September 10, 2021, 8:22AMUpdated December 31, 2021, 7:15AMNuclear NewsThomas R. Wellock An aerial view of the Hanford reservation and Columbia River that shows the N (nearest), KE/KW (center), and B (top right) reactors. (Photo: U.S. DOE )
In March 1972, Stephen Hanauer, a technical advisor with the Atomic Energy Commission, met with Norman Rasmussen, a nuclear engineering professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The AEC had recruited Rasmussen to develop a report, The Reactor Safety Study (WASH-1400), to estimate the probabilities and consequences of a major nuclear power plant accident. With thousands of safety components in a modern reactor, the task was mind-boggling. Rasmussen proposed a novel approach based on more powerful computers, “fault tree” methodology, and an expanding body of operational data. By calculating and aggregating probabilities for innumerable failure chains of components, he believed he could develop a meaningful estimate of overall accident risk. WASH-1400 would be a first-of-its-kind probabilistic risk assessment (PRA).
July 2, 2021, 2:15PMUpdated December 30, 2021, 7:15AMNuclear NewsSusan Gallier A hot cell at Argonne National Laboratory was used to demonstrate a process for purifying molybdenum-99, an important diagnostic medical isotope. (Photo: Wes Agresta/ANL)
The biggest impact of radiation in our lives may come not from radiation itself, but from regulations and guidelines intended to control exposures to man-made sources that represent a small fraction of the natural radiation around us.
Decades of research have been unable to discern clear health impacts from low levels of ionizing radiation, leading to calls for a new research program—one with a strategic research agenda focused on how the scientific understanding of the health effects of low doses (below 100 millisievert) and low dose rates (less than 5 mSv per hour) can best be augmented, applied, and communicated.
Building instrumentation and control technologies into the design of the next generation of advanced nuclear reactors will help the industry meet zero-carbon-emissions goals.
December 23, 2021, 3:00PMNuclear NewsAlexander Heifetz, Matthew Weathered, Nathan Hoyt, Mark Anderson, Scott Sanders, Anthonie Cilliers Kairos Power’s Instrumentation Test Unit
As a source of carbon-free electricity, nuclear energy currently dominates in the United States. However, the light water reactors in the U.S. are approaching the end of their licensed service lives. Meanwhile, low-cost electricity generated by fossil fuel–based sources (such as natural gas) poses an ongoing challenge to the economic viability of commercial nuclear reactors. To enhance the competitiveness of the nuclear industry, we need to bring down the high operating and maintenance (O&M) costs through savings available from utilizing modern, efficient sensing and automation technologies.
The Tihange nuclear power plant in Belgium. (Photo: Electrabel)
Belgium’s seven-party coalition government this morning announced via press conference a tentative agreement to close the nation’s two nuclear power plants by 2025, confirming a commitment made in October of last year when it took office. Plant closures are scheduled to begin in 2022.
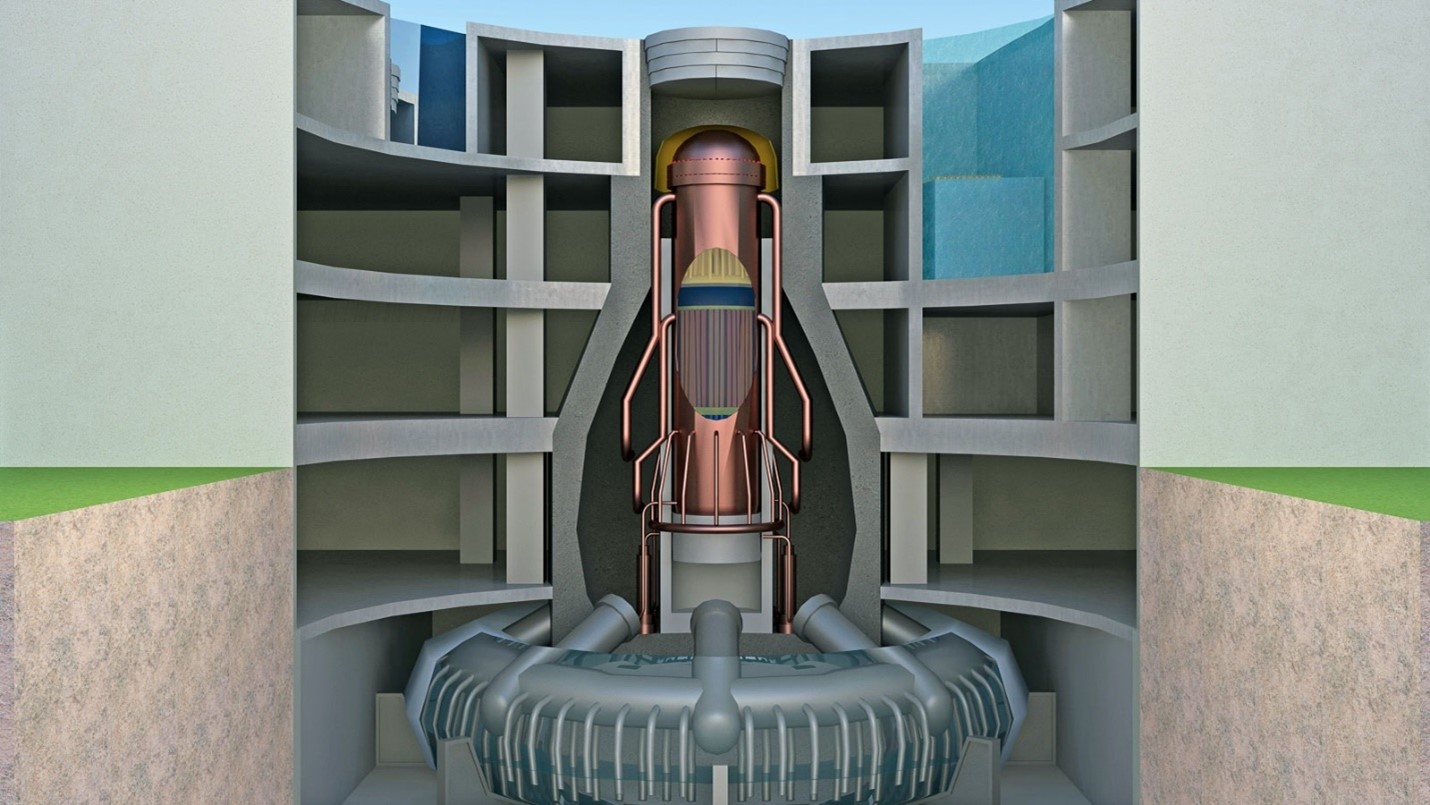
A cutaway view of a nuclear reactor. Its construction consists of two essential material types: fuel, which comprises the rods and cores that hold the fuel (center vertical bands); and structural, those parts of the reactor that house the fuel materials. (Graphic: Shutterstock/petrov-k)
Researchers from the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are developing a “tool kit” based on artificial intelligence that will help better determine the properties of materials used in building a nuclear reactor.
Reactor operators in the control room at Kursk I-1, as the unit is powered down for good. (Photo: Rosenergoatom)
After 45 years of producing electricity, the first unit at Russia’s Kursk nuclear power plant has been retired, plant operator Rosenergoatom announced on Monday. Kursk I-1, one of the facility’s four 925-MWe light water–cooled graphite-moderated reactors, model RBMK-1000 (a Chernobyl-type reactor), was permanently shut down at 00:24 Moscow time on December 19.
The Summit supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory began operations in 2018. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy has announced $9.25 million for research into the behavior and properties of structural materials under molten salt reactor conditions through collaborations using the DOE’s high-performance supercomputers.