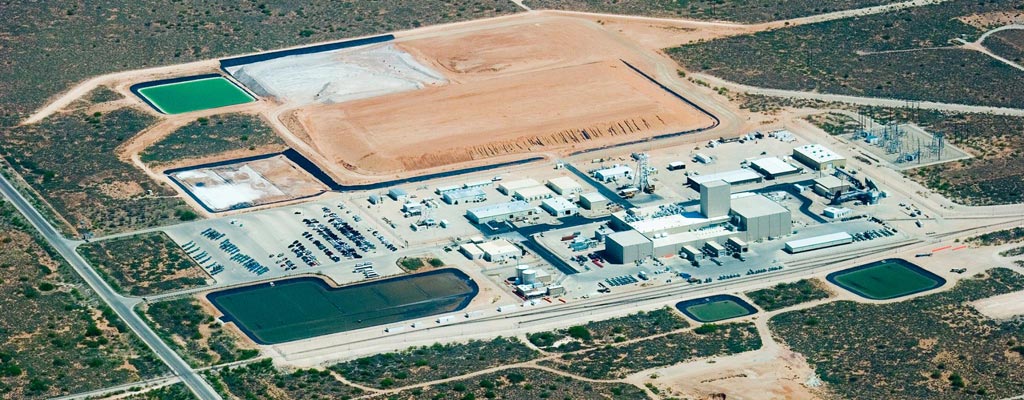
An elk herd at the DOE’s Hanford Site in Washington state. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy has released the first request for information (RFI) related to the department’s Cleanup to Clean Energy initiative, which aims to repurpose certain DOE-owned lands, portions of which were previously used in the nation’s nuclear weapons program, into sites for clean energy generation.
The site in Piketon, Ohio, where Oklo plans to deploy two microreactors under an agreement with Southern Ohio Diversification Initiative. (Photo: Oklo)
Oklo Inc. and Centrus Energy announced a new memorandum of understanding on August 28 to support the deployment of Oklo’s microreactor design, dubbed Aurora, near the Piketon, Ohio, site where Centrus plans to operate a high-assay, low-enriched uranium (HALEU) enrichment demonstration under contract to the Department of Energy by the end of the year.
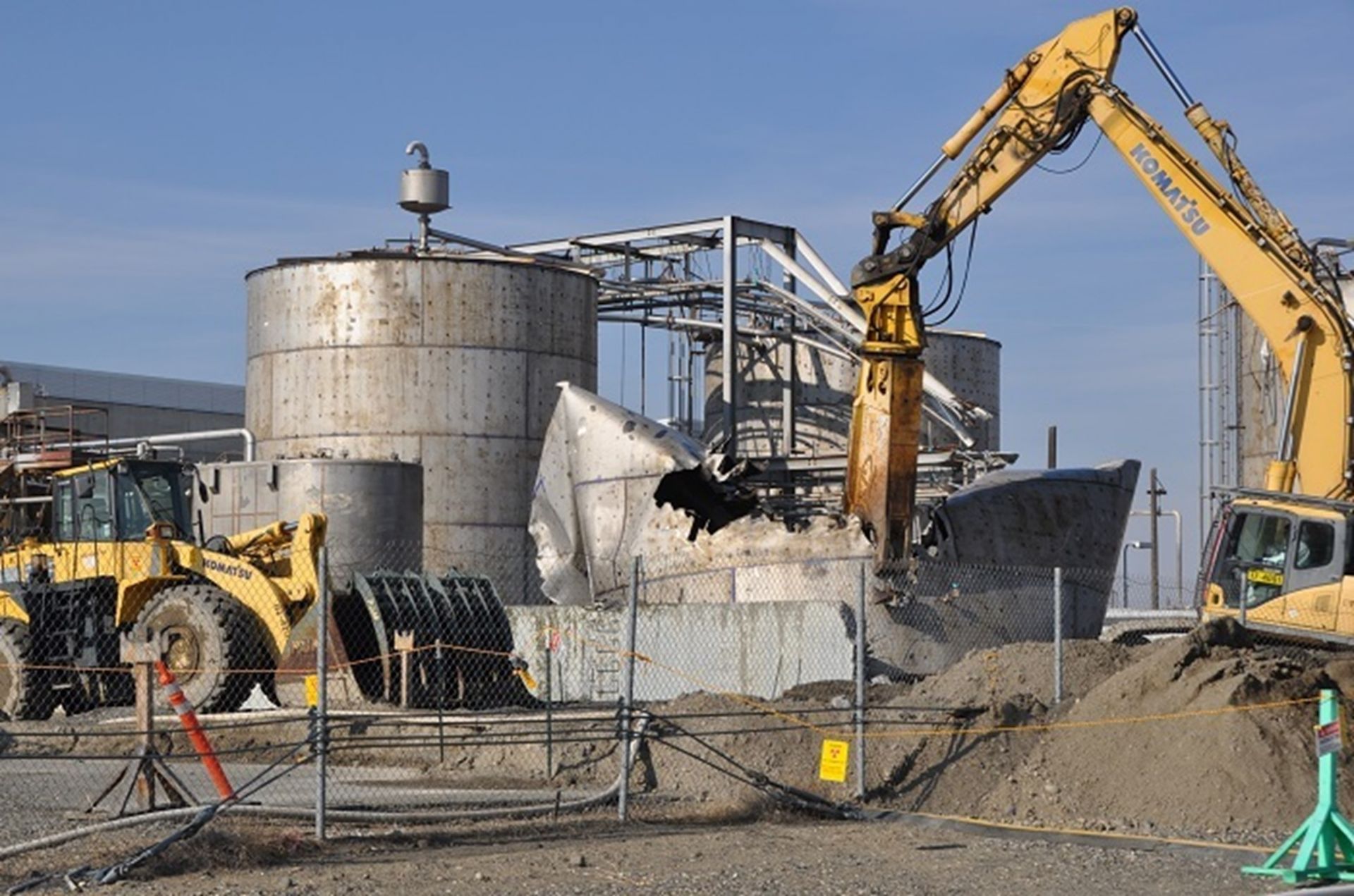
Work crews remove old infrastructure near the Hanford Site’s Cold War–era PUREX plant. (Photo: DOE)
Demolition is underway on several former chemical storage tanks and associated infrastructure near the Plutonium Uranium Extraction (PUREX) plant, the final and most advanced chemical separations facility at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site.
The project is expected to be completed by the end of September.
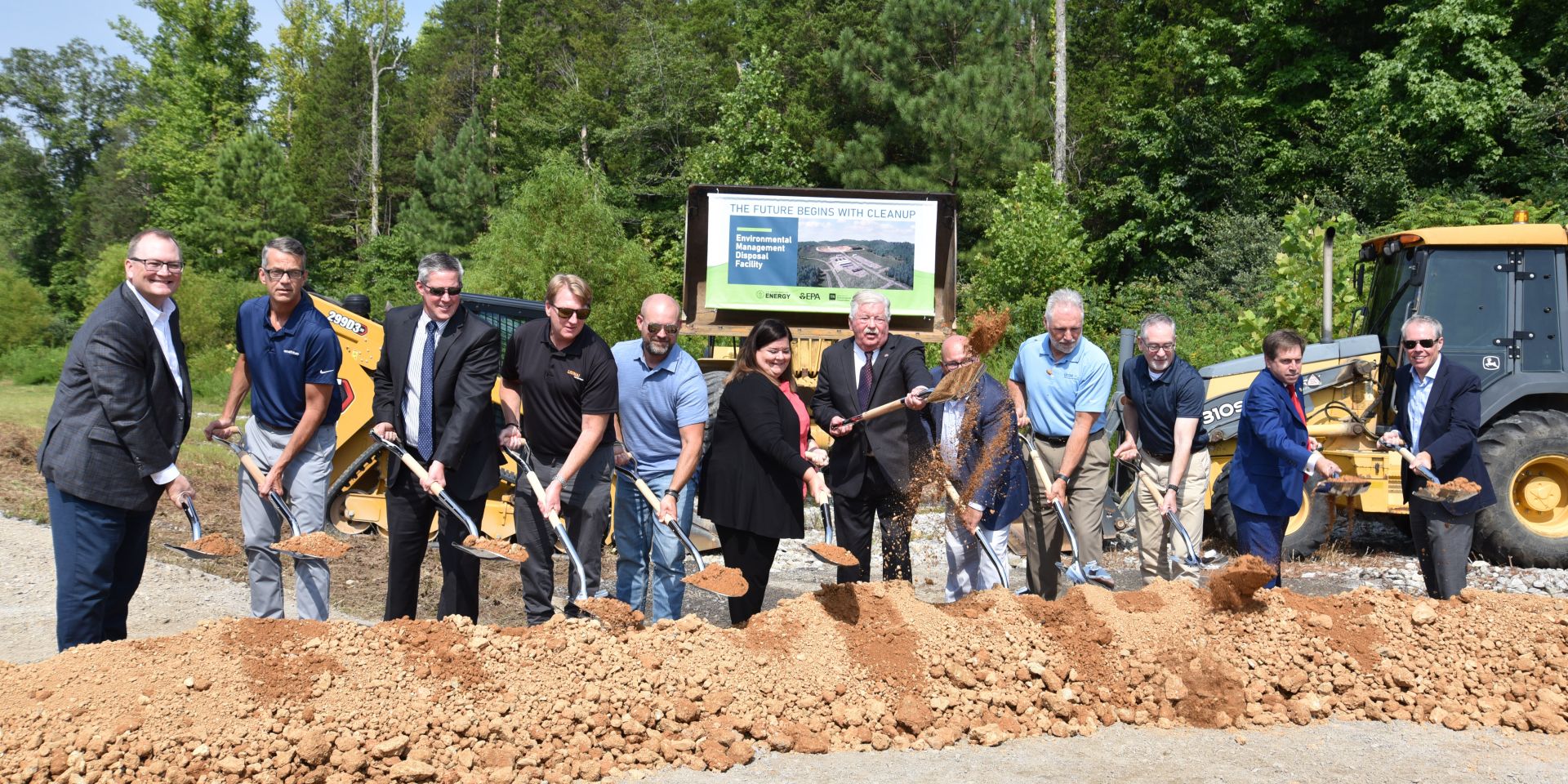
Taking part in the Environmental Management Disposal Facility groundbreaking, from left, were Steve Arnette of Jacobs; Mark Whitney of Amentum,; Wade Creswell, a Roane Co., Tenn., executive; Brent Booker of the Laborers’ International Union of North America; Kevin Adkisson of North America’s Building Trades Unions; Jeaneanne Gettle of the EPA; Lt. Gov. Randy McNally; David Salyers of TDEC; Ken Rueter of UCOR; Jay Mullis of OREM; U.S. Rep. Chuck Fleischmann; and DOE-EM’s William “Ike” White. (Photo: DOE)
National, state, and local leaders joined the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Office of Environmental Management (OREM) and its lead cleanup contractor, United Cleanup Oak Ridge (UCOR), earlier this month to celebrate the groundbreaking for a new on-site disposal facility at the Oak Ridge Reservation in Tennessee.
Watch a video highlighting the Environmental Management Disposal Facility groundbreaking ceremony here.
DOE assistant secretary for nuclear energy Kathryn Huff and NEA director general William D. Magwood IV affirmed U.S. membership in the NEA Data Bank at DOE headquarters in Washington, D.C. (Photo: OECD NEA)
The United States has joined the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) Data Bank, a decision that marks “a significant stride in international collaboration for nuclear energy research, safety, and knowledge exchange,” according to the August 16 NEA announcement. “As a country renowned for its scientific and technological excellence, the United States will undoubtedly enrich the Data Bank's repository of data, software, and benchmarks and enhance its role in fostering responsible nuclear development.”
An October 2022 photo showing various SDUs at SRS. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina will begin a leak tightness test on what it called “the fourth megavolume saltstone disposal unit (SDU)” at the site.
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy today announced a noncompetitive financial assistance cooperative agreement with Southeast New Mexico College, located in Carlsbad, N.M., for educational programs to enhance the knowledge, skills, and abilities of current Waste Isolation Pilot Plant employees while also building and training WIPP’s next-generation workforce.