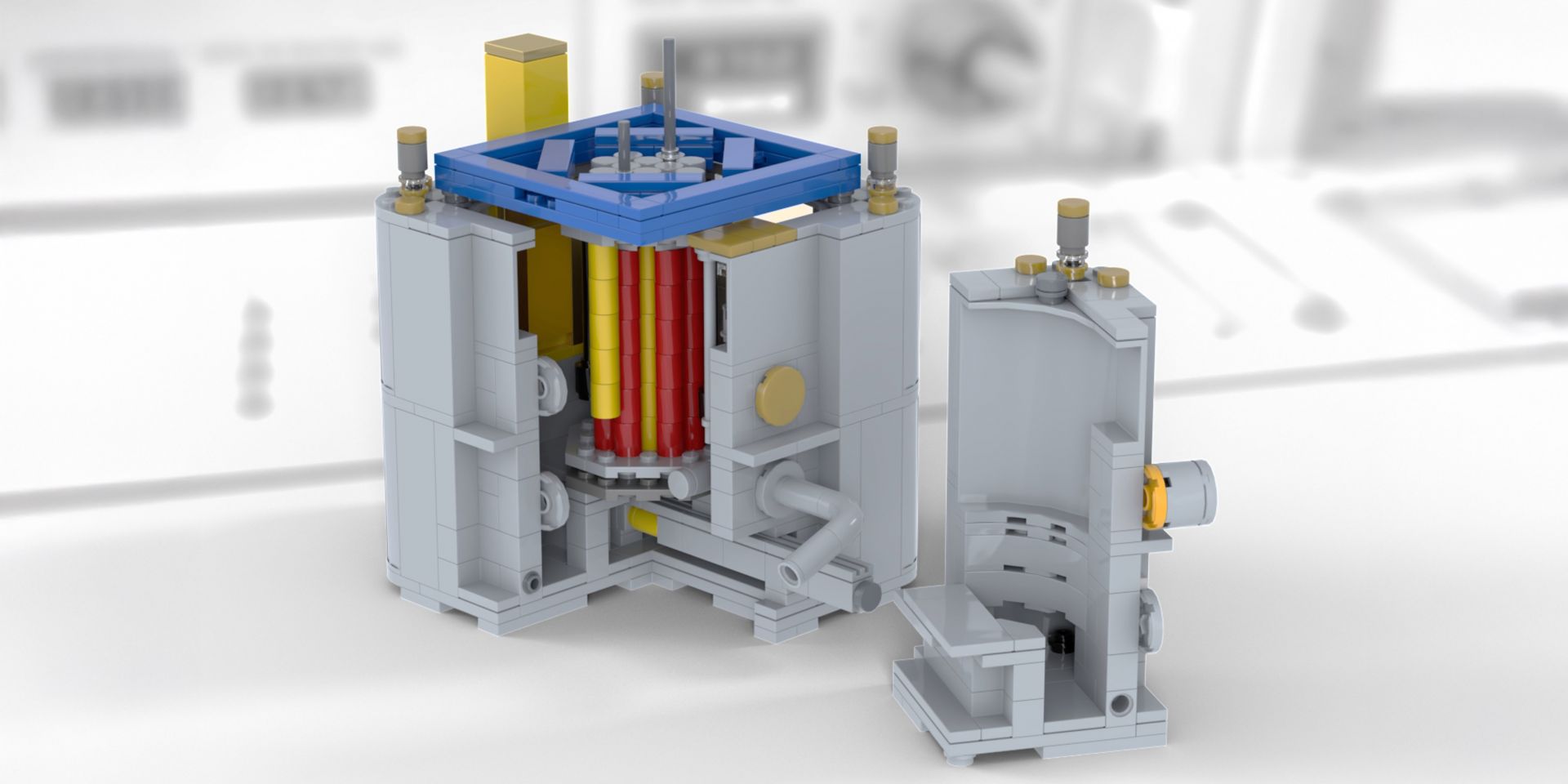
Detailed view of the Lego CROCUS reactor (as seen with Lego Studio software), with the vessel open to reveal the core structure. (Image: Vincent Lamirand)
For many of us, the height of our accomplishments with Lego blocks might have been constructing little square houses as children. For others, these versatile building blocks are a medium for creating complex models of sophisticated machinery—models that have practical and educational applications. One such individual is ANS member Vincent Lamirand, a reactor physicist at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Systems Behavior (LRS) in Switzerland.
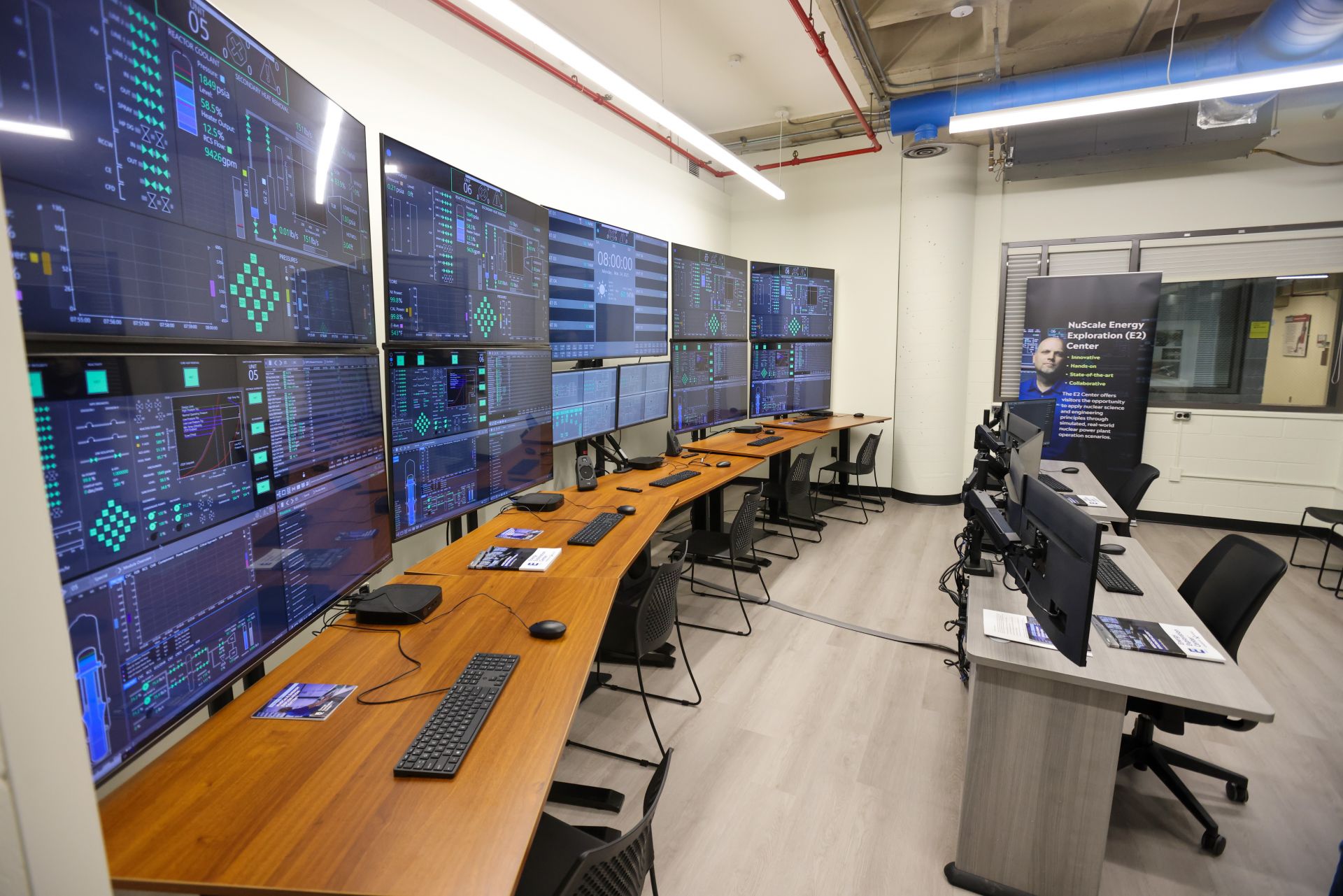
NuScale E2 Center work stations at RPI ready for student use. (Photo: RPI)
The opening of an Energy Exploration (E2) Center at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, N.Y., was announced by NuScale Power Corporation on March 24. The training center will provide students from RPI’s School of Engineering an opportunity to gain a firsthand understanding of advanced nuclear technology and the role it will play in the global energy transition, as well as of the features and functionality of NuScale’s small modular reactor technology.
Learn more about NuScale E2 Centers here.
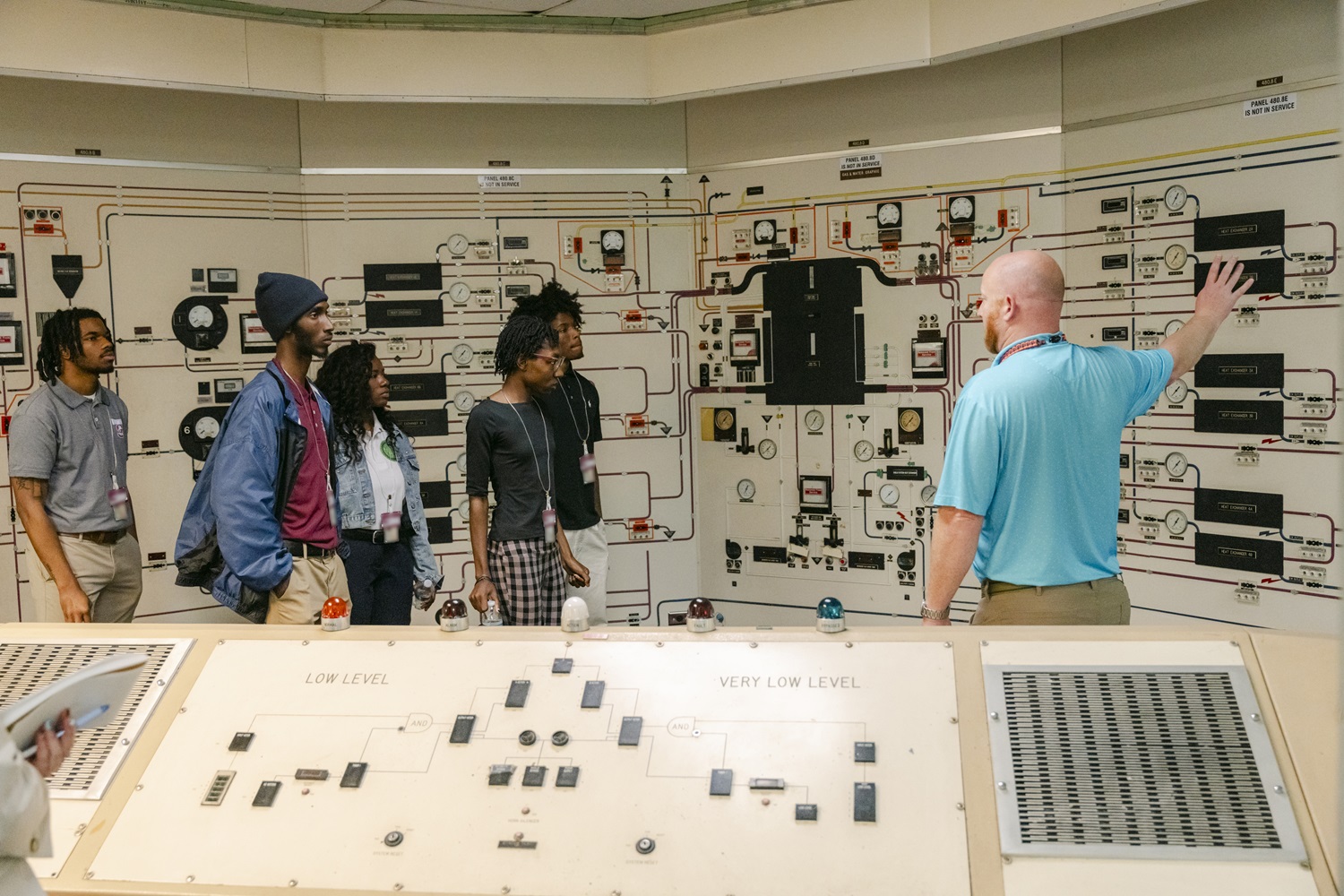
Students from South Carolina State University and Claflin University listen to Tristan Downey about the legacy control panels found in the Savannah River Site's L Area. (Photo: DOE)
A group of students recently visited the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site, near Aiken, S.C., to get a close look at L Area, a facility the DOE considers critical to nuclear materials management and nonproliferation missions at the site.
Representatives of First Light Fusion stand outside Sandia’s Z Pulsed Power Facility. (Photo: First Light Fusion)
First Light Fusion announced last week that it has set a new record for the highest quartz pressure achieved on Sandia National Laboratories’ Z machine using its amplifier technology to achieve an output pressure of 3.67 terapascal (TPa)—roughly doubling the pressure the company reached in its first experiment on the machine one year ago.
Meanwhile, Russian-backed media report Ukraine is responsible for ZNPP strikes
Energoatom’s Zaporizhzhia plant, in southeastern Ukraine, as it appeared in a photo posted to the DOE website in June 2021. (Photo: Energoatom)
Amid recent ceasefire talks between Russia and Ukraine, President Donald Trump suggested the U.S. should take control of Ukraine’s nuclear power plants for long-term security, the Associated Press reported.
“American ownership of those plants could be the best protection for that infrastructure,” Trump suggested, according to a later statement.
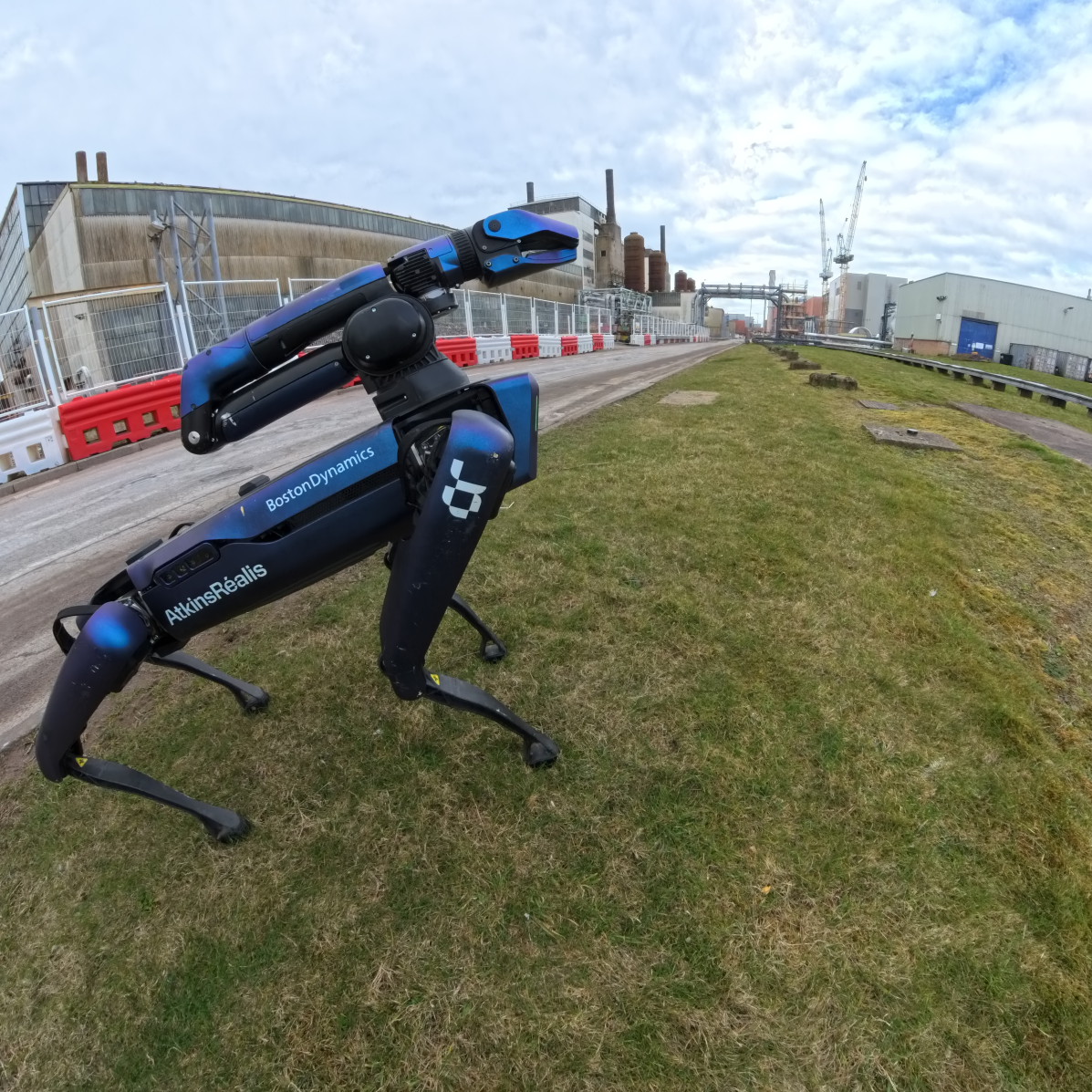
Spot, the robot dog, on-site at Sellafield. (Photo: AtkinsRéalis)
Sellafield Ltd. and AtkinsRéalis have successfully operated a robotic dog from a remote location in what might be the first time such an operation has happened at a nuclear licensed site, according to the companies in a March 18 press release.
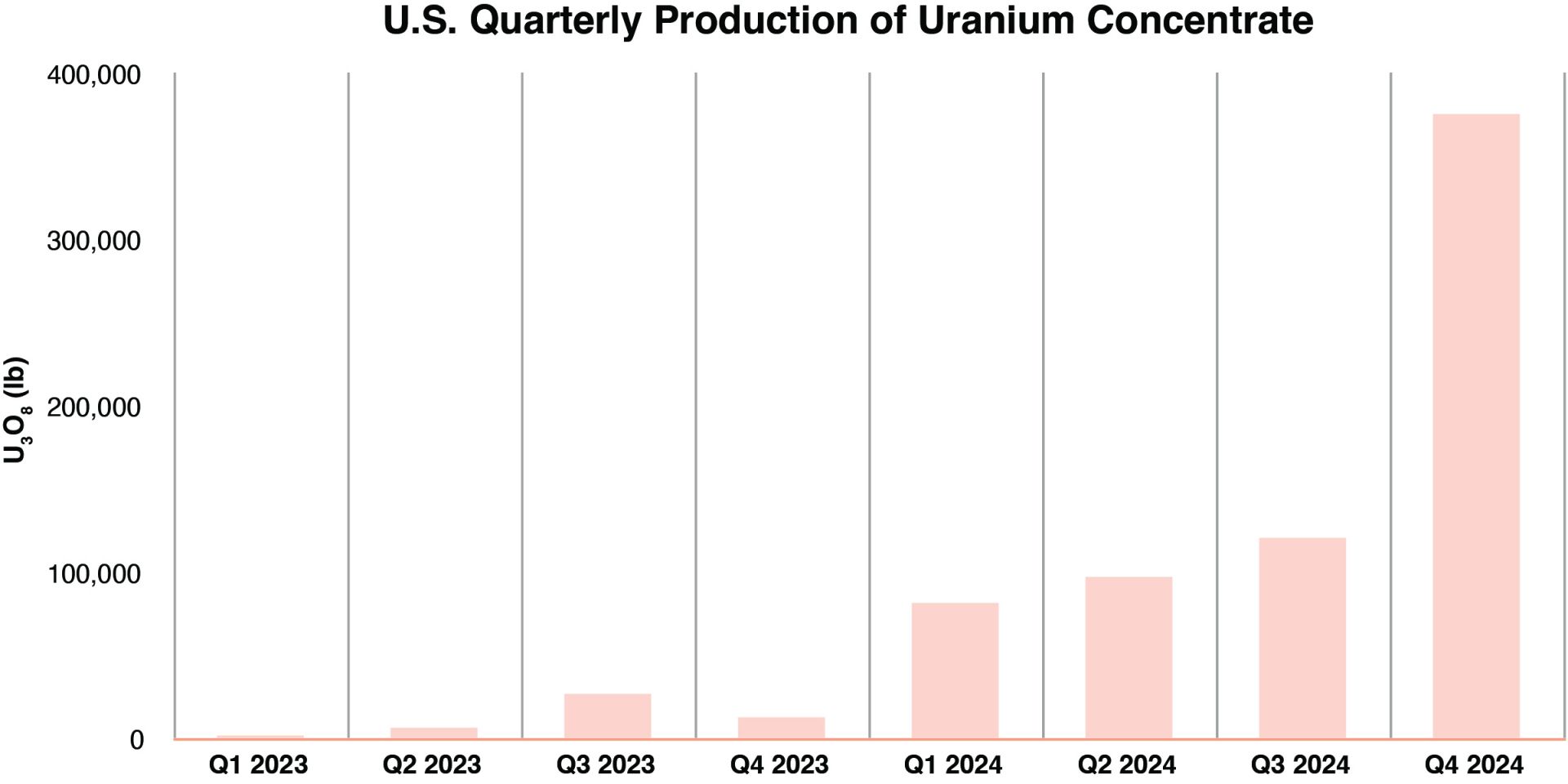
Graph: Nuclear News; data source: U.S. EIA
U.S. uranium production increased throughout 2024, with more growth planned in 2025. The producers who can make that happen, however, were burned before by a “renaissance” that didn’t take off. Now they are watching and waiting for signals from Washington, D.C., including the impacts of tariffs, shifting relationships with global uranium producers, and funding for the enrichment task orders designed to boost demand for U.S. uranium.
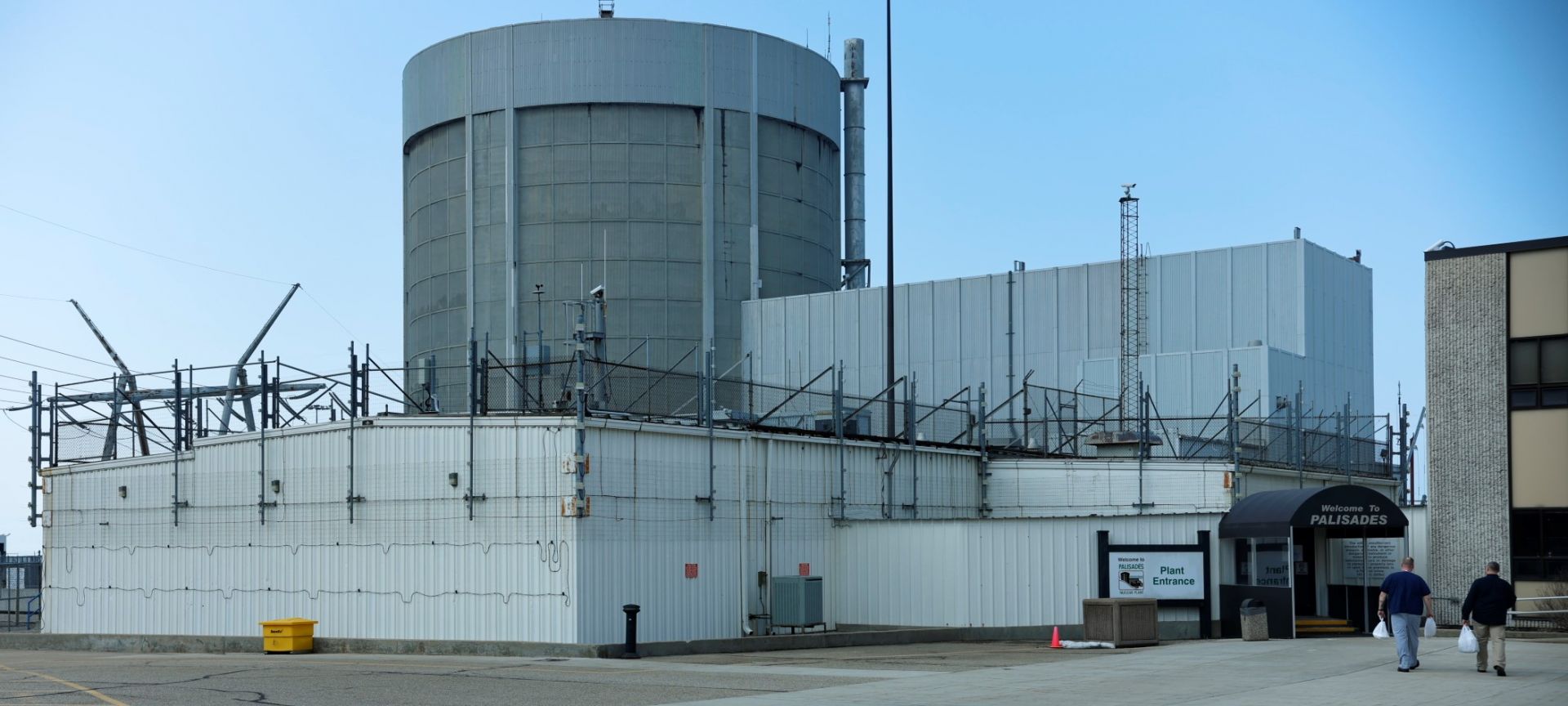
A part of the Palisades nuclear power plant. (Photo: Holtec)
Energy Secretary Chris Wright announced this week the release of the second part of Holtec’s loan disbursement for the Palisades nuclear plant restart plans in Michigan.