From left: GLE’s Stephen Long, Scott Steuer, Jesus Diaz-Quiroz, Nima Ashkeboussi, and Timothy Knowles, with the NRC’s Matt Bartlett, Samantha Lav, Robert Sun, Shana Helton, Andrea Kock, and Kimyata Morgan-Butler. (Photo: GLE)
Global Laser Enrichment announced that it has submitted its safety analysis report to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission for the planned Paducah Laser Enrichment Facility (PLEF). This follows GLE’s December 2024 submission of the plant’s environmental report, now completing GLE’s full license application for NRC review.
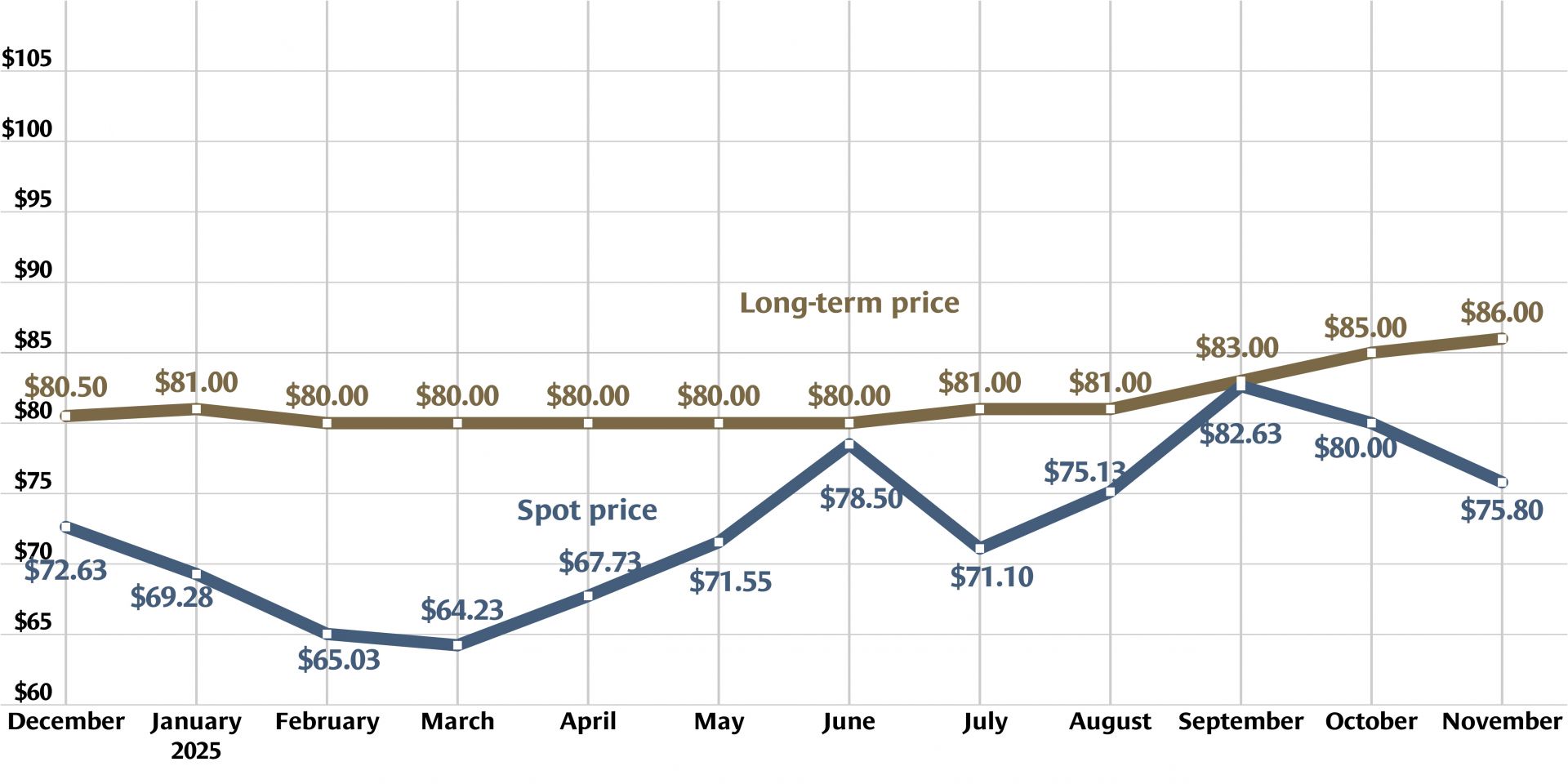
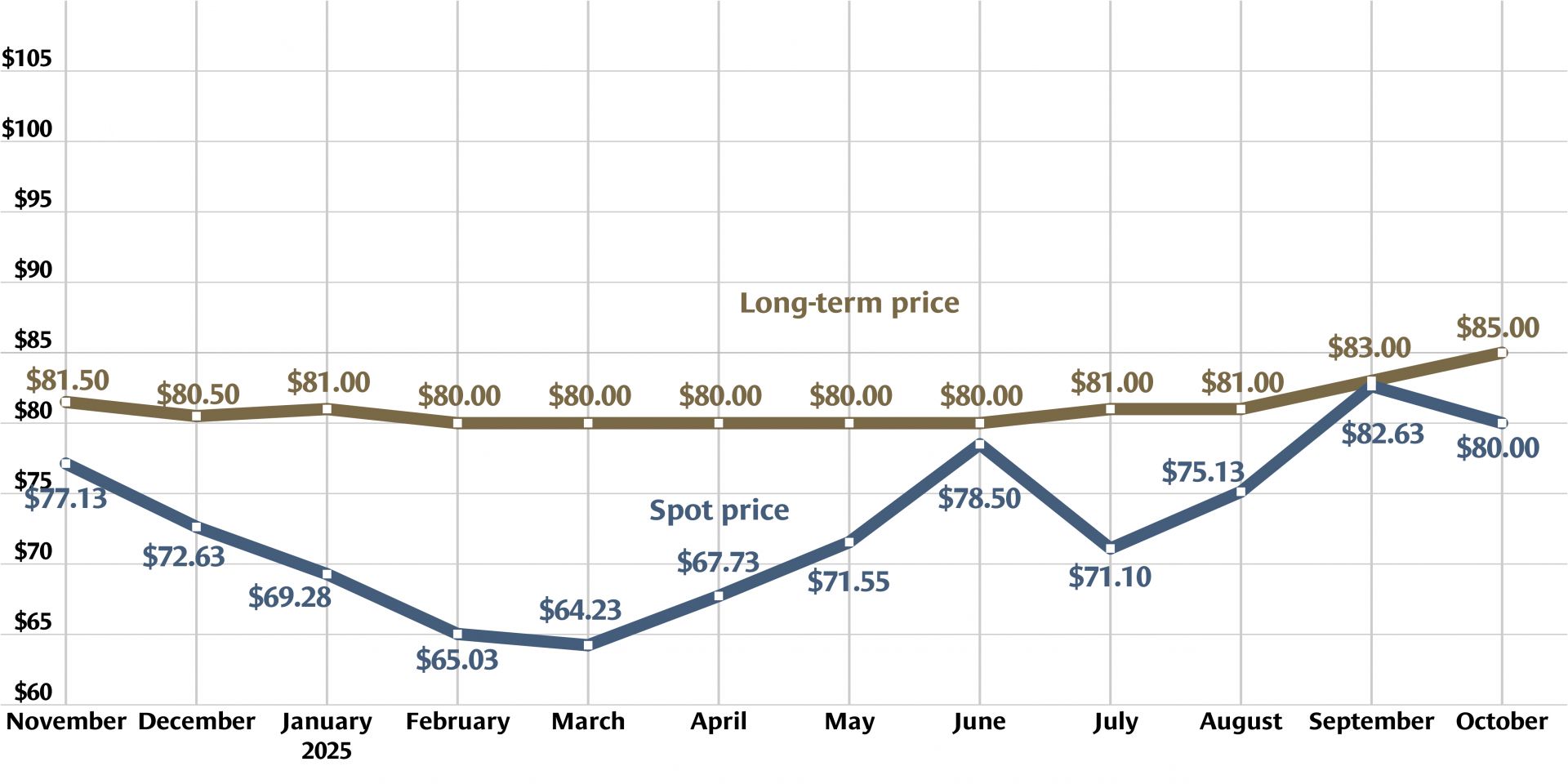
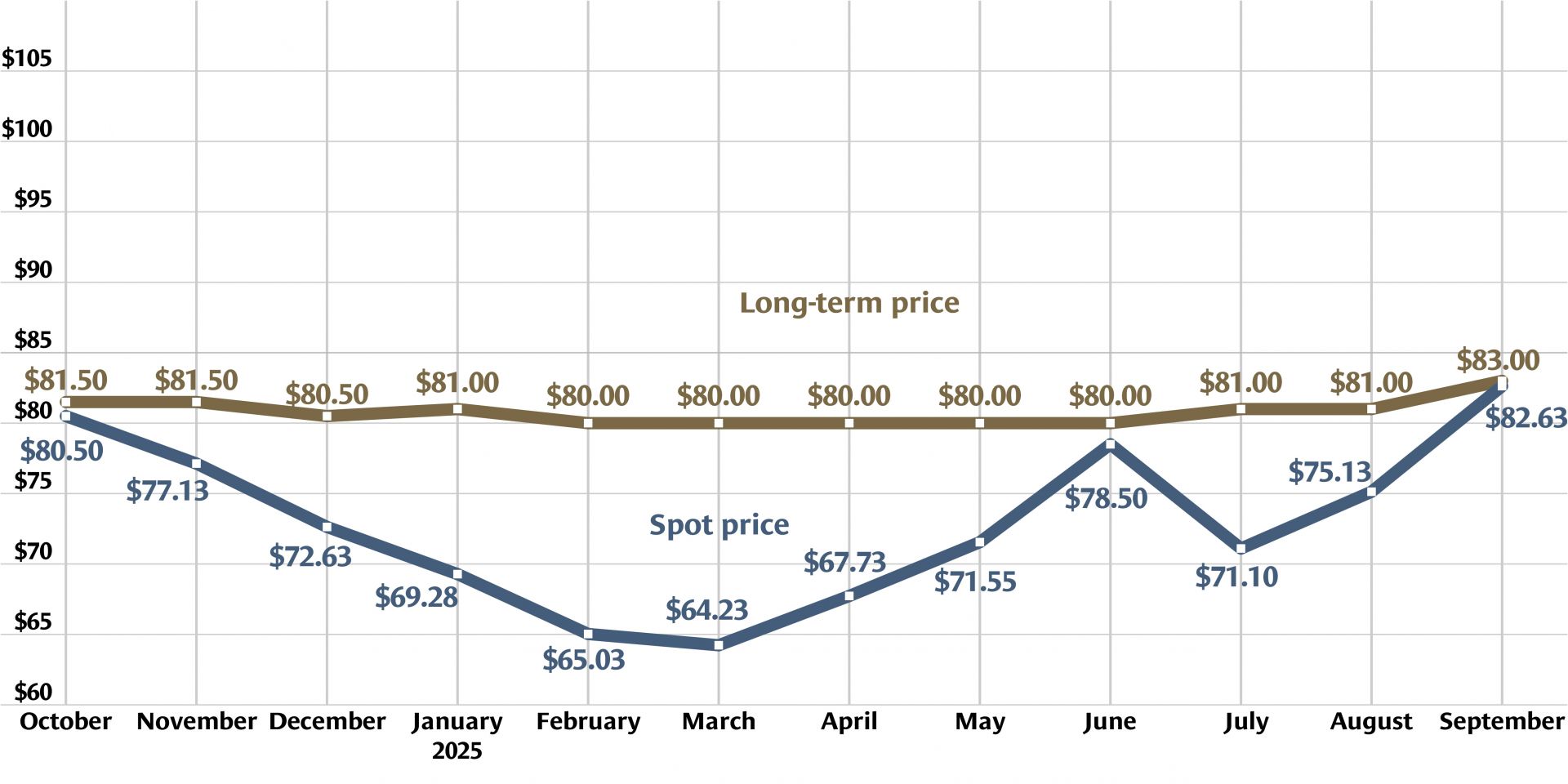
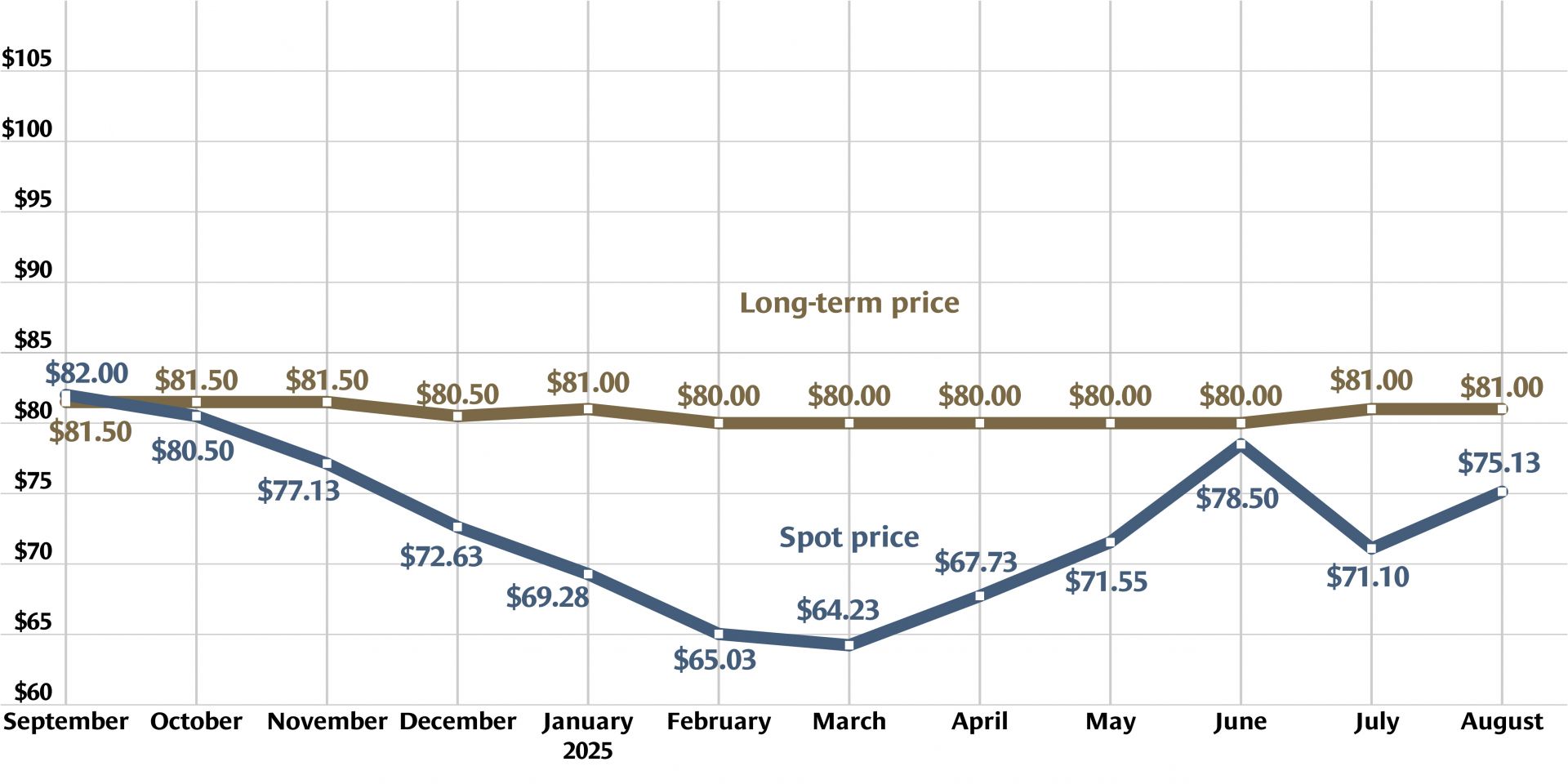
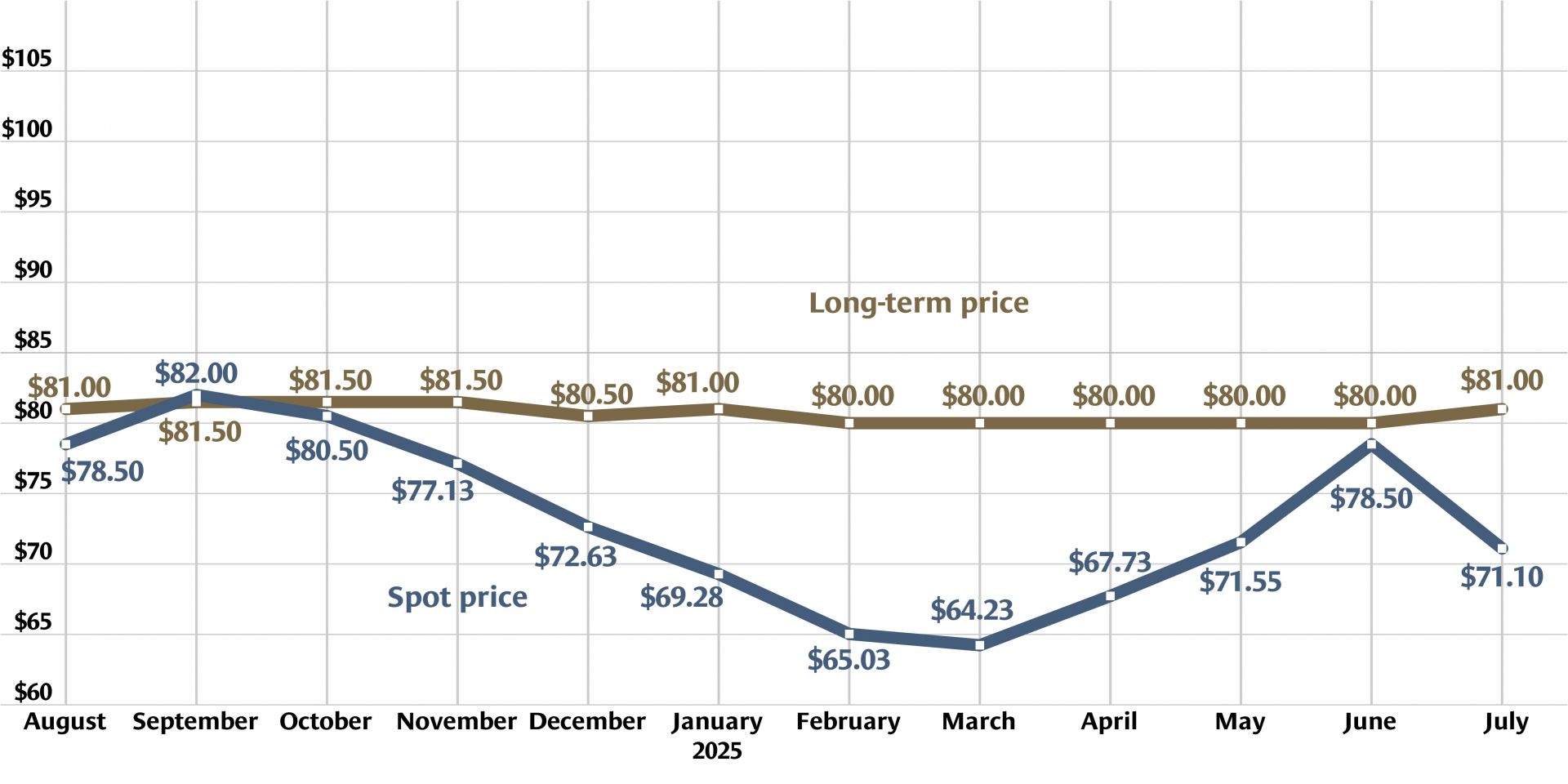
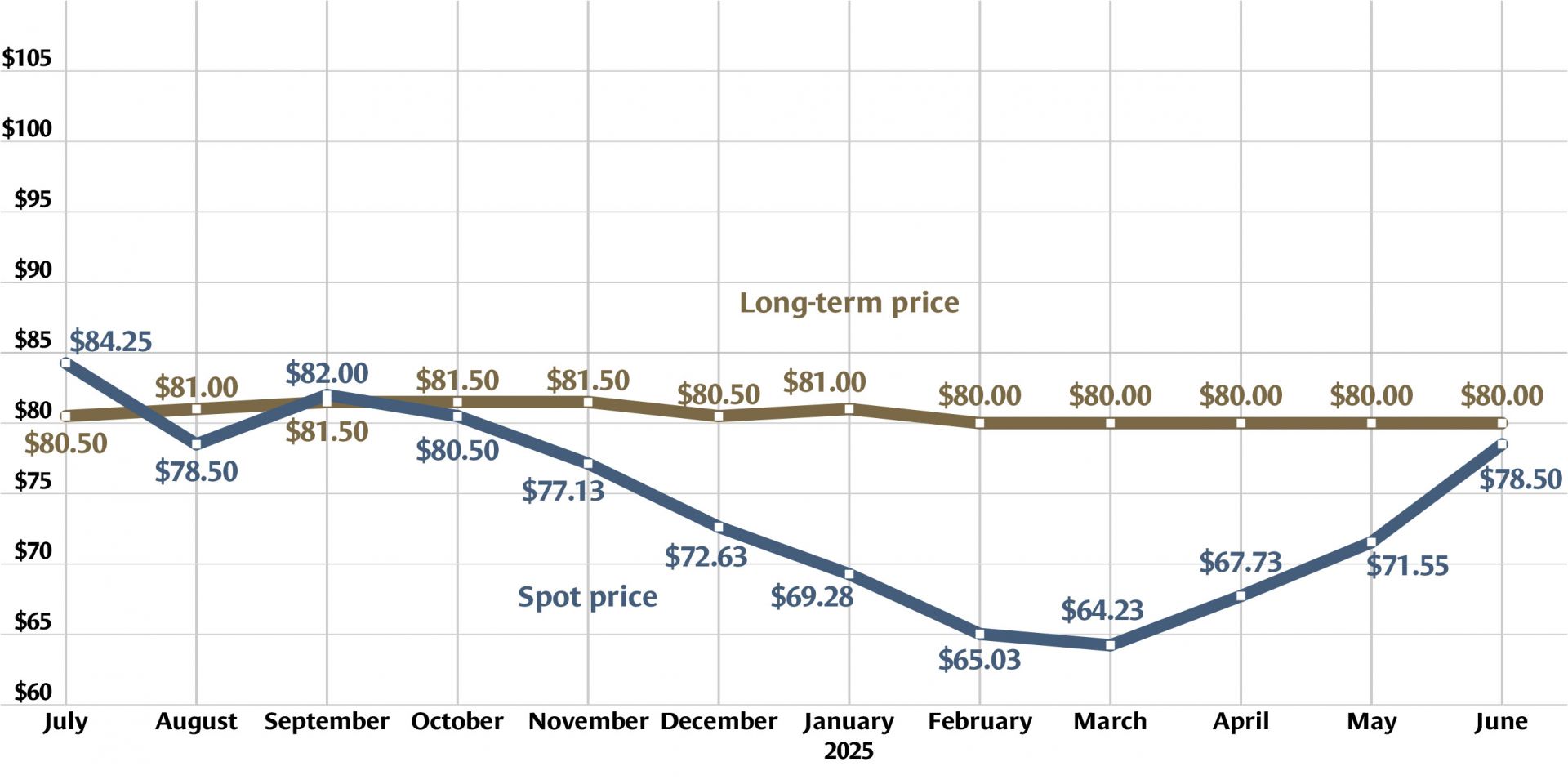
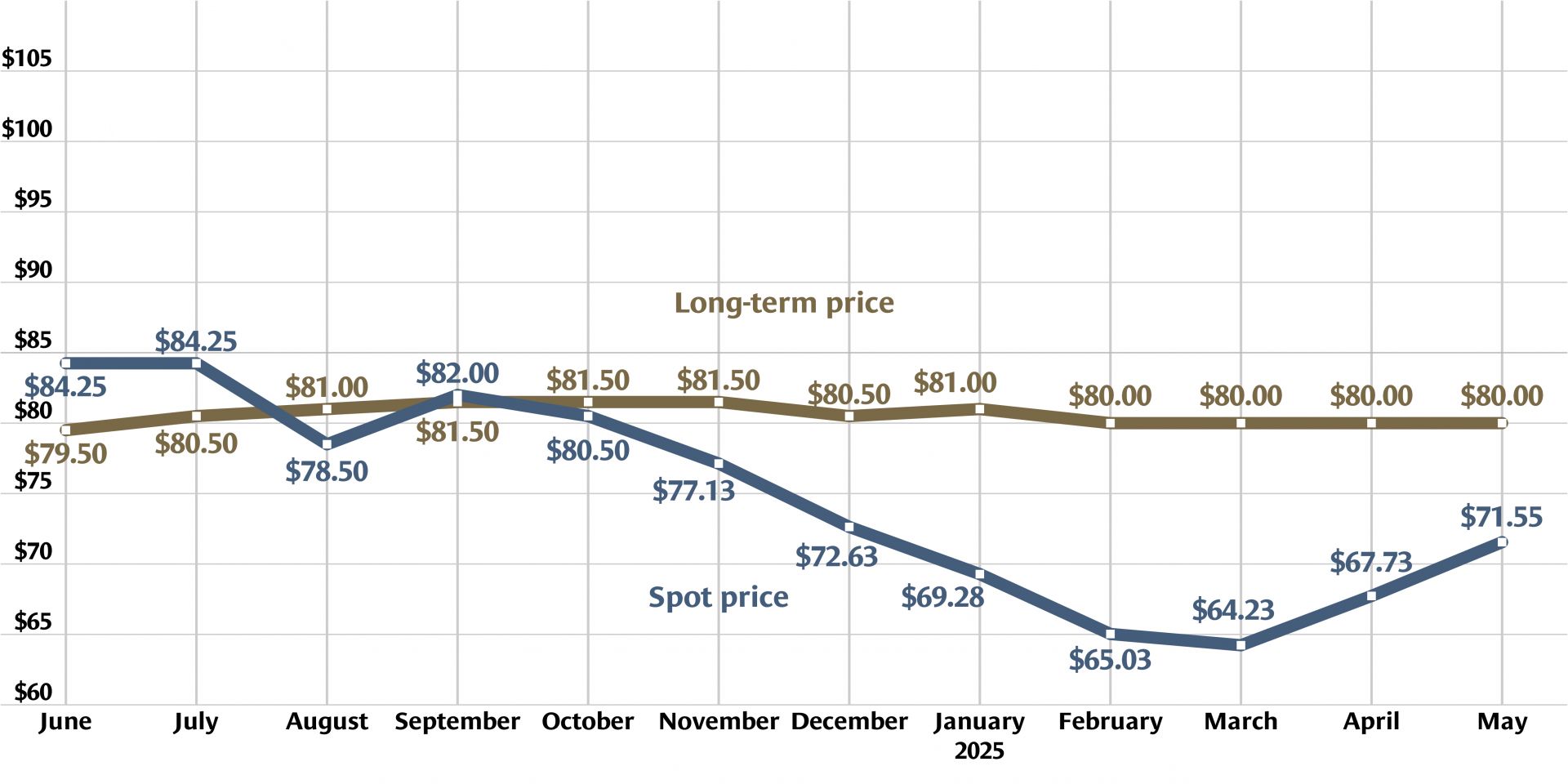
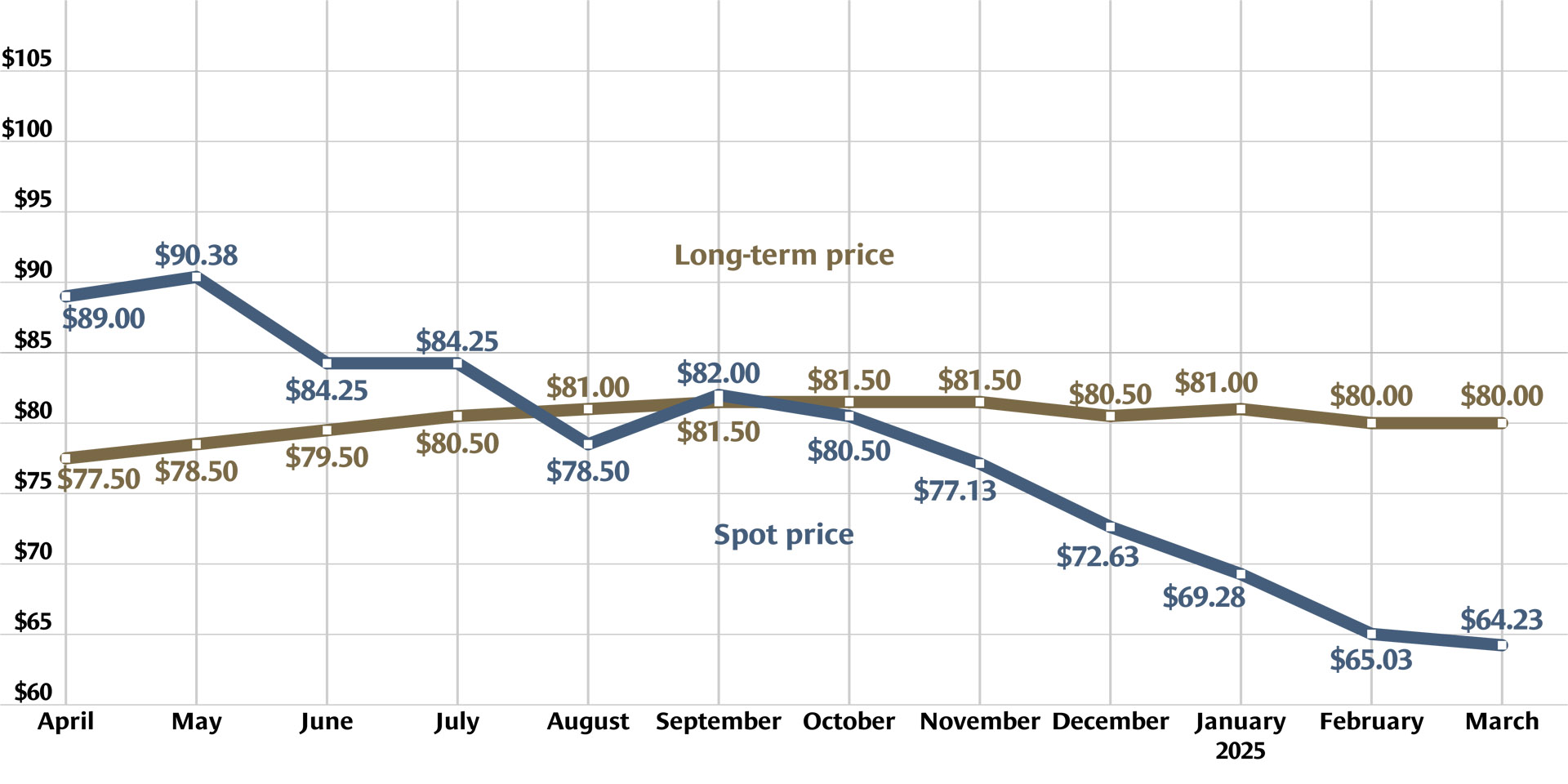
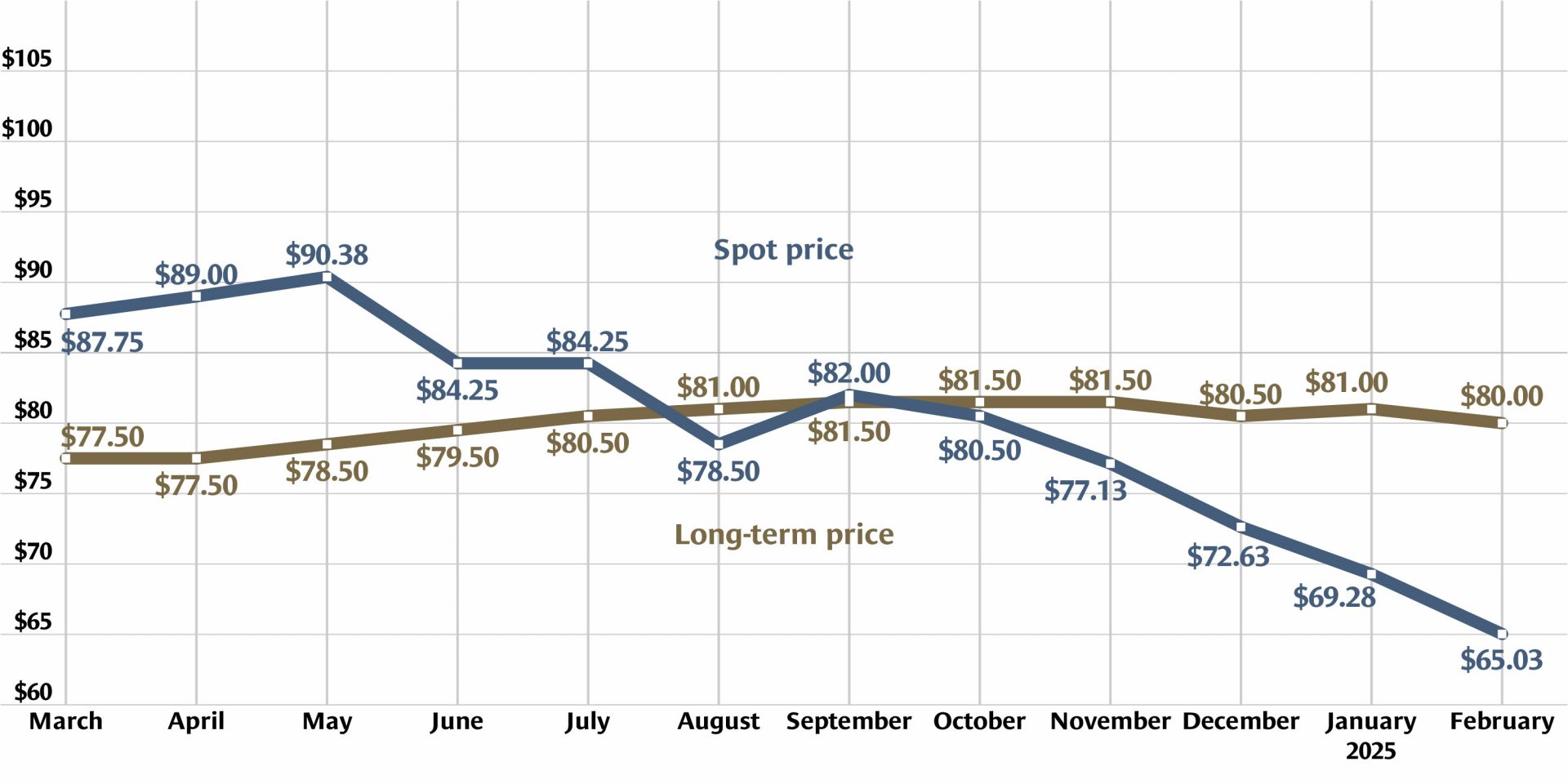
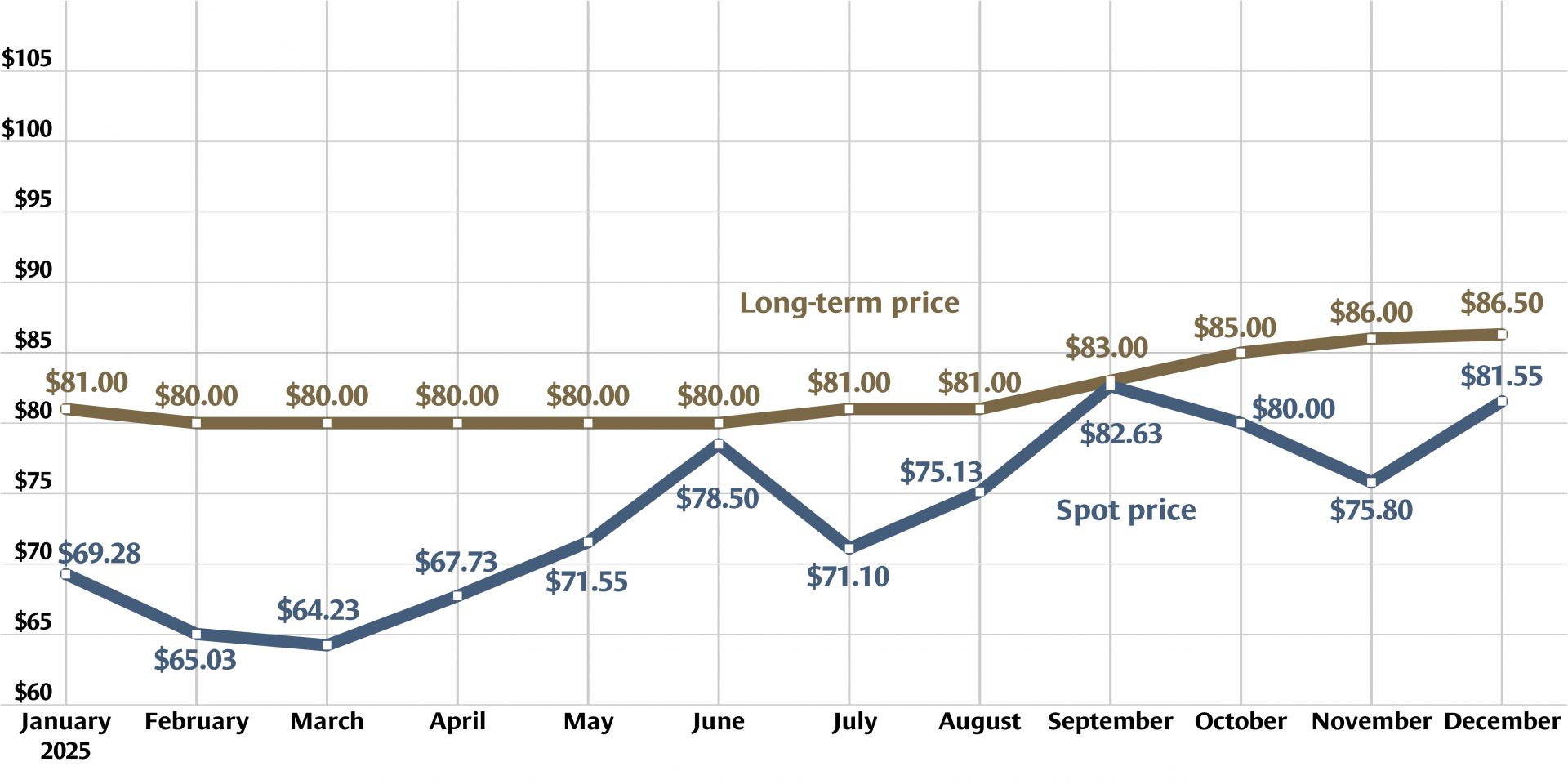
Graph: Nuclear News; data source: U.S. EIA
U.S. uranium production increased throughout 2024, with more growth planned in 2025. The producers who can make that happen, however, were burned before by a “renaissance” that didn’t take off. Now they are watching and waiting for signals from Washington, D.C., including the impacts of tariffs, shifting relationships with global uranium producers, and funding for the enrichment task orders designed to boost demand for U.S. uranium.
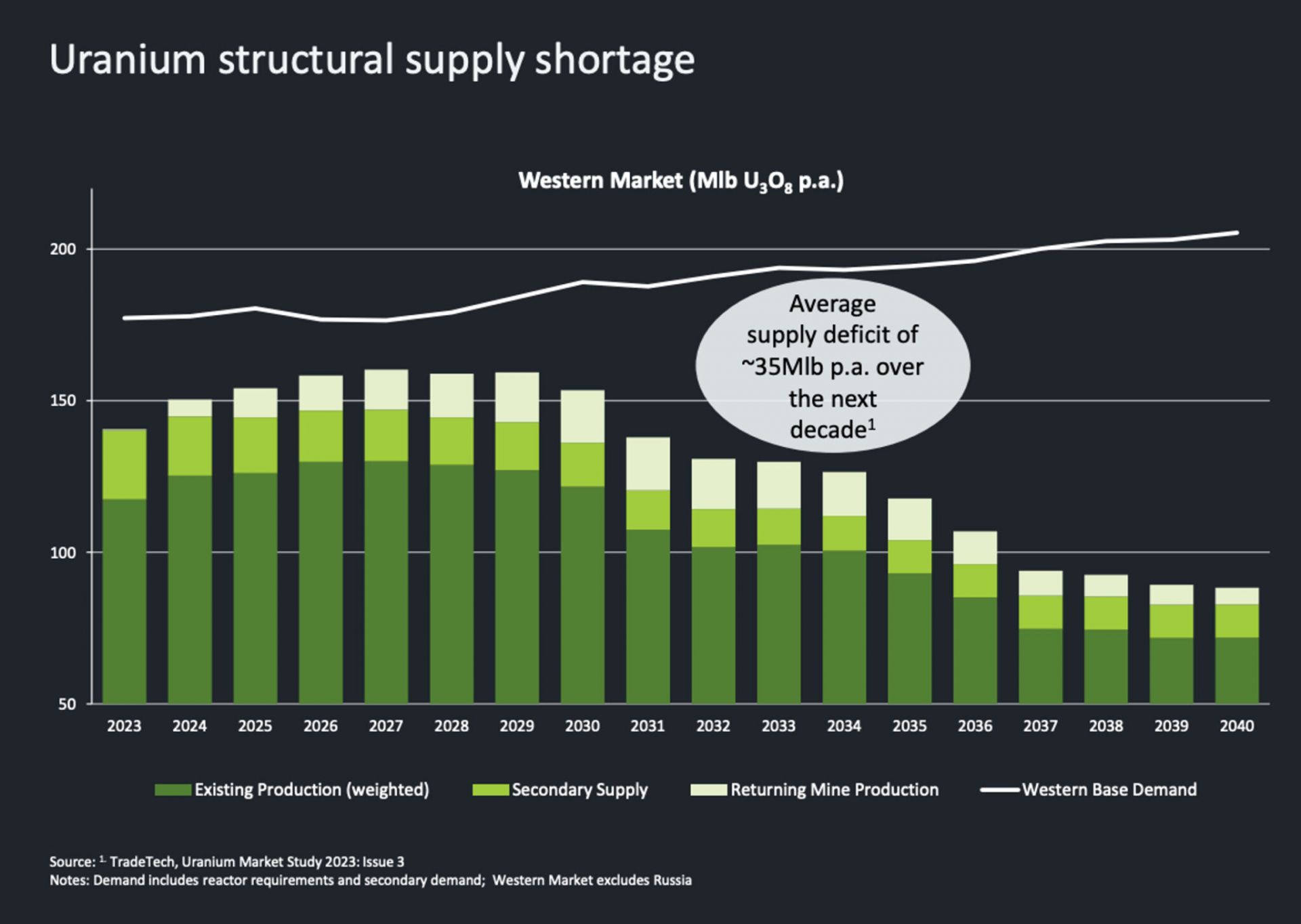
[Click to see full graphic] Western base demand (white line) for uranium will continue to outpace the combined existing production (dark green), secondary supply (middle green), and returning mine production (light green) through 2040, according to projections. (Image: Paladin Energy)
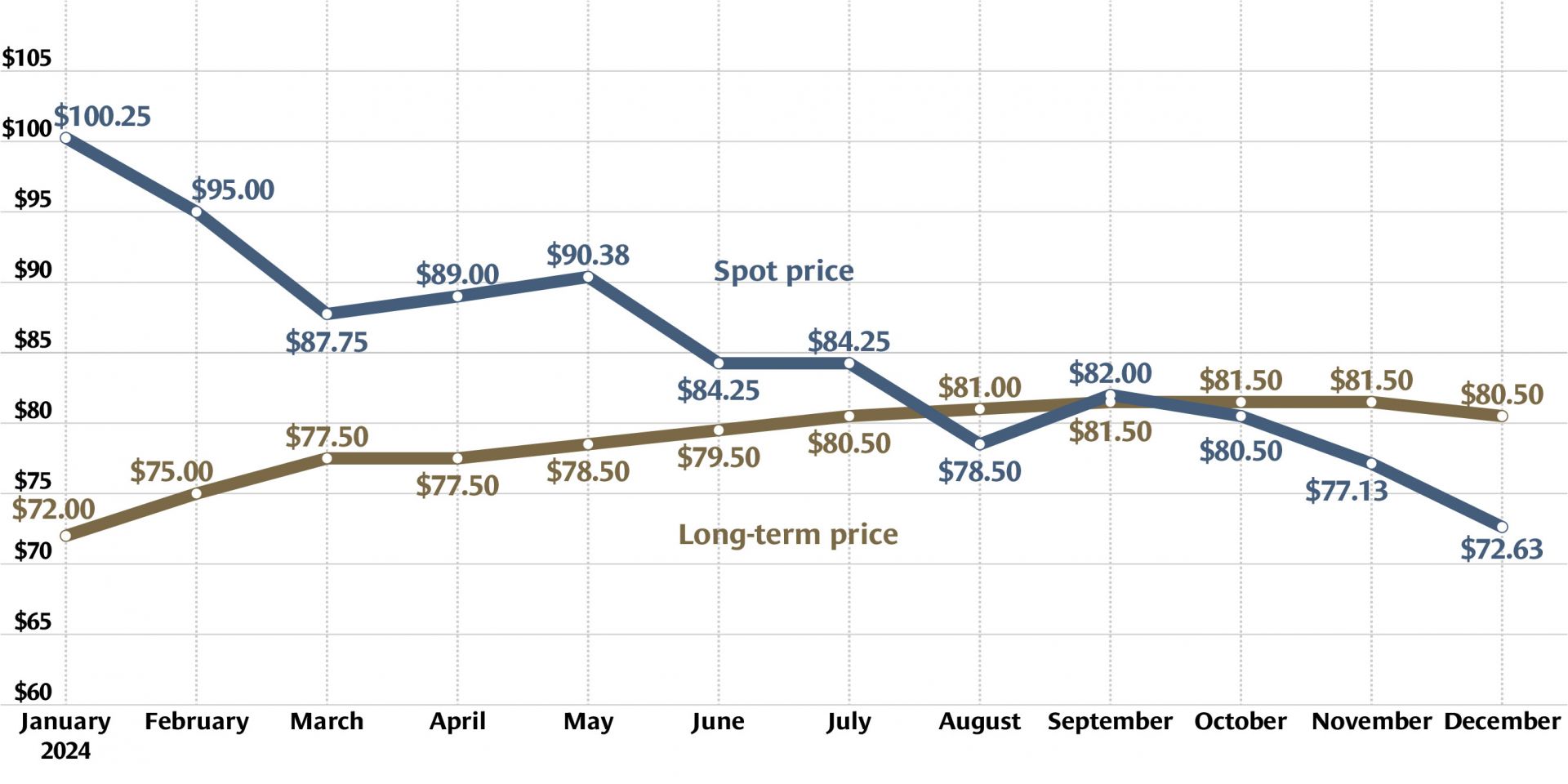
Investors continue to be bullish on uranium, according to a number of recent news reports. Stockhead recently trumpeted, “Uranium has started 2024 the same way it ended 2023—like a bull in a china shop. Spot prices are now agonizingly close to US$100/lb for the first time since 2008, with term pricing not far behind.” Similarly, Mining.com noted, “The spot price of uranium continues to rise, boosted by pledges to triple nuclear power by mid-century, supply hiccups from producers such as Cameco . . . , and the looming threat of a ban on Russian exports to the West.”

-3 2x1.jpg)