The ALCF AI Testbed includes the AI systems represented in this collage: Cerebras, Graphcore, Groq, and SambaNova. (Image: Argonne National Laboratory)
Generative artificial intelligence paired with advanced diagnostic tools could detect potential problems in nuclear power plants and deliver a straightforward explanation to operators in real time. That’s the premise of research out of the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, and just one example of the DOE’s increasing exploration of AI applications in nuclear science and technology research. Training and restraining novel AI systems take expertise and data, and the DOE has access to both. According to a flurry of reports and announcements in recent months, the DOE is setting out its plans to ensure the United States can use AI to its advantage to enhance energy security and national security.
The company has awarded nearly $6 million for STEM education and research programs since the program launched in 2010
Constellation is taking applications for its 2024 E2 Energy to Educate grant program, which provides funding for student projects focusing on energy innovation.
Educators and students in grades 6–12 can apply for program grants of up to $25,000, and those in two- and four-year colleges can apply for grants of up to $50,000.
Company celebrates Browns Ferry’s 50 years in service
Bellefonte nuclear power plant. (Photo: TVA)
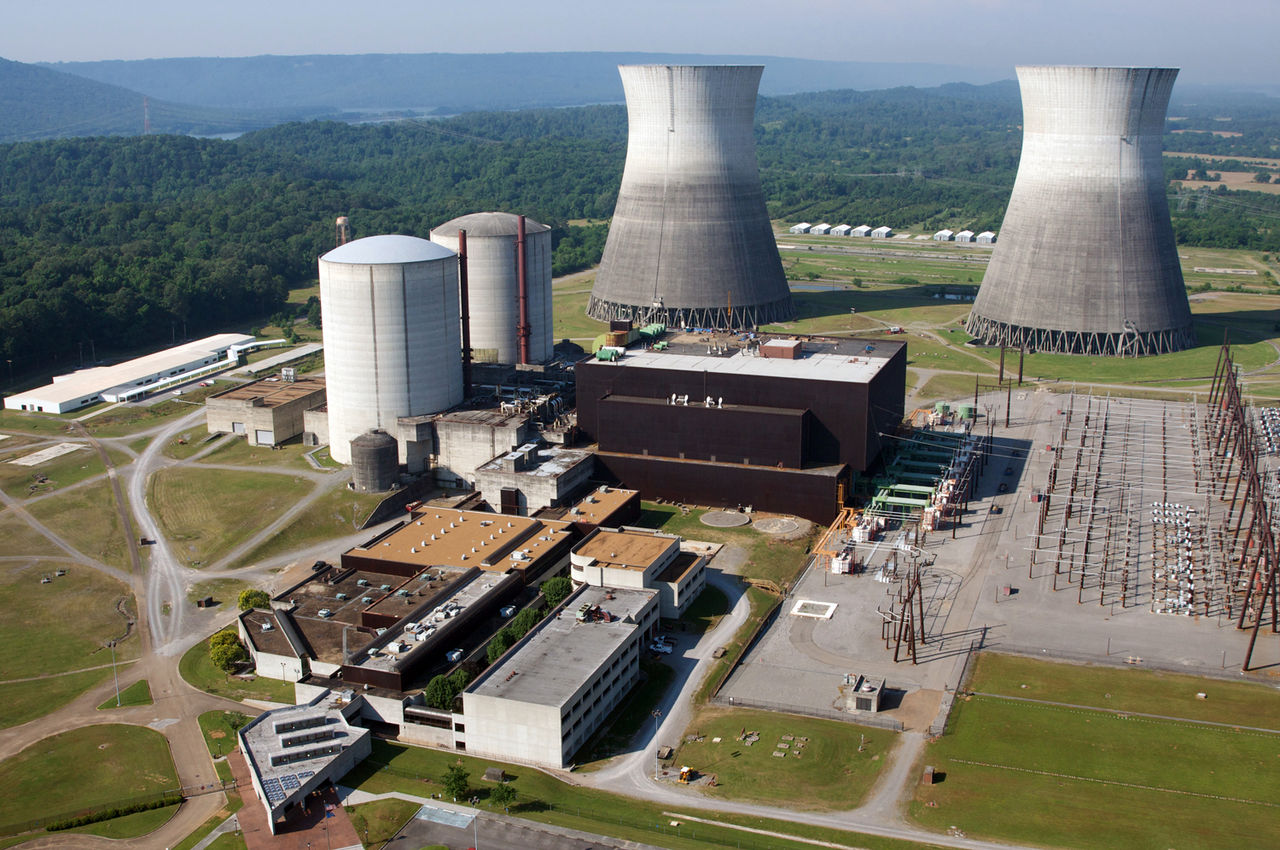
The Tennessee Valley Authority this week discussed the potential for new nuclear technology at its sites during its second-quarter earnings call.
TVA and GE Hitachi signed an agreement in 2022 to develop and deploy a BWRX-300 small modular reactor at the Clinch River site near Oak Ridge, Tenn.
Urenco’s Capenhurst enrichment site in the U.K. (Photo: Urenco)
A plan to build up a high-assay low-enriched uranium fuel cycle in the United Kingdom to support the deployment of advanced reactors is still in place after the Labour party was voted to power on July 4, bringing 14 years of conservative government to an end. A competitive solicitation for grant funding to build a commercial-scale HALEU deconversion facility opened days before the election, and the support of the new government was confirmed by a set of updates on July 19. But what does the U.K. HALEU program entail, and how does it differ from the U.S. HALEU Availability Program?
Rendition of a Rolls-Royce SMR site.(Image: Rolls-Royce)
The small modular reactor design from Rolls-Royce has cleared step two of the United Kingdom’s generic design assessment (GDA) and is moving to the third and final step.
The company announced its progress and lauded “Rolls-Royce SMR’s position ahead of any other SMR in Europe” in a July 30 press release. Rolls-Royce SMR touts its ability to deliver new nuclear power based on proven technology, providing a “factory-built” power station to provide enough energy for a million homes for a 60-year stretch.
Comanche Peak nuclear power plant. (Photo: Meranda Cohn/Vistra)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has renewed the operating licenses of Comanche Peak Units 1 and 2 for an additional 20 years.
Unit 1’s operating license now expires on February 8, 2050, and Unit 2’s on February 2, 2053.
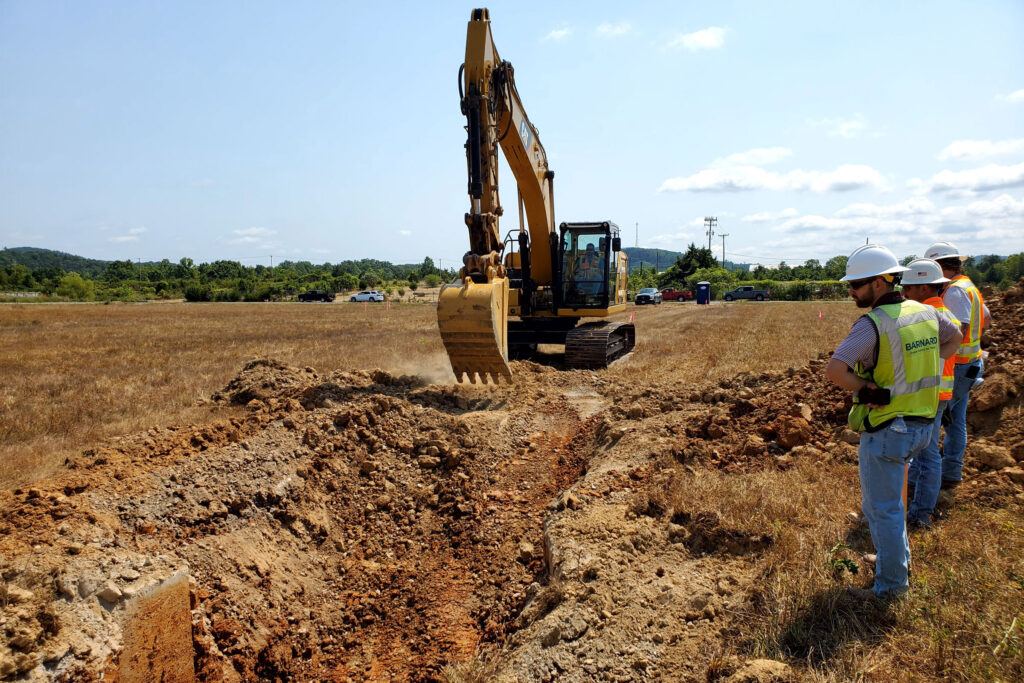
Workers begin construction at the Hermes site in Oak Ridge, Tenn. (Photo: Kairos Power)
Earlier today, on a site in Oak Ridge, Tenn., that was formerly home to the K-33 Gaseous Diffusion Plant, Kairos Power marked the start of construction on its low-power demonstration reactor. Named Hermes, the 35-MWt test reactor claims status as the first Gen IV reactor to be approved for construction by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the first non–light water reactor to be permitted in the United States in more than 50 years.
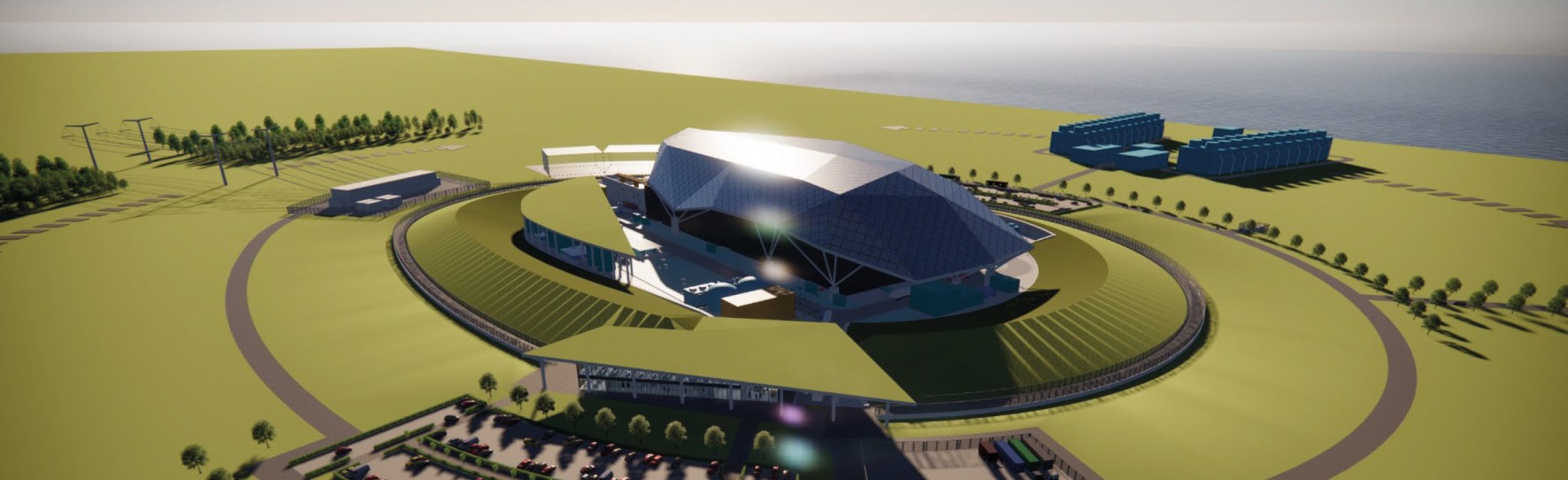
A screengrab from a video released by the STEP program on July 23 illustrating the future home of the prototype fusion power plant. (Image: UKAEA/STEP)
Japan’s recent moves to boost fusion power in the nation’s energy plan and accelerate the timeline for a prototype fusion power plant come in response to increased global attention on fusion energy. Even as ITER faces delays, more than 40 private fusion developers are pursuing different technologies and competing for attention. And so are other countries, including the United Kingdom, which announced its plans for a fusion pilot plant back in 2019. Fusion companies and nations alike are responding to a growing sense that there is a race—or at least collective momentum—to commercialize fusion energy.
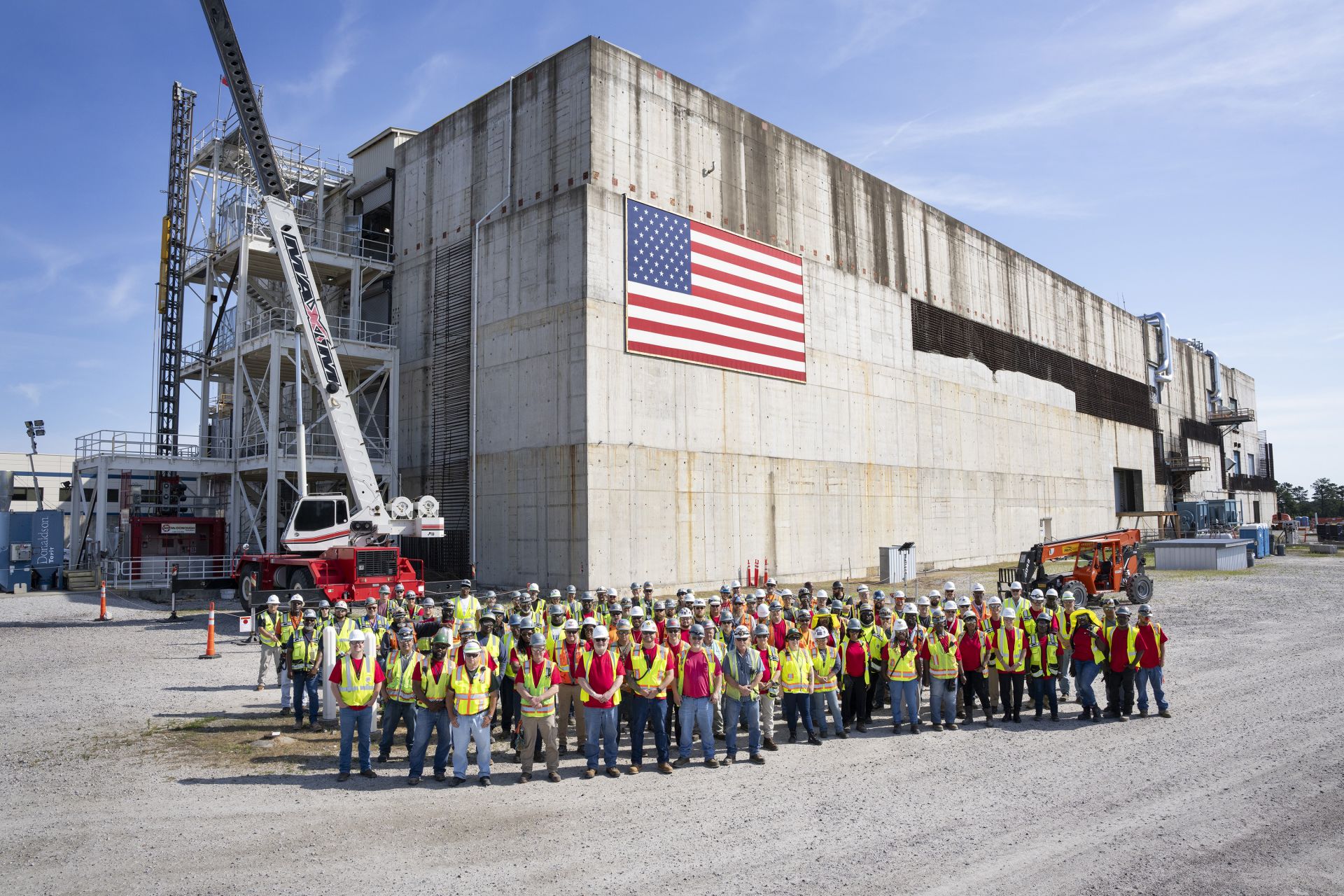
Aecon-Wachs workers performed the D&R of equipment and commodities from the plutonium processing facility at SRS. ( Photo: SRS)
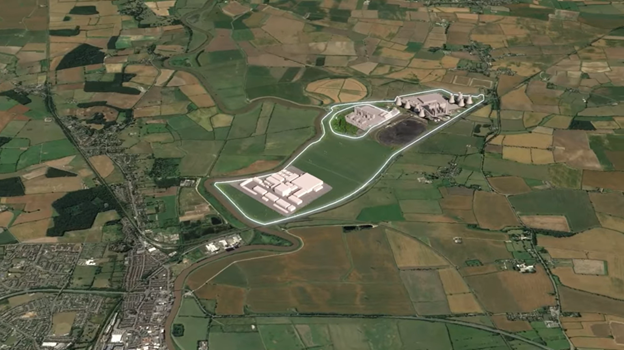
A major milestone has been reached in the construction of a plutonium pit production facility at the Savannah River Site, located near Aiken, S.C.
After 18 months of work involving local trade unions, the dismantlement and removal (D&R) of commodities and equipment throughout the Savannah River Plutonium Processing Facility (SRPPF), previously installed by the Mixed Oxide (MOX) project, was completed in June 2024, the Department of Energy reported on July 24.
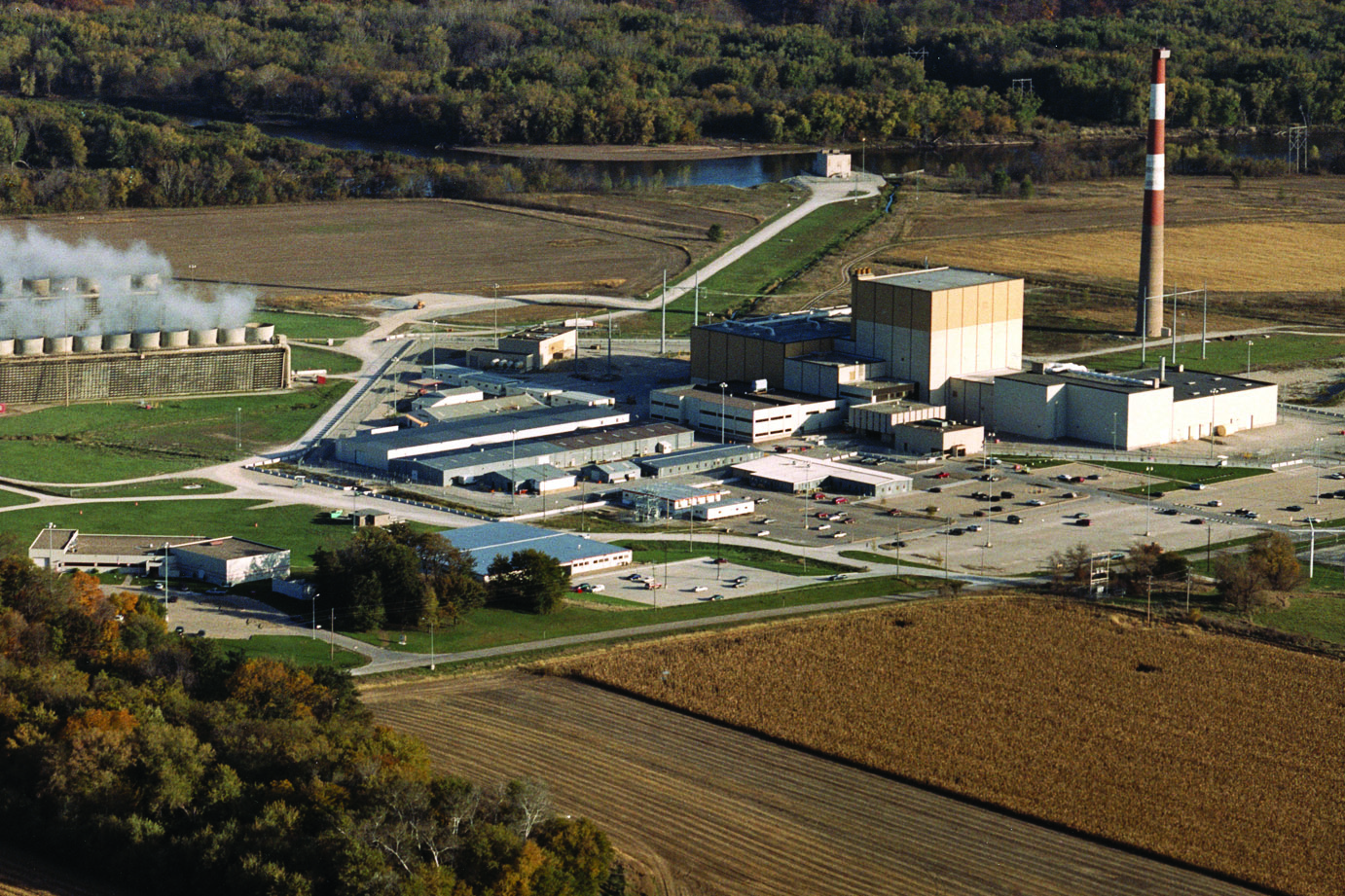
The Duane Arnold Energy Center in Palo, Iowa. (Photo: NextEra Energy)
The Duane Arnold nuclear power plant in Iowa could see new life, according to NextEra Energy chief executive officer John Ketchum.
“There would be opportunities and a lot of demand from the market if we were able to do something with Duane Arnold,” Ketchum said on Wednesday this week during the company’s second-quarter earnings call.
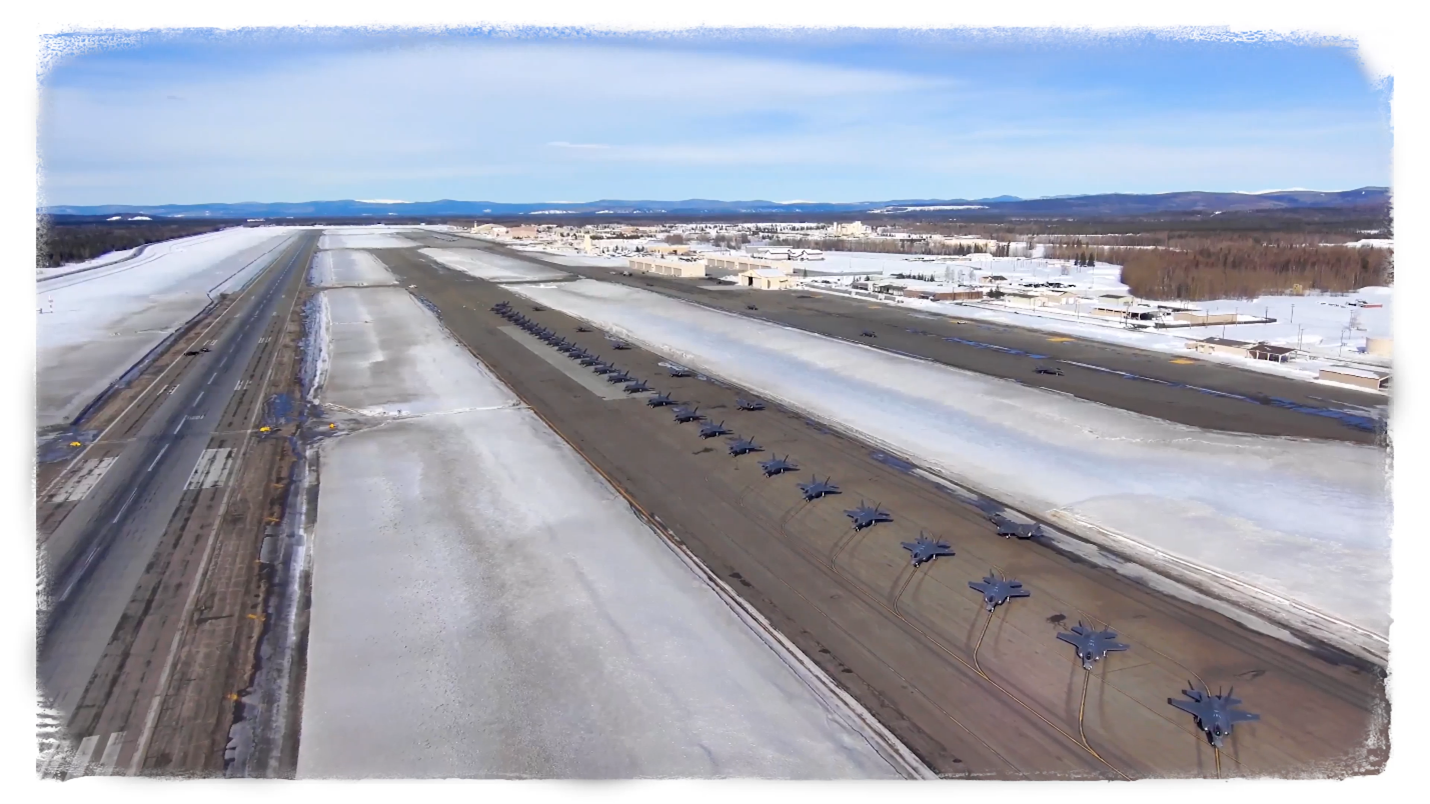
Eielson Air Force Base is shown in this screen grab from a video hosted on the base’s website. (Image: DOD)
Eielson Air Force Base in central Alaska has been the preferred location to demonstrate the benefits of microreactors to the U.S. Air Force—and by extension the Defense Department—since 2018. Now, a protracted solicitation process is nearing an end, and the Air Force and the Defense Logistics Agency Energy (DLA Energy) expect to announce a final procurement decision by the end of the summer—or about one year after Oklo Inc. announced that it had been tentatively selected to supply a microreactor under a 30-year power purchase agreement.
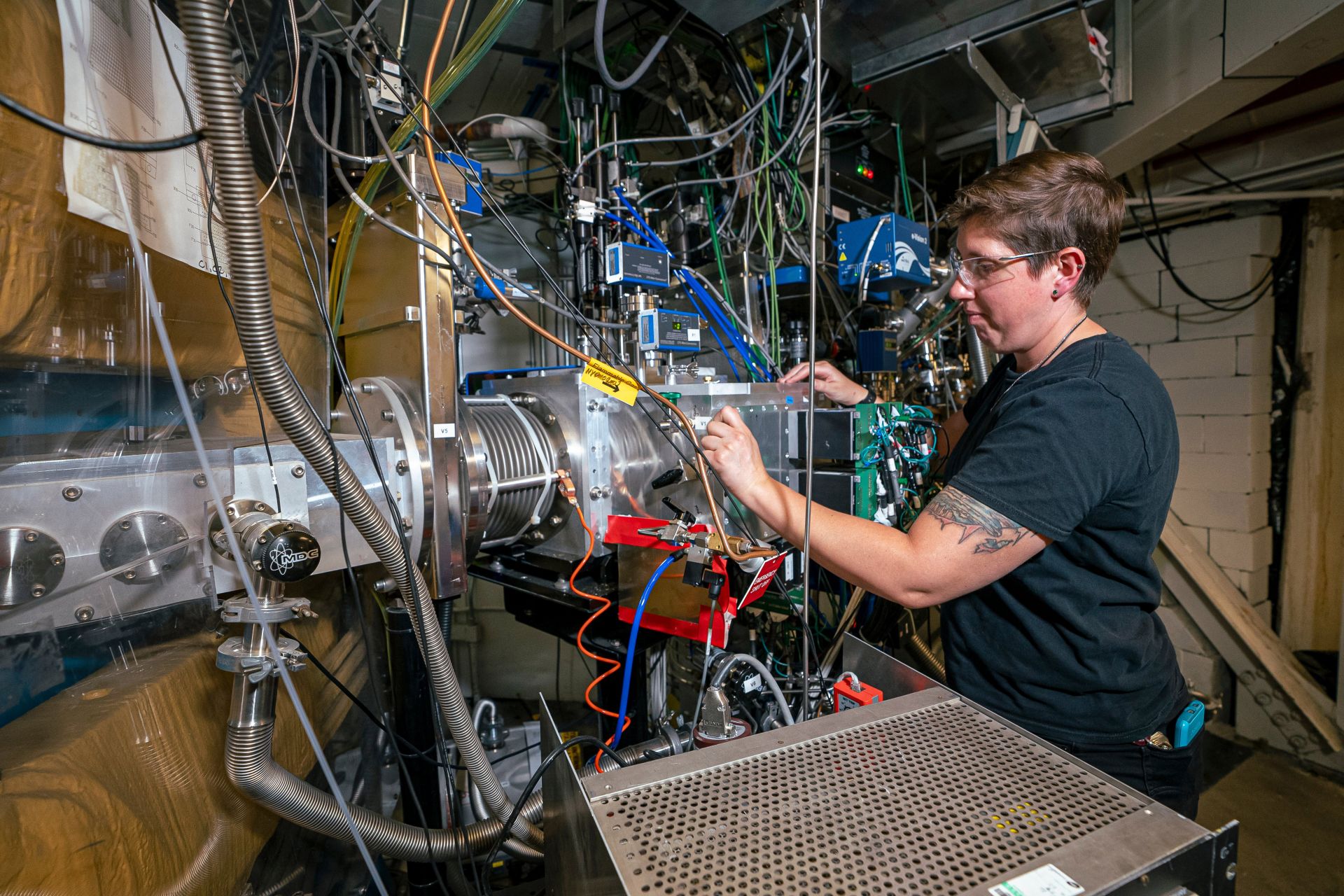
Scientist Jacklyn Gates at the Berkeley Gas-filled Separator used to separate atoms of element 116, livermorium. (Photo: Marilyn Sargent/Berkeley Lab)
A plutonium target bombarded with a beam of titanium-50 in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory’s 88-Inch Cyclotron for 22 days has yielded two atoms of the superheavy element 116, in a proof of concept that gives Berkeley Lab researchers a path to pursue the heaviest element yet—element 120. The result was announced July 23 at the Nuclear Structure 2024 conference; a paper has been submitted to the journal Physical Review Letters and published on arXiv.
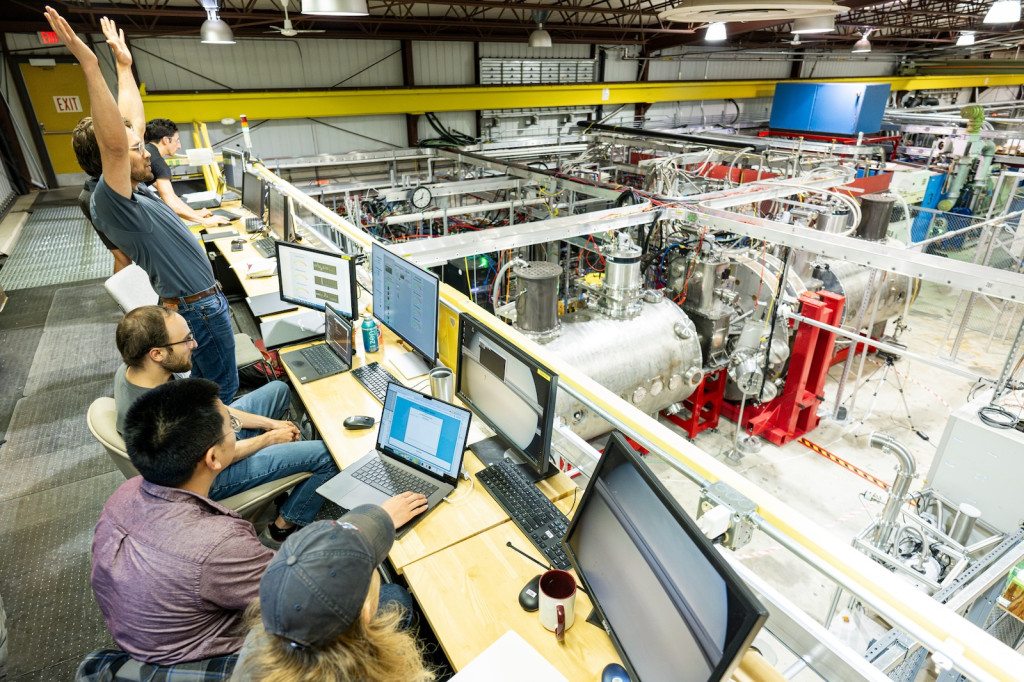
Elliot Claveau, honorary fellow in the UW–Madison Department of Physics and experimental scientist at Realta Fusion, raises his arms in celebration of achieving a plasma in WHAM at the Wisconsin Plasma Physics Laboratory. The device is seen on the floor of the lab. (Photo: Bryce Richter/UW–Madison)
The magnetic mirror fusion concept dates to the early 1950s, but decades ago it was sidelined by technical difficulties and researchers turned to tokamak fusion in their quest for confinement. Now it’s getting another look—with significantly more powerful technology—through WHAM, the Wisconsin HTS Axisymmetric Mirror, an experiment in partnership between startup Realta Fusion and the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
.png)

-3 2x1.jpg)