Researchers at the University of Sheffield are exploring new cement technologies to safely encapsulate nuclear waste. (Photo: University of Sheffield)
The University of Sheffield announced that it has engaged in a new £1 million (about $1.29 million) research partnership with Sellafield Ltd., the U.K. Nuclear Decommissioning Authority, and the U.K. National Nuclear Laboratory that will seek to address some of the challenges of nuclear waste encapsulation by looking at new cement technologies to provide safe and reliable disposal solutions.
The KIF document is meant to engage the reader to share, imagine, and renew nuclear waste information. (Photo: Per Wistbo Nibell)
The preservation of records, knowledge, and memory is recognized as an important component of nuclear waste management, preventing future generations from unnecessary interference with a waste repository and supporting future societies to make informed decisions about such sites.
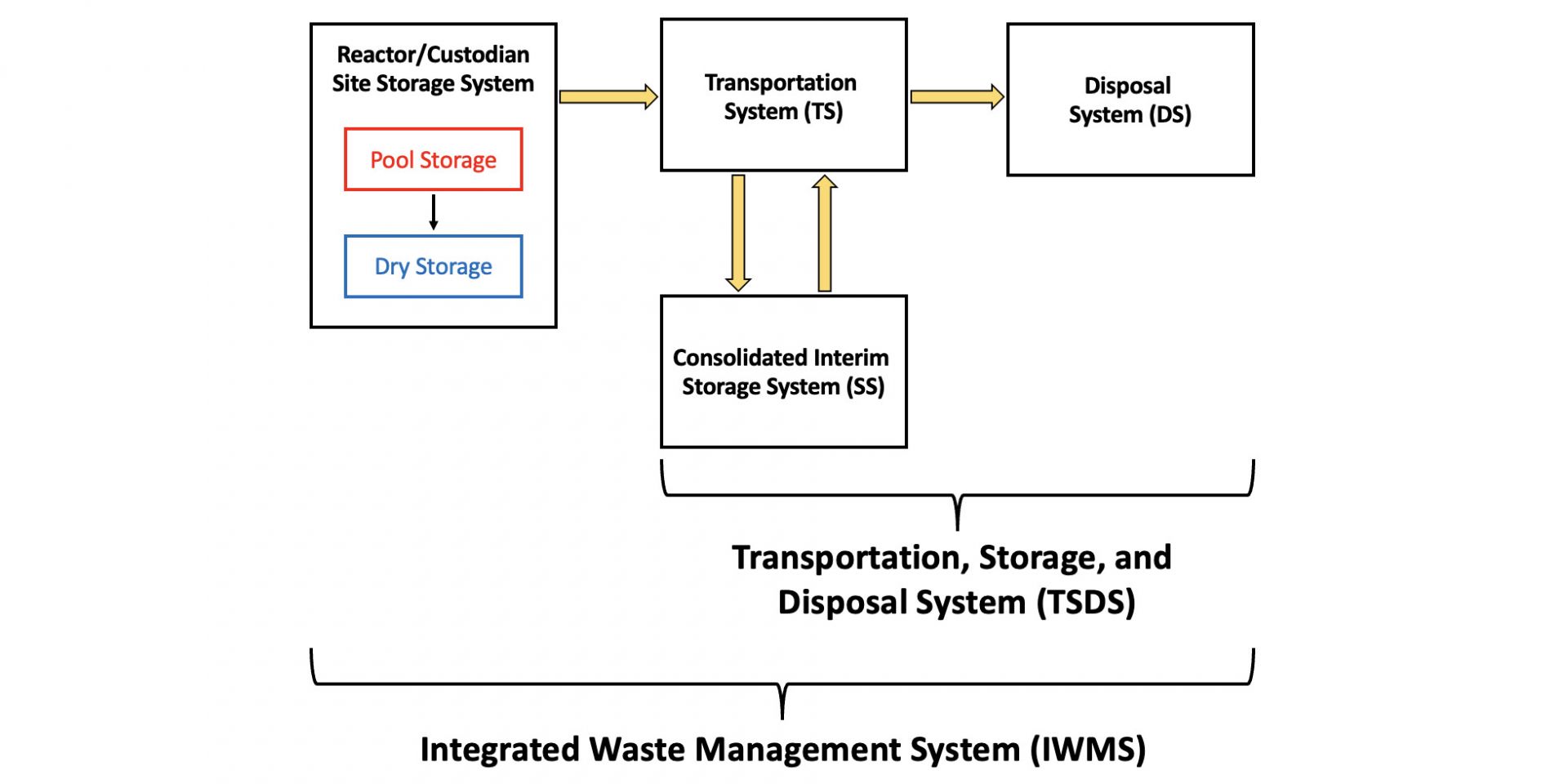
Fig. 1. The systems that make up the IWMS and their interdependencies.
Nuclear energy produces about 9 percent of the world’s electricity and 19 percent of the electricity in the United States, which has 94 operating commercial nuclear reactors with a capacity of just under 97 gigawatts-electric. Each reactor replaces a portion of its nuclear fuel every 18 to 24 months. Once removed from the reactor, this spent (or used) nuclear fuel (SNF or UNF) is stored in a spent fuel pool (SFP) for a few years then transferred to dry storage.
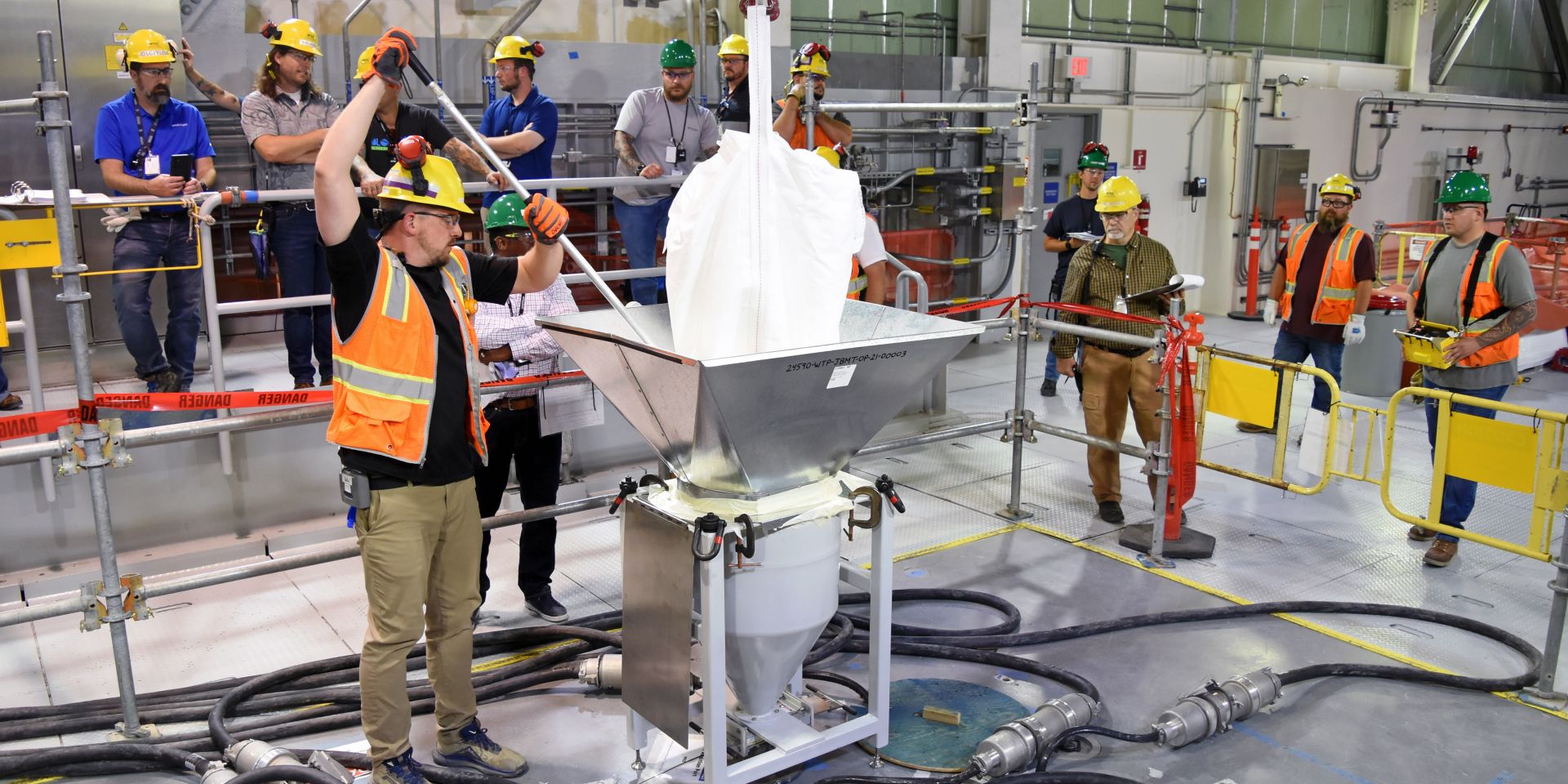
An international team of researchers have collaborated to reduce operational risk and realize a vision of long-term success for the Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant (WTP) at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site near Richland, Wash.
Above: WTP workers add glass beads, called “frit,” to the melter inside the plant’s Low-Activity Waste Facility. (Photo: Bechtel National Inc.)
For over a decade, the DOE’s Hanford Field Office (HFO) has been working with national laboratories, universities, and glass industry experts to establish capabilities and generate data to increase the confidence in a successful startup and transition to full-time operations at the WTP.
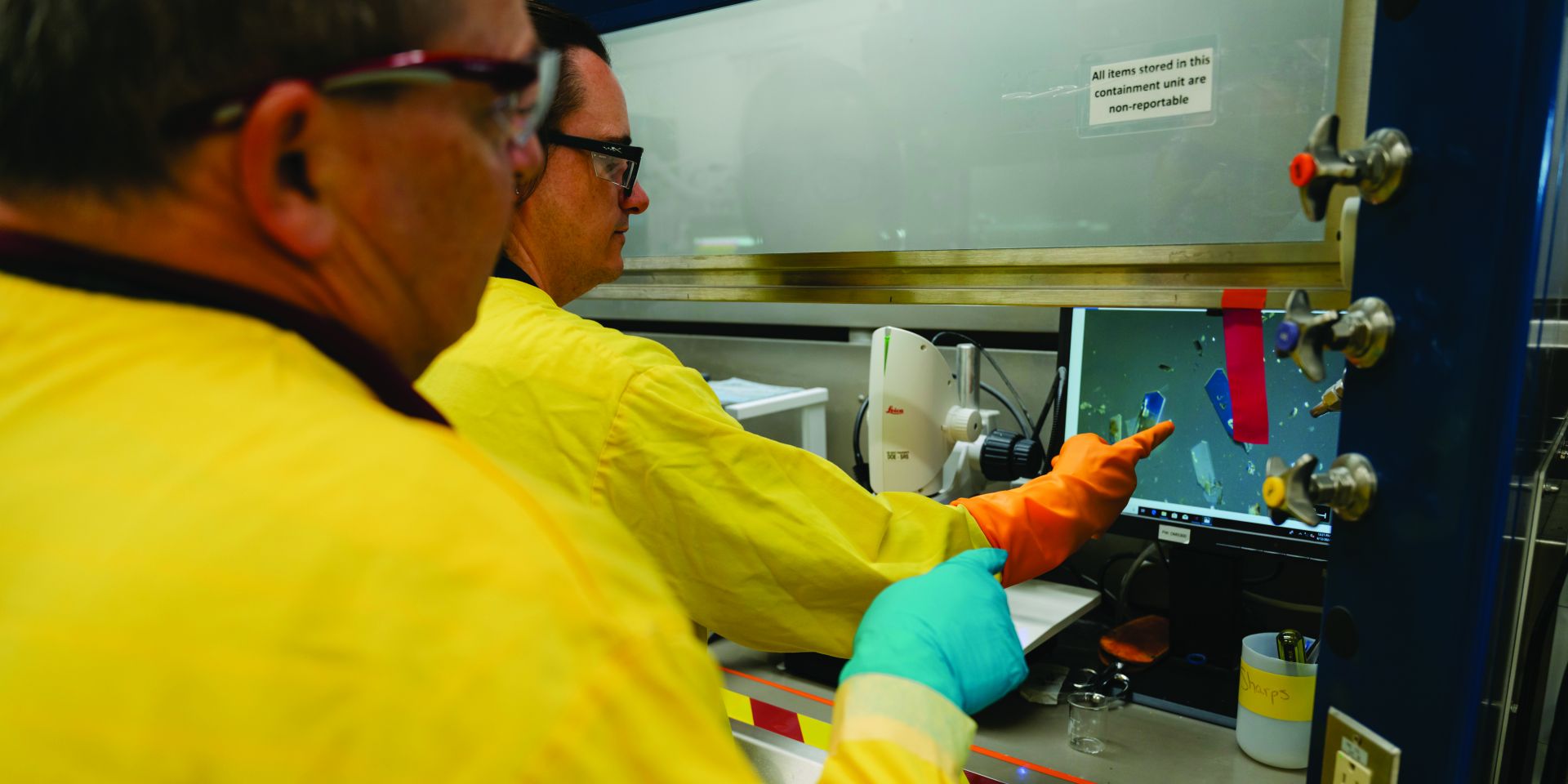
SRNL senior scientist Travis Deason demonstrates for lab fellow David Diprete the search for appropriate crystals of novel actinide materials using a microscope located in a radiological containment unit. (Photo: SRNS/Lj Gay)
Savannah River National Laboratory researchers are building on the laboratory’s legacy of using cutting-edge science to effectively immobilize nuclear waste in innovative ways. As part of the Center for Hierarchical Waste Form Materials, SRNL is leveraging its depth of experience in radiological waste management to explore new frontiers in the industry.
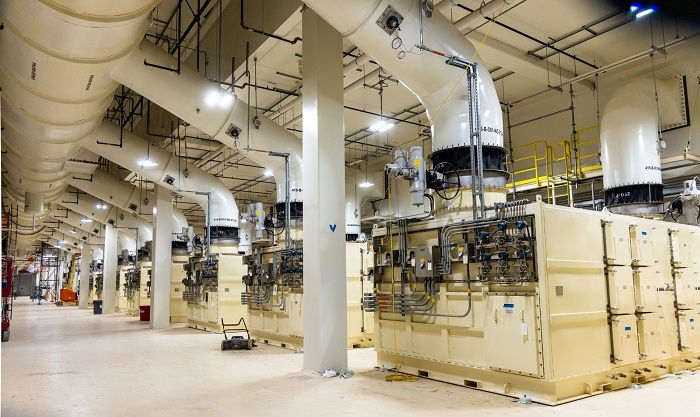
HEPA filters located within the Safety Significant Confinement Ventilation System facility at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced that it has completed the commissioning of a new, nearly $500 million, large-scale ventilation system at its Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, the DOE’s geologic repository for defense-related transuranic waste in New Mexico.
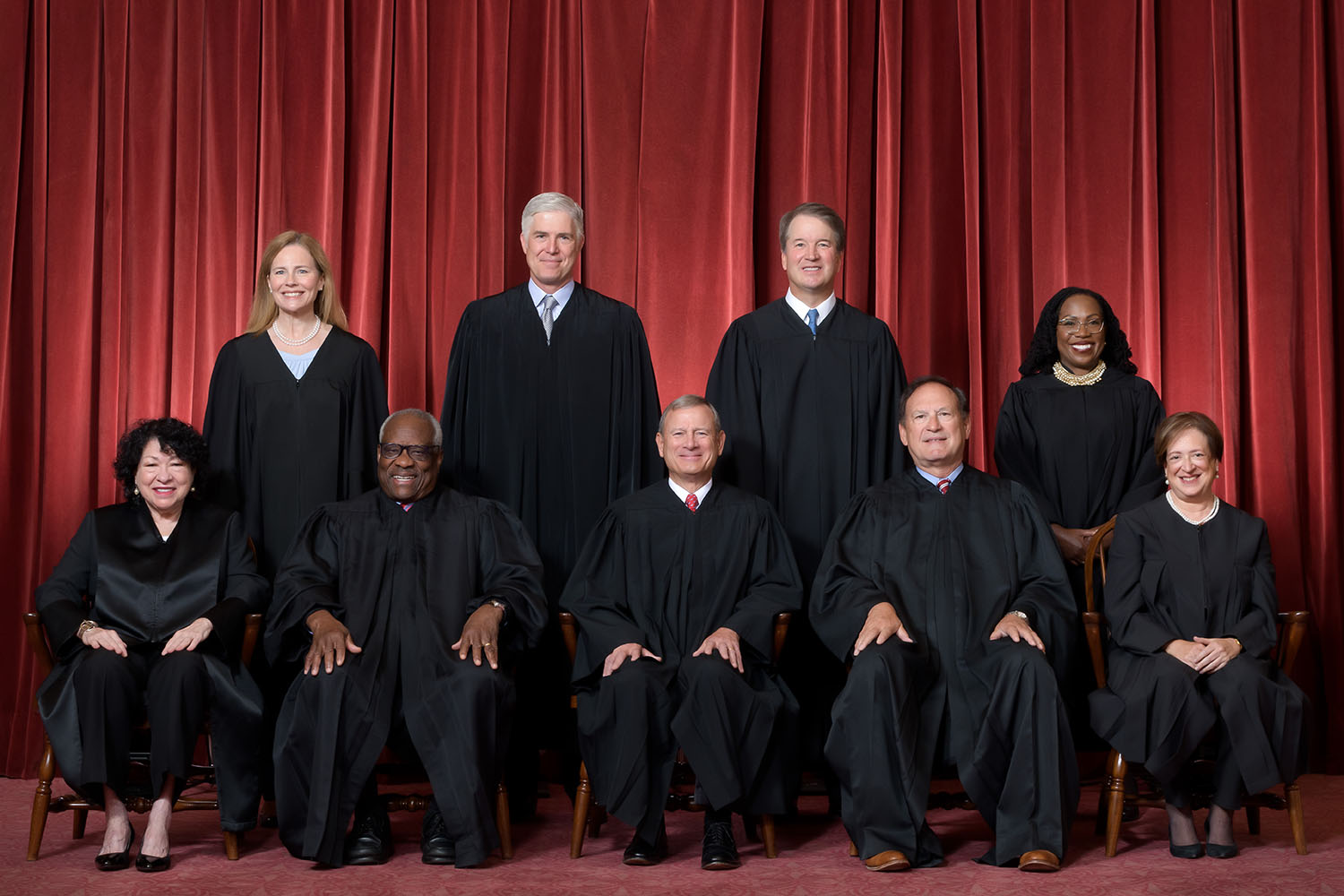
The U.S. Supreme Court. Front row, from left: Associate Justice Sonia Sotomayor, Associate Justice Clarence Thomas, Chief Justice John G. Roberts, Jr., Associate Justice Samuel A. Alito, Jr., and Associate Justice Elena Kagan. Back row, from left: Associate Justice Amy Coney Barrett, Associate Justice Neil M. Gorsuch, Associate Justice Brett M. Kavanaugh, and Associate Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson. (Photo: Fred Schilling, Collection of the Supreme Court of the United States)
The U.S. Supreme Court heard oral arguments on Wednesday in the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s licensing of Interim Storage Partners’ consolidated interim storage facility in Andrews County, Texas. Both the NRC and ISP petitioned the Supreme Court to review a decision by the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals that invalidated the NRC-granted license for the facility. Those two cases were consolidated into one, NRC v. Texas, which was heard by the court.
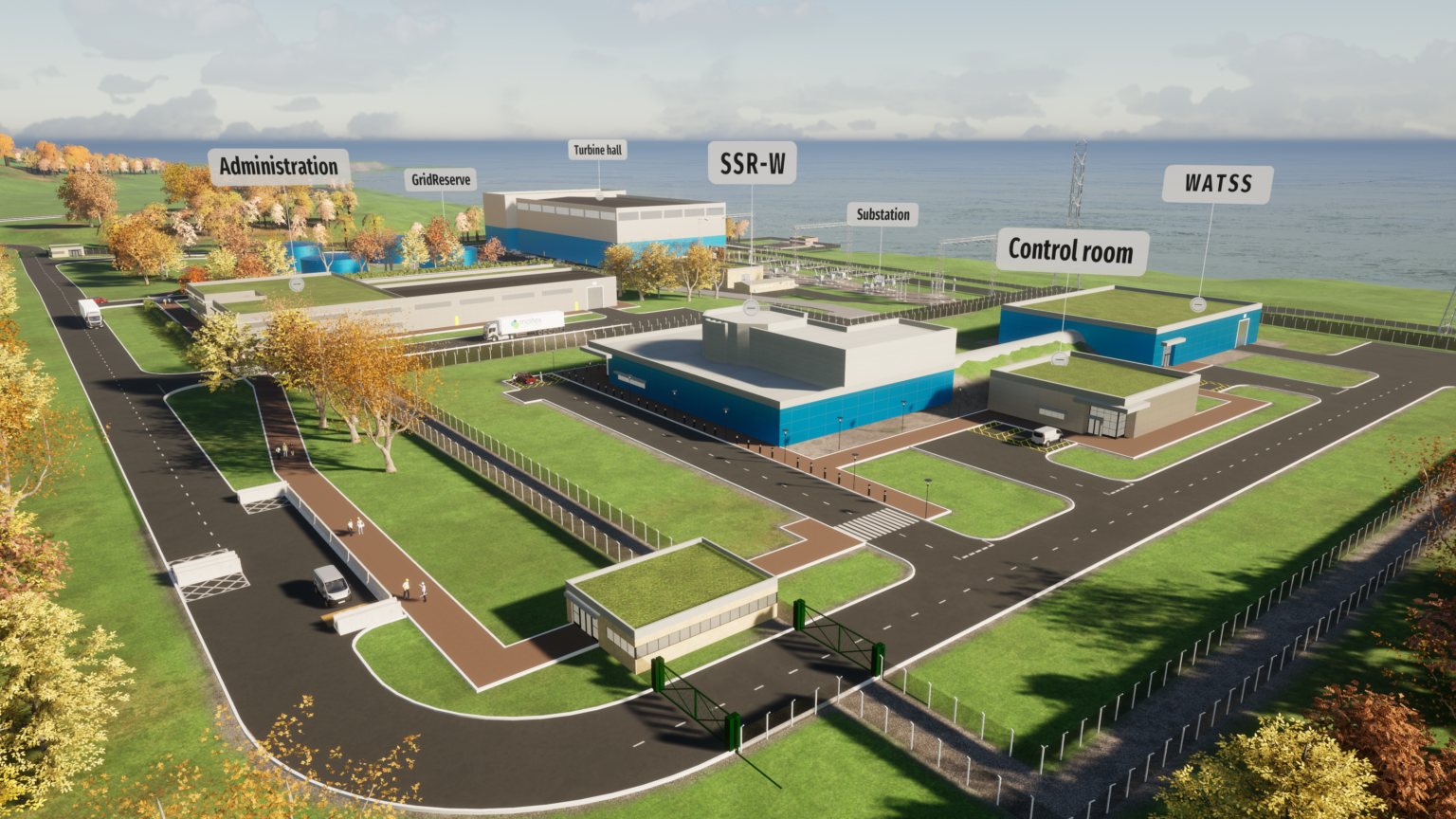
Concept art of Moltex’s SSR–W and WATSS facility. (Image: Moltex)
Advanced reactor company Moltex Energy Canada said it has successfully validated its waste to stable salt (WATSS) process on used nuclear fuel bundles from an unnamed Canadian commercial reactor through hot cell experiments conducted by Canadian Nuclear Laboratories.
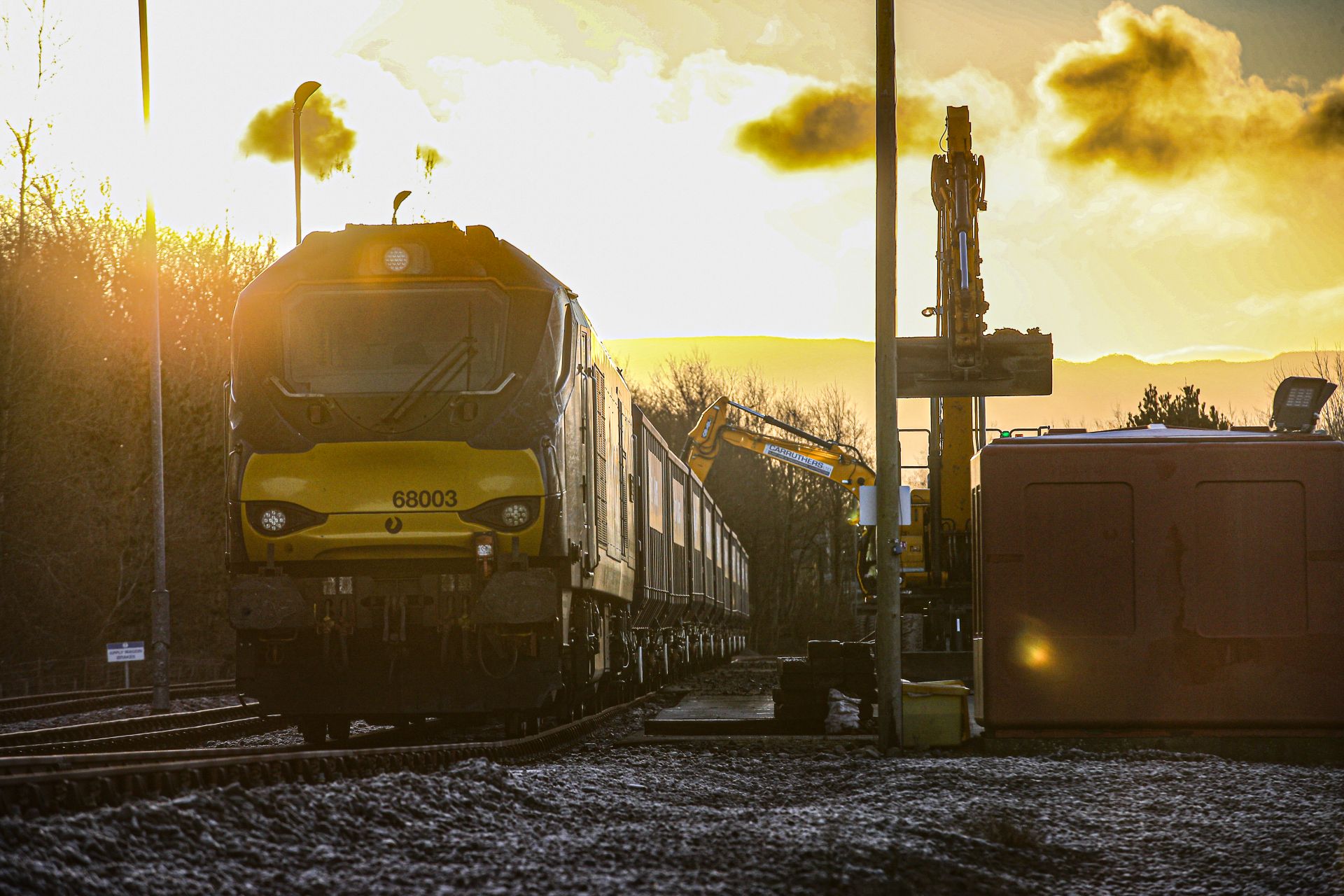
Aggregate is delivered by rail to the U.K.’s Low-Level Waste Repository site. (Photo: NWS)
Nuclear Waste Services (NWS), which manages the disposal of the United Kingdom’s low-level radioactive waste, announced this week that a major milestone has been reached at its Low Level Waste Repository in West Cumbria, England, as work begins on the final capping of legacy disposal trenches and vaults at the site.
The Oyster Creek ISFSI. (Photo: Holtec International)
The Tax Court of New Jersey has ruled that Oyster Creek’s spent nuclear fuel storage casks are subject to taxation as real property.
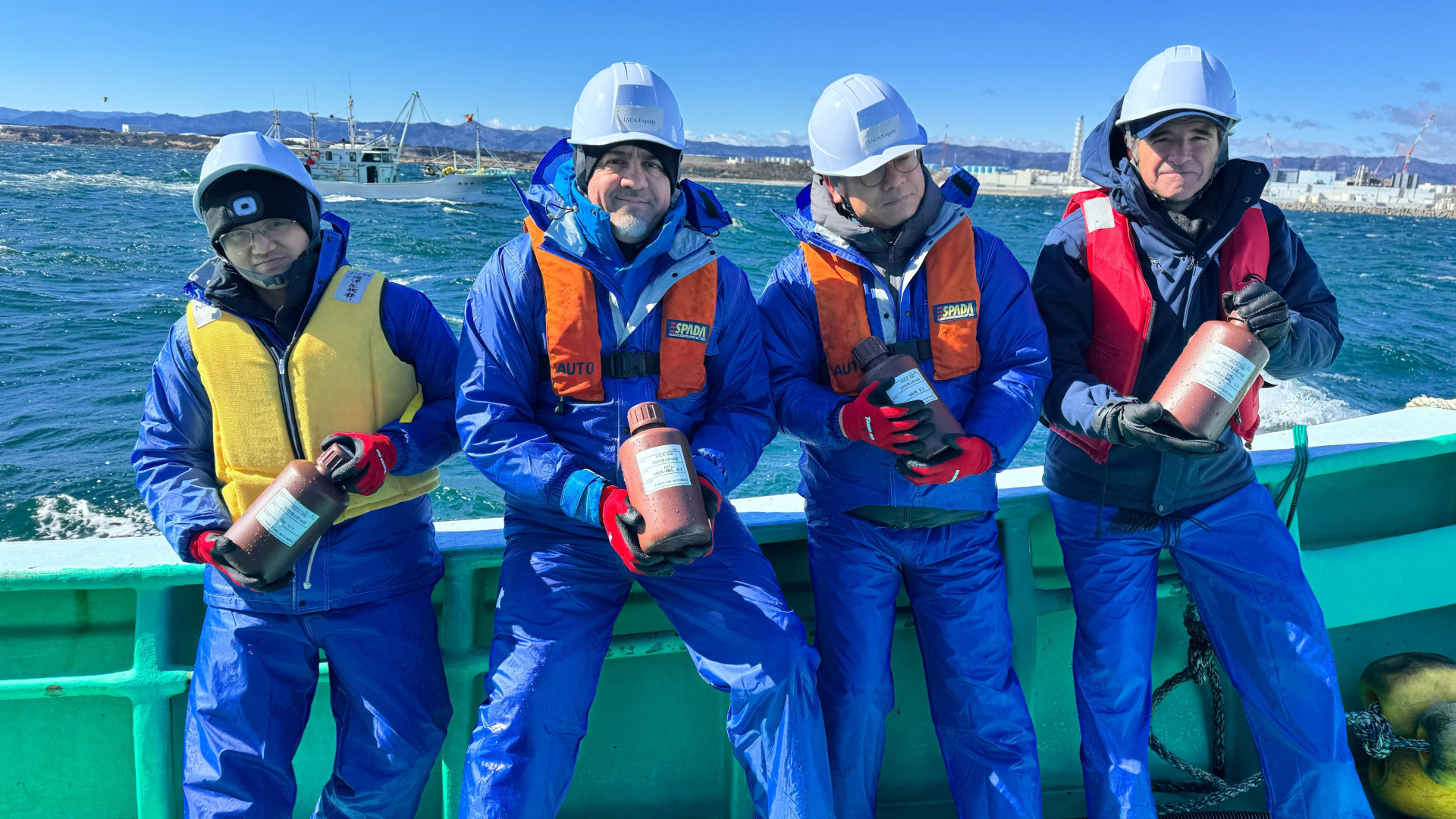
The IAEA’s Rafael Mariano Grossi (far right) and other IAEA experts joined scientists from China, South Korea, and Switzerland as they collected seawater samples near the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. (Photo: Dean Calma/IAEA)
International Atomic Energy Agency director general Rafael Mariano Grossi visited Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi site on February 19, where he joined scientists from the Third Institute of Oceanography in China, the Korean Institute for Nuclear Safety in South Korea, and the Spiez Laboratory in Switzerland in collecting seawater samples from a boat near the damaged nuclear power plant.
Idaho Cleanup Project crews with the Calcine Disposition Project watch as robotics equipment is tested remotely inside a full-scale replica of a calcine bin set. (Photo: DOE)
A team with the Department of Energy’s Idaho Cleanup Project successfully tested robotic equipment being developed to retrieve radioactive calcine, a granular solid waste, at the Idaho National Laboratory Site, the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management has announced.
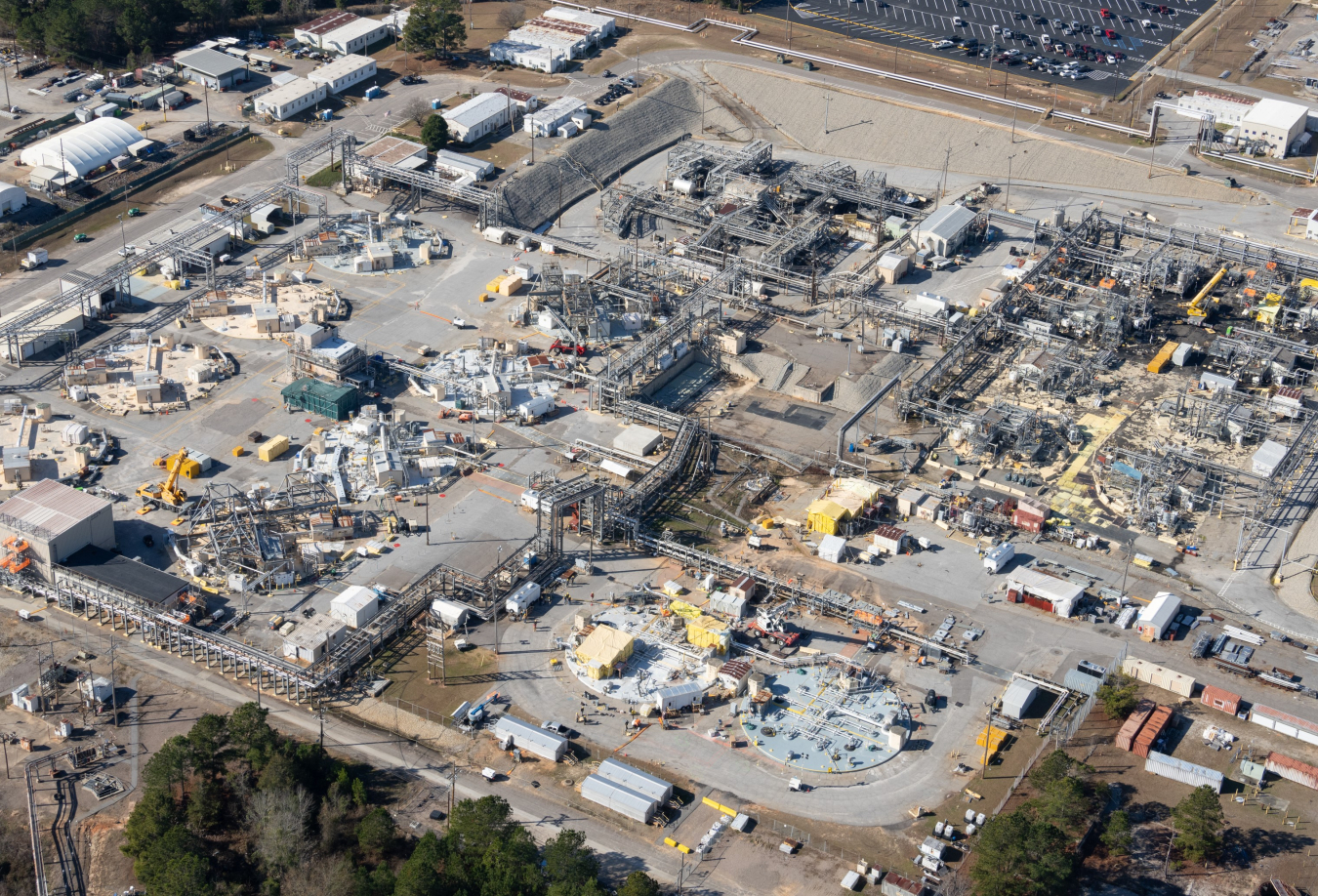
The Savannah River Site’s F Tank Farm, where Tank 4 completed preliminary cease waste removal a year ahead of schedule. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management said it has reached a regulatory milestone ahead of schedule in preparing radioactive waste tanks for closure at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. DOE-EM said it received concurrence in January from the South Carolina Department of Environmental Services (SCDES) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency that SRS had successfully removed waste from the site’s Tank 4 and may now proceed to waste sampling and analysis of that tank ahead of its closure.
A rendering of a possible geologic disposal facility on the coast of northwest England. (Image: NWS)
The U.K. government’s Nuclear Waste Services said it has identified three “areas of focus” in its search to find a suitable site and a willing community to host a geologic disposal facility (GDF) for the country’s most hazardous radioactive waste. The areas are within three communities currently involved in the siting process—Mid Copeland and South Copeland in Cumbria, and East Lincolnshire, England.
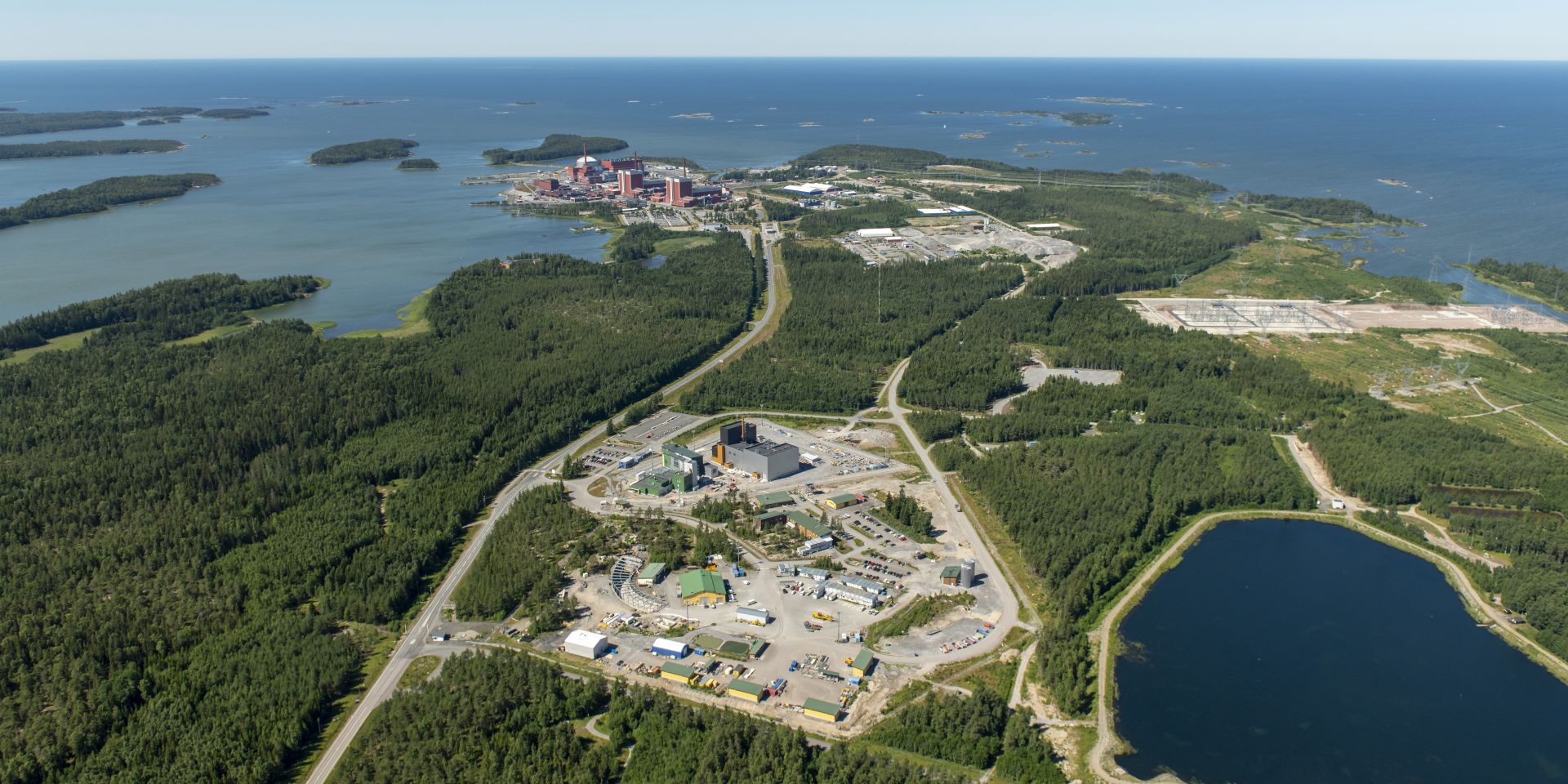
The site of the Onkalo deep geological repository in Finland, with the Olkiluoto nuclear power plant in the background. (Photo: Posiva)
Finland’s Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority (STUK) stated that if everything goes well, it can complete the assessment of the operating license for the country’s deep geologic repository for spent nuclear fuel “well before the end of the year.”