NRC names four MSI recipients of scholarships and fellowships

Four minority-serving institutions (MSIs) have been named by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission as recipients of scholarship and fellowship grants worth a total value of $1.78 million.

A message from Goodway Technologies
Optimizing Maintenance Strategies in Power Generation: Embracing Predictive and Preventive Approaches

Four minority-serving institutions (MSIs) have been named by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission as recipients of scholarship and fellowship grants worth a total value of $1.78 million.

On May 13, President Biden signed the Prohibiting Russian Uranium Imports Act, unlocking the $2.72 billion that Congress conditionally appropriated in March to increase production of low-enriched uranium (LEU) and high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU).

The American Nuclear Society, in partnership with the Department of Energy’s Office of Nuclear Energy, is hosting its next Educator Training event, “K-12 Classroom Investigations: Exploring Background Radiation,” this Thursday, May 16, from 6:00 to 7:00 p.m. (EDT).
Register now. The event is complimentary and open to all.

Korsnick
Nuclear Energy Institute president and CEO Maria Korsnick delivered her State of the Nuclear Energy Industry address at NEI’s 2024 Nuclear Energy Policy Forum yesterday. The forum this year is taking place May 14–16 in Washington, D.C., and serves to gather industry leaders, executives, and experts for pivotal conversations about the federal and state nuclear policy landscapes.
Korsnick updated attendees on policy priorities of the industry and gave her perspective on nuclear energy’s present and future.
She centered her talk on national and global priorities to secure a clean energy future at the same time as achieving energy independence and security—all while meeting a massive increase in demand for power. “Nuclear energy remains the key” to addressing these priorities, she said.

Kristin Hirsch
Radioactive materials are used in medical, research, and commercial facilities to treat cancer, irradiate blood, sterilize food and equipment, and build economies worldwide. In the wrong hands, however, even a small amount of radioactive material can do a great deal of harm. A radiological dispersal device (RDD), otherwise known as a “dirty bomb,” is believed to be an attractive weapon for terrorist groups due to its scale of impact—panic, physical contamination, costly remediation, and denial of access to facilities and locations.
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration Office of Radiological Security (ORS) enhances global security by preventing high-activity radioactive materials from being used in acts of terrorism. ORS implements its mission through three strategies: protecting radioactive sources used for vital medical, research, and commercial purposes by securing facilities that utilize radioactive isotopes; removing and disposing of disused sources; and encouraging the adoption and development of nonradioisotopic alternative technologies such as X-ray and electron beam irradiators.
The University of Michigan’s Fastest Path to Zero Initiative has launched the Global Fusion Forum, an online platform focused on fusion energy. It was created to foster international engagement and collaboration in the area of fusion technology.

This year marked the 50th anniversary of Waste Management Symposia’s Waste Management Conference, held March 10–14 in Phoenix, Ariz. The event has grown significantly since the first Waste Management Conference in 1974, which attracted about 200 attendees. This year’s conference saw a record attendance of around 3,300 people from more than 20 different countries and boasted 235 technical sessions and 89 exhibitors.
For the second consecutive year, the Ukrainian Nuclear Society (UkrNS) held its Nuclear Innovators competition, which was organized in partnership with the American Nuclear Society and other leading institutions in the nuclear sector worldwide. The two winners were announced on May 7.
A bill being considered in the U.S. Senate seeks to remove the requirement for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to hold a public hearing for every nuclear reactor application.
Current law requires public hearings to be held by the NRC toward the end the reactor license application process, in addition to the statutorily required environmental and safety reviews that provide public engagement opportunities for stakeholders and citizens.

After completing its business combination with AltC Acquisition Corp, Oklo Inc. began trading on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol OKLO this past Friday, May 10.
The company is aiming to provide clean, reliable, affordable nuclear energy to customers across the artificial intelligence, data center, energy, defense, and industrial markets. Sam Altman, chairman of Oklo since 2015 and former chief executive of AltC, called the first day on the NYSE a milestone for the entire team.

Shikha Prasad
High-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) has emerged as a popular fuel choice for advanced small modular reactors due to its long power production periods before refueling. It is currently being pursued by TerraPower, X-energy, BWX Technologies, Kairos, Oklo, and other reactor companies. HALEU has a uranium-235 enrichment ranging from 5 percent to 20 percent, whereas traditional LWRs use low-enriched uranium fuel enriched up to 5 percent.
HALEU will provide power for longer durations, compared with traditional LWRs. But could it also provide an opportunity for more rapid proliferation, as is speculated in a 2023 National Academy of Sciences report on advanced nuclear reactors (nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/26630/)?
If a nuclear proliferator conspires to divert fresh nuclear fuel for weapons production when it has not been used in a reactor, the effort required in separative work units (SWUs) to enrich U-235 from 5 percent to 90 percent and that required to enrich from 20 percent to 90 percent are both very small, compared with the effort required to enrich U-235 from its natural abundance to the initial 5 percent.
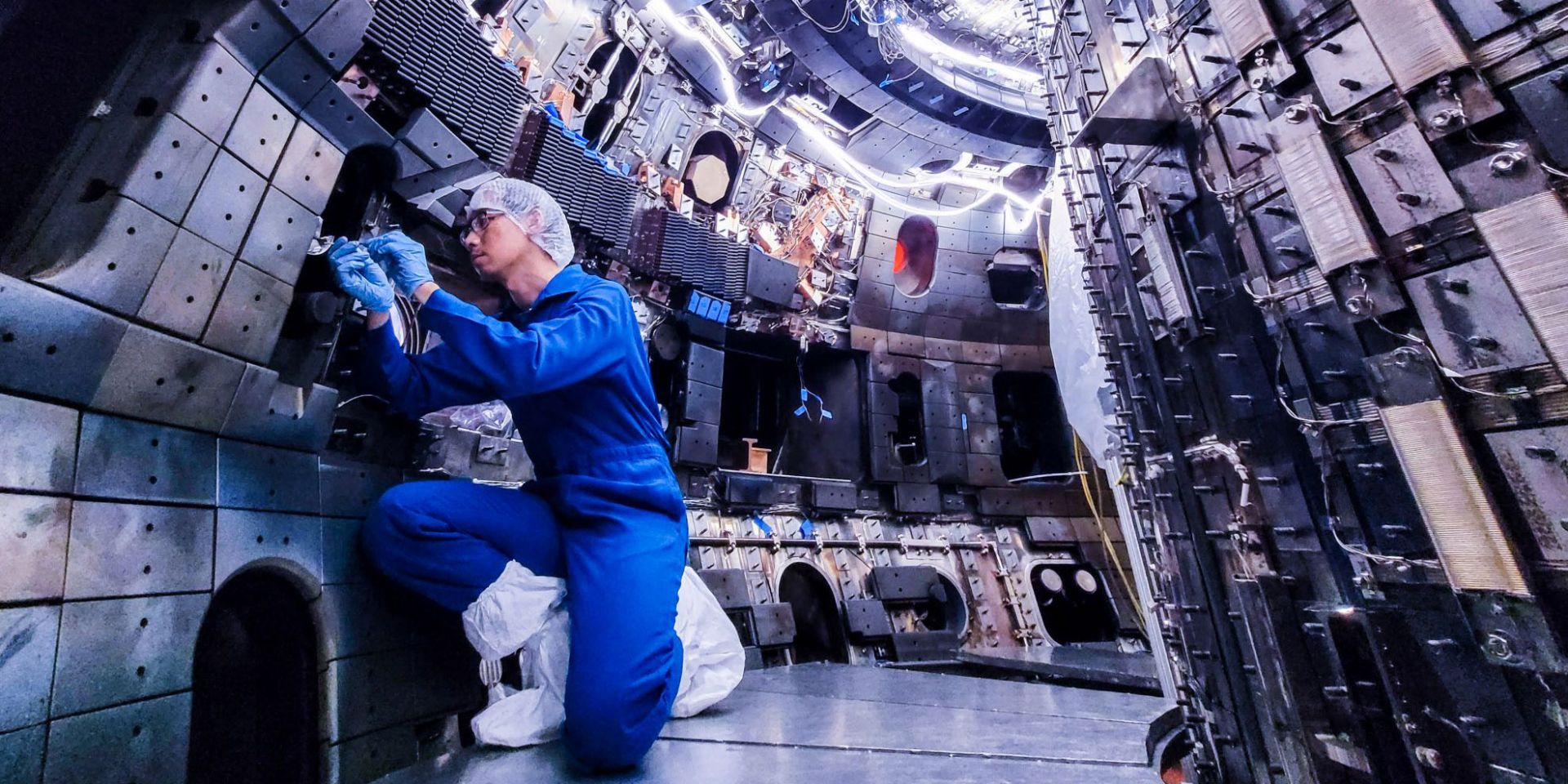

The DIII-D National Fusion Facility is starting up after an eight-month experimental hiatus, equipped with new and improved plasma control and diagnostic systems. The upgrades will help researchers from around the nation and the world resolve key physics questions to bridge the gap between current magnetic confinement fusion research and the first fusion power pilot plants. General Atomics, which operates DIII-D for the Department of Energy, announced the completion of upgrades on May 8.

Investor’s Business Daily reported May 10 that the first-quarter earnings of Constellation Energy, the largest operator of nuclear power plants in the United States, surged 858 percent to reach a share price of $2.78, partly as a result of promising expectations regarding demand for artificial intelligence data centers. The S&P 500 stock value of Constellation jumped 3.7 percent on May 8 to $208.
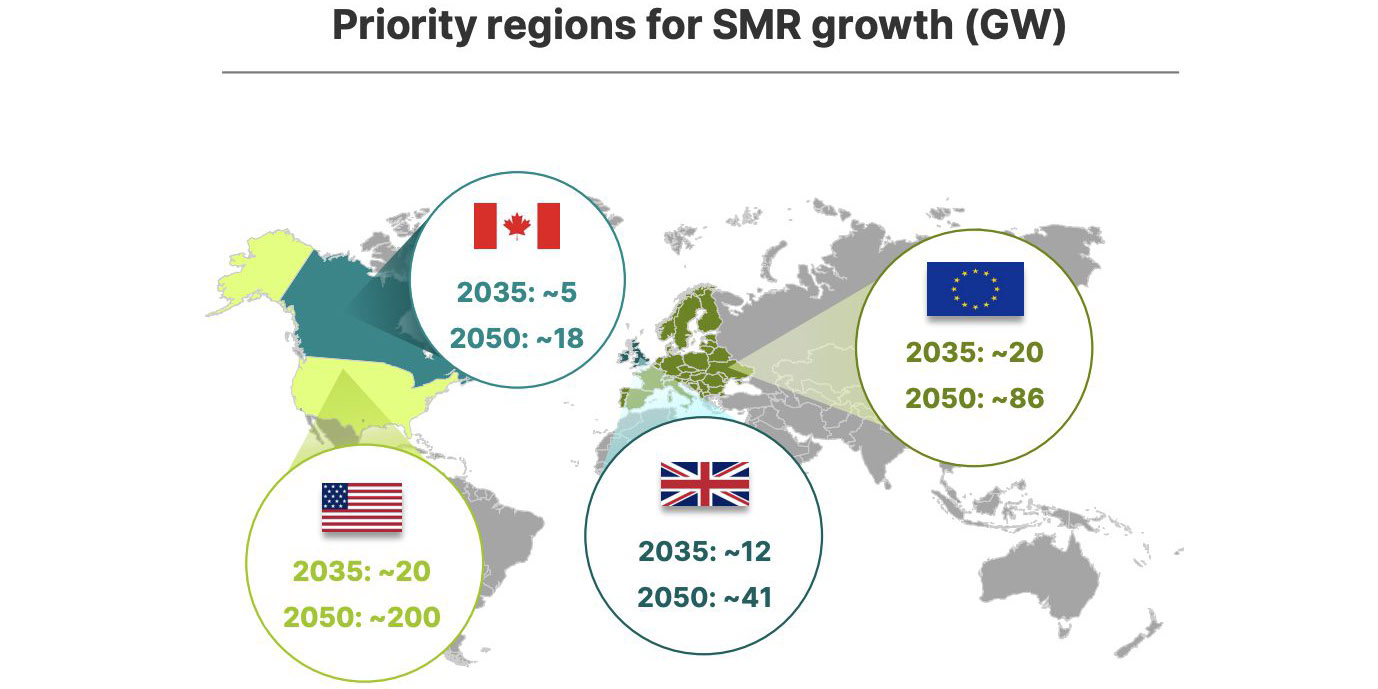
GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH)—the nuclear business unit of Massachusetts-based GE Vernova in partnership with Japan’s Hitachi—has announced that it is forming a group of qualified supply chain companies to advance the manufacture, commercialization, and international deployment of its BWRX-300 small modular reactor. The company stated that it is forming the group to help ensure “a reliable, cost-effective and innovative” process for getting its SMR commercialized and deployed around the world.

Baseload nuclear generation doesn’t get the respect it deserves, if you ask nuclear operators. But the hyperscale data centers that process our digital lives—like the one right next to the Susquehanna plant in northeastern Pennsylvania—are pushing electricity demand up. Clean, reliable capacity now looks a lot more valuable.

When the U.S. Fusion Energy Outreach Team declared the second week of May as Fusion Energy Week, they were recognizing the May 10 birthday of Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin—the British-born American astronomer who applied principles of quantum physics, chemistry, and astronomy to become the first to realize—at the age of 25—that stars and the universe itself are mostly composed of hydrogen and helium, and that the stars could be sorted by their spectra into groups that corresponded to the temperature of the stars.
The Department of Energy has received initial approval, known as “Critical Decision-0” (CD-0), for siting a federal consolidated interim storage facility for commercial spent nuclear fuel. Paul Murray, deputy assistant secretary of energy within the DOE’s Office of Nuclear Energy, confirmed to Nuclear Newswire that the DOE received CD-0 approval on May 6.

The U.K. government this week announced a $245 million (£196 million) award to help Urenco build Europe’s first advanced reactor fuel manufacturing plant, which will be located in northwest England at the company’s Capenhurst site. Urenco, which is part-owned by the U.K. government, will cofund the project.

By late 1960, when the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission authorized plans to build a Molten Salt Reactor Experiment (MSRE) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the lab already had about 13 years of experimentation with molten salt reactors under its longest-serving lab director, Alvin Weinberg. The MSRE operated from 1965 to 1969, proving that molten salt reactors could operate reliably, and with alternatives to uranium-235 too.
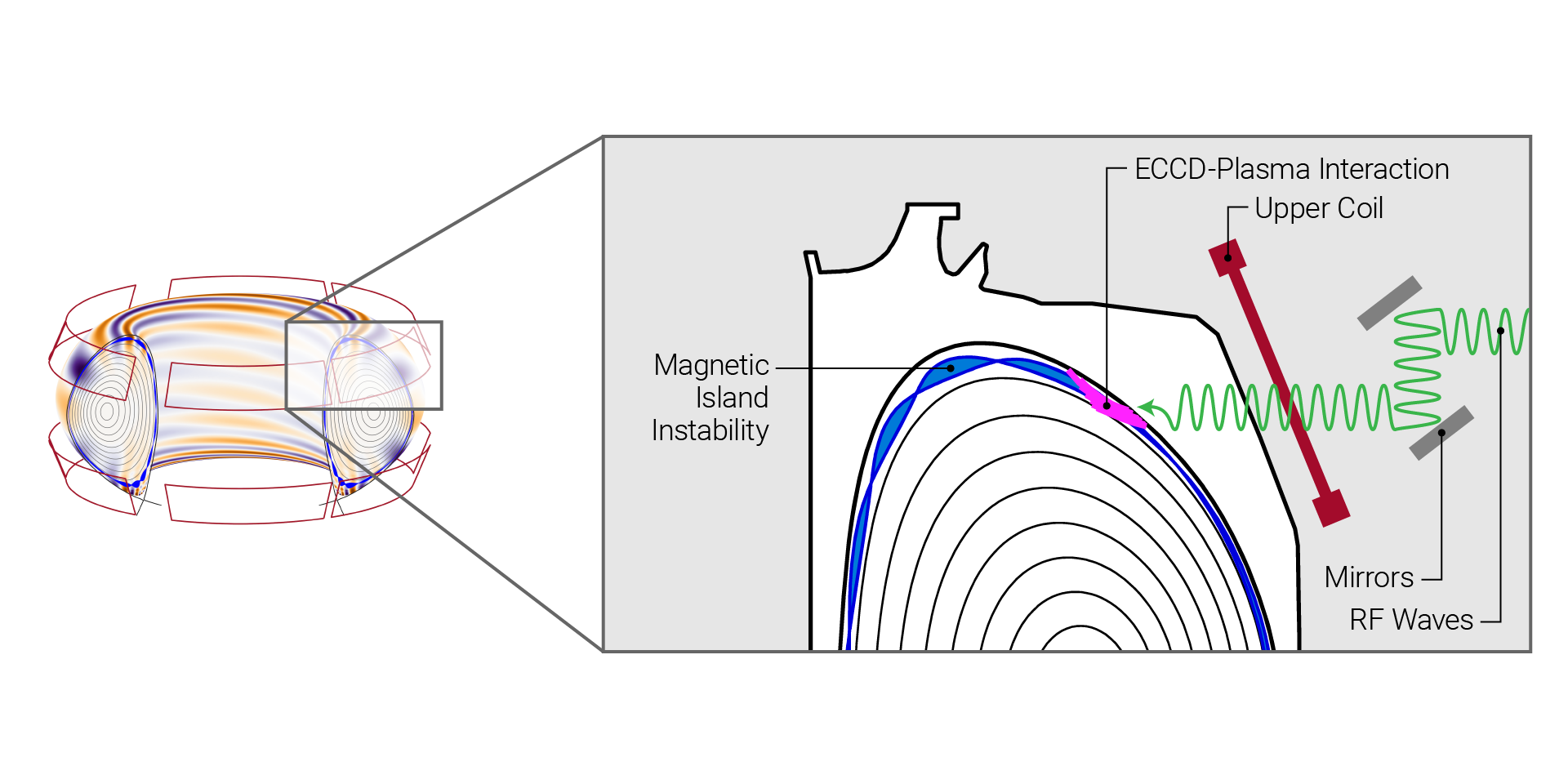
The combination of two previously known methods for managing plasma conditions can result in enhanced control of plasma in a fusion reactor, according to a simulation performed by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory.