The Hanford Site’s B Complex area tank farm containing waste created during the production of plutonium at the site. (Photo: DOE)
After nearly three years of discussions and more than 60 mediation sessions, the Department of Energy, Washington State Department of Ecology, and the Environmental Protection Agency announced that they have reached a conceptual agreement on revising plans for managing millions of gallons of waste stored in tanks at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash.
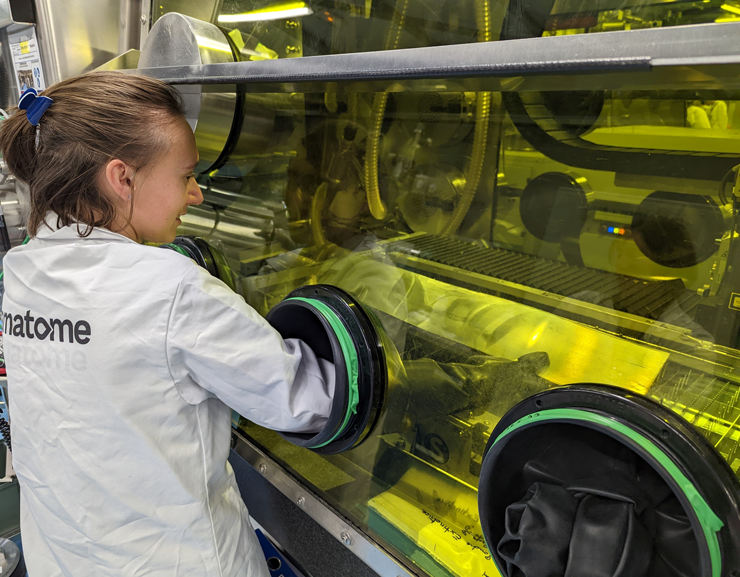
A Framatome operator fabricates U-Mo foils at CERCA. (Photo: Framatome)
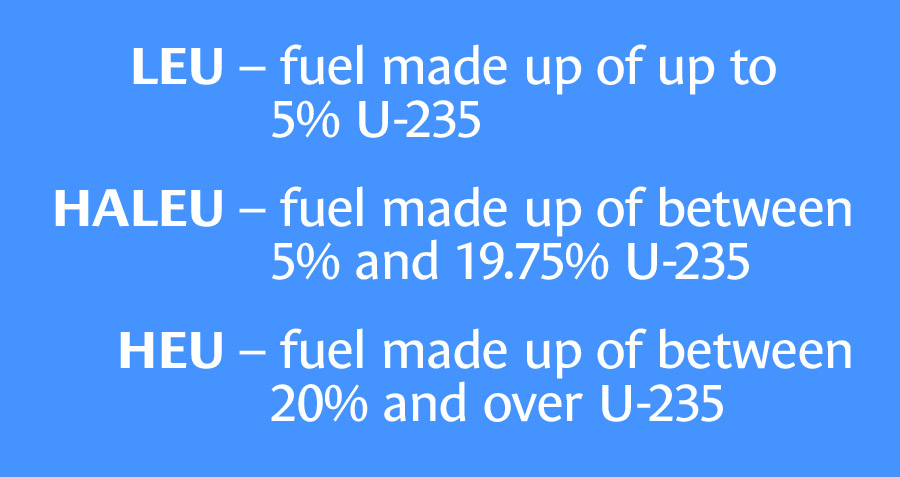
Framatome is prepared to manufacture a novel molybdenum-uranium (U-Mo) fuel to extend the life and safe operation of the Forschungsreaktor München II (FRM II) research reactor in Germany. A new fuel supply—one that uses uranium enriched to less than 20 percent U-235—means the FRM II can continue to supply neutrons to industry and the scientific community. The fuel is “Europe’s low-enriched fuel with the highest density ever realized for research reactor operations,” according to Framatome’s April 27 announcement.
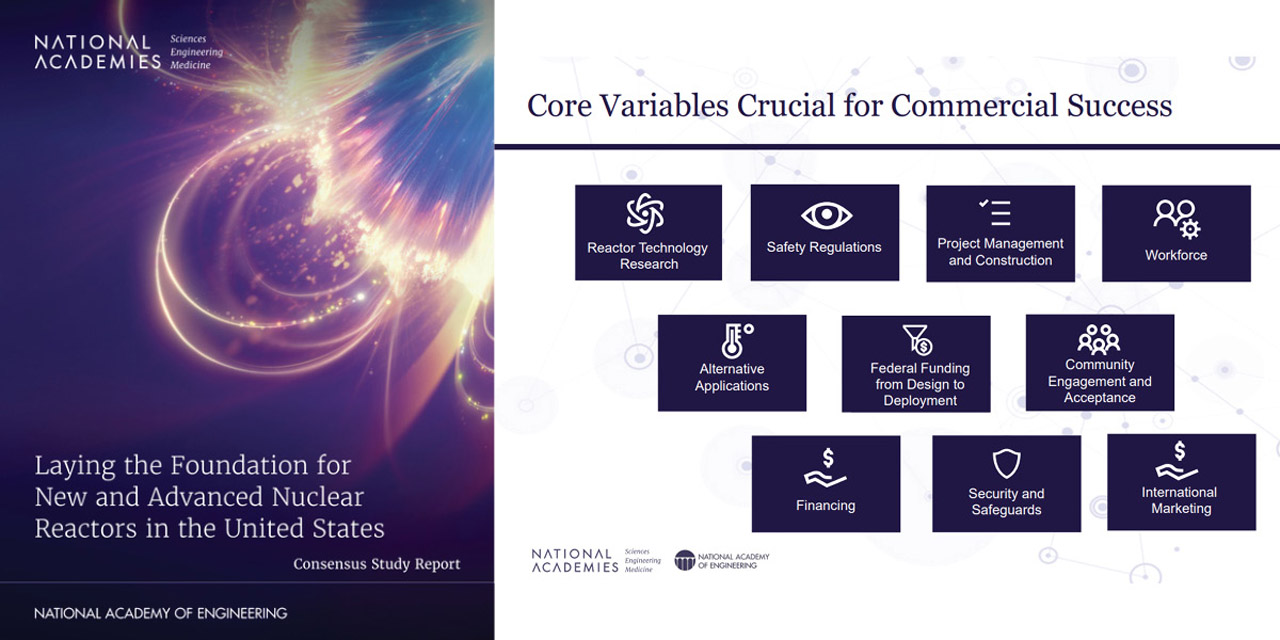
This slide on the right from the consensus committee’s public briefing identifies 10 core variables that are important to the success of advanced reactor deployments. (Image: NASEM, Laying the Foundation for New and Advanced Nuclear Reactors in the United States)
The DOE's Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
The Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB) is scheduled to visit the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina the week of May 8 to discuss ongoing safety concerns and the protection of the public and workforce, as well as the DOE’s effectiveness in addressing those concerns.
Pictured at the DOE's EM headquarters, from left, are Ana Han, foreign affairs specialist, EM International Program; Joceline Nahigian, director, EM Office of Intergovernmental and Stakeholder Programs; Scott Whiteford, deputy director, DOE Office of Legacy Management; William “Ike” White, EM senior advisor; Masaki Nakagawa, special advisor to executive directors, NDF; Tokuhiro Yamamoto, executive director, NDF; Shin Morita, managing director, International Affairs Group, NDF; Taro Hokugo, managing director, International Affairs Group, NDF; Jeff Avery, EM principal deputy assistant secretary; Angela Watmore, deputy assistant secretary, EM Office of Acquisition and Project Management; and Ming Zhu, EM senior advisor for laboratory policy. (Photo: DOE)
Representatives from the Japan Nuclear Damage Compensation and Decommissioning Facilitation Corporation (NDF) recently visited the Department of Energy's Office of Environmental Management (EM) headquarters in Washington, D.C., and the Hanford Site in Washington state to promote collaboration and provide updates on the status and plans to decommission Japan's Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. The Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011, caused damage to the plant and surrounding communities. The NDF was created in September 2011 to oversee the decommissioning and cleanup of the plant, which is owned by the Tokyo Electric Power Company.
These graphs illustrate how rapidly scaling the nuclear industrial base would enable nearer-term decarbonization and increase capital efficiency, versus a five-year delay to reach the same 200 GW deployment by 2050. (Source: DOE, Pathways to Commercial Liftoff: Advanced Nuclear, Fig. 1)
The Department of Energy released Pathways to Commercial Liftoff: Advanced Nuclear earlier this month. It is one of the first in a series of reports on clean energy technologies and the private and public investments needed to overcome hurdles to full-scale deployment. The report makes a clear case for investment in nuclear power and challenges potential investors and operators to move beyond the current “wait and see” stalemate and generate “a committed orderbook . . . for 5–10 deployments of at least one reactor design by 2025.”
William “Ike” White addresses the audience at INTEC, which gathered to celebrate the completion of the spent fuel wet-to-dry project at the INL site. (Photo: DOE)
At Idaho National Laboratory, Department of Energy leaders joined tribal, state, and local officials; contractors; and workers on March 28 to mark a recent milestone with the state of Idaho nearly 25 years in the making. The milestone was the completion of a spent fuel wet-to-dry project more than nine months ahead of a 1995 Idaho Settlement Agreement deadline.
MCRE could be built inside the ZPPR cell (shown here) at INL’s Materials and Fuels Complex. (Photo: INL)
A tiny 200-kWt reactor the Department of Energy says would be the first critical fast-spectrum circulating fuel reactor and the first fast-spectrum molten salt reactor (MSR) could be built and operated inside the Zero Power Physics Reactor (ZPPR) cell at Idaho National Laboratory’s Materials and Fuels Center (MFC). Details included in the Molten Chloride Reactor Experiment (MCRE) draft environmental assessment (EA)—released on March 16 for two weeks of public comment (later extended to four weeks, through April 14)—covered the potential environmental impacts associated with the development, construction, operation, and decommissioning of MCRE at INL, facilitated by the National Reactor Innovation Center (NRIC).
Participants in a job fair at the recent 2023 Waste Management Symposia visited a booth hosted by DOE representatives. A virtual component of the job fair is available through March 31. (Photo: DOE)
More than 300 employees from the Department of Energy's Office of Environmental Management (EM) have recently retired, resulting in a large amount of job vacancies across the cleanup program, according to the DOE.
EM’s Workforce Management Office is implementing recruitment efforts to fill the vacancies with college graduates, early career professionals, mid-career candidates, and seasoned veterans.
According to the DOE, "The open positions offer opportunities across many different disciplines, including engineering, science, business, management, safety and information technology."
Panelists speak at the 2023 Waste Management Symposia “Hot Topics” session. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has made great progress in accomplishing its cleanup of legacy radioactive waste but has yet to tackle its most challenging tasks, including the treatment of liquid tank waste at the Hanford, Idaho, and Savannah River sites. That was the consensus of the DOE-EM officials who took part in a panel session of the 2023 Waste Management Symposia, held February 26–March 2 in Phoenix, Ariz.
A technical collaboration agreement was signed by (seated from left) Jay Wileman, GEH; Jeff Lyash, TVA; Ken Hartwick, OPG; and Rafał Kasprów, SGE; and was observed by dignitaries and an audience both in-person and online. (Photo: TVA)
“I’m glad you came to our party!” said GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) chief nuclear officer Nicole Holmes as she prepared to announce that Wilmington, N.C.–based GEH will develop a standard design for its BWRX-300 boiling water small modular reactor with not one but three power producers representing three countries: Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), Ontario Power Generation (OPG), and Synthos Green Energy (SGE). Celebration was a theme throughout the March 23 event held in Washington, D.C., which was flush with dignitaries representing the United States, Canada, and Poland.
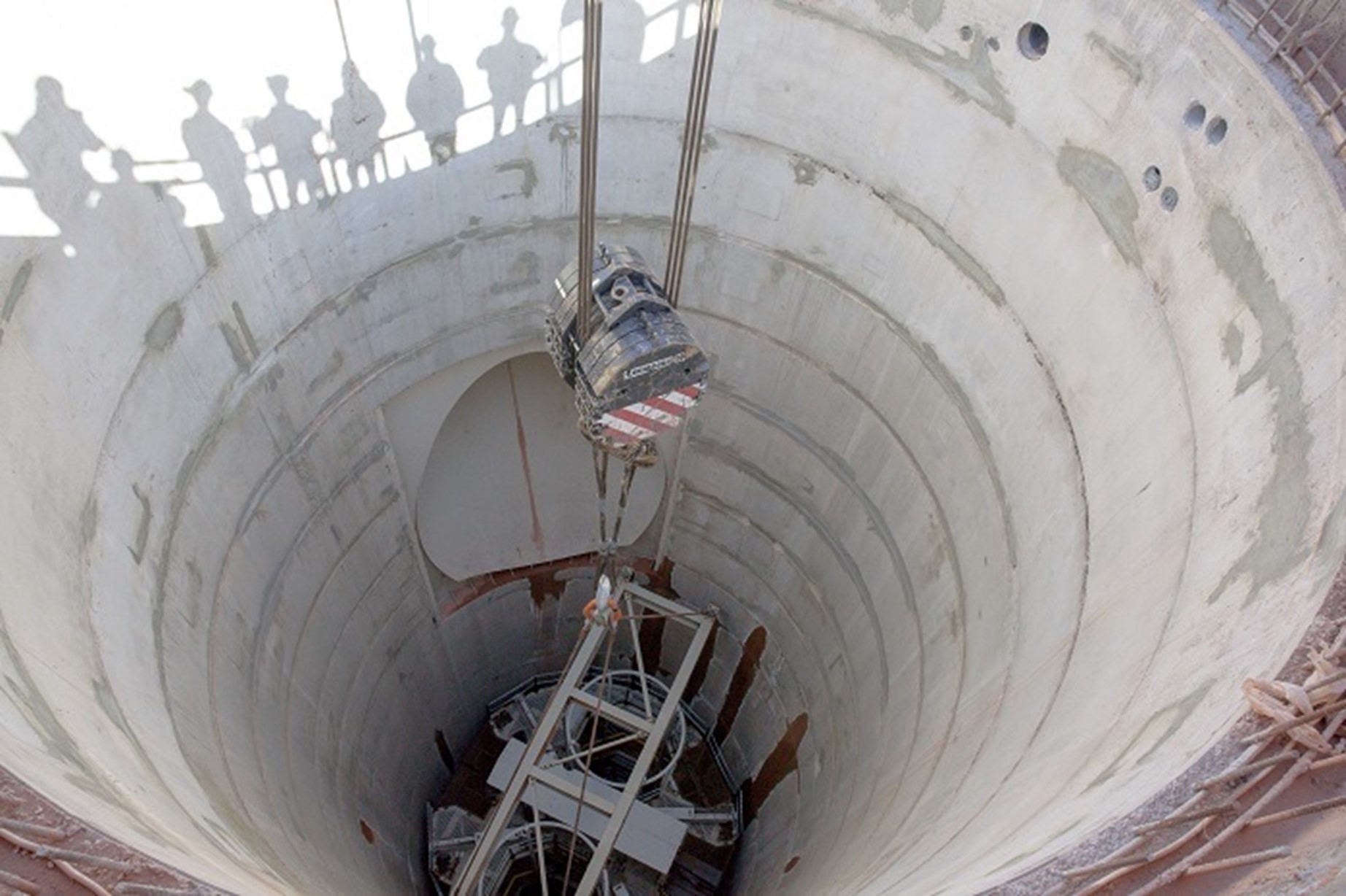
The Galloway is lowered into the utility shaft at WIPP. (Photo: DOE)
Progress continues on a new utility shaft at the Department of Energy’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico as shaft-sinking crews recently surpassed the midway point at a depth of 1,076 feet. When complete, the full shaft depth will be 2,275 feet, with the team now halfway to the WIPP repository depth of 2,150 feet.