The U.S. ITER Project Office in Oak Ridge, Tenn. U.S. ITER has received $256 million in Inflation Reduction Act funding. (Photo: U.S. ITER)
Just days before COP27 and the U.S. midterm elections, the White House announced $1.55 billion in Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) funding for national laboratories and the launch of a Net-Zero Game Changers Initiative based on a new report, U.S. Innovation to Meet 2050 Climate Goals. Out of 37 research and development opportunities identified, fusion energy was selected as one of just five near-term priorities for the new cross-agency initiative. Together, the announcements signal policy and infrastructure support for fusion energy—the biggest chunk of Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC) IRA funding went to ITER, via Oak Ridge National Laboratory—and for advanced nuclear technologies to power the grid and provide process heat to hard-to-decarbonize industrial sectors.
ANS's “Powering Our Future: The Coal to Nuclear Opportunity” panel discussion featured (top left, clockwise) Jessica Lovering, Patrick Burke, Kenya Stump, Andrew Griffith, Christine King, and Carol Lane. (ANS screenshot)
Since at least June of last year—when TerraPower and PacifiCorp announced plans to site the Natrium reactor demonstration project at one of Wyoming’s retiring coal plants—the concept of repurposing those plants to host nuclear reactors has been a popular topic of conversation among the energy cognoscenti.
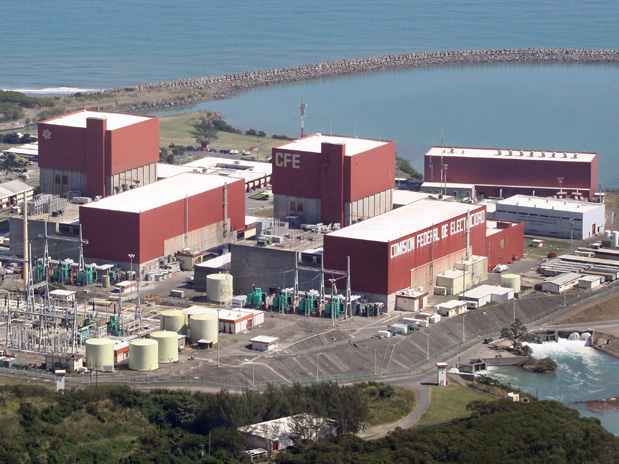
Mexico's Laguna Verde nuclear power plant, on the coast of the Gulf of Mexico in the state of Veracruz.
An agreement between the United States and Mexico on civil nuclear cooperation has entered into force, the U.S. State Department announced last week. While first proposed in 2016 and finalized and signed in 2018, the pact only received approval from the Mexican Senate this March.
A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft Sally Ride aboard (so named for first American woman to fly in space), launched at 5:32 a.m. EST on November 7, from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The rocket is captured just after liftoff in this still image from NASA’s live broadcast of the event.
Seeds from the joint laboratories of the International Atomic Energy Agency and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) are onboard a Cygnus spacecraft launched from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia early on November 7. Now orbiting the Earth en route to the International Space Station, the seeds are part of a commercial resupply mission with a payload that includes resources to support more than 250 scientific investigations.
Curie and Meitner (Photos: Wikicommons)
Marie Curie was born in Warsaw in 1867 on this day, 155 years ago. Exactly 11 years later, in 1878, Lise Meitner was born in Vienna. November 7 is also the date when, in 1911, the Swedish Royal Academy of Science decided to award Curie a second Nobel Prize for her 1898 discovery of the elements radium and polonium (coincidentally, her 44th birthday). Curie, who at age 36 had shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics with her husband, Pierre Curie, and Henri Becquerel, later accepted the chemistry prize on December 10, 1911. She remains to this day the only person—man or woman—to receive two Nobel Prizes in two different fields of science. (Linus Pauling was also awarded Nobel Prizes in two categories: chemistry and peace.) On this unofficial day of women in nuclear science, let’s take a moment to acknowledge the fundamental discoveries of both Curie and Meitner.
From left: Kimberly Cook-Nelson, John Dinelli, and Bill Maguire. (Photos: Entergy)
New Orleans-based Entergy Corporation yesterday announced changes to its senior leadership, including the selection of Kimberly Cook-Nelson as executive vice president and chief nuclear officer, replacing Chris Bakken.
Cook-Nelson, Entergy’s first female CNO, will be based in Jackson, Miss., the company’s nuclear operations headquarters. She joined Entergy in 1996 as a design engineer at the Waterford nuclear plant in Killona, La., rising to general manager of plant operations in 2011. Most recently, she held the position of chief operating officer, nuclear operations. (In addition to the Waterford facility, Entergy owns and operates Arkansas Nuclear One in Russellville, Ark., Grand Gulf in Port Gibson, Miss., and River Bend in St. Francisville, La.)
Participating in the forum were (from left) John Hopkins (NuScale Power), Renaud Crassous (EDF), Daniel Poneman (Centrus Energy), Adriana Cristina Serquis (CNEA), and Boris Schucht (Urenco).
The nuclear industry leaders assembled in Washington, D.C., last week to discuss small modular reactor supply chains agreed that lost generation capacity from the expected retirement of hundreds or thousands of coal power plants over the next decade—a cliff, in one panelist’s words—represents an opportunity that developers of SMRs and advanced reactors are competing to meet.
“I think in total 80 projects are ongoing,” said Boris Schucht, panel moderator and chief executive officer of Urenco Group, as he opened the forum. “Of course not all of them will win, and we will discuss today what is needed so that they can be successful.”
Constellation Energy's Clinton nuclear power plant. (Photo: NRC)
Constellation Energy, owner and operator of the nation’s largest reactor fleet, will ask the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to extend the operating licenses of the Clinton and Dresden reactors by 20 years, the company announced Monday, adding that it expects to file license applications with the agency in 2024.
Bruce's Unit 7 is now producing Lutetium-177, used in targeted cancer therapeutics. (Photo: Bruce Power)
An international collaboration between Bruce Power, Isogen (a Kinectrics and Framatome company), and ITM Isotope Technologies Munich SE (ITM) announced they have begun commercial production of lutetium-177 using Unit 7 of the Bruce nuclear power plant in Kincardine, Ontario. According to the companies, this marks the first time a commercial power reactor has been used to commercially produce short-lived medical radioisotopes.
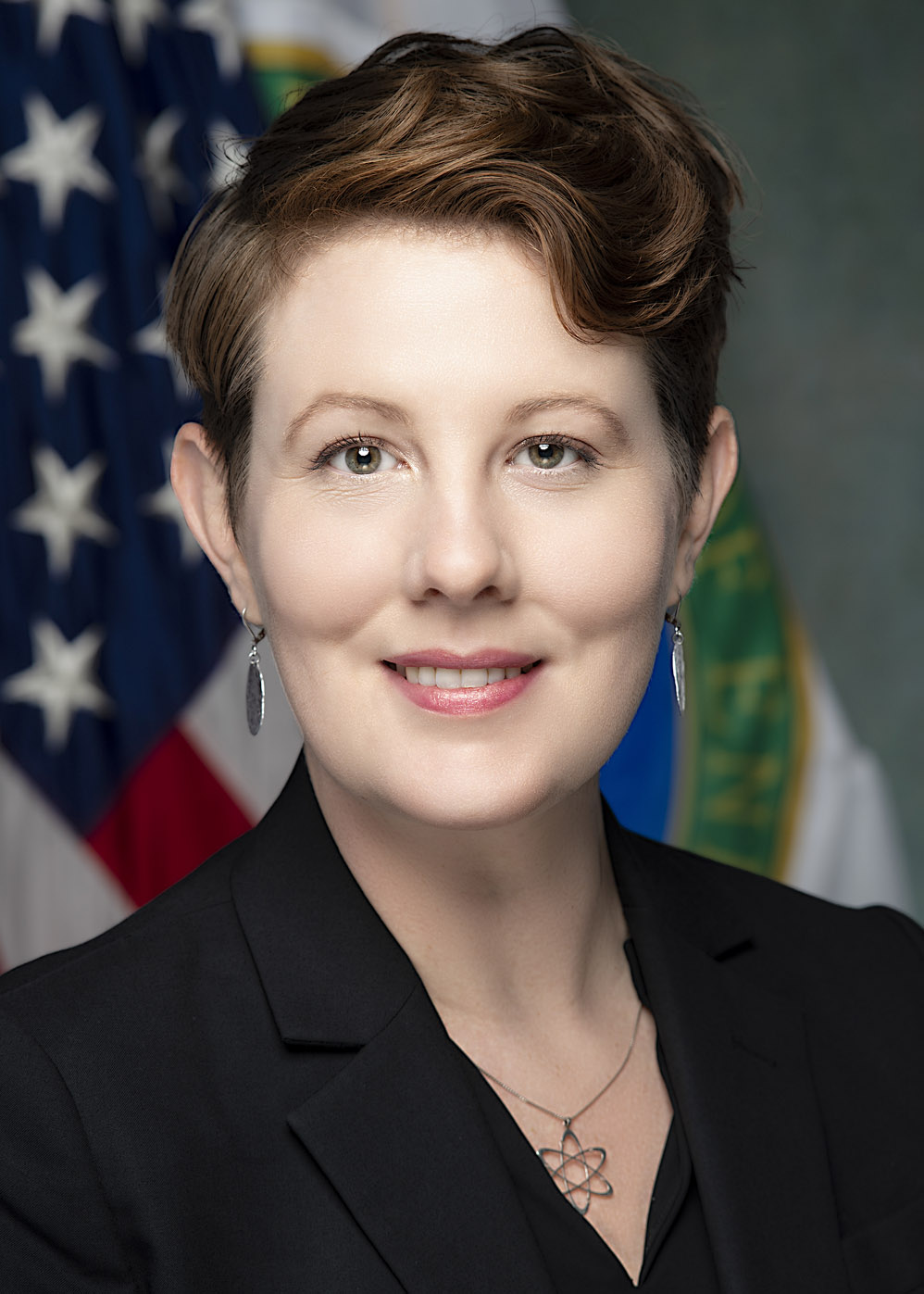
From left: U.S. undersecretary of state for arms control and international security Bonnie Jenkins; Japan’s state minister of economy, trade, and industry Fusae Ōta; Ghana’s deputy minister of Energy William Owuraku Aidoo; and U.S. assistant secretary for nuclear energy Kathryn Huff. (Photo: DOE Office of Nuclear Energy)
The United States and Japan have announced Winning an Edge Through Cooperation in Advanced Nuclear (WECAN)—a new agreement aimed at supporting the deployment of small modular reactors and other advanced reactor technologies in partner countries.
Conceptual layout and deployment of a Prodigy SMR Marine Power Station with 12 NuScale Power Modules. (Graphic: Business Wire)
NuScale Power and Prodigy Clean Energy announced on October 26 that they have developed a conceptual design for a transportable, marine-based small modular reactor. The companies plan to present the design to utilities, regulators, and shipyard manufacturers. Prodigy, a Canadian company “specializing in the development of transportable nuclear power plants,” and NuScale signed a memorandum of understanding in 2018 agreeing to pursue the development of an SMR marine facility.