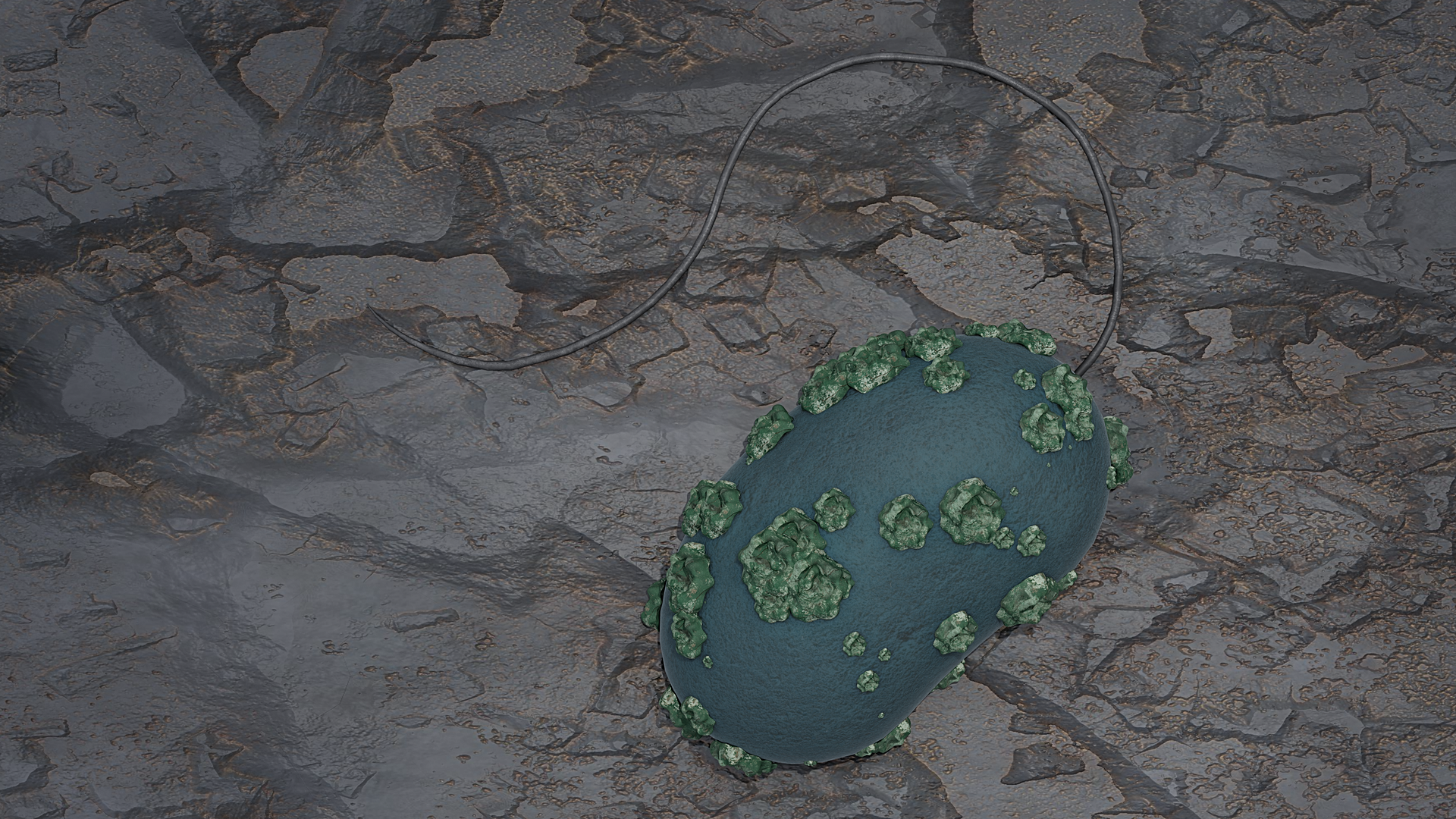
An artistic representation of a Desulfosporosinus cell with immobilized uranium on the surface. (Image: B. Schröder/HZDR)
Researchers at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) research laboratory in Germany have investigated a microorganism capable of transforming water-soluble hexavalent uranium [U(VI)] to the less-mobile tetravalent uranium [U(IV)]. The researchers found that the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfosporosinus hippei, a relative of naturally occurring microorganisms present in clay rock and bentonite, showed a relatively fast removal of uranium from clay pore water.
Vit Plant crews begin adding frit into Hanford’s second melter. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management recently announced that crews at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant, recently brought the second of two 300-ton melters up to the operating temperature of 2,100°F.
The DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory in Lemont, Ill. (Photo: DOE)
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are developing and deploying ARG-US (from the Greek Argus, meaning “Watchful Guardian”) remote monitoring systems technologies to enhance the safety, security, and safeguards (3S) of packages of nuclear and other radioactive material during storage, transportation, and disposal.
As part of its DUF6 conversion program, the DOE is shipping converted depleted uranium oxide to WCS for disposal.
The first major shipment of depleted uranium oxide for disposal departs the DOE’s Paducah Site in Kentucky in early 2023 for disposal at the WCS facility in Texas.
Last year in late August, 120 storage cylinders of depleted uranium oxide (DUOx) safely arrived by rail in West Texas, having been shipped from the Department of Energy’s Portsmouth Site in Ohio. It was the first such shipment of the stable crystalline powder from the Portsmouth Site and was another milestone in the DOE Office of Environmental Management’s (EM) efforts to ship DUOx for off-site disposal.
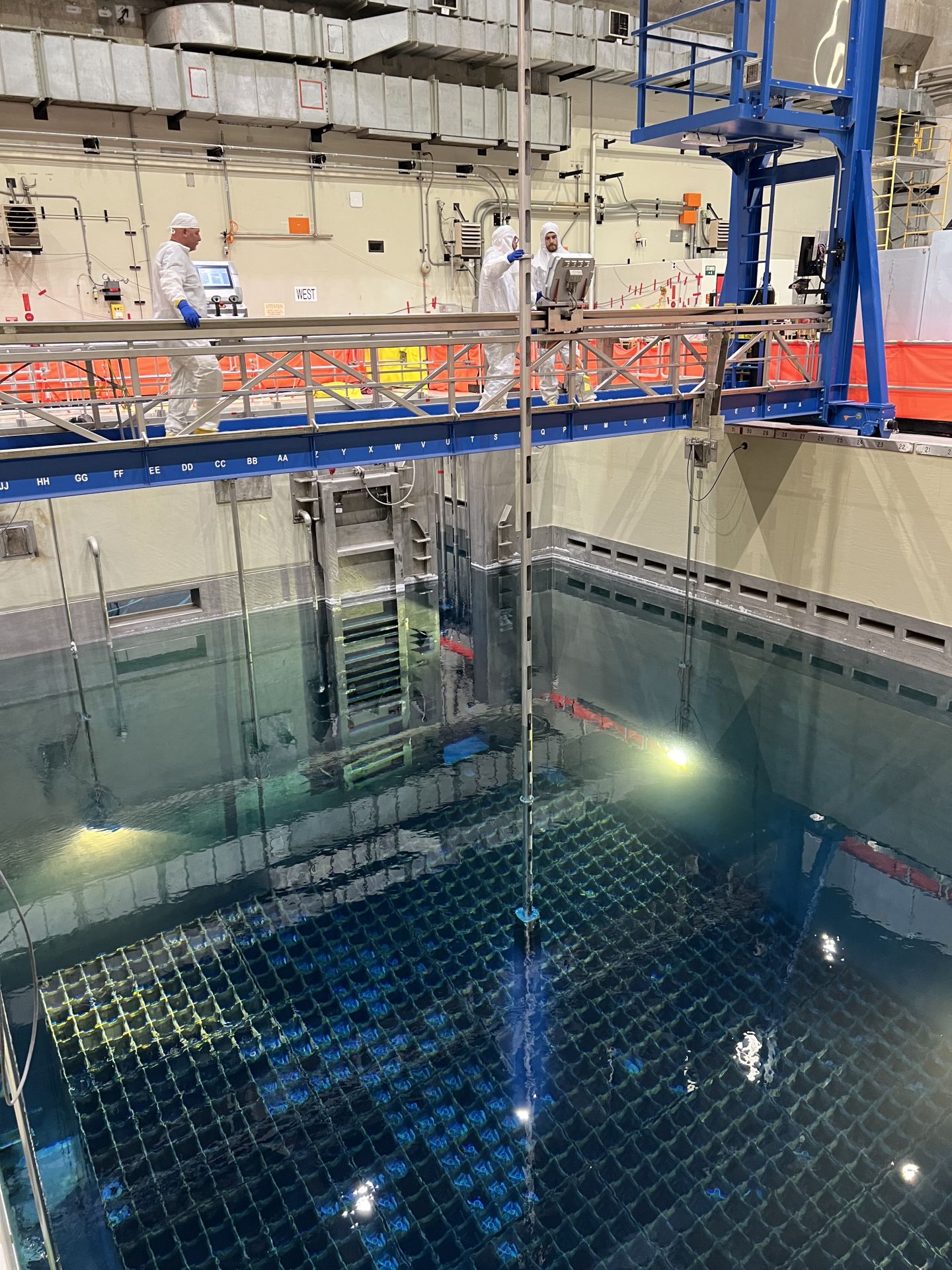
Upgrades are under way at the Hanford Site's 222-S Laboratory, including replacing the Cold War-era windows in the labs hot cells. Photo: DOE)
A screen shot of a video marking the 25th anniversary of operations at the WIPP disposal facility. (Image: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management celebrated a major milestone for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant last week, marking the 25th anniversary of the receipt of the first waste shipment at the disposal facility in New Mexico’s Chihuahuan Desert.
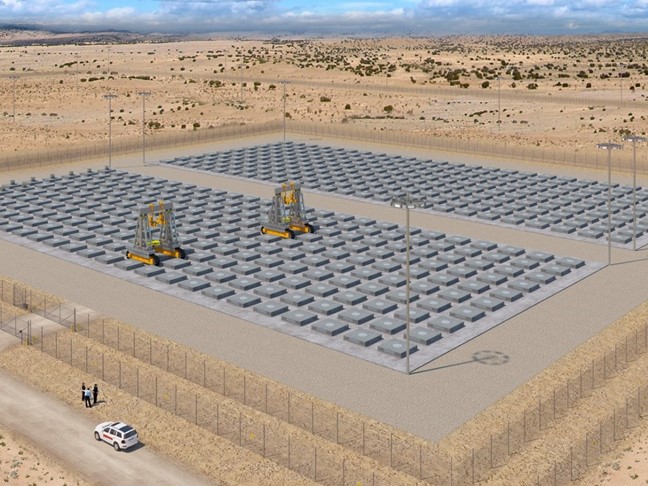
Concept art of Holtec’s proposed HI-STORE CISF in New Mexico. (Image: Holtec)
The 5th Circuit Court of Appeals has vacated Holtec International’s license to build and operate a consolidated interim storage facility (CISF) for spent nuclear fuel near the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in southeastern New Mexico. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission granted the license for the Holtec facility, called the HI-STORE CISF in May 2023.
SRS successfully made the first transfer of decontaminated salt solution directly from one waste processing facility to the other, bypassing a hold tank previously used in the transfer process. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management’s liquid waste contractor at the Savannah River Site this month marked the first direct transfer of decontaminated waste from the Salt Waste Processing Facility (SWPF) to the Saltstone Production Facility (SPF). This is a new step in optimizing waste processing, according to the DOE.
The site of the Maine Yankee nuclear power plant, which was decommissioned in 2005. As with its sister plants Yankee Rowe and Connecticut Yankee, all that remains of the site is the plant ISFSI. Without a national waste management solution, spent fuel will continue to sit at sites such as these. (Photo: Maine Yankee Atomic Power Company)
After decades of false starts, U-turns, and stasis, the United States has arrived at a de facto solution for its high-level nuclear waste: Leave it in storage where it was produced, no matter how many tens of billions of dollars it costs, what impediments it raises for nuclear expansion, or what burdens it creates for the reuse of old reactor sites.
Dumb as it sounds, this is keeping all the major players happy. And it avoids alternative pathways, each of which has problems.
Waste drums at the Winfrith site's treated radwaste storage facility. (Photo: NWS)
More than 1,000 drums of low-level radioactive waste in the United Kingdom have been safely disposed of earlier than expected. The project was completed through the collaborative work of Nuclear Waste Services (NWS), Nuclear Restoration Services (NRS), and Nuclear Transport Solutions (NTS).
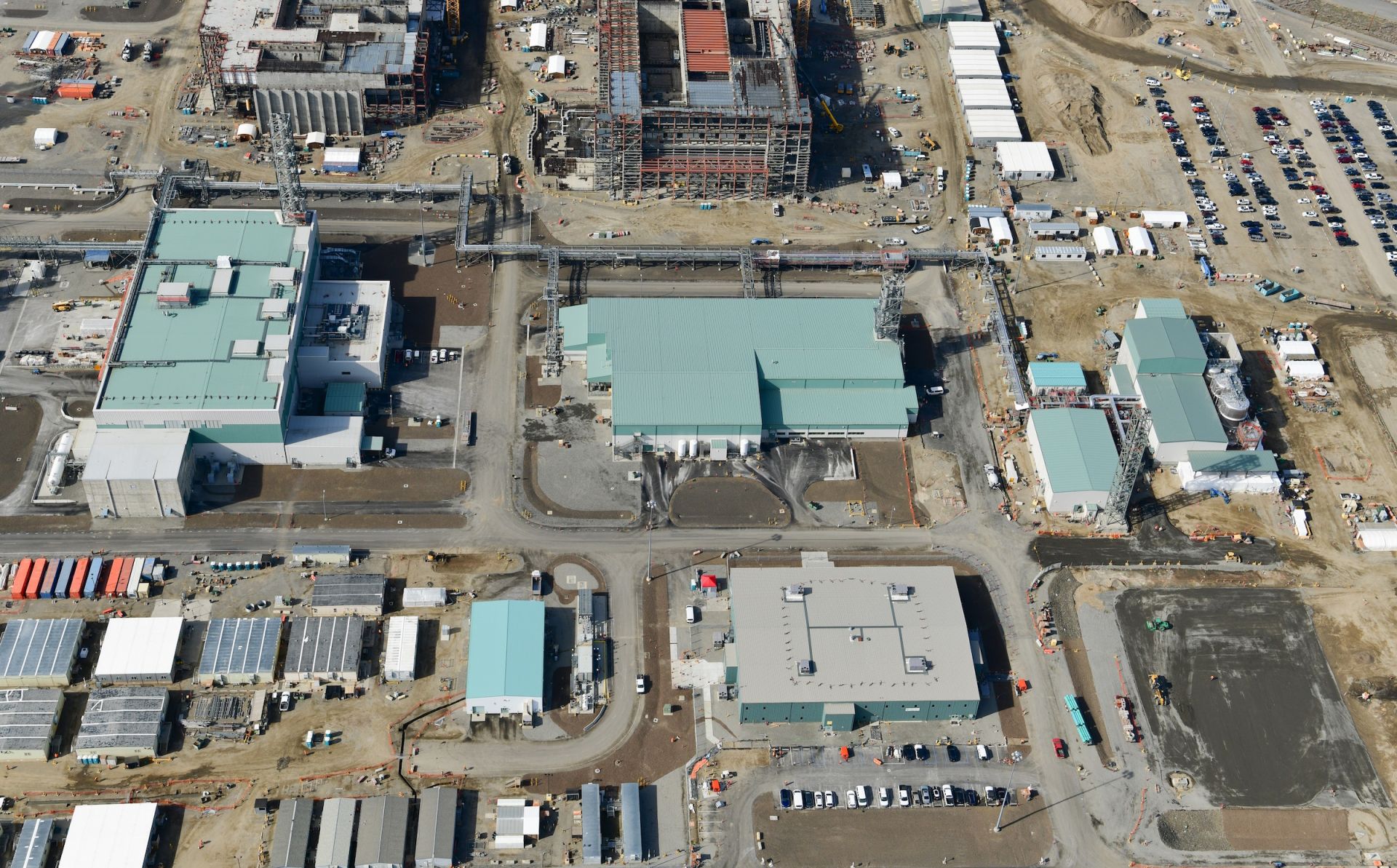
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management once again awarded a 10-year, $45 billion contract to Hanford Tank Waste Operations and Closure (H2C) of Lynchburg, Va., for the cleanup of tank waste at the Hanford Site.
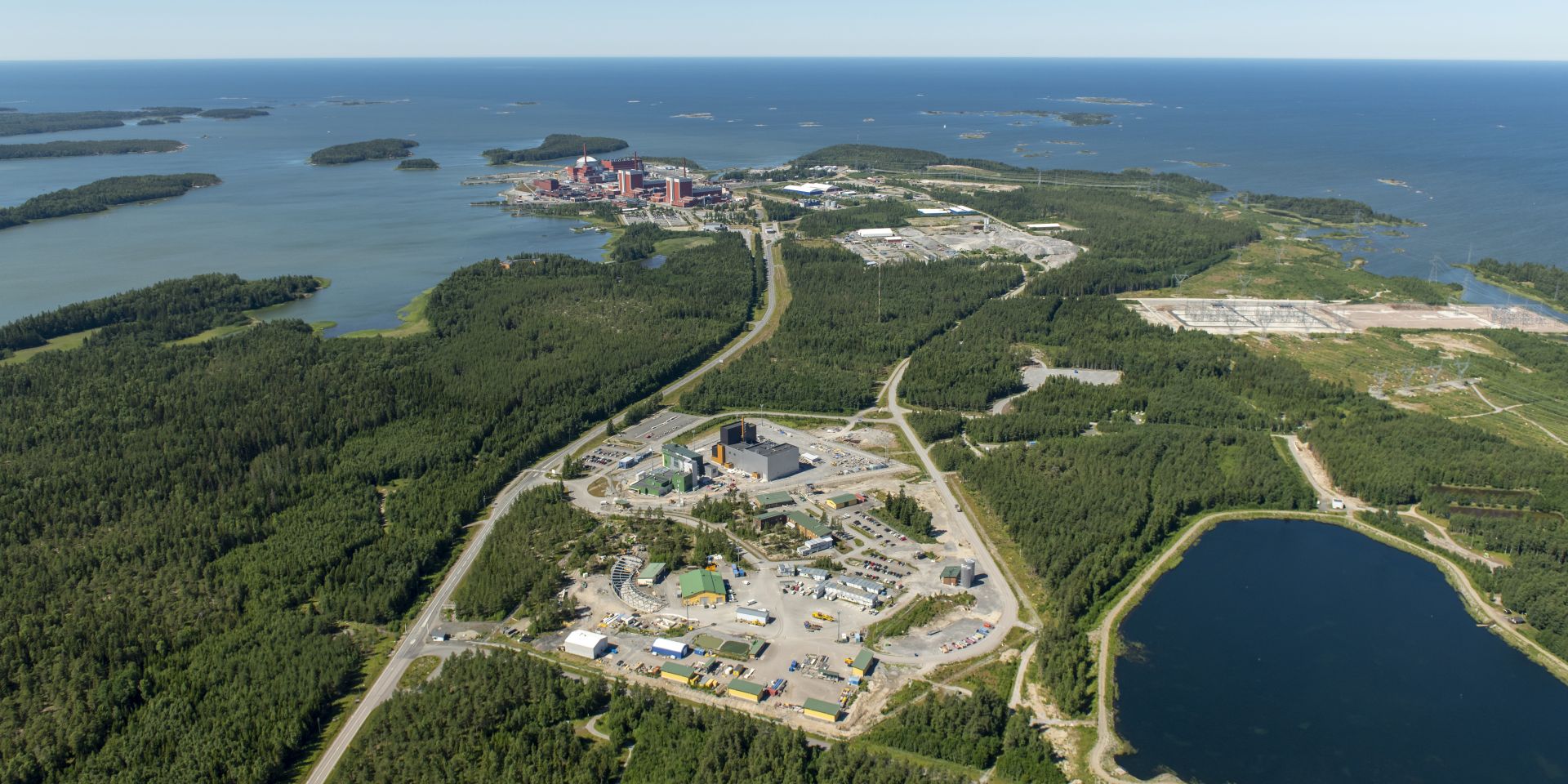
March 1, 2024, 3:03PMRadwaste SolutionsEdited by Tim Gregoire. Photos courtesy of Tapani Karjanlahti/Posiva. The site of the Onkalo deep geological repository near Eurajoki in southwestern Finland with the Olkiluoto nuclear power plant in the background. In 2015, Posiva received a construction license from the Finnish government for the repository, which will be constructed to a depth of 1,300 to 1,500 feet.
The year 2024 is shaping up to be a historic one for Posiva, the waste management organization owned by Finland’s two nuclear power plant utilities, Fortum and Teollisuuden Voima. The company is looking to receive regulatory approval of its operating license for the Onkalo deep geological repository for high-level radioactive waste by the end of the year.
Orano CEO Nicolas Maes (left) and SHINE Technologies founder and CEO Greg Piefer shake hands after agreeing to cooperate on a pilot used fuel recycling facility. (Photo: Orano)
Orano and SHINE Technologies have agreed to cooperate in the development of a pilot plant capable of recycling used nuclear fuel from light water reactors on a commercial scale. In announcing the signing of a memorandum of understanding on Thursday, the companies said the selection of a site for the pilot U.S. facility is expected by the end of this year.
Schematic of a deep horizontal borehole repository for nuclear waste. (Image: Deep Isolation)
Waste disposal start-up Deep Isolation and fusion tech company SHINE Technologies have announced the completion of a collaborative study assessing the costs of disposing of radioactive byproducts from a pilot spent nuclear fuel recycling facility.
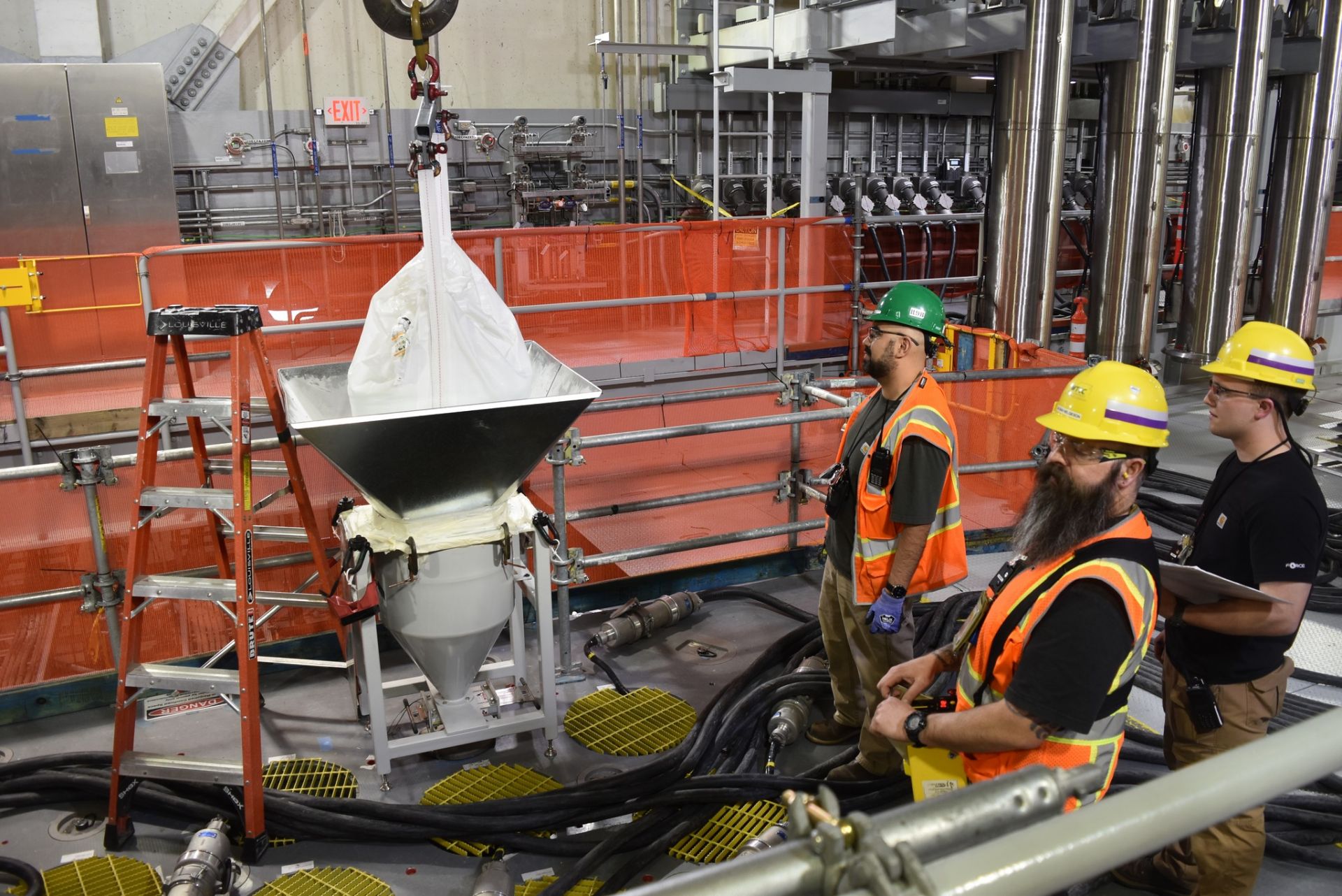
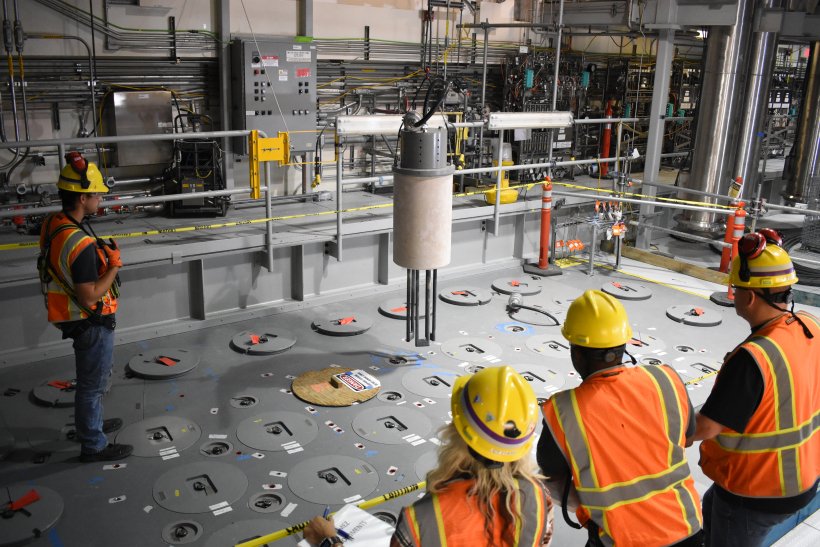
One of 18 startup heaters is installed in Hanford’s second melter, which will be used to vitrify liquid waste. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced that crews at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant, recently installed 18 temporary startup heaters in the second of two melters in the plant’s Low-Activity Waste Facility.