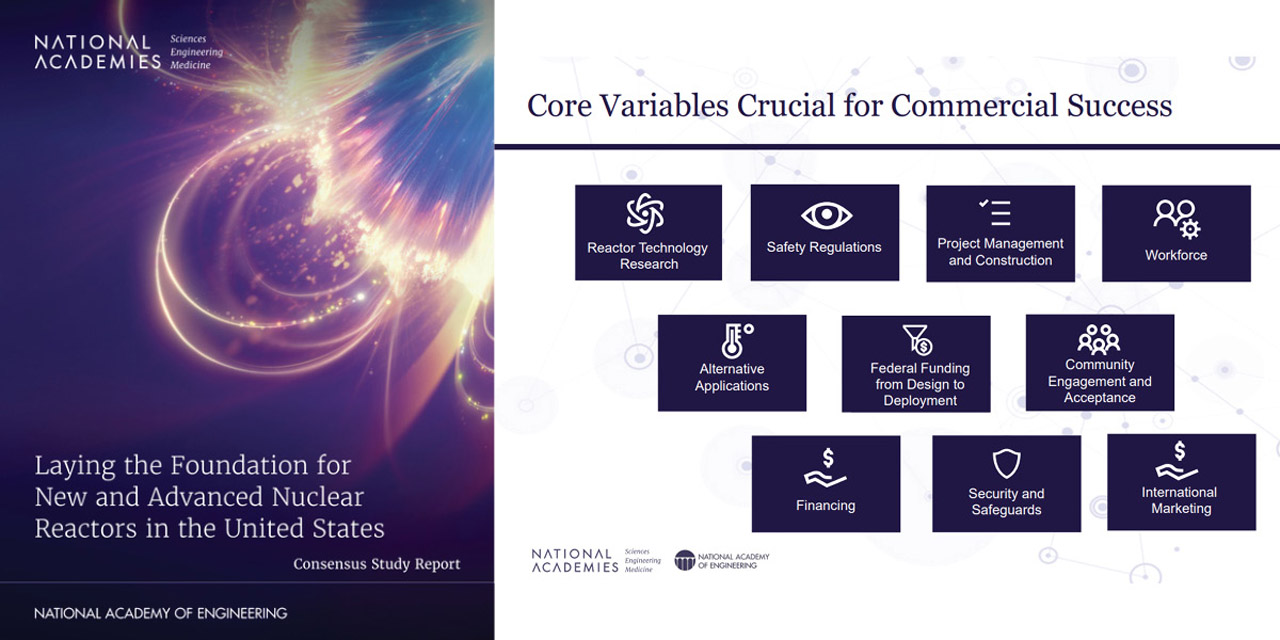
This slide on the right from the consensus committee’s public briefing identifies 10 core variables that are important to the success of advanced reactor deployments. (Image: NASEM, Laying the Foundation for New and Advanced Nuclear Reactors in the United States)
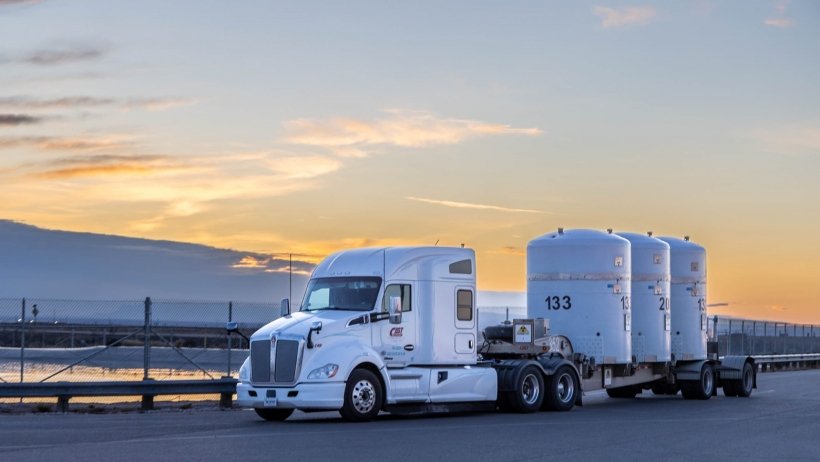
A CAST Specialty Transportation truck delivering TRU waste packages to WIPP. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) recently marked a milestone after its drivers exceeded 16 million safe miles without a serious accident or injury—equivalent to 33 round trips to the moon or more than 642 trips around the world, the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management announced.
The ANS staff headquarters building in 2022.
After being on the market for two years, the American Nuclear Society headquarters in La Grange Park, Ill., has been sold to a local real estate developer. This move was first set in motion in 2021. Following a year of first fully remote, then hybrid remote work as a result of the COVID pandemic, ANS leadership decided the time was right for a change. Even before the pandemic, it was noted that the nearly 30,000-square-foot building, a former elementary school, was much too large for the 35 full-time staff (some of whom are fully remote, living in states from California to Florida).
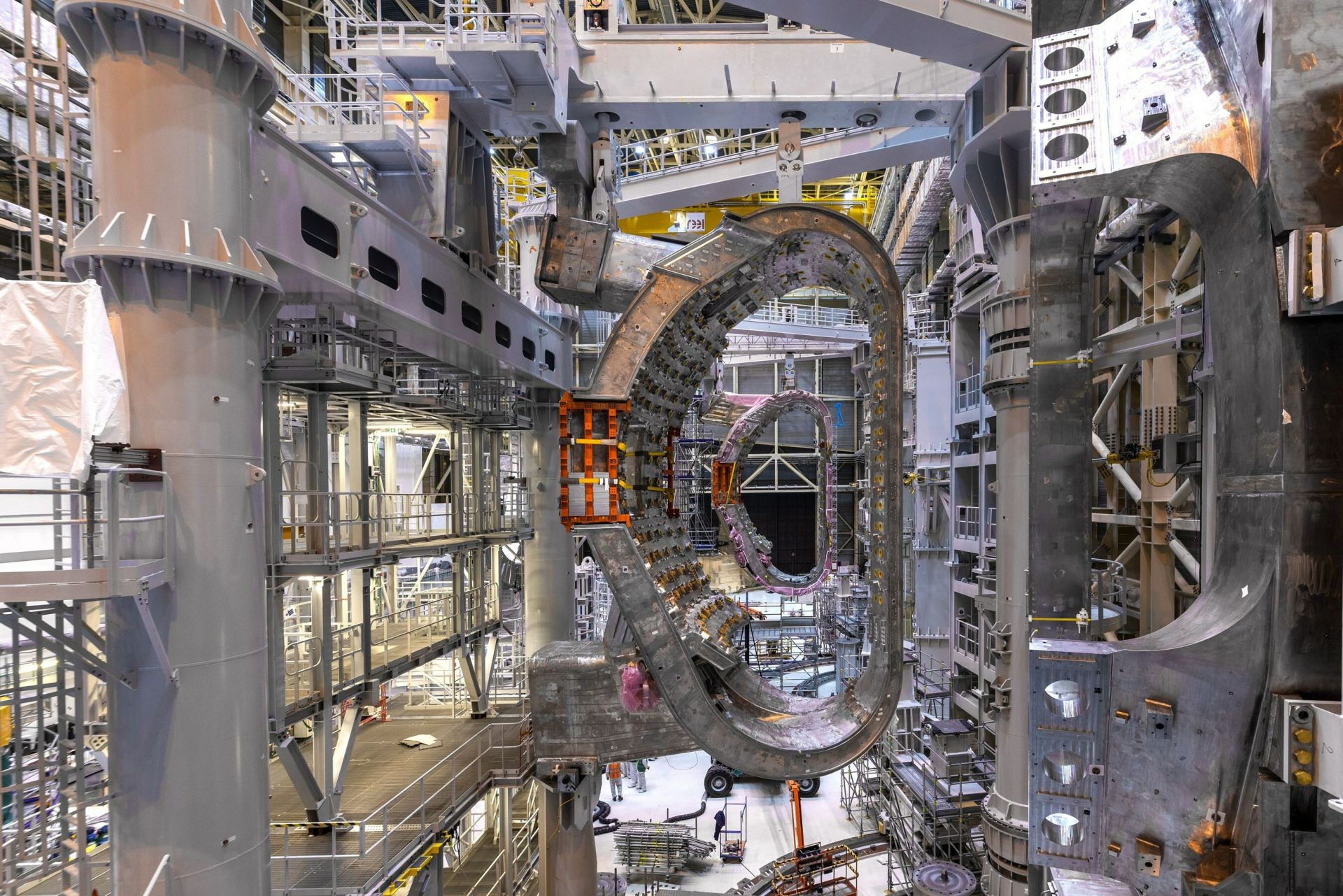
Inside the ITER tokamak assembly hall. (Photo: ITER Organization)
The engineering company Jacobs announced last week that it has been awarded a four-year contract to design and engineer remotely operated tools for the ITER fusion project in southern France. The contract, which includes a possible two-year extension, covers work on up to 25 diagnostic ports and systems used for operating and sustaining the ITER experimental machine, which is currently under construction.
SHINE’s Mo-99 production building under construction in October 2022. (Photo: SHINE)
Fusion development company SHINE Technologies announced that it will begin offering radiation effects testing in a dedicated facility on the company’s Janesville, Wis., campus later this year. SHINE will use high-energy fusion neutrons to test mission-critical components that are susceptible to radiation-harsh environments on behalf of its aerospace and defense customers.
A south-facing view of the Dillard Science and Engineering Research Center at Abilene Christian University, scheduled for completion in the summer of 2023. The new facility will provide space for ACU’s NEXT Lab, as well as for research in chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Abilene Christian University’s Nuclear Energy eXperimental Testing (NEXT) Lab continues to make progress toward building a molten salt research reactor (MSRR) on the university’s campus. NEXT Lab submitted an application for a construction permit to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission last August, and in November the agency announced it had docketed the application—the first for a new research reactor in more than 30 years.
April 27, 2023, 9:30AMUpdated April 27, 2023, 9:30AMNuclear News At table, from left: Navid Samandari, chief executive officer of Seaborg Technologies; Jooho Whang, CEO of KHNP; and Jintaek Jeong, CEO of Samsung Heavy Industries. (Photo: Seaborg Technologies)
Denmark-based Seaborg Technologies, developer of the compact molten salt reactor (CMSR), has teamed with two South Korean firms—shipbuilder Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) and nuclear plant owner and operator Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP)—to form a consortium for the development of floating nuclear plants featuring the CMSR. The consortium agreement was signed in Seoul on April 20.
April 26, 2023, 12:00PMEdited April 26, 2023, 12:00PMNuclear News LLNL design physicist Annie Kritcher is honored as one of the TIME100 Most Influential People. (Photo: Blaise Douros/LLNL)
Physicist Andrea “Annie” Kritcher’s dedication to fusion target design has earned her a spot on the TIME100 Most Influential People list for 2023. Today, Kritcher and 99 other individuals on that list—among them Elon Musk, King Charles, Judy Blume, Patrick Mahomes, Beyoncé, Lionel Messi, Janet Yellen, and MrBeast—are being honored at the TIME100 Summit and Gala at the Lincoln Center in New York City.
A side-by-side comparison of a standard plasma configuration (at left) and the plasma created during the negative triangularity campaign at DIII-D, which was made possible by the installation of a temporary divertor region. (Image: General Atomics)
The DIII-D National Fusion Facility in San Diego, Calif., has completed a monthlong research campaign using a negative triangularity plasma configuration inside its fusion tokamak and produced initial data that “appear very encouraging,” according to an April 24 news release from General Atomics (GA), which operates the Office of Science user facility on behalf of the Department of Energy. Full experimental results on “the highest-powered negative triangularity experiments in the history of the U.S. fusion research program” are expected this summer, according to GA.
 Citizens for Nuclear Technology Awareness (CNTA), a charitable nuclear educational organization based in Aiken, S.C., has announced the winners of its 17th annual High School Essay Contest. The contest was open to high school juniors and seniors in Aiken, Allendale, and Barnwell counties in South Carolina and Burke, Columbia, and Richmond counties in Georgia, as well as homeschool students in the region and students of CNTA member families.
Citizens for Nuclear Technology Awareness (CNTA), a charitable nuclear educational organization based in Aiken, S.C., has announced the winners of its 17th annual High School Essay Contest. The contest was open to high school juniors and seniors in Aiken, Allendale, and Barnwell counties in South Carolina and Burke, Columbia, and Richmond counties in Georgia, as well as homeschool students in the region and students of CNTA member families.






 Academy Award–winning director
Academy Award–winning director 



 The Nuclear Decommissioning Authority, the governmental organization responsible for the cleanup and decommissioning of the United Kingdom’s 17 nuclear sites, has released its business plan for the fiscal years running from April 1, 2023, through March 31, 2026. The plan provides a summary of the activities and progress the NDA expects to make at its nuclear sites over the next three years.
The Nuclear Decommissioning Authority, the governmental organization responsible for the cleanup and decommissioning of the United Kingdom’s 17 nuclear sites, has released its business plan for the fiscal years running from April 1, 2023, through March 31, 2026. The plan provides a summary of the activities and progress the NDA expects to make at its nuclear sites over the next three years.