SRNS engineers (from left) Will Jolin, John Bradley, and Joao Cardoso-Neto discuss a plan to move and repurpose equipment used at 19 soil cleanup sites. Photo: DOE
A project to passively remove nonradioactive contaminants from the soil and groundwater at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina is coming to an end, as workers prepare to remove solar-power “plugs” from 19 soil remediation locations at the site.
The NRC-licensed independent spent fuel storage installation at Zion, Ill.
A radiological worker surveys the inside of a TRUPACT-II containment lid during waste handling operations at WIPP. Photo: DOE
Crews move equipment used to inspect drums holding diluted plutonium into a storage site in K Area at the Savannah River Site. Photo: DOE
Workers at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina recently finished transferring equipment to the site’s K Area in preparation of shipping downblended plutonium to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico for disposal. The plutonium is part of the 34 metric tons of surplus plutonium the National Nuclear Security Administration plans to ship to WIPP under the “dilute and dispose” option the department adopted following the cancellation of the MOX Fuel Fabrication Facility project.
Workers remove asbestos siding panels from a Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant building. Photo: Business Wire
Fluor-BWXT Portsmouth, a joint venture of Fluor and BWX Technologies, along with engineering company Jacob, have received a contract extension valued at up to $690 million, including options, from the Department of Energy. The contract, announced April 6, is for environmental management work at the former Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant near Piketon, Ohio.
Dry cask storage at the closed San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station in Southern California. Photo: Southern California Edison
Saying they are cautiously optimistic that the Biden administration can change the U.S. trajectory on nuclear waste, some Stanford University experts have offered their recommendations on how it can be done in a recent Stanford news posting.
A front-and-back illustration of the new Hanford ETF filter system, which is intended to eliminate the need to shut down operations every 12 hours to replace filters during wastewater processing. Image: DOE
A new wastewater filter system being installed at Hanford’s Effluent Treatment Facility (ETF) is expected to increase waste processing throughput, improve efficiency, and save money as the site in southeastern Washington gears up to treat tank waste, the Department of Energy announced.
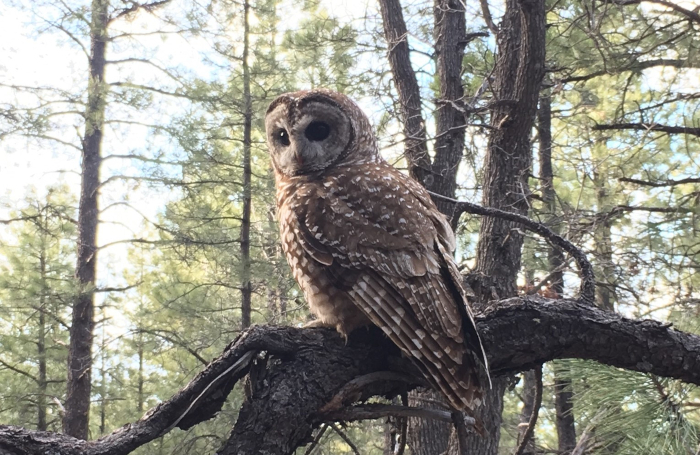
The Mexican spotted owl, which finds a home in northern New Mexico’s canyons and forests, is a threatened species that the DOE strives to protect. Photo: Don Ulrich, taken in Flagstaff, Ariz.
To protect a treasured ecological species of northern New Mexico, the Los Alamos Field Office (EM-LA) of the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management and its contractor N3B this month began their annual task of modifying legacy waste cleanup activities at Los Alamos National Laboratory ahead of the Mexican spotted owl breeding season.
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) listed the owl as a threatened species in 1993, when population numbers were decreasing drastically due to the loss, degradation, and fragmentation of their habitat.
Holtec’s proposed HI-STORE interim storage facility. Image: Holtec
New Mexico attorney general Hector Balderas has filed suit against the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the United States, seeking to stop Holtec International’s application to build and operate its HI-STORE consolidated interim storage facility for used nuclear fuel in the state. The complaint, filed in the U.S. District Court of New Mexico on March 29, seeks a declaratory judgment that the NRC is acting beyond the scope of its authority and an injunction preventing the licensing from moving forward.
The Three Mile Island nuclear generating station in 2010.
A community advisory board has been formed for the decommissioning of Unit 2 of the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant, according to a March 23 report by StateImpact Pennsylvania, a collaboration of National Public Radio member stations. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission approved in December the transfer of TMI-2 and its license to TMI-2 Solutions for decommissioning. TMI-2 Solutions is a subsidiary of EnergySolutions.
According to the report, the TMI-2 Community Advisory Panel (CAP) is made up of 15 people who represent the plant and its neighbors, including townships, school districts, first responders, nuclear planners, and state historians. The group is being led by Londonderry Township manager Steve Letavic.
TMI-2 Solutions said that it will provide quarterly decommissioning updates to the TMI-2 CAP. As a volunteer non-regulatory organization, the CAP will provide community feedback to TMI-2 Solutions, including any issues or concerns related to TMI-2 decommissioning activities.
Savannah River’s DWPF has been pouring high-level waste canisters for a quarter of a century. Photo: DOE
The month of March marked the 25th year of radiological operations for the Defense Waste Processing Facility (DWPF) at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina. Radiological operations at DWPF, which is used to treat Savannah River’s high-level radioactive tank waste, began on March 12, 1996, with the first canister of vitrified waste poured on April 29 that year.
To date, more than 4,200 stainless steel canisters of vitrified waste have been poured at DWPF, according to the DOE.
The only operating waste vitrification plant in the nation, DWPF is operated by Savannah River Remediation, the DOE’s liquid waste contractor at the site. According to the DOE, DWPF operations are expected to continue for approximately 15 more years, and about 4,000 more canisters are scheduled to be produced. The DOE expects to begin hot operations at a second waste vitrification plant later this year at its Idaho National Laboratory site.
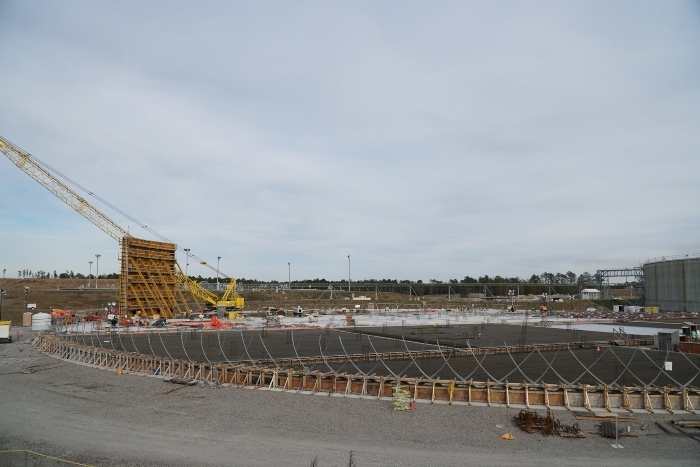
The first wall section of Saltstone Disposal Unit 8 is being constructed at the Savannah River Site. Source: DOE
The first wall section of Saltstone Disposal Unit 8 (SDU 8) at the Department of Energy's Savannah River Site in South Carolina was installed earlier this month.
SDU 8 will stand 43 feet tall and 375 feet in diameter, and have a 33-million-gallon capacity, just like two SDUs built recently at the site. The 25 wall sections of SDU 8 are being constructed using high-strength, reinforced concrete and will be wrapped with seven layers of more than 300 miles of steel cable for added strength.
The flooring of SDU 8 is more than halfway complete. The concrete floor sits on top of a multilayer foundation: a geosynthetic clay liner and high-density plastic liner sandwiched between two concrete layers called “mud mats.” The floor is being completed in 14 sections.
The disposal units are built to safely and permanently contain decontaminated salt solution processed at Savannah River, the DOE reported on March 9.