A shot from a coal mine in Poland. (Photo: IAEA)
Point Lepreau nuclear power plant. (Photo: Andre Bussiere)
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission has renewed the operating license of the reactor at the Point Lepreau nuclear plant for a period of 10 years. As a result, the facility’s 660-MWe CANDU-6 unit, the five-year license for which was set to expire on June 30, is now permitted to operate until the end of June 2032. License holder NB Power had requested an unprecedented 25-year extension.
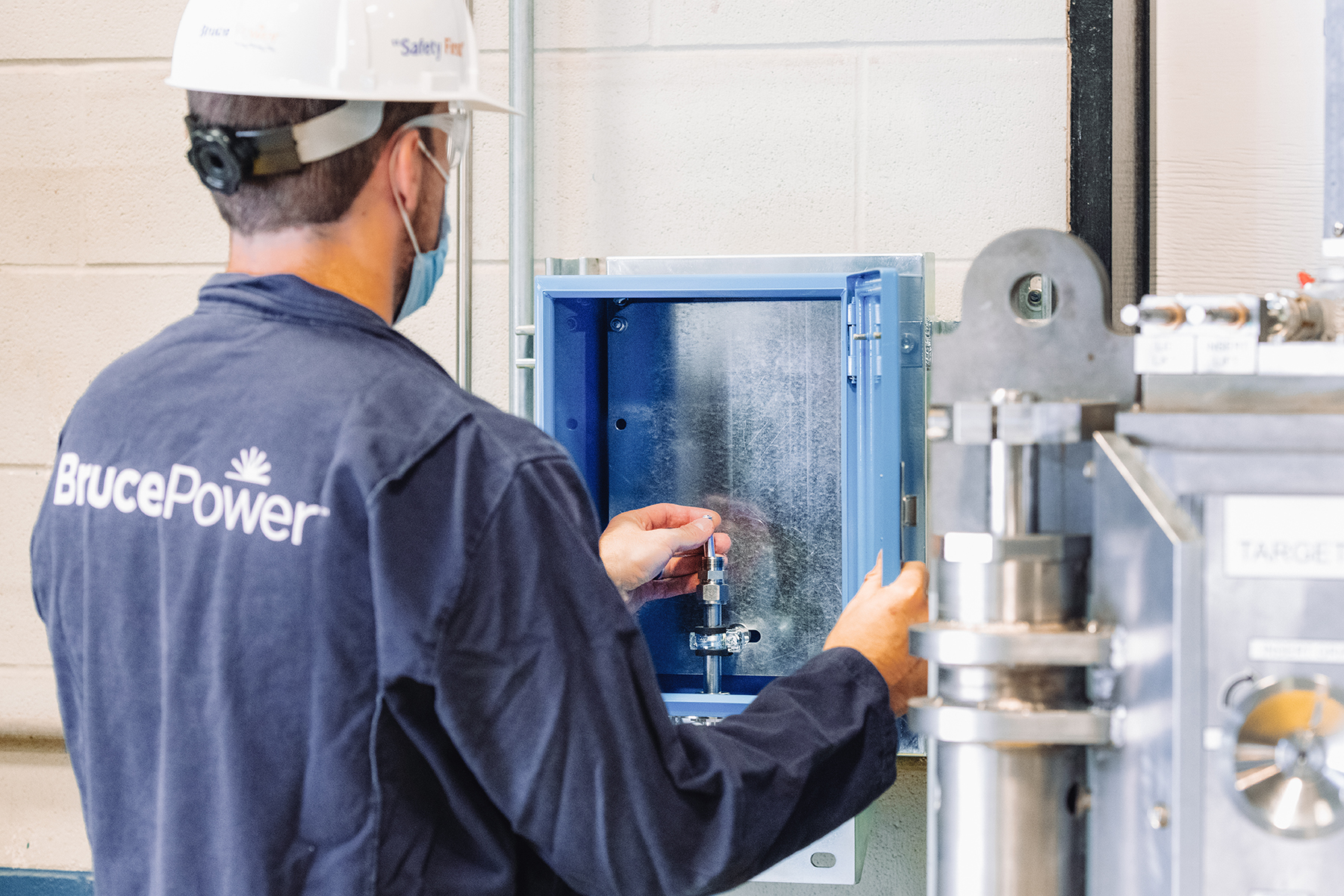
The new IPS installed in Bruce Power’s Unit 7 will produce Lu-177 for treating cancer. (Photo: Bruce Power)
An international collaboration between Bruce Power, Isogen (a joint venture of Kinectrics and Framatome), and ITM Isotope Technologies Munich SE, announced a milestone marking the first time that lutetium-177, a short-lived medical radioisotope, has been produced in a commercial nuclear power reactor.
Vogtle Units 3 and 4, with Units 1 and 2 in the background. (Photo: Georgia Power)
Both Oglethorpe Power Corporation and the Municipal Electric Authority of Georgia (MEAG), two co-owners of the Vogtle nuclear plant, have filed lawsuits against Southern Company subsidiary Georgia Power, the facility’s primary owner.
Oglethorpe and MEAG are 30 percent and 22.7 percent owners, respectively, of Vogtle. Georgia Power holds a 45.7 percent share. (Dalton Utilities, which owns 1.6 percent of the plant, is not involved in the suits.)
Turkey Point nuclear plant. (Image: FPL)
Florida Power & Light (FPL) has submitted a supplemental environmental report to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in support of the subsequent renewed licenses for Turkey Point Units 3 and 4. According to a June 22 NRC press release, FPL’s report was submitted on June 10 to satisfy a “deficiency” in subsequent license renewal applications (SLRA) that rely on the generic environmental impact statement (GEIS) on license renewal and is being reviewed prior to docketing. William D. Maher, director of nuclear licensing projects at FPL, submitted the report, noting that “FPL’s review did not identify any information materially changing the impact assessments” in the NRC’s supplemental GEIS for the Turkey Point licenses.
A rendering of the MCRE. (Image: Southern Company)
The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) awarded vouchers to Orano Federal Services and TerraPower on June 22, giving them access to specialized facilities and expertise at Department of Energy national laboratories. Orano is partnering with Oak Ridge National Laboratory on a new technical study that updates the physical chemistry limits for the safe transport of uranium hexafluoride (UF6) gas enriched up to 10 percent in existing shipping containers, and TerraPower is turning to Los Alamos National Laboratory’s neutron testing capabilities to measure the properties of chlorine isotopes and determine how they will behave in the Molten Chloride Reactor Experiment (MCRE).
The Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP), shown here, is a government-backed prototype fusion energy plant planned for operation in the U.K. in the early 2040s. (Image: UKAEA)
Future fusion energy facilities will continue to be regulated by the Environment Agency (EA) and Health & Safety Executive (HSE), the U.K. government announced June 20, and existing law on nuclear regulations will be amended to exclude fusion energy facilities from nuclear fission regulatory and licensing requirements. The move was announced by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) with the expectation it would provide “clarity to developers of prototype/demonstration fusion facilities currently being planned to support rapid commercialization.”
A conceptual illustration of a fission surface power system. (Image: NASA)
Three teams have been picked to design a fission surface power system that NASA could deploy on the moon by the end of the decade, NASA and Idaho National Laboratory announced today. A fission surface power project sponsored by NASA in collaboration with the Department of Energy and INL is targeting the demonstration of a 40-kWe reactor built to operate for at least 10 years on the moon, enabling lunar exploration under NASA’s Artemis program. Twelve-month contracts valued at $5 million each are going to Lockheed Martin (partnered with BWX Technologies and Creare), Westinghouse (partnered with Aerojet Rocketdyne), and IX (a joint venture of Intuitive Machines and X-energy, partnered with Maxar and Boeing).
Barakah-3 (Photo: Nawah Energy Company)
The United Arab Emirates’ Federal Authority for Nuclear Regulation (FANR) has issued the operating license for the Barakah nuclear plant’s Unit 3 reactor, the Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation announced yesterday. In addition, following receipt of the license, ENEC subsidiary Nawah Energy Company began the process of loading fuel assemblies into the unit, according to the announcement.
(Photo: Clean Core Thorium Energy)
The Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) at Idaho National Laboratory will soon be irradiating fuel pellets containing thorium and high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) developed by Clean Core Thorium Energy for use in pressurized heavy water reactors (PHWRs). Clean Core announced on June 14 that it will proceed with irradiation testing and qualification under an agreement with the Department of Energy; the plans have been in the works since at least 2020, when the DOE filed a National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) disclosure for the work.
Finland’s Olkiluoto-3. (Photo: TVO)
Teollisuuden Voima Oyj (TVO), owner and operator of Finland’s Olkiluoto nuclear power plant, has announced a further delay to the start of regular electricity generation at Unit 3. Commercial operation is now projected to begin this December, rather than the previously announced September. A report from Reuters puts the date at December 10.
According to TVO, material that had detached from the steam guide plates was found in the turbine’s steam reheater last month, requiring inspection and repair work.
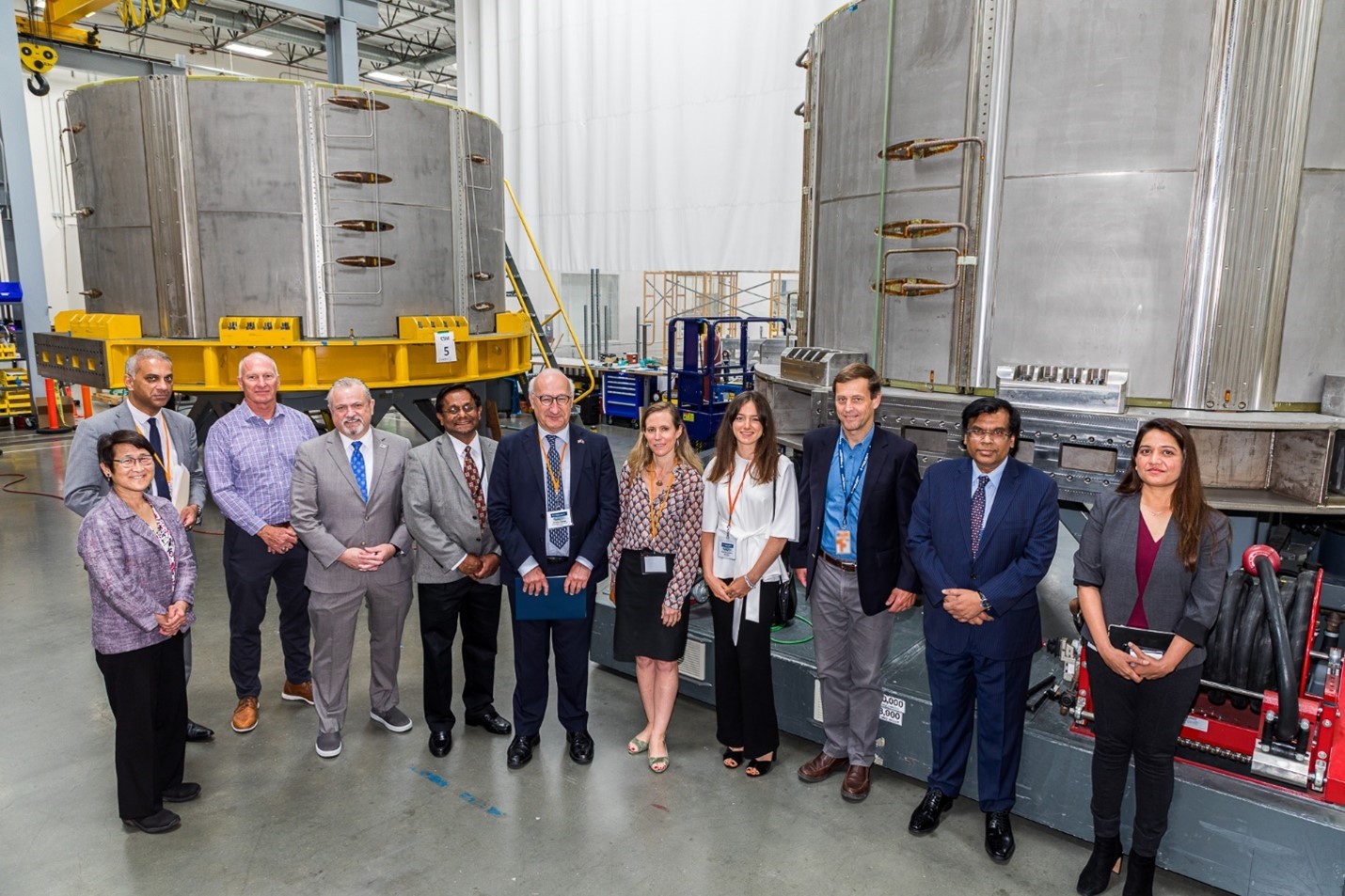
Ambassador Philippe Étienne (sixth from left) and staff from the Consulate General of France with senior leaders from General Atomics at the GA Magnet Technologies Center in Los Angeles. In the background are two partially completed ITER central solenoid modules. (Photo: GA)
General Atomics’ Magnet Technologies Center in Poway, Calif., played host last week to French ambassador Philippe Étienne, the company announced June 16. During the visit, which was hosted by Vivek Lall, chief executive of the General Atomics Global Corporation, Étienne viewed ITER central solenoid modules—all destined for shipment to France—in several stages of the fabrication process.
“General Atomics and French organizations have a strong relationship in both the defense and energy sectors, as well as in the unmanned field, that meet both France’s and the United States’ important interests,” Étienne remarked during his visit.