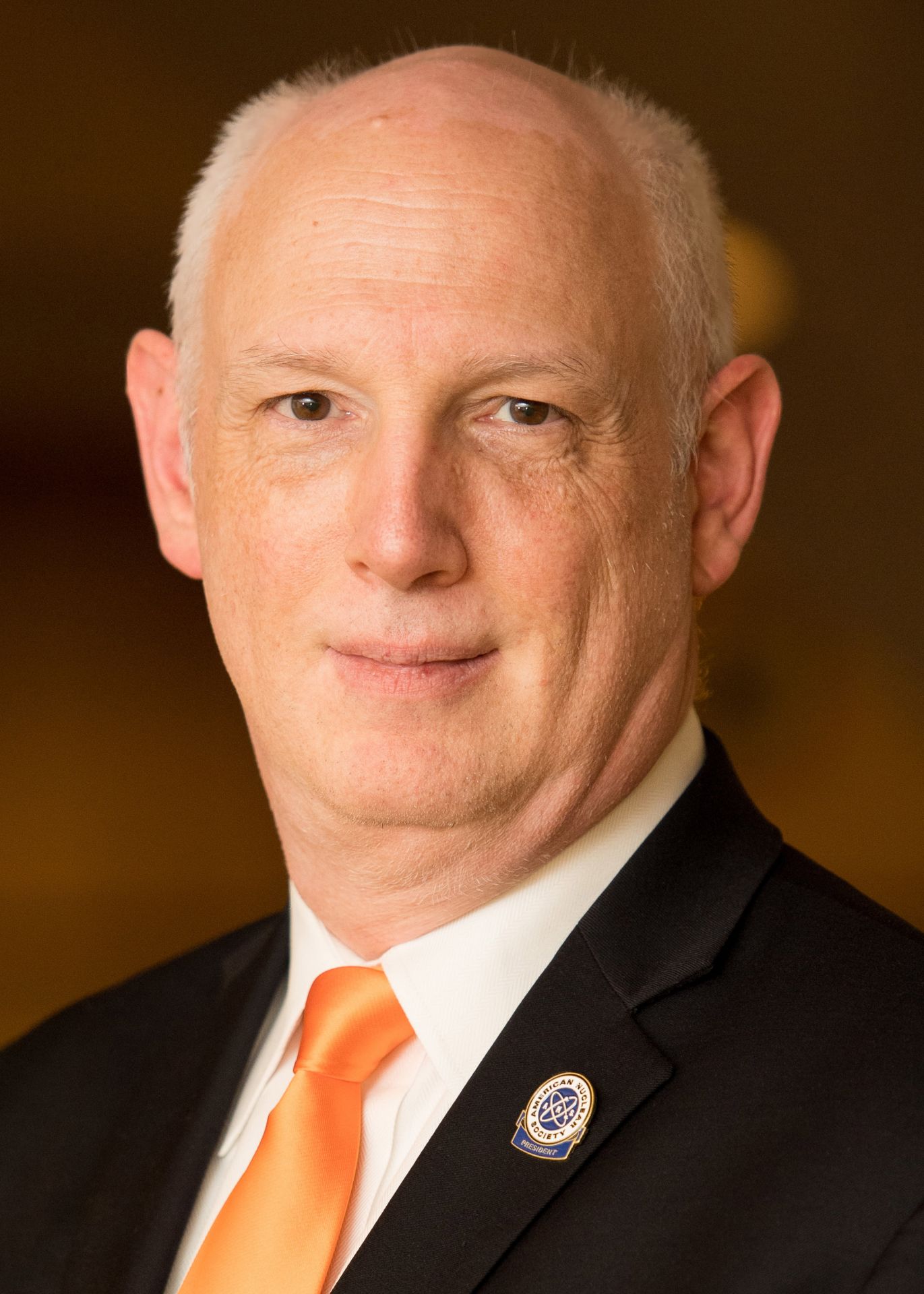
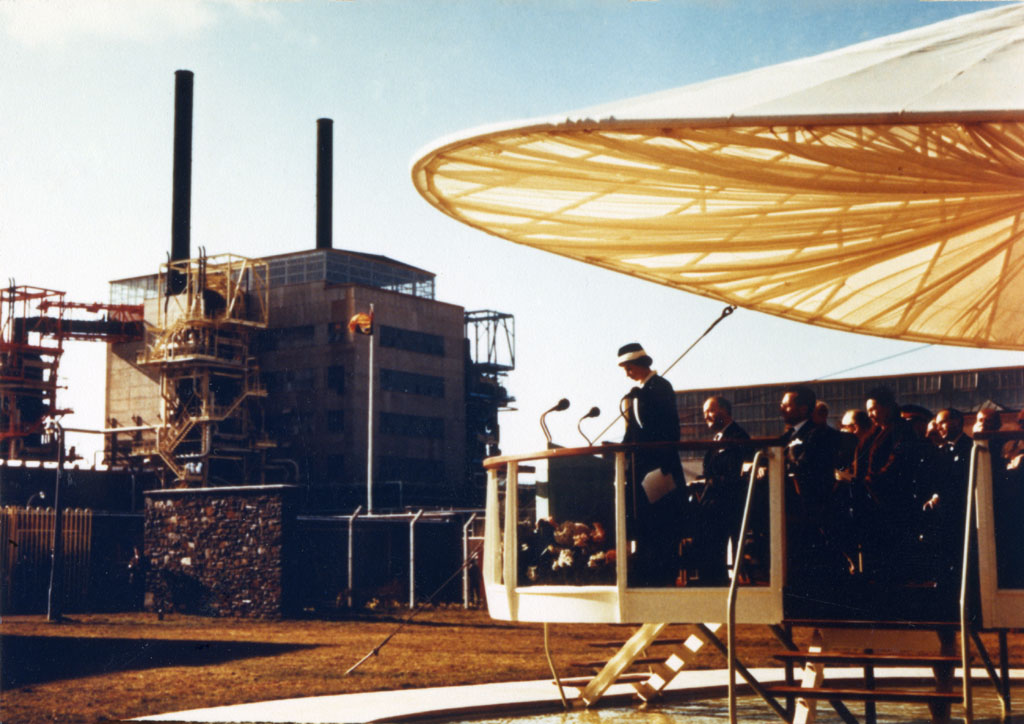
Queen Elizabeth II visits Calder Hall for its ceremonial opening in 1956. (Photo: U.K. Nuclear Decommissioning Authority)
As citizens of the United Kingdom and others around the world mourn the death of Queen Elizabeth II, many have reflected on how the world has changed during the seven decades of the queen’s reign—the same decades that saw the rise of civilian nuclear power.
Calder Hall was already under construction at the Sellafield site in West Cumbria when Princess Elizabeth became queen in 1953. Queen Elizabeth traveled to the site in October 1956 and declared, in a televised ceremony, that “It is with pride that I now open Calder Hall, Britain’s first atomic power station.” Watch the fanfare in a historical clip uploaded to YouTube by Sellafield Ltd below.
The Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant.
The International Atomic Energy Agency’s board of governors has adopted a resolution calling for an immediate end to the Russian occupation of Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant. According to a report from Reuters, the 35-member board voted 26–2 yesterday in favor of the resolution, with seven abstentions. The two “no” votes were cast, unsurprisingly, by Russia and China, while abstentions came from Burundi, Egypt, India, Pakistan, Senegal, South Africa, and Vietnam.
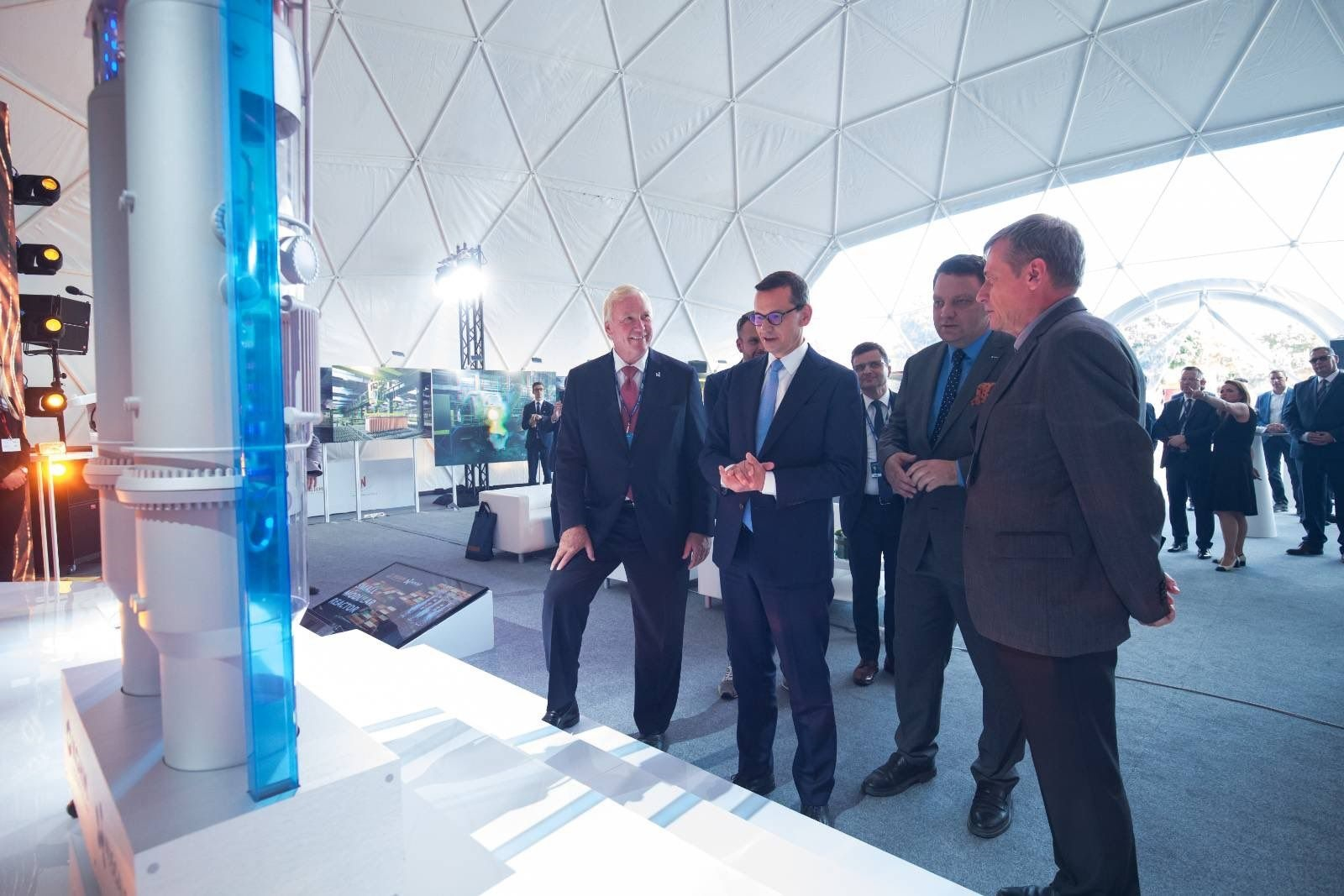
From left: NuScale president and CEO John Hopkins, Poland prime minister Mateusz Morawiecki, KGHM CEO Marcin Chludziński, and Ludwik Pieńkowski from AGH University of Science and Technology view a model of NuScale’s SMR technology. (Photo: Business Wire)
Portland, Ore.–based NuScale Power and KGHM Polska Miedź S.A. have signed the first task order and a statement of commencement to begin work under an agreement signed in February to initiate deployment in Poland of NuScale’s small modular reactor technology, the American firm announced this week. The task order was inked September 7 at the 31st Economic Forum, held September 6–8 in Karpacz, Poland.
Entergy’s Waterford nuclear plant, in Killona, La. (Photo: Entergy)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is increasing its oversight of the Waterford Steam Electric Station’s Unit 3 reactor due to a decade-long miscalibration of a radiation monitor.
In a September 13 letter to Entergy Operations, the NRC classified the issue at the Killona, La., facility as a “white finding”—agency parlance for a problem of low to moderate safety significance. (The NRC’s Reactor Oversight Process uses color-coded inspection findings and indicators to measure plant performance, starting at green and increasing to white, yellow, and red, commensurate with the safety significance of the issues involved.)
The Naughton coal-fired power plant near Kemmerer, Wyo., has two units set to retire in 2025 and be replaced by a TerraPower Natrium reactor. (Photo: PacifiCorp)
Nuclear power generation surpassed coal generation in the United States for the first time in 2020. As utilities continue to retire coal-fired plants, reusing the shuttered sites to host nuclear reactors could help the nation reach the goal of net-zero emissions by 2050 and prove economically beneficial both for nuclear deployments and for the communities impacted by fossil fuel generation. That’s according to a Department of Energy report released this week, detailing how hundreds of U.S. coal power plant sites that have recently retired or plan to close within the decade could be suitable for new nuclear power plants. Nuclear power’s high capacity factors mean those plants could deliver an added benefit—delivering more baseload power to the grid from the nameplate capacity replacement.
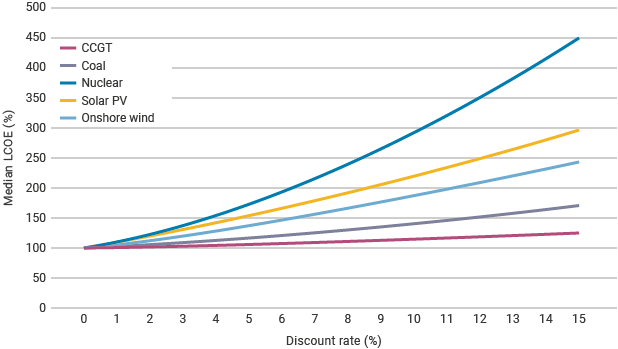
Interest rates have an outsized impact on nuclear power costs compared to those for other methods of power generation. (Source: World Nuclear Association)
In an essay titled “How the Fed will Strangle New Nukes,” published this week by American Thinker, nuclear engineer and writer Joseph Somsel warns that despite current expectations of a nuclear construction boom, “As in the late 1970s, rising interest rates will put the kibosh on new nukes.” Somsel therefore urges the financing and building of new nuclear facilities right now, before ongoing inflation and increasingly high interest rates “kill a lot of the plans” for new nuclear power plants.
Demolition has begun on the Bulk Shielding Reactor at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. It marks the first teardown of a former reactor at the site. (Photo: DOE).
In a first for the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Site, a former reactor facility is being demolished. The site’s cleanup contractor, UCOR, began tearing down the Bulk Shielding Reactor, also known as Building 3010, last week.
“While this project is not the biggest demolition we’ve undertaken, it carries a lot of significance,” said Laura Wilkerson, acting manager for the Oak Ridge Office of the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM). “It is the first removal of a former reactor at [Oak Ridge National Laboratory], and it is a signal of much more to come at the site in the immediate future.”
The Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility at Jefferson Lab. (Source: Jefferson Lab)
Research with the Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (Jefferson Lab) has revealed new insights into short-range correlations—the brief pairings of nucleons (protons with neutrons, protons with protons, or neutrons with neutrons) in the nuclei of atoms. The study, published in Nature, used precision measurements to determine that short-range correlations differ depending on the density of the nucleus, that is, how many nucleons it contains.
An illustration of Switzerland’s proposed deep geological repository. (Image: Nagra)
Nagra, Switzerland’s national cooperative for the disposal of radioactive waste, has announced that it has selected Nördlich Lägern as the site for a deep geological repository for radioactive waste. According to Nagra, extensive investigations have shown that Nördlich Lägern, located in northern Switzerland near the German border, is the most suitable area for a geologic repository with the best overall safety reserves.
An aerial view of Westinghouse’s Columbia Fuel Fabrication Facility in Hopkins, S.C. (Photo: Westinghouse)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission yesterday announced that it has issued a renewed license for Westinghouse Electric Company’s Columbia Fuel Fabrication Facility (CFFF), authorizing operations at the plant for another 40 years—through September 12, 2062.
Located in Hopkins, S.C., the CFFF manufactures fuel rods for use in commercial nuclear reactors. According to Westinghouse, 10 percent of the nation’s electricity comes from the fuel manufactured at the facility.
A clinical dose of At-211 is prepared at the University of Washington for use in a Fred Hutchison Cancer Center clinical trial. (Photo: UW/Don Hamlin)
Scientists in the Departments of Radiation Oncology and Medicine at the University of Washington (UW) and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center (Fred Hutch) are directly targeting cancerous cells traveling through patients’ bloodstreams with diseases such as leukemia and lymphoma using an intravenous injection of the radioactive isotope astatine-211 (At-211). The work, its challenges, and its promise were described in a recent news release from the National Isotope Development Center (NIDC), which is managed by the Department of Energy’s Isotope Program.
The Palisades nuclear power plant. (Photo: Entergy)
Maybe hold off commenting on those Palisades decommissioning plans for now: Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer last Friday penned a letter to energy secretary Jennifer Granholm pledging state support for a Holtec International plan to restart the recently shuttered Palisades nuclear plant in Covert, Mich. It was Whitmer’s second letter to the Department of Energy head expressing support for Palisades and touting its value to the state.


-3 2x1.jpg)