The Dukovany nuclear power plant. (Photo: CEZ Group)
A Westinghouse-Bechtel team, France’s EDF, and Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power have all submitted their initial bids for securing the contract to build a fifth reactor at the Czech Republic’s Dukovany plant, Czech utility ČEZ has announced.
These gas centrifuges operated in the Piketon facility from 2013 to 2016 as part of a 120-machine low-enriched uranium demonstration cascade. (Photo: Centrus Energy)
Centrus Energy confirmed on December 1 that its wholly owned subsidiary American Centrifuge Operating signed a contract with the Department of Energy, which was first announced on November 10, to complete and operate a demo-scale high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) gaseous centrifuge cascade.
The electron accelerator that will be used for Mo-99 production at NorthStar’s newly completed facility in Wisconsin. (Photo: NNSA)
NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes has completed construction and all equipment installation at its new facility in Beloit, Wis., to produce the medical radioisotope molybdenum-99 without the use of high-enriched uranium, the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration announced last week.
A total of about 23 kilometers (about 14 miles) of piping are welded to the surface of the thermal shield panels. The piping on a vacuum vessel thermal shield panel is clearly visible in this photo. (Photo: ITER Organization)
The ITER Organization is working on a new baseline schedule for the magnetic confinement fusion experiment launched in 1985 and now under construction in southern France. First plasma was scheduled for December 2025 and deuterium-tritium operations for 2035 under a schedule approved in November 2016 that will soon be shelved. In addition to impacts from COVID-19 delays and uncertainty resulting from Russia’s war in Ukraine, ITER leaders must now factor in repair time for “component challenges.”
Westinghouse’s Kirsty Armer and Studsvik’s Mikael Karlsson sign a technology license agreement to develop a metals recycling and treatment facility at the Westinghouse Springfields site in Lancashire, U.K. (Photo: Westinghouse)
Westinghouse Electric Company has announced the signing of a long-term technology license agreement with Swedish engineering services firm Studsvik to develop a metals recycling and treatment facility at Westinghouse’s Springfields site.
Located near Preston, Lancashire, in northwestern England, Springfields is the United Kingdom’s only site for nuclear fuel manufacturing, supplying all its advanced gas-cooled reactor fuel. According to Westinghouse, Springfields fuel is responsible for about 32 percent of Britain’s low-carbon electricity generation. In addition, the site exports other nuclear fuel products to customers around the globe.
December 2, 2022, 3:03PMNuclear NewsBrian Dassatti, Kamila Blain, and Jenn Sinkiewicz Teledyne FLIR PackBot® conducts visual inspections in a hazardous area.
Mobile unmanned systems, also known as MUS, encompass a range of robotic devices, including drones, ground vehicles, crawlers, and submersibles. They are used for a wide range of industrial and defense applications to automate operations and assist humans or completely remove human workers from hazardous conditions. Robotics are ubiquitous in industrial manufacturing. Military robots are routinely employed in combat support applications, such as reconnaissance, inspection, explosive ordnance disposal, and transportation. Drones are used in many industries for security and monitoring, to conduct aerial inspections or surveys, and to capture digital twins. Wind and solar farms use MUS technologies for day-to-day operations and maintenance.
Workers walk down a passageway in Panel 8 at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in November. (Photo: DOE)
Employees have begun emplacing defense-related transuranic (TRU) waste in Panel 8 of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) in New Mexico, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced in November. TRU waste is permanently disposed of at WIPP in rooms mined in a Permian salt bed 2,150 feet below the surface.
From left: Christina Leggett (Booz Allen Hamilton), Morris Hassler (IB3 Global Solutions), Everett Redmond (Oklo), Andy Griffith (DOE-NE), Ben Jordan (Centrus), Stephen Long (GLE), and Magnus Mori (Urenco).
Whether commercial demand for high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) fuel ultimately falls at the high or low end of divergent forecasts, one thing is certain: the United States is not ready to meet demand, because it currently has no domestic HALEU enrichment capacity. But conversations happening now could help build the commercial HALEU enrichment infrastructure needed to support advanced reactor deployments. At the 2022 American Nuclear Society Winter Meeting, representatives from three potential HALEU enrichers, the government, and industry met to discuss their timelines and challenges during “Got Fuel? Progress Toward Establishing a Domestic US HALEU Supply,” a November 15 executive session cosponsored by the Nuclear Nonproliferation Policy Division and the Fuel Cycle and Waste Management Division.
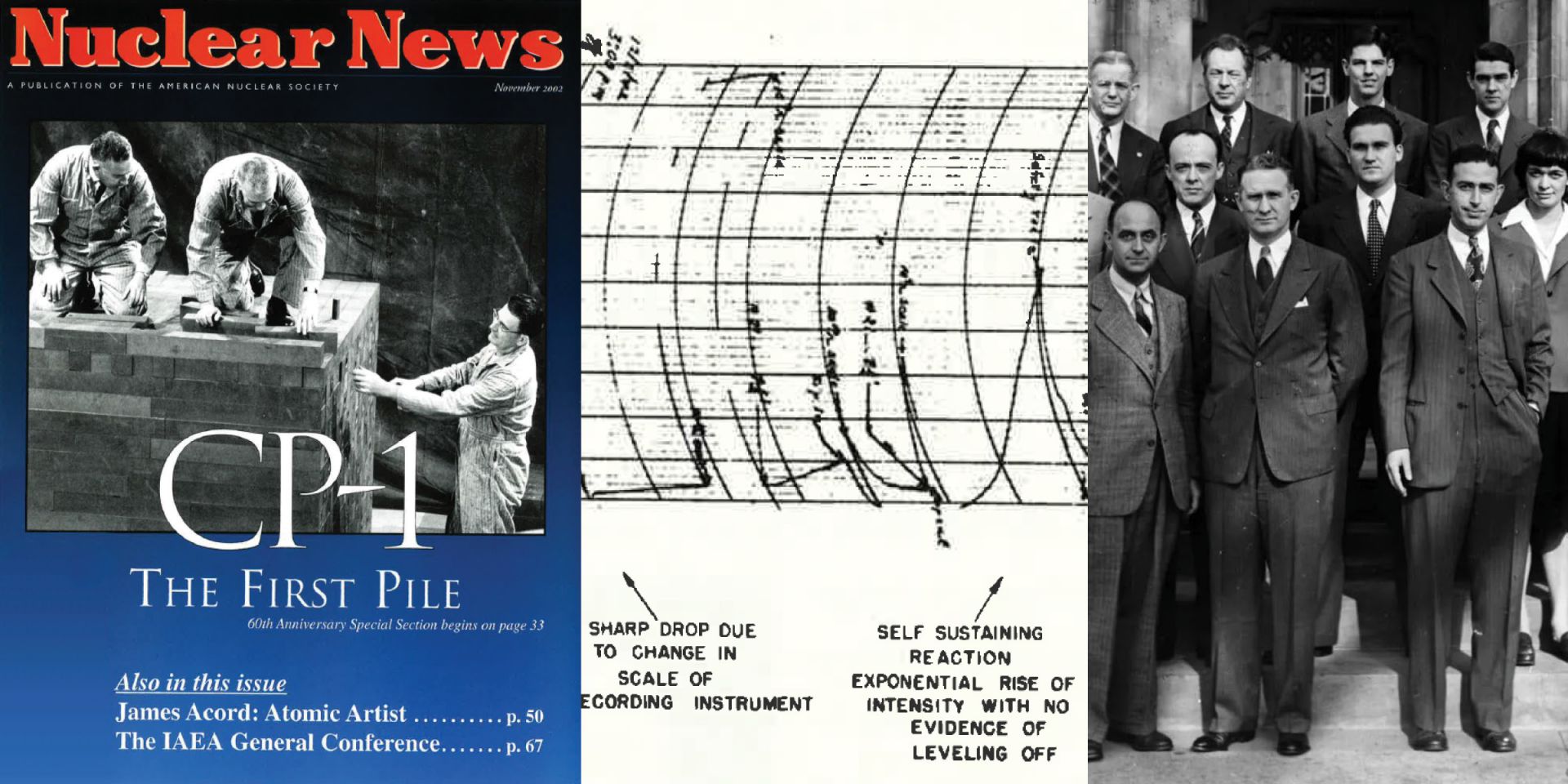
On December 2, 1942, a group of 49 scientists led by Enrico Fermi created the world’s first controlled, self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction underneath the University of Chicago’s Stagg Field football stadium. Some of those present went on to found Argonne National Laboratory. (Image: Argonne)
At a moment of global crisis, in a windowless squash court below the football stadium bleachers at the University of Chicago, a group of scientists changed the world forever.
On December 2, 1942, a team of researchers led by Enrico Fermi, an Italian refugee, successfully achieved the world’s first human-created, self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. Racing to beat Nazi Germany to the creation of an atomic weapon, the team of researchers, working as part of the Manhattan Project, split uranium atoms contained within a large graphite pile—Chicago Pile-1, the first nuclear reactor ever built.
Westinghouse employee completing visual inspection of I&C part
Obsolescence and the ability to obtain qualified replacement and spare parts are primary concerns in the nuclear industry. In fact, approximately 35% of installed equipment is obsolete.
Westinghouse Parts Business (WPB) has over 50 years of experience replacing and upgrading systems for operating nuclear power plants with access to original design information as the original equipment manufacturer (OEM).
WPB provides innovative, cost-efficient solutions for Westinghouse and non-Westinghouse systems in order to increase reliability of I&C systems, including enhanced replacement components, repair and refurbishment services. Recently, WPB has supported numerous customers in obsolescence and Reverse Engineering (RE) services.





.png)