Kris Singh (front left), Holtec International president and chief executive officer, signs the cooperation agreement between Holtec and Ukraine’s Energoatom, alongside other Holtec officials. (Photo: Holtec)
Small modular reactor developer Holtec International and Energoatom, Ukraine’s nuclear plant operator, signed a cooperation agreement last Friday that envisions the construction of up to 20 of the American firm’s SMR-160 units in Ukraine, with grid connection for the pilot project achieved by March 2029. In addition, the agreement calls for building a Ukrainian manufacturing facility to localize the production of equipment required for SMR-160 construction.
Olsen was part of the IAEA team that inspected the Rivne nuclear power plant in Ukraine last year. (Photo: IAEA)
Student members are the future of the American Nuclear Society, and ANS believes in the importance of supporting students those who have shown academic, service, and leadership excellence as they navigate their early careers. Robert Olsen, now a nuclear security officer with the International Atomic Energy Agency in Vienna, Austria, was one such beneficiary.
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission announced that an agency licensing board will hold oral arguments in a challenge to Pacific Gas and Electric’s application to renew its license for the Diablo Canyon independent spent fuel storage installation in California.
The arguments, which will be open to the public, will be heard by an NRC Atomic Safety and Licensing Board on May 24 beginning at 1 p.m. eastern time.
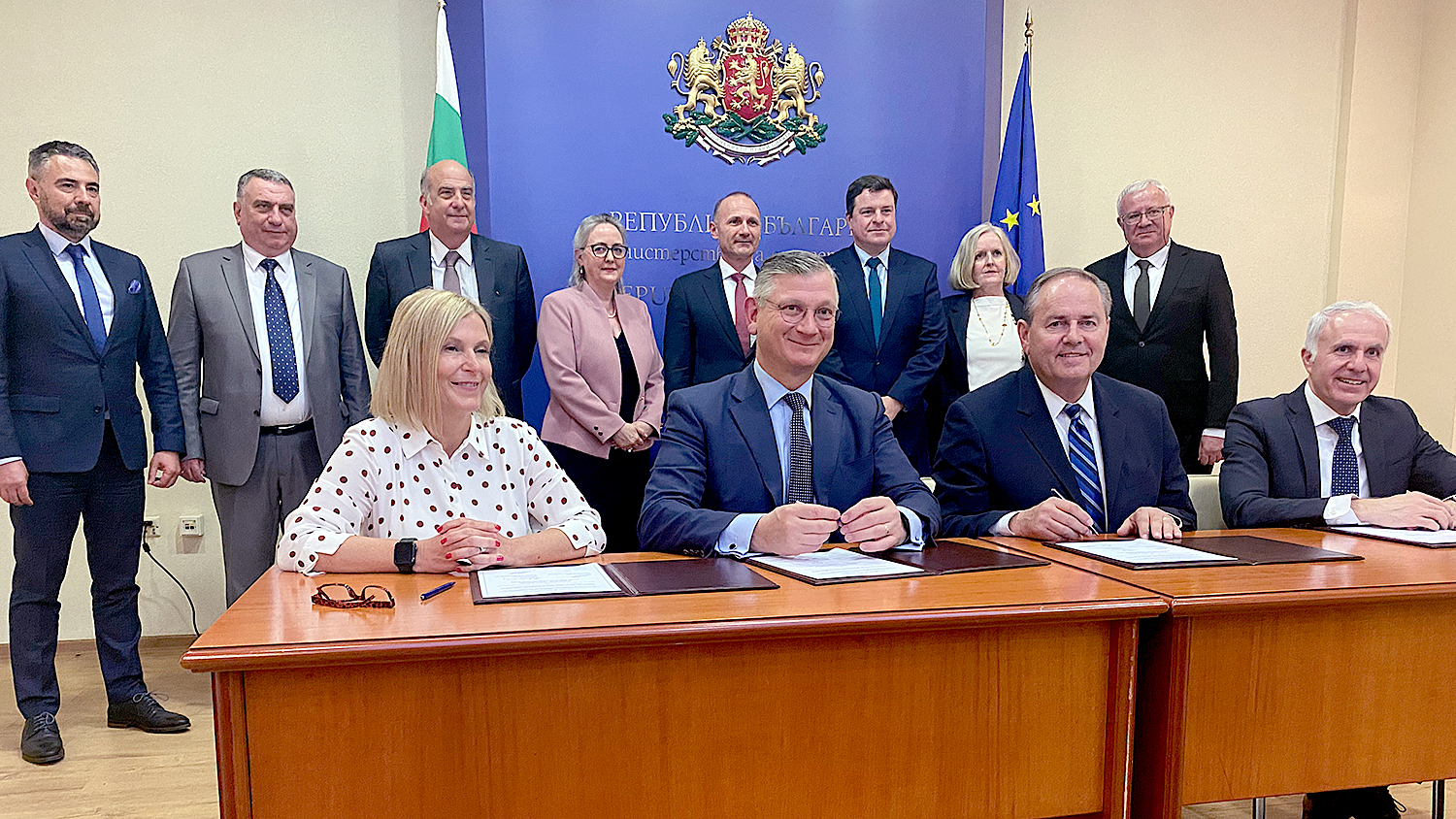
Various officials (back row) look on at the fuel supply contract signing in Sofia, Bulgaria. Front row, from left: Angie Darkey, Uranium Asset Management’s managing director; Boris Schucht, Urenco CEO; Tim Gitzel, Cameco president and CEO; and Aziz Dag, Westinghouse senior vice president of global BWR & VVER fuel business.
Canada’s Cameco and U.K.-based Urenco last week jointly announced the signing of agreements to become part of a Westinghouse-led fuel supply chain for Bulgaria’s Kozloduy nuclear power plant. (Also included in the partnership is Uranium Asset Management.)
From left: Francesco Venneri, chief executive officer of USNC; Hong Hyun-seong, CEO of Hyundai Engineering; and Park Kyung-il, CEO of SK ecoplant, following the signing of an MOU for the construction of a hydrogen micro hub. (Photo: USNC)
Seattle’s Ultra Safe Nuclear (USNC) has announced a partnership with two South Korean firms—Hyundai Engineering and SK ecoplant—for research and development on carbon-free hydrogen production. The three companies signed a memorandum of understanding on April 20 regarding the construction of a “hydrogen micro hub” at SK ecoplant’s headquarters in Seoul’s Jongno-gu district.
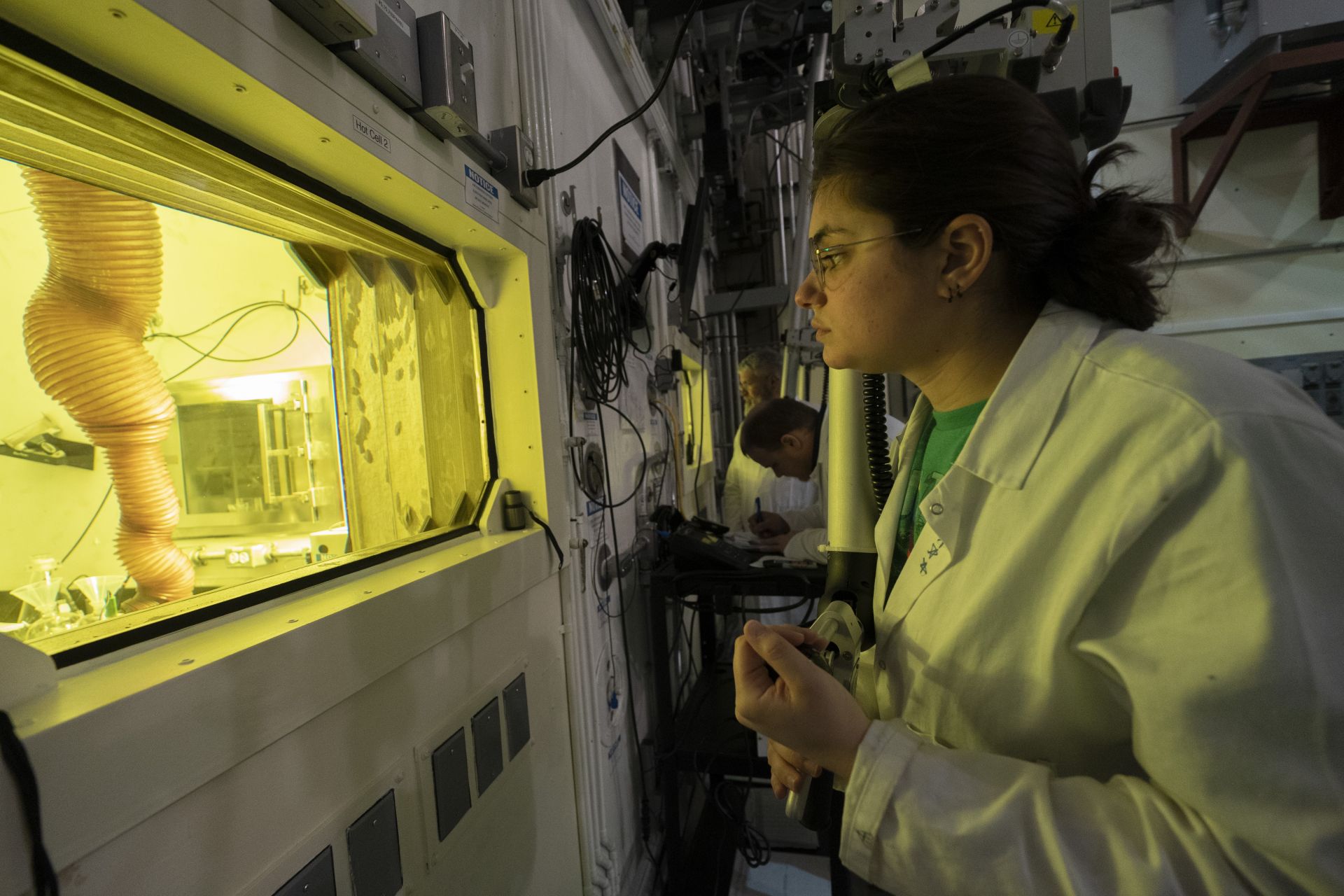
A member of Brookhaven’s MIRP team in the new hot cell area used for processing targets to make medical isotopes such as actinium-225. (Photo: BNL)
A refurbished hot cell laboratory is allowing the Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory to streamline the production and shipment of actinium-225 to support clinical trials of cancer therapies.
From left: Billy Mack, president of Accelerant Solutions; Pamela Cowan, president of global engineered systems and solutions at Westinghouse; and Francisco Sanchez, vice president of safety, operation, and training at Tecnatom, after signing the teaming agreement creating the Nuclear Excellence Academy. (Photo: Westinghouse)
Westinghouse Electric Company has signed an agreement with engineering firm Tecnatom and training/consulting services provider Accelerant Solutions to launch a nuclear training program for utilities in the United States and Canada. (Westinghouse completed a 50 percent acquisition of Spain-based Tecnatom in March of last year.)
The program—the Nuclear Excellence Academy (NEXA)—will combine Westinghouse and Accelerant Solutions’ industry expertise with Tecnatom’s digital products and services to provide in-person, digital, and on-demand training for nuclear personnel, according to an April 18 Westinghouse announcement.
April 21, 2023, 3:19PMNuclear NewsSal Oriti, Ernestina Wozniak, and Max Yang The multimission radioisotope thermoelectric generator for NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is tested at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in 2020. The choice of an MMRTG as the rover’s power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover’s landing site and in planning its surface operations. (Photo: NASA)
Under the Radioisotope Power Systems Program, NASA and the Department of Energy have been advancing a novel radioisotope power system (RPS) based on dynamic energy conversion. This approach will manifest a dynamic RPS (DRPS) option with a conversion efficiency at least three times greater than a thermoelectric-based RPS. Significant progress has recently been made toward this end. A one-year system design phase has been completed by NASA industry partner Aerojet Rocketdyne, which resulted in a DRPS with power of 300 watts-electric (We) with convertor-level redundancy. In-house technology development at the NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC) has demonstrated the conversion devices in relevant environments and has shown all requirements can be met. Progress has also been made on the control electronics necessary for dynamic energy conversion. Flight-like controllers were recently upgraded and achieved an 11-percentage-point increase in efficiency. Control architectures have been developed to handle the multiconvertor arrangements in the latest DRPS design. A system-level DRPS testbed is currently being assembled that will experimentally demonstrate the DRPS concept being pursued.
Joo Han-Gyu, KAERI president, on teleconference with Albertan ministers Brian Jean and Rajan Sawhney during the signing of the MOU. (Photo: KAERI)
The Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) and the government of Alberta have agreed on a comprehensive cooperation framework to explore the viability of using small modular reactors to help decarbonize the province—Canada’s biggest energy producer and its biggest polluter. The announcement comes the same week that Alberta’s United Conservative Party government released a climate plan aimed at reaching net zero by 2050.
Photos taken inside Hanford’s Tank AX-101 before workers started removing radioactive and chemical waste from it in January. As of April 18, crews have removed 35 percent of the tank waste. (Photos: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) said in an April 18 release that workers have so far removed almost 150,000 gallons, or about 35 percent, of the radioactive and chemical waste from Tank AX-101 at the department’s Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. Retrieval from this tank began in January.
A rendition of Terrestrial Energy’s IMSR. (Image: NRC)
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) has completed phase two of its prelicensing vendor design review for Terrestrial Energy’s Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR), the Ontario-based advanced nuclear technology firm announced Tuesday. Phase one of the VDR commenced in April 2016 and was completed in November of the following year.
The ministers representing their respective nations as the statement on civil nuclear fuel cooperation was announced were (from left) Jonathan Wilkinson, minister of natural resources of Canada; Yasutoshi Nishimura, Japan’s minister of economy, trade, and industry; Jennifer Granholm, U.S. energy secretary; Grant Shapps, U.K. energy security secretary; and Agnes Pannier-Runacher, French minister for energy transition.
A civil nuclear fuel security agreement between the five nuclear leaders of the G7—announced on April 16 on the sidelines of the G7 Ministers’ Meeting on Climate, Energy and Environment in Sapporo, Japan—establishes cooperation between Canada, France, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States to flatten Russia’s influence in the global nuclear fuel supply chain.