December 2, 2022, 3:03PMNuclear NewsBrian Dassatti, Kamila Blain, and Jenn Sinkiewicz Teledyne FLIR PackBot® conducts visual inspections in a hazardous area.
Mobile unmanned systems, also known as MUS, encompass a range of robotic devices, including drones, ground vehicles, crawlers, and submersibles. They are used for a wide range of industrial and defense applications to automate operations and assist humans or completely remove human workers from hazardous conditions. Robotics are ubiquitous in industrial manufacturing. Military robots are routinely employed in combat support applications, such as reconnaissance, inspection, explosive ordnance disposal, and transportation. Drones are used in many industries for security and monitoring, to conduct aerial inspections or surveys, and to capture digital twins. Wind and solar farms use MUS technologies for day-to-day operations and maintenance.
The Yakutia awaits launch at St. Petersburg’s Baltic Shipyard on Nov. 22. (Photo: TASS/Valentin Yegorshin)
Advancing its efforts to develop the Arctic and establish new energy markets, Russia launched a new nuclear-powered icebreaker, the Yakutia, in St. Petersburg during a November 22 ceremony. At the launching in the northern Russian port city, the Russian flag was raised on another nuclear icebreaker, the Ural. Overseeing the events via video link from the Kremlin, Russian president Vladimir Putin said that the icebreakers “were laid down as part of a large serial project and are part of our large-scale, systematic work to reequip and replenish the domestic icebreaker fleet, to strengthen Russia's status as a great Arctic power.”
Philippine president Ferdinand R. Marcos Jr. and Vice President Harris meet in Manila on November 21. (Photo: Office of the Press Secretary, Republic of the Philippines)
During a recent weeklong trip to Southeast Asia aimed at bolstering U.S. economic and security ties in the region, Vice President Kamala Harris announced the launch of nuclear energy partnerships with Thailand and the Philippines.
Currently, neither country enjoys the benefits of nuclear power. Both rely primarily on some mix of petroleum, natural gas, and coal for their energy needs.
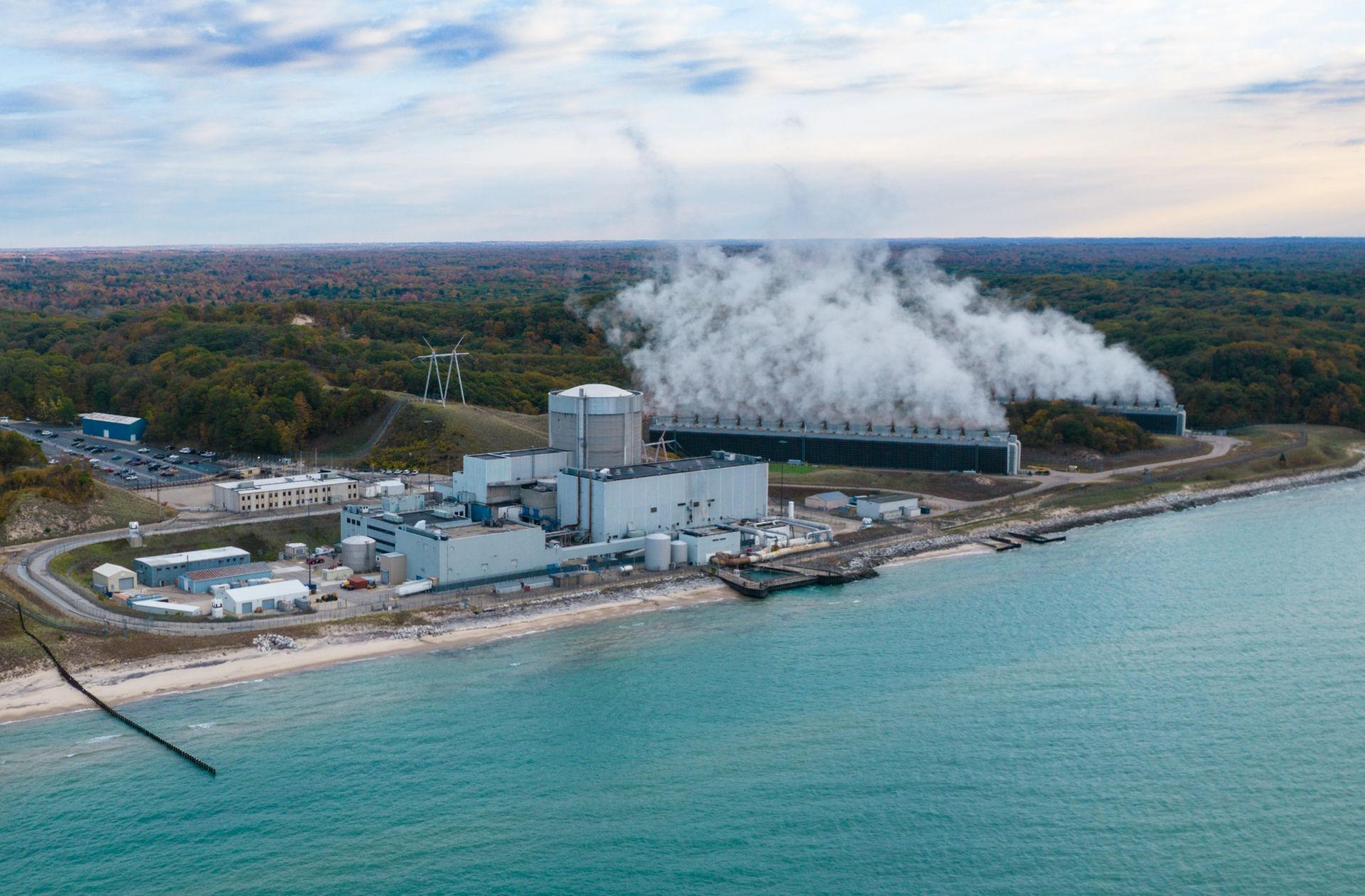
The Palisades nuclear power plant, in Michigan, before it was permanently closed. (Photo: Holtec)
Pacific Gas & Electric’s two-unit Diablo Canyon plant—California’s lone operating nuclear power facility—has been deemed eligible for the initial round of funding from the Civil Nuclear Credit (CNC) Program, the Department of Energy announced yesterday.
The decision was welcomed by a nuclear community disappointed by last Friday’s news that the DOE had rejected Holtec International’s CNC application for the recently closed Palisades nuclear plant in Michigan, despite support for the effort from Gov. Gretchen Whitmer.
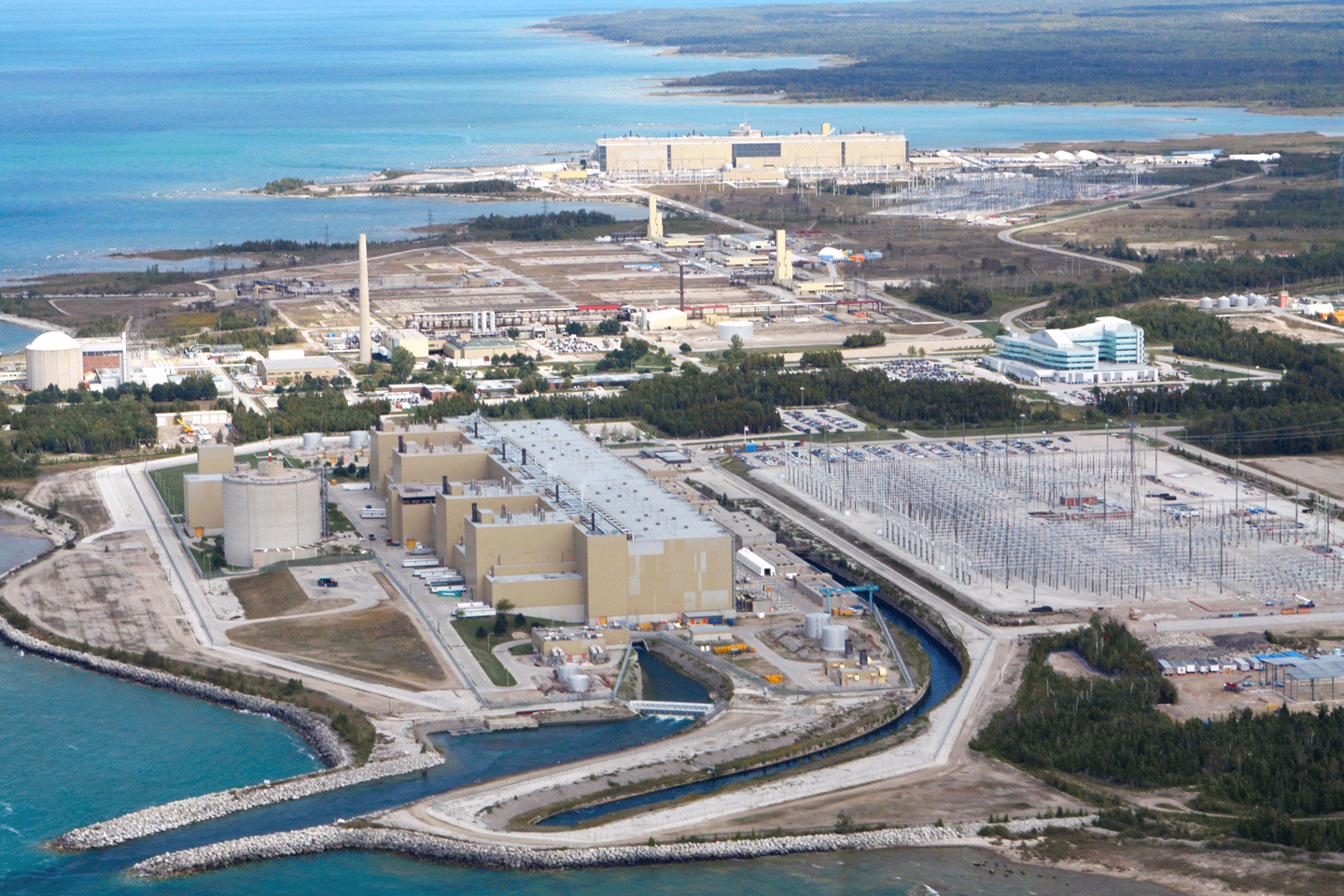
The Bruce Power A and B nuclear power plants. (Photo: CNSC)
Canada’s Bruce Power, operator of the eight-unit Bruce nuclear plant in Kincardine, Ontario, has announced a “made-in-Ontario solution” to the net-zero challenges faced by industries: allowing new incremental nuclear output to be accredited for an avoided emissions benefit.
U.S. special envoy for climate John Kerry at COP27. (Photo: Embassy of Ukraine in the United States of America)
U.S. special envoy for climate John Kerry and Ukraine’s minister of energy German Galushchenko have announced a two-to-three-year pilot project aimed at demonstrating the commercial-scale production of clean hydrogen and ammonia from small modular reactors in Ukraine using solid oxide electrolysis.
The North Anna nuclear power plant. (Photo: Stuartmj/Wikipedia)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is seeking public comment on the scope of its supplemental environmental impact statement (SEIS) concerning Dominion Energy’s subsequent license renewal (SLR) application for North Anna-1 and -2, the agency announced earlier this week.
From left: Romanian minister of energy Virgil Popescu, U.S. Export-Import Bank president and chair Reta Jo Lewis, Romanian president Klaus Iohannis, U.S. special presidential envoy for climate John Kerry, and U.S. State Department assistant secretary Geoffrey Pyatt. (Photo: ExIm)
The Export-Import Bank of the United States has issued two letters of interest (LOIs) for the financing of U.S.-sourced pre-project technical services in connection with the proposed reactor construction project at Romania’s Cernavoda nuclear plant, the bank announced last week.
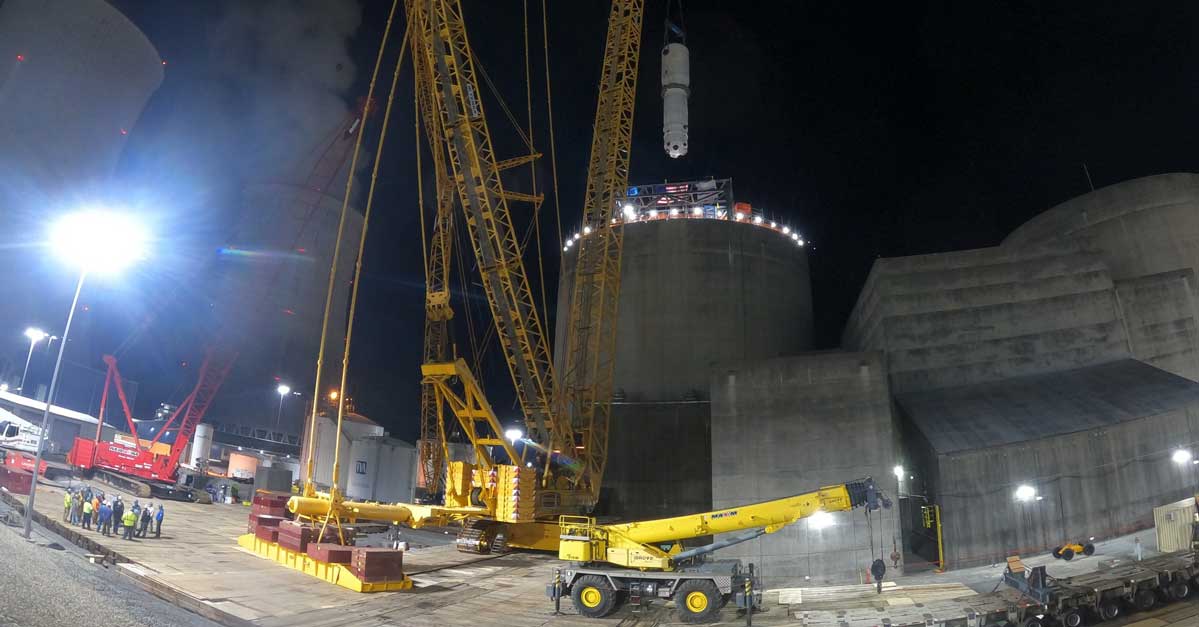
A steam generator is lifted into Watts Bar Unit 2. (Photo: Framatome)
The Steam Generating Team (SGT)—a joint venture of Framatome and United Engineers & Constructors Inc.—has completed a project to replace the Unit 2 steam generators at the Watts Bar nuclear plant, Framatome announced last week.
Watts Barr’s owner and operator, the Tennessee Valley Authority, awarded Framatome the contract for the work in early 2020.
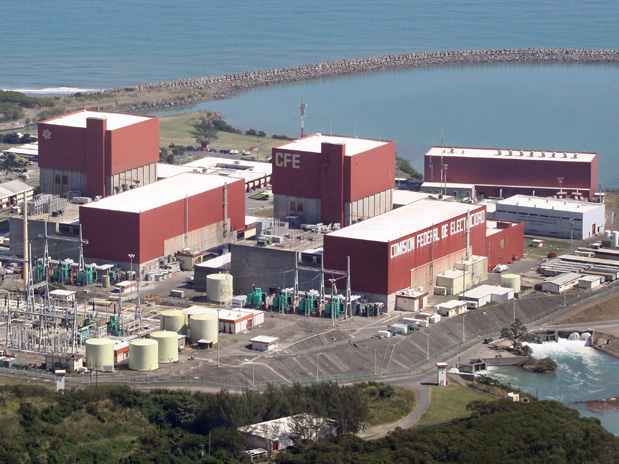
Mexico's Laguna Verde nuclear power plant, on the coast of the Gulf of Mexico in the state of Veracruz.
An agreement between the United States and Mexico on civil nuclear cooperation has entered into force, the U.S. State Department announced last week. While first proposed in 2016 and finalized and signed in 2018, the pact only received approval from the Mexican Senate this March.
Participating in the forum were (from left) John Hopkins (NuScale Power), Renaud Crassous (EDF), Daniel Poneman (Centrus Energy), Adriana Cristina Serquis (CNEA), and Boris Schucht (Urenco).
The nuclear industry leaders assembled in Washington, D.C., last week to discuss small modular reactor supply chains agreed that lost generation capacity from the expected retirement of hundreds or thousands of coal power plants over the next decade—a cliff, in one panelist’s words—represents an opportunity that developers of SMRs and advanced reactors are competing to meet.
“I think in total 80 projects are ongoing,” said Boris Schucht, panel moderator and chief executive officer of Urenco Group, as he opened the forum. “Of course not all of them will win, and we will discuss today what is needed so that they can be successful.”
Constellation Energy's Clinton nuclear power plant. (Photo: NRC)
Constellation Energy, owner and operator of the nation’s largest reactor fleet, will ask the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to extend the operating licenses of the Clinton and Dresden reactors by 20 years, the company announced Monday, adding that it expects to file license applications with the agency in 2024.