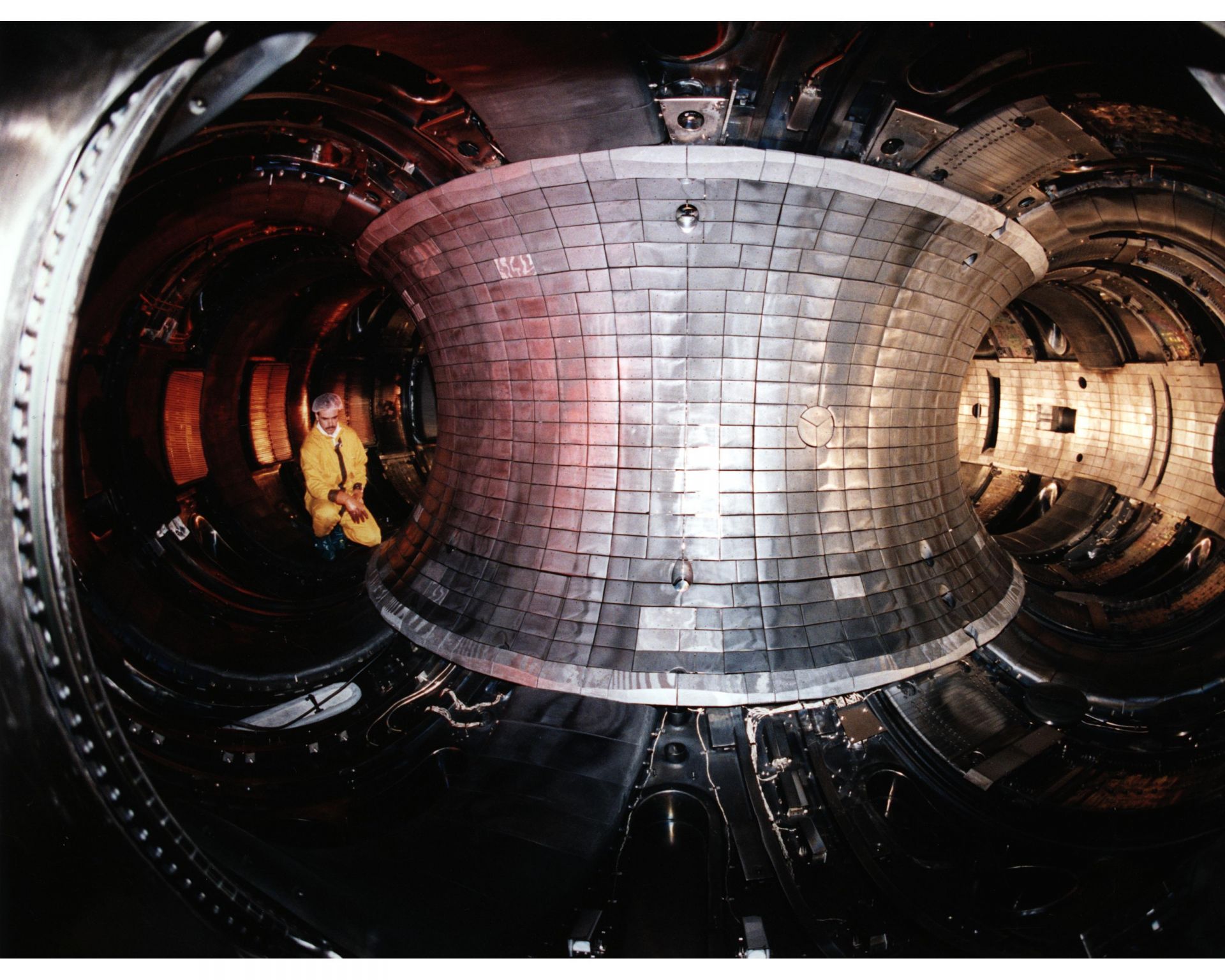
Approval from French regulator ASN is required before ITER vacuum vessel welding can begin. (Photo: ITER)
In a February 28 article posted on the ITER Organization website, Gilles Perrier, head of ITER’s Safety and Quality Department, addressed the decision by French nuclear safety regulator ASN (Autorité de sûreté nucléaire) to delay the anticipated February 1 release of a preset tokamak assembly “hold point.”
The interior of JET with a superimposed plasma. (Image: EUROfusion)
A new record has been set by the world’s largest operating tokamak, the Joint European Torus (JET). According to the EUROfusion scientists and engineers who work on JET at the U.K. Atomic Energy Authority’s Culham Centre for Fusion Energy, the landmark experiment, announced on February 9, which produced 59 megajoules of fusion energy over five seconds, is powerful proof of fusion’s potential as a clean energy source.
Taken from above, this photo of the subassembly tool shows the complex system of alignment units used to slowly swing two toroidal field coils (bottom left and right) into position around the vacuum vessel sector. In the background, poloidal field coil #5 sits on the floor of the Assembly Hall, awaiting installation in the assembly pit in mid-September. (Photo: ITER)
Inside the ITER Assembly Hall, aided by a 20-meter-tall sector subassembly tool known as SSAT-2, the first of nine 40-degree wedge-shaped subassemblies that will make up the device’s tokamak is taking shape. On August 30, the ITER Organization announced that all the components of the first subassembly were in place on the SSAT-2. After the wings of the subassembly tool slowly close, locking two vertical coils in place around the outside of a vacuum vessel section that is already wrapped in thermal shielding, the completed subassembly will be ready for positioning in the ITER assembly pit in late October.
ITER CS Module 1 (shown here at right with the General Atomics fabrication team) is being loaded onto a specialized heavy transport vehicle for shipment to Houston, Texas, where it will be placed on a ship for transit to France. (Photo: General Atomics)
After a decade of design and fabrication, General Atomics (GA) is preparing to ship the first module of the central solenoid—the largest of ITER’s magnets—to the site in southern France where 35 partner countries are collaborating to build the world’s largest tokamak and the first fusion device to produce net energy.
Plasma in MAST. (Photo: UKAEA/EUROfusion)
As governments around the world cooperate on the ITER tokamak and, in parallel, race each other and private companies to develop commercial fusion power concepts, it seems that “game-changing” developments are proclaimed almost weekly. Recently, the United Kingdom and China announced new fusion program results.
The outside of the DIII-D tokamak, where testing that supports the development of the Compact Advanced Tokamak has been performed. Photo: General Atomics
Scientists at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility have published research on a compact fusion reactor design they say could be used to develop a pilot-scale fusion power plant. According to General Atomics (GA), which operates DIII-D as a national user facility for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, the Compact Advanced Tokamak (CAT) concept uses a self-sustaining configuration that can hold energy more efficiently than in typical pulsed configurations, allowing the plant to be built at a reduced scale and cost.