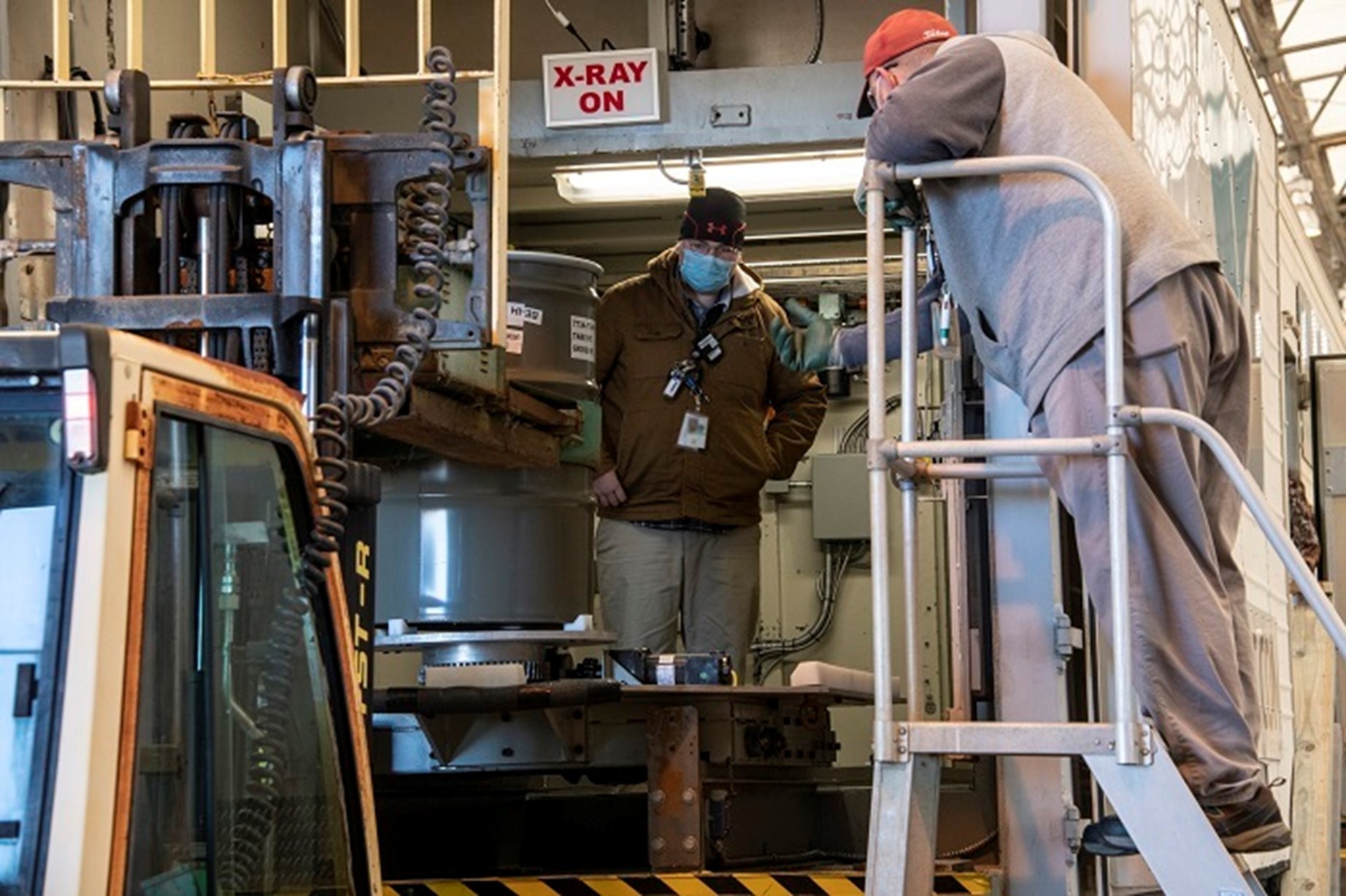
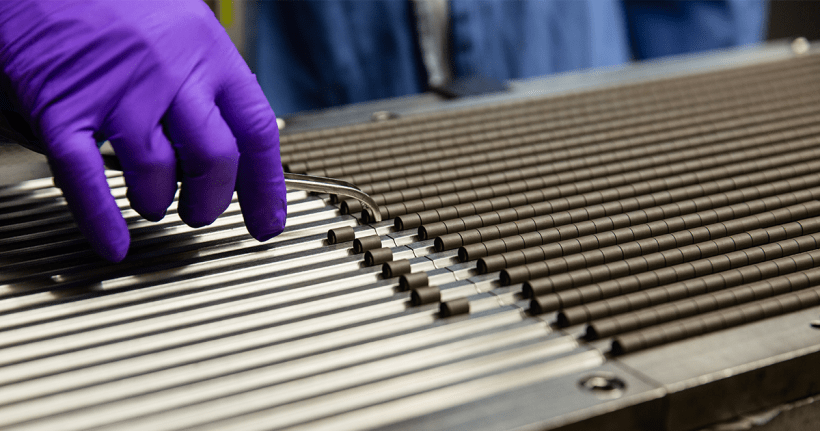
Operators load a TRU waste drum into a real-time radiography unit for characterization at the Solid Waste Management Facility at the Savannah River Site. (Photos: DOE)
Operators at the Savannah River Site’s Solid Waste Management Facility can now characterize and certify newly generated TRU waste through the use of a real-time radiography unit that uses an X-ray system to examine the contents of waste containers. The equipment was recently installed to meet updated requirements set by the Department of Energy’s National TRU Program that involve evaluating the containers for chemical compatibility and oxidizing chemicals.
The shipments of TRU waste from SRS, in South Carolina, are sent to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP), in New Mexico, for disposal.
The Moab cleanup site in Utah in 2018. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (DOE-EM) has awarded a cleanup contract to North Wind Portage, Inc. for completion of environmental remediation of a uranium ore processing site near Moab, Utah. North Wind Portage is located in Idaho Falls, Idaho.
More information about the Moab project is available here.
This image is described by the Alaska Center for Energy and Power as a conceptual layout of a generic small modular reactor or microreactor. (Image: ACEP)
Alaska Gov. Mike Dunleavy (R.) introduced “An act relating to microreactors” (SB 177) in the Alaska state legislature on February 1 that would modify existing state law on nuclear energy by specifying that microreactors are not subject to certain nuclear reactor siting and permitting regulations in Alaska. The bill defines a microreactor as an advanced nuclear fission reactor that would be capable of generating no more than 50 MWe.
An SRNS subcontractor technician takes radiological readings of soil near Lower Three Runs, part of a major project to complete the cleanup of a contaminated 25-mile-long stream corridor at SRS. (Photo: DOE) (CLICK TO SEE FULL PHOTO)
Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS), the Department of Energy’s management and operating contractor for the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, has reached an agreement with the state of South Carolina and federal environmental regulators on the final cleanup of a 25-mile-long stream corridor at the site that was radiologically contaminated as a result of operations during the Cold War.
The corridor consists of Par Pond, nine miles of canals adjacent to the pond, and a stream named Lower Three Runs. The stream begins near the center of the site, just above Par Pond, and winds its way southward across SRS.
ADOPT fuel pellets developed by Westinghouse through the DOE's Accident Tolerant Fuel Program. (Photo: Westinghouse)
Westinghouse Electric Company and Southern Nuclear have agreed to a plan to install four Westinghouse lead test assemblies in Vogtle-2, a 1,169-MWe pressurized water reactor located in Waynesboro, Ga. Four lead test assemblies containing uranium enriched up to 6 percent U-235 will be loaded in Vogtle-2 in 2023, marking the first time that fuel rods with uranium enriched above 5 percent U-235 are put in use in a U.S. commercial power reactor.
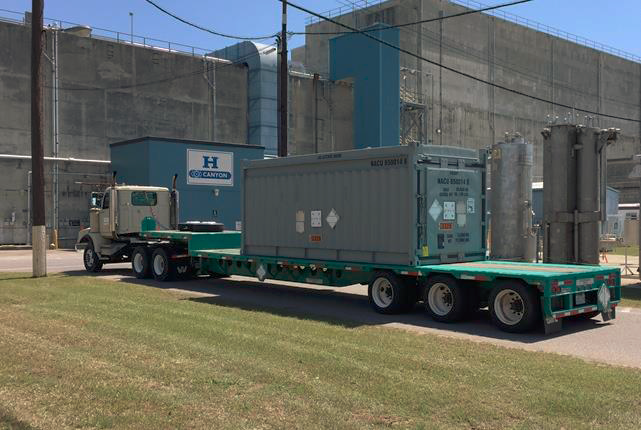
A cask of HEU arrives at the H Canyon facility. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy announced yesterday that Secretary of Energy Achievement Awards were presented to a team of Savannah River Site employees for the completion of the multiyear Target Residue Material (TRM) campaign to support global nuclear security goals.
SRS is a 310-square-mile site located in South Carolina. It encompasses parts of Aiken, Barnwell, and Allendale counties and is bordered on the west by the Savannah River and the state of Georgia.
An illustration of the two inertial confinement fusion designs reaching the burning plasma regime, as published in a recent article in Nature. (Image: LLNL)
One of the last remaining milestones in fusion research before attaining ignition and self-sustaining energy production is creating a burning plasma, where the fusion reactions themselves are the primary source of heating in the plasma. A paper published in the journal Nature on January 26 describes recent experiments at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) that have achieved a burning plasma state.
Oak Ridge before-and-after views: At left is the Oak Ridge Gaseous Diffusion Plant when it was closed in the late 1980s, and at right is a view of the site today, known as the East Tennessee Technology Park. (Photo: DOE)
Energy secretary Jennifer Granholm honored a Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management (EM) team from Oak Ridge with the Secretary of Energy’s Achievement Award during a virtual ceremony yesterday for successfully removing a former uranium enrichment complex. The project cleared 13 million square feet of deteriorated, contaminated structures from the site.
Click to see full image. (Photo: DOE)
Department of Energy contractor Central Plateau Cleanup Company recently completed final demolition activities at the Hanford Site’s former Plutonium Finishing Plant, which was once one of the most hazardous facilities in the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) cleanup complex.
Check out this time-lapse video of the plant’s demolition from October 2016 through November 2021.
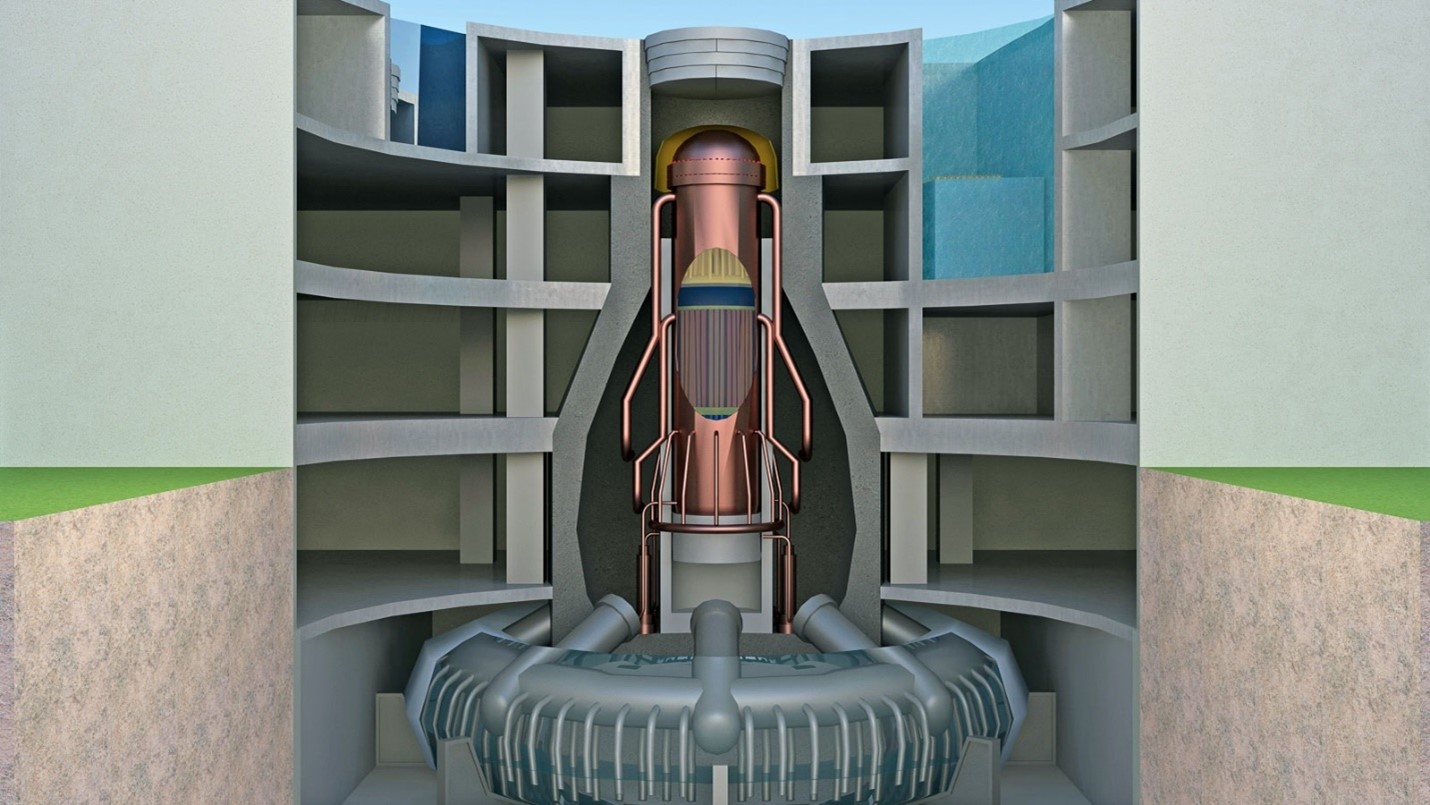
A cutaway view of a nuclear reactor. Its construction consists of two essential material types: fuel, which comprises the rods and cores that hold the fuel (center vertical bands); and structural, those parts of the reactor that house the fuel materials. (Graphic: Shutterstock/petrov-k)
Researchers from the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are developing a “tool kit” based on artificial intelligence that will help better determine the properties of materials used in building a nuclear reactor.
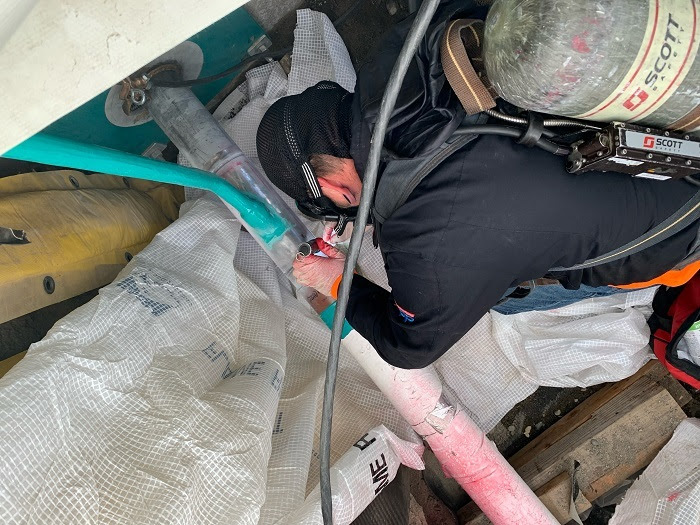
A worker installing new waste transfer lines between Hanford’s large underground tanks and evaporator facility welds a secondary encasement on one of the lines. (Photo: DOE)
As the Department of Energy's Hanford Site prepares for around-the-clock operations for tank waste disposal, workers at the site's 242-A Evaporator are upgrading equipment used to remove water from the tank waste and the systems that transfer waste to and from large underground containers. The upgrades will also extend the evaporator’s service life.