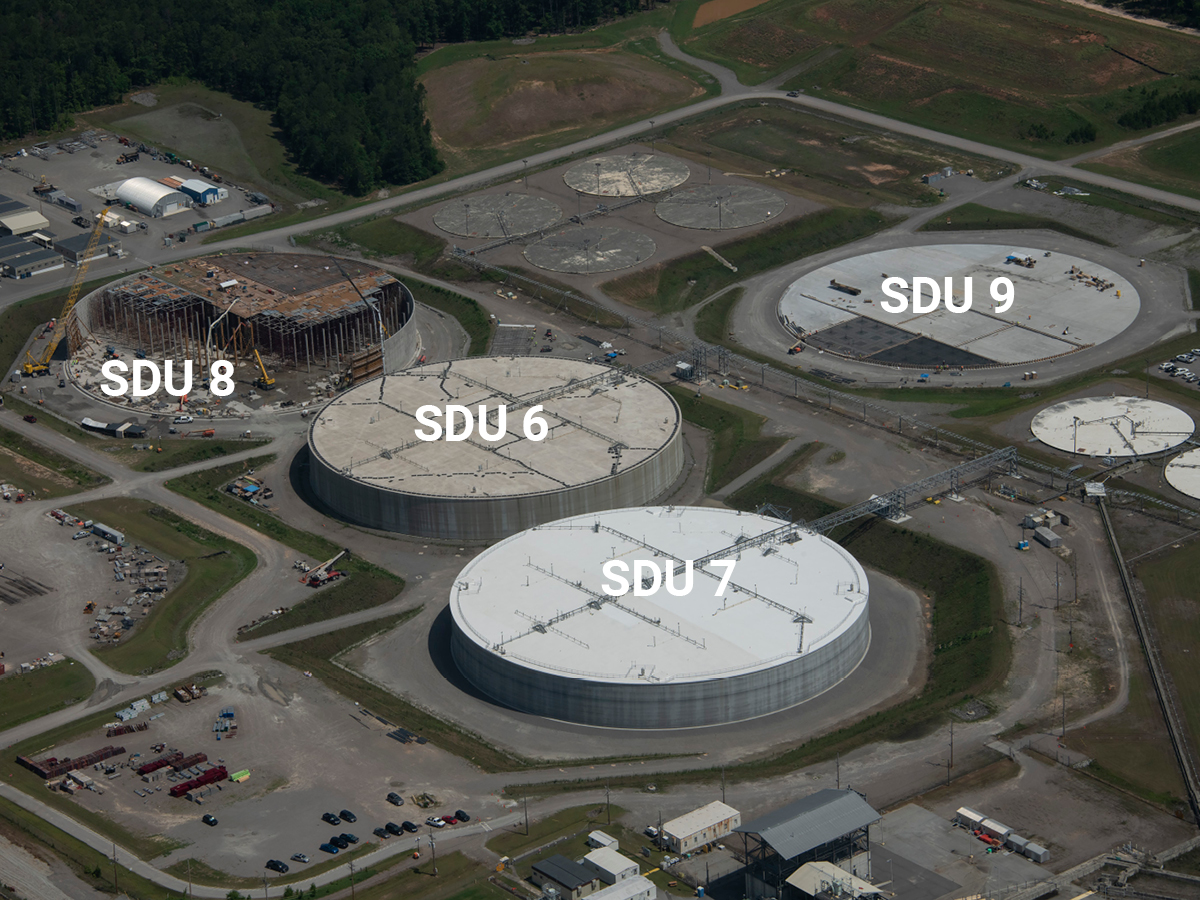
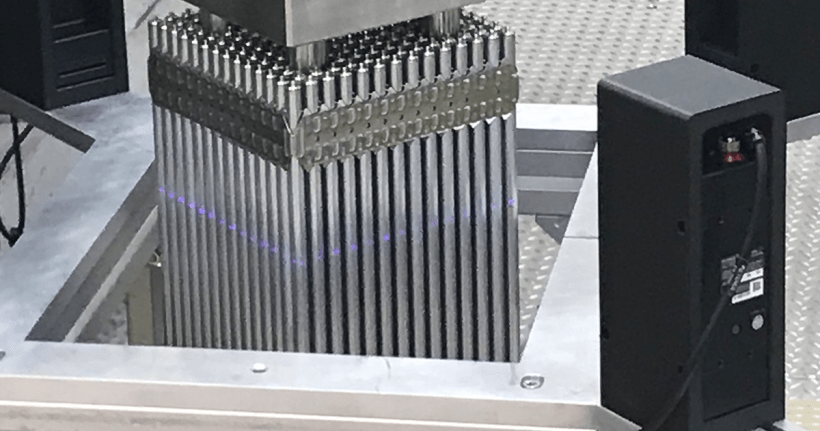
Framatome’s PROtect accident tolerant fuel assembly undergoes final inspection before delivery to Exelon’s Calvert Cliffs-2 in Lusby, Md.
The nuclear industry’s first 100 percent accident tolerant fuel assembly is in operation at Exelon Generation’s Calvert Cliffs plant, the Department of Energy announced yesterday. The advanced fuel will operate in the reactor for the next four to six years and will be routinely inspected to monitor its performance, the DOE said.
Located in Lusby, Md., Calvert Cliffs houses two pressurized water reactors. Unit 1 is rated at 907 Mwe, and Unit 2 at 881 Mwe.
More than 550 employees will join Framatome as part of its acquisition of Rolls-Royce’s I&C business. (Photo: Business Wire)
French nuclear reactor company Framatome has completed its purchase of Rolls-Royce Civil Nuclear Instrumentation and Control. Framatome announced in December 2020 that it had agreed to acquire Rolls-Royce’s I&C business, which has operations in France, the Czech Republic, and China.
According to Framatome, the transaction builds on the company’s engineering expertise, enlarges its industrial footprint, and expands its global I&C systems development and deployment capabilities.
Crews pump waste from Hanford’s single-shell tanks to more stable double-shell tanks. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy is considering solidifying 2,000 gallons of Hanford’s tank waste and disposing of it as low-level radioactive waste at an off-site facility. A virtual public meeting on the proposed disposal plan is scheduled for November 18.
DOE liquid waste contractor Savannah River Remediation is moving forward with Saltstone Disposal Unit projects to support the Salt Waste Processing Facility at the Savannah River Site.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has authorized the use of a second mega-volume saltstone disposal unit (SDU) at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. Savannah River Remediation (SRR), EM’s liquid waste contractor at SRS, received Critical Decision-4 for Saltstone Disposal Unit 7, marking the final step in the approval process before beginning operations.
A truck loaded with waste crosses the scale at the East Tennessee Technology Park at Oak Ridge. Each truck used by Oak Ridge contractor UCOR is equipped with a unique radio frequency identification card that logs its movements and weight and registers the data in a database.
UCOR, the primary contractor for the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Office of Environmental Management (OEM), recently transitioned to a new waste tracking system that improves how shipments are tracked from work sites to disposal locations.
The new system includes upgraded radio frequency identification (RFID) tracking for trucks, as well as new hardware and software, allowing for an automated tracking operation that delivers up-to-the-minute waste disposal data.
Southern California Edison has a plan—and it just might build momentum to solve the nation’s spent nuclear fuel disposal dilemma.
Imagine it’s January 1998. A specially equipped train from the Department of Energy rolls up to the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS) to pick up spent nuclear fuel and take it to the Yucca Mountain repository in Nevada. This scene is repeated thousands of times at nuclear plant sites across the U.S. over the ensuing decades. The solution to permanent spent fuel disposal as outlined in the Nuclear Waste Policy Act (and its amendments) is working as intended. The nation’s commercial spent fuel is safely isolated deep underground for the long term.
But that is not what happened. Work on Yucca Mountain has been stalled for a full decade, and the organization within the DOE that by law is responsible for managing the spent fuel program has been defunded and disbanded.
The Barakah nuclear power plant. Unit 3 is the second from left. (Photo: Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation)
The construction of Unit 3 at the United Arab Emirates’ Barakah nuclear power plant has been completed, the Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation (ENEC) announced yesterday on the sidelines of COP26, the high-profile climate confab taking place in Scotland this week and next.
According to ENEC’s announcement, Barakah-3 will now undergo operational readiness activities and is on track to start up in 2023.
From left, Shannon Bragg-Sitton, Paul Chodak, and Michael J. Guastella appear before the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources on November 4.
As Congress awaited key votes yesterday on spending bills that include production tax credits for at-risk plants and a new amendment adding $500 million in supplemental funding over five years to increase the availability of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU), the U.S. Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee held a Full Committee Hearing On Potential Non-Electric Applications Of Civilian Nuclear Energy. Sen. Joe Manchin (D., W.V.), chairman of the committee, emphasized that “advanced nuclear reactors hold enormous potential to provide opportunity to communities across the country with zero-emission baseload power” and made it clear he expects new reactors to replace retiring coal plants in his home state of West Virginia.
Speaking before the committee were Shannon Bragg-Sitton of Idaho National Laboratory, Paul Chodak III of American Electric Power, and Michael J. Guastella of the Council of Radionuclides and Radiopharmaceuticals.
SRNS's Communications and Media Services Department was honored with two 2021 Telly Awards. Members of the department include, from left, Robin Adney, Ian Rojas-Godoy, Brad Bohr, Nathan Lester, Steve Ashe, and Laura Russo. (Photo: DOE)
Along with established entertainment mediums such as Jennifer Garner’s “Pretend Cooking Show” and the Nickelodeon TV channel, Department of Energy contractor Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) has been named a winner in two categories of this year’s Telly Awards.
SRNS’s Communications and Media Services Department won a Gold Telly for the video “Savannah River Site Overview” in the non-broadcast, corporate image category, and a Bronze Telly for “SRNS Now: September 2020” in the non-broadcast, employee communications category.
North Dakota Sen. Kevin Cramer speaks at a November 3 press conference announcing the American Energy, Jobs & Climate Plan.
A trio of Republican lawmakers from Western states—Sens. Dan Sullivan (Alaska), Kevin Cramer (N.D.), and Cynthia Lummis (Wyo.)—held a press conference at the Capitol yesterday to announce the American Energy, Jobs & Climate Plan, a response to what they termed the “Biden-Kerry Green New Deal.” Also in attendance were fellow Republican senators Ted Cruz (Texas), John Kennedy (La.), and Rob Portman (Ohio).
The plan is “an innovative clean energy and climate strategy with the potential to reduce global [greenhouse gas] emissions by up to 40 percent from today’s levels by 2050 and create thousands of jobs for hard-working Americans,” according to a press release from Sullivan’s office.
In April, the Biden administration announced a target of net-zero GHG emissions by 2050, with an interim target of a 50–52 percent reduction from 2005 levels by 2030.
Wisconsin’s Kewaunee nuclear power plant, which shut down in 2013, is being transitioned to decommissioning. (Photo: Wikimedia Commons)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission on Wednesday approved a proposed rule to amend its regulations for nuclear power plants that are transitioning from operations to decommissioning. After changes requested by the NRC commissioners are made by agency staff, the proposed rule will be published in the Federal Register, initiating a 75-day comment period.
Artist rendering of a NuScale SMR plant.
On the sidelines of the COP26 Conference in Glasgow yesterday, John Kerry, the Biden’s administration’s special presidential envoy for climate, joined Romanian president Klaus Iohannis to announce plans to build a first-of-a-kind small modular reactor plant in Romania. The SMR technology is to be provided by NuScale Power, based in Portland, Ore.
(Source: Peter Schrank/The Economist)
“Where nuclear power was once a source of unity for Europe, today it is a source of discord.” So states The Economist’s October 30 “Charlemagne” column—a regular source of commentary on European politics in the weekly publication—before deftly dissecting nuclear power’s continental divide and picking a winner.