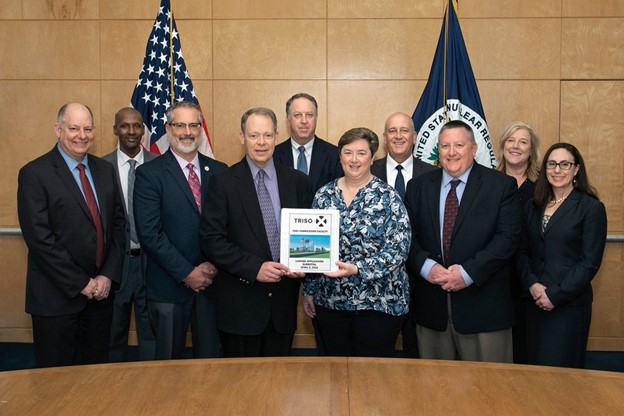
Pictured from left to right: John Tappert, NRC; Jonathan Rowley, NRC; Jacob Zimmerman, NRC; Matthew Bartlett, NRC; Tim Beville, DOE; Jennifer Wheeler, TRISO-X; John Lubinski, NRC; Pete Pappano, TRISO-X; Jill Caverly, NRC; and Shana Helton, NRC. (Photo: X-energy)
Ingots of HALEU derived from pyroprocessing of EBR-II driver fuel at Idaho National Laboratory. (Photo: INL)
On April 7, U.S. Sen. John Barrasso (R., Wyo.), ranking member of the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources, introduced the Fueling Our Nuclear Future Act of 2022. The bill would ensure a domestic supply of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) for advanced nuclear reactors by directing the Department of Energy to prioritize establishing a domestic HALEU enrichment capability and to use enriched uranium held by the DOE and the National Nuclear Security Administration to fuel advanced reactor demonstrations until U.S. commercial enrichment is available. The bill explicitly excludes uranium sourced or processed by any entity owned or controlled by the governments of Russia and China.
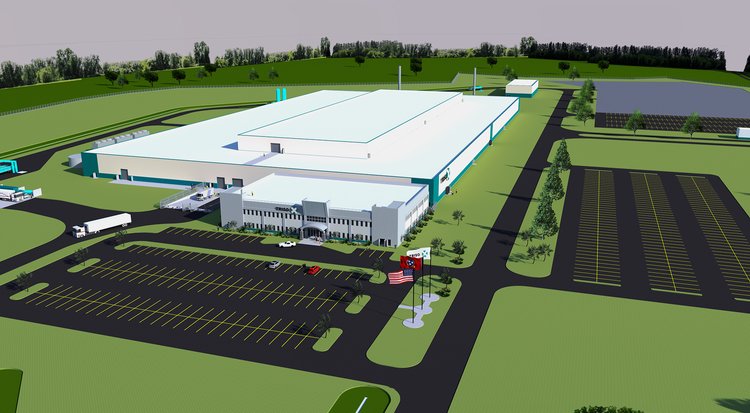
Artist's rendering of the proposed TRISO-X Fuel Fabrication Facility (TF3) at the Horizon Center Industrial Park, in Oak Ridge, Tenn. (Image: X-energy)
X-energy has announced that its wholly owned subsidiary, TRISO-X, plans to build the TRISO-X Fuel Fabrication Facility, dubbed TF3, at the Horizon Center Industrial Park in Oak Ridge, Tenn. X-energy has produced kilogram quantities of fuel at its pilot plant at Oak Ridge National Laboratory through a public-private partnership.
The commercial plant will use high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) to produce TRISO particles, which are fabricated into fuel forms, including the spherical graphite “pebbles” needed to fuel the company’s Xe-100 high-temperature gas reactor. Site preparation and construction are expected to get underway in 2022, and commissioning and start-up are scheduled for as early as 2025, according to X-energy.
Cover of the April 1962 issue of Nuclear News (left), ATR core diagram appearing in October 1969 issue of Nuclear News (center), and cover of the October 1969 issue of Nuclear News (right).
The Department of Energy and Idaho National Laboratory announced this week that the sixth major core overhaul of the Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) is complete, after an 11-month outage that began in April 2021. The ATR was built as a key piece of mission support for U.S. Navy programs and first reached full power in 1969. Today it remains “the world’s largest, most powerful and flexible materials test reactor,” in the words of INL—quite a feat for a reactor that was planned over 60 years ago.
A screenshot of the panelists for the ANS spent fuel management webinar.
The Department of Energy’s new consent-based process for siting an interim storage facility for the nation’s spent nuclear fuel faces many challenges, but it could be successful if correctly implemented by the department, according to the panelists of the American Nuclear Society’s webinar “Spent Nuclear Fuel Management: Wasting Away or Chance for Progress?” ANS President Steve Nesbit moderated the webinar, held on March 23.
A panel on the status and benefits of fusion technology featured, from left, Kimberly Budil (moderator), of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory; Kathy McCarthy, of Oak Ridge National Laboratory; Abdalla Darwish, of Dillard University; Anne White, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Steven Cowley, of Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory; and Mark Berry, of Southern Company.
The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy and the Department of Energy cohosted the White House Summit on Developing a Bold Decadal Vision for Commercial Fusion Energy on March 17. The livestreamed event brought together fusion leaders from government, industry, academia, and other stakeholder groups to showcase recent achievements in fusion research and discuss the administration’s strategy to support the development of commercial fusion energy. Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm’s announcement of a new agency-wide fusion energy initiative and a funding opportunity worth $50 million for magnetic confinement fusion research made March 17 a lucky day indeed for the U.S. fusion energy community.
An artist’s rendering of the K East Reactor safe-storage enclosure. (Photo: DOE)
Preparations are being made to enclose, or “cocoon,” the K East Reactor, the seventh of nine former reactors at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site. The cocooning project is expected to be completed by the end of the year.
Watch this video for more on the project.
An illustration of a potential mobile microreactor site at Test Pad D in INL’s Critical Infrastructure Test Range Complex for the grid operation phase of Project Pele. (Image: DOD)
The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) is looking to reduce its reliance on local electric grids and diesel-fueled generators at military installations. Project Pele is designed to demonstrate the technical and safety features of mobile microreactors capable of generating up to 5 MWe.
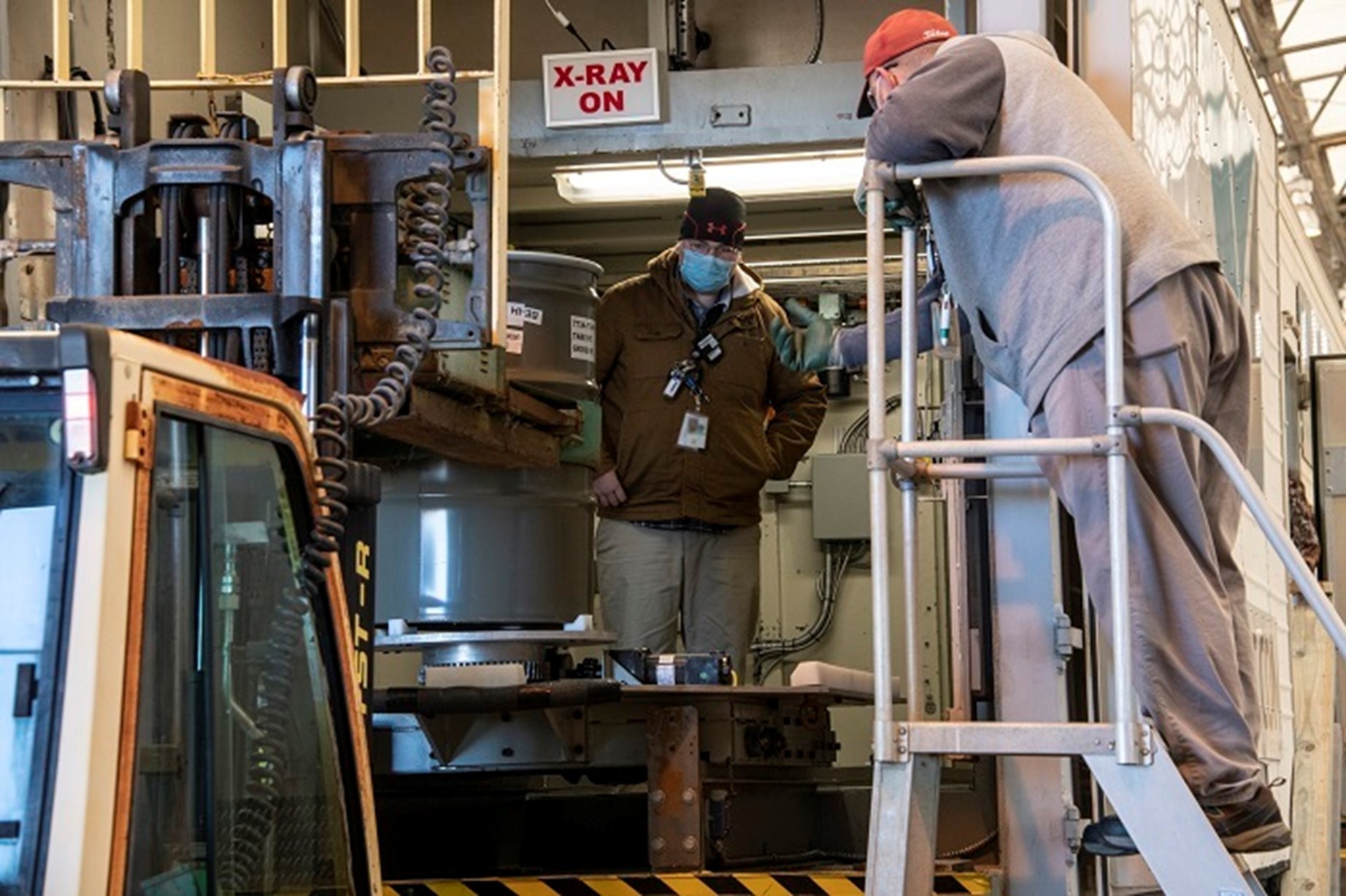
Operators load a TRU waste drum into a real-time radiography unit for characterization at the Solid Waste Management Facility at the Savannah River Site. (Photos: DOE)
Operators at the Savannah River Site’s Solid Waste Management Facility can now characterize and certify newly generated TRU waste through the use of a real-time radiography unit that uses an X-ray system to examine the contents of waste containers. The equipment was recently installed to meet updated requirements set by the Department of Energy’s National TRU Program that involve evaluating the containers for chemical compatibility and oxidizing chemicals.
The shipments of TRU waste from SRS, in South Carolina, are sent to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP), in New Mexico, for disposal.
The Moab cleanup site in Utah in 2018. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (DOE-EM) has awarded a cleanup contract to North Wind Portage, Inc. for completion of environmental remediation of a uranium ore processing site near Moab, Utah. North Wind Portage is located in Idaho Falls, Idaho.
More information about the Moab project is available here.
This image is described by the Alaska Center for Energy and Power as a conceptual layout of a generic small modular reactor or microreactor. (Image: ACEP)
Alaska Gov. Mike Dunleavy (R.) introduced “An act relating to microreactors” (SB 177) in the Alaska state legislature on February 1 that would modify existing state law on nuclear energy by specifying that microreactors are not subject to certain nuclear reactor siting and permitting regulations in Alaska. The bill defines a microreactor as an advanced nuclear fission reactor that would be capable of generating no more than 50 MWe.
An SRNS subcontractor technician takes radiological readings of soil near Lower Three Runs, part of a major project to complete the cleanup of a contaminated 25-mile-long stream corridor at SRS. (Photo: DOE) (CLICK TO SEE FULL PHOTO)
Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS), the Department of Energy’s management and operating contractor for the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, has reached an agreement with the state of South Carolina and federal environmental regulators on the final cleanup of a 25-mile-long stream corridor at the site that was radiologically contaminated as a result of operations during the Cold War.
The corridor consists of Par Pond, nine miles of canals adjacent to the pond, and a stream named Lower Three Runs. The stream begins near the center of the site, just above Par Pond, and winds its way southward across SRS.









 The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has issued EM Strategic Vision 2022-2032, a blueprint for planned nuclear-related cleanup efforts over the next decade. The document outlines environmental cleanup priorities for 2022–2032, focusing on safety, innovation, and improved performance.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has issued EM Strategic Vision 2022-2032, a blueprint for planned nuclear-related cleanup efforts over the next decade. The document outlines environmental cleanup priorities for 2022–2032, focusing on safety, innovation, and improved performance.