Focus on Ukraine

We’ve sifted through facts and statistics on nuclear power in Ukraine to offer some choice insights here. Want more international nuclear data? Check out the March 2022 Nuclear News Reference Issue.
-3 2x1.jpg)
A message from Curtiss-Wright
High-Temperature neutron flux detectors for Generation IV reactors and SMRs

We’ve sifted through facts and statistics on nuclear power in Ukraine to offer some choice insights here. Want more international nuclear data? Check out the March 2022 Nuclear News Reference Issue.
.jpg)
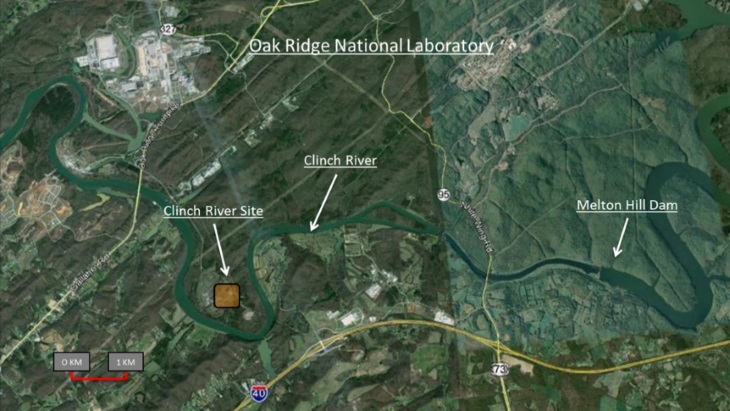
Last week’s announcement from the Tennessee Valley Authority about its “New Nuclear Program,” which outlines the potential development of the Clinch River site near Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Eastern Tennessee, is the catalyst for this week’s #ThrowbackThursday post. The Clinch River site was originally planned to be the location for the Clinch River Breeder Reactor, a project that, at the time, was meant to be the future of the nuclear industry in the United States.

The San Luis Obispo County Board of Supervisors earlier this week endorsed extending the life of Diablo Canyon—California’s last operating nuclear power facility—which owner and operator Pacific Gas and Electric Company has scheduled for permanent closure in 2025. The two-unit, 2,289-MWe plant is located in San Luis Obispo County, near Avila Beach.

Holtec International announced yesterday that its India-based subsidiary, Holtec Asia, has received an order from Mumbai-based Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) for two HI-STAR 149 transport casks to serve the away-from-reactor storage facility for the Kudankulam nuclear power plant.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Nuclear Energy has officially launched its $6 billion civil nuclear credit program, which is intended to support nuclear power reactors at risk of shutting down because of economic factors. A notice of intent and request for information (NOI/RFI) regarding the program was published in the February 15 Federal Register. The DOE-NE had announced the program with the release of a pre-publication version of the NOI/RFI on February 10.
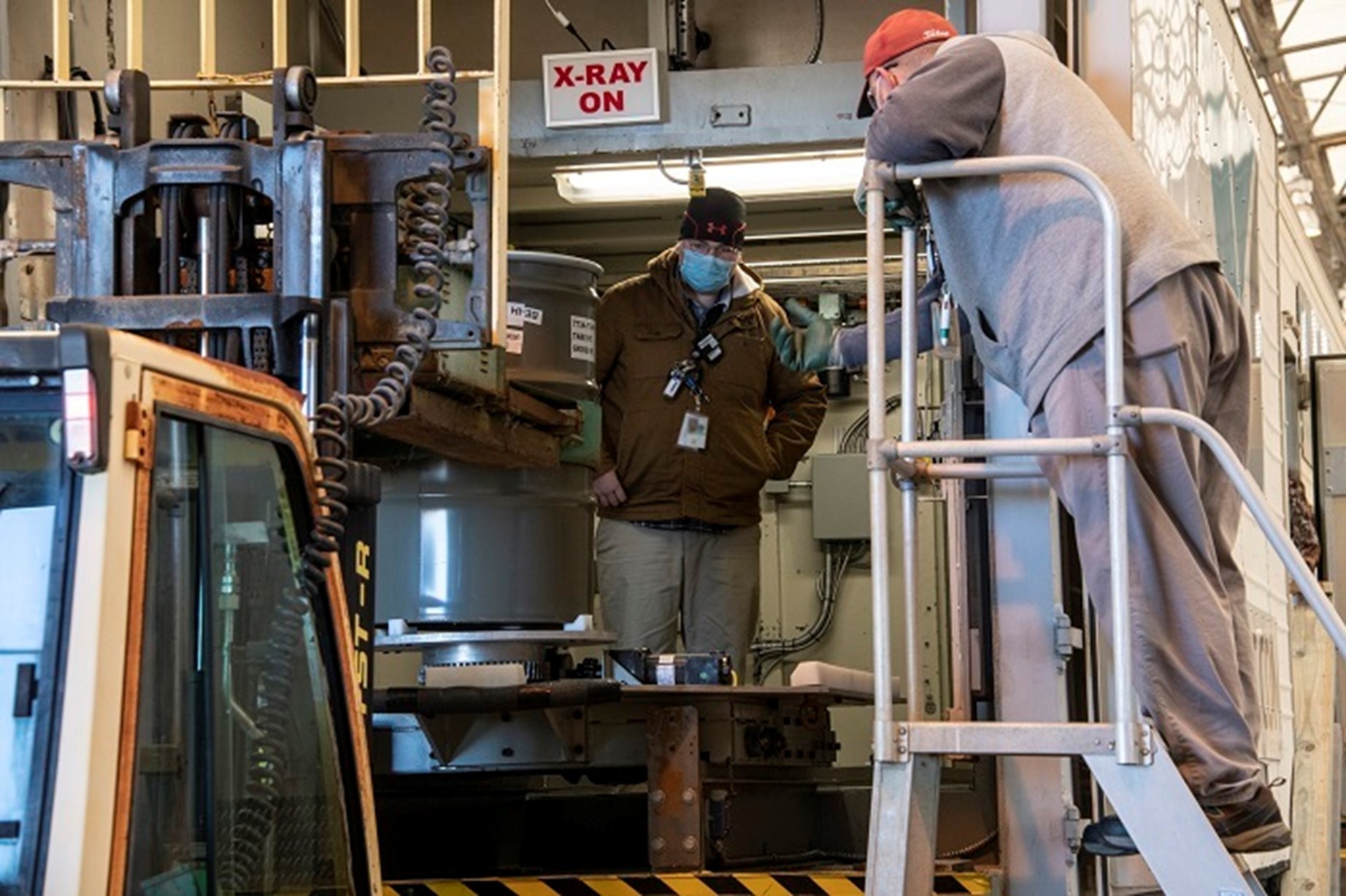

Operators at the Savannah River Site’s Solid Waste Management Facility can now characterize and certify newly generated TRU waste through the use of a real-time radiography unit that uses an X-ray system to examine the contents of waste containers. The equipment was recently installed to meet updated requirements set by the Department of Energy’s National TRU Program that involve evaluating the containers for chemical compatibility and oxidizing chemicals.
The shipments of TRU waste from SRS, in South Carolina, are sent to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP), in New Mexico, for disposal.

Issa

Levin
Reps. Mike Levin (D., Calif.) and Darrell Issa (R., Calif.) have reintroduced bipartisan legislation that would make the San Onofre nuclear power plant in Southern California one of the highest priority sites in the United States for the removal of spent nuclear fuel. The bill is being cosponsored by Reps. Scott Peters (D., Calif.), Michelle Steel (R., Calif.), Katie Porter (D., Calif.), and Young Kim (R., Calif.).
The Spent Fuel Prioritization Act would amend the Nuclear Waste Policy Act to require the Department of Energy to prioritize spent fuel removal from decommissioned reactors based on the size of the population near the plant, the seismic hazard associated with the area, and any national security concerns. The bill does not call for a permanent repository or consolidated interim storage, nor does it authorize the transfer of spent fuel to any non-consenting state or locality.

Graham

Menendez
Sens. Bob Menendez (D., N.J.), chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, and Lindsey Graham (R., S.C.) have introduced a resolution calling for the U.S. government to adopt a policy that would permit any Middle Eastern state access to nuclear fuel via a regional fuel bank, provided it agrees to abstain from uranium enrichment and reprocessing.
Modeled on the International Atomic Energy Agency’s nuclear fuel bank in Kazakhstan, the proposed regional fuel bank would allow the commercial development of nuclear power throughout the Middle East while at the same time eliminating the need for dangerous and destabilizing domestic nuclear programs, according to a February 11 press release from the legislators.

At an event held on February 14 at the Chamber of Commerce in Washington, D.C., small modular reactor developer NuScale Power inked an agreement with KGHM Polska Miedz S.A., to initiate deployment of NuScale’s SMR technology in Poland.

The Department of Energy has announced an $18 million funding opportunity for research and development in particle accelerator science and technology for nuclear physics research. Provided through the DOE’s Office of Science, the funding is intended to support “efforts essential to developing world-leading core competencies and transformative technologies that significantly advance the state-of-the-art accelerator capabilities.”

It seems like only yesterday that former ANS President Andy Klein announced the nine ANS Nuclear Grand Challenges that need to be addressed to ensure that existing and emerging nuclear technologies benefit current and future generations. The Fuel Cycle and Waste Management Division (FCWMD) immediately began tackling the grand challenge of closing the nuclear fuel cycle by sponsoring recurring panel sessions on the topic at subsequent ANS meetings.

Counterfeit, fraudulent, and suspect items (CFSI) are present in U.S. operating nuclear power plants, potentially increasing safety risks, a “special inquiry” report released last Thursday from the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s Office of the Inspector General has concluded. The term “CFSI” can refer to parts that have been intentionally altered to imitate a legitimate product or those that have been misrepresented with intent to deceive, as well as parts that merely fail to meet intended product specifications.
The OIG initiated the report to look into allegations that CFSI are present in most, if not all, U.S. nuclear plants, that the NRC has lowered its CFSI oversight standards, and that the agency has failed to address CFSI concerns.

Walker
Despite its status as the number one state in nuclear generating capacity (with 11 power reactors)—and despite having provided a sizeable financial boost to its reactor fleet last September—Illinois currently prohibits new nuclear power plant construction.
The ban, however, is now being targeted by state Rep. Mark Walker (D., Arlington Heights), who is sponsoring a measure in the Illinois General Assembly to have it repealed.
The bill: On January 31, Walker introduced H.B. 5589, which would amend the Illinois Public Utilities Act by deleting language stating that “no construction shall commence on any new nuclear power plant to be located within this state, and no certificate of public convenience and necessity or other authorization shall be issued therefore by the Illinois Commerce Commission, until the director of the [Illinois] Environmental Protection Agency finds that the United States government, through its authorized agency, has identified and approved a demonstrable technology or means for the disposal of high-level nuclear waste, or until such construction has been specifically approved by a statute enacted by the General Assembly.”

The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced on February 10 that it is set to deactivate and demolish the prototype for the reactor used for the USS Nautilus, the world’s first operational nuclear-powered submarine and the first submarine to complete a submerged transit of the North Pole.

The Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) and the Environment Agency (EA) have found the UK HPR1000 reactor suitable for construction in the United Kingdom, the regulators jointly announced last week.

Citing “improving market sentiment,” Tim Gitzel, president and chief executive officer of the Canadian uranium mining company Cameco, announced on February 9 the planned restart of operations at the McArthur River mine in Saskatchewan.

Macron
As part of its drive for carbon neutrality by 2050, France will build at least six new nuclear reactors in the coming decades, according to a February 10 article from Reuters. "What our country needs, and the conditions are there, is the rebirth of France's nuclear industry," French president Emmanuel Macron said as he announced France’s new nuclear strategy.
Macron also said that he wanted to extend the life spans of France’s existing nuclear plants.
The price tag: The six new plants would be built and operated by state-controlled energy provider EDF, which has estimated the cost of those plants total at about 50 billion euros (about $57 billion), depending on financing conditions, according to the article.
The first new reactor, an evolution of the European Pressurized Reactor (EPR), would come on line by 2035, Macron said. The article added that the country would embark on a study to determine whether a further eight reactors beyond the initial six would be needed.

Regalbuto
High-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) is the power-dense feedstock of choice for a slew of advanced reactor designs. There’s just one problem: It isn’t available . . . yet. Downblending high-enriched uranium owned by the Department of Energy to between 5 and 19.75 percent fissile U-235 is a stopgap measure at best, and no U.S. facility can yet produce commercial quantities of uranium above the 5 percent U-235 limit for low-enriched uranium.
The problem is one not of technology, but of economics: Enrichment companies want to see clear market signals that advanced reactors will be deployed in quantity, leading to long-term purchase agreements that will justify investments made today.
ANS Fellow Monica Regalbuto is director of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Strategy at Idaho National Laboratory, tasked with leveraging her more than 30 years of fuel cycle experience to ensure an adequate domestic supply of HALEU. She was invited to speak about her work during the opening plenary session of the 2021 ANS Winter Meeting.

The Department of Energy’s Office Nuclear Energy has launched a $6 billion program aimed at preserving the existing U.S. fleet of nuclear power reactors. Established under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, the Civil Nuclear Credit Program will allow owners and operators of commercial nuclear power reactors at economic risk of shutting down to apply for credits via a sealed bid process.
.jpg)
The Tennessee Valley Authority’s board of directors has given the go-ahead for a program that will explore the development and potential deployment of small modular reactors as part of the utility’s decarbonization strategy.