ITER CS Module 1 (shown here at right with the General Atomics fabrication team) is being loaded onto a specialized heavy transport vehicle for shipment to Houston, Texas, where it will be placed on a ship for transit to France. (Photo: General Atomics)
After a decade of design and fabrication, General Atomics (GA) is preparing to ship the first module of the central solenoid—the largest of ITER’s magnets—to the site in southern France where 35 partner countries are collaborating to build the world’s largest tokamak and the first fusion device to produce net energy.
Plasma in MAST. (Photo: UKAEA/EUROfusion)
As governments around the world cooperate on the ITER tokamak and, in parallel, race each other and private companies to develop commercial fusion power concepts, it seems that “game-changing” developments are proclaimed almost weekly. Recently, the United Kingdom and China announced new fusion program results.
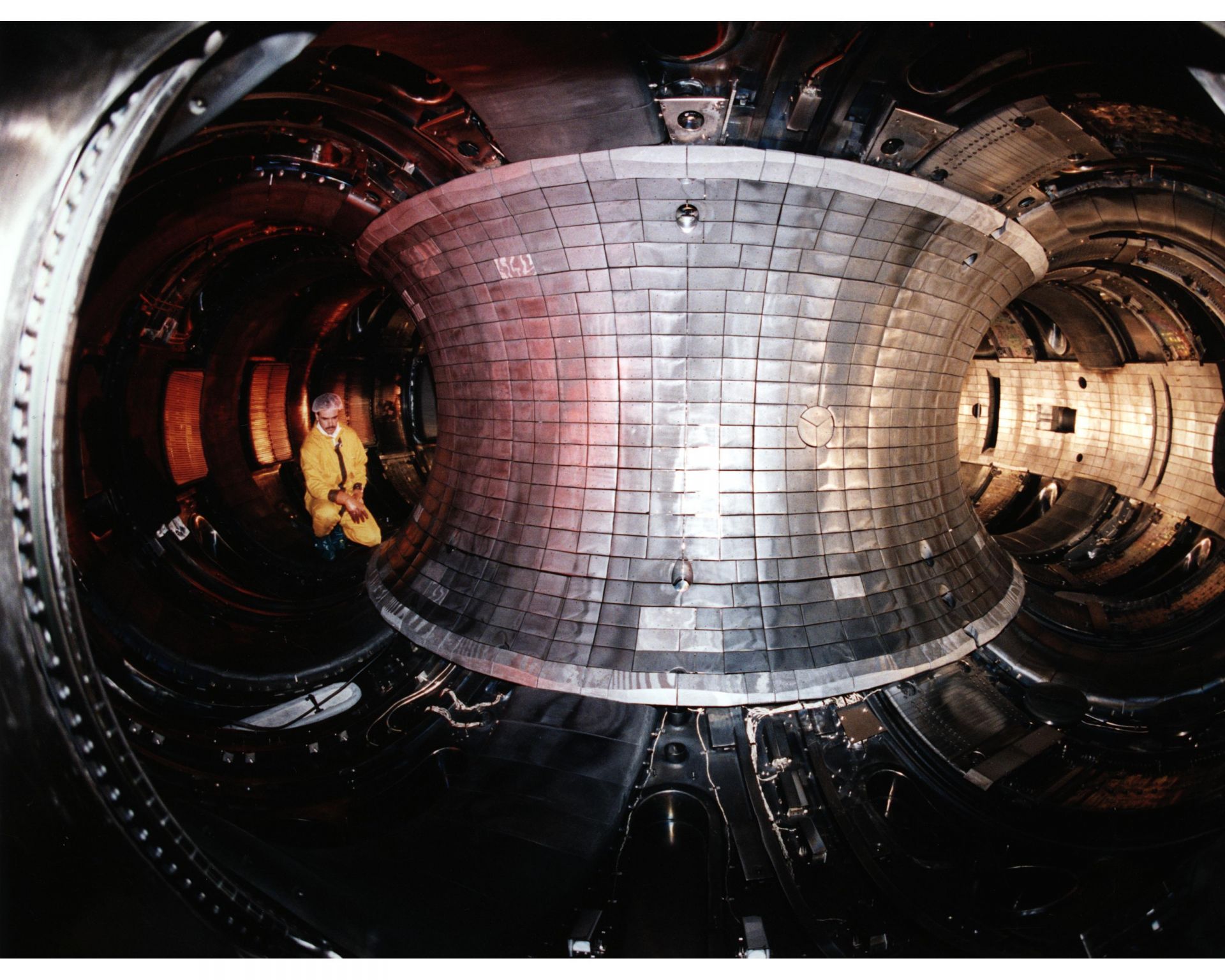
The outside of the DIII-D tokamak, where testing that supports the development of the Compact Advanced Tokamak has been performed. Photo: General Atomics
Scientists at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility have published research on a compact fusion reactor design they say could be used to develop a pilot-scale fusion power plant. According to General Atomics (GA), which operates DIII-D as a national user facility for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, the Compact Advanced Tokamak (CAT) concept uses a self-sustaining configuration that can hold energy more efficiently than in typical pulsed configurations, allowing the plant to be built at a reduced scale and cost.