Savannah River begins test of saltstone disposal mega unit
The Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina will begin a leak tightness test on what it called “the fourth megavolume saltstone disposal unit (SDU)” at the site.

A message from NV5, Inc.
Seconds Matter: Rethinking Nuclear Facility Security for the Modern Threat Landscape
The Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina will begin a leak tightness test on what it called “the fourth megavolume saltstone disposal unit (SDU)” at the site.
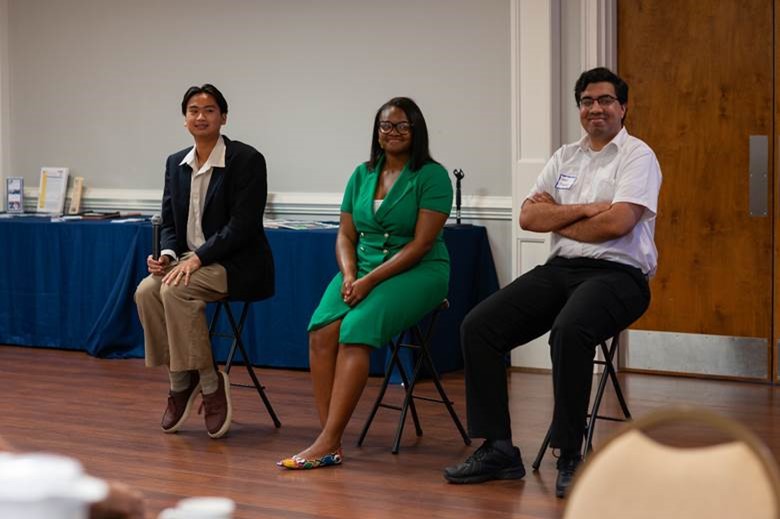

Three college interns from the Savannah River Site were the keynote speakers at a recent Up & Atom Breakfast hosted by Citizens for Nuclear Technology Awareness (CNTA). The breakfast was held at Newberry Hall in Aiken, S.C.
The Department of Energy is planning to ship contaminated process equipment from its Savannah River Site in South Carolina to Waste Control Specialists’ federal low-level radioactive waste facility in Andrews County, Texas.

A three-day Minority Serving Institutions Partnership Program (MSIPP) event, led by Savannah River National Laboratory researcher Simona Hunyadi Murph, was held recently at the South Carolina site, according to a release by the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (DOE-EM). The event included a collaborative workshop, job shadowing, and a tour of the laboratory and Savannah River Site field activities.

For almost four decades, the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina and the Ruth Patrick Science Education Center at the University of South Carolina–Aiken (USC Aiken) have partnered to bring science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) education to the area's kindergarten through 12th grade students.

Work crews at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina recently replaced a motor on a crane in the 70-year-old H Canyon Chemical Separations Facility. H Canyon is the only production-scale, radiologically shielded chemical separations plant in operation in the United States.

Savannah River Nuclear Solutions, the managing and operating contractor at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site near Aiken, S.C., was recognized by the American Heart Association for its commitments to employee health and well-being. The company received a gold level, as measured by the association’s 2022 Workforce Well-being Scorecard.

The Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB) is scheduled to visit the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina the week of May 8 to discuss ongoing safety concerns and the protection of the public and workforce, as well as the DOE’s effectiveness in addressing those concerns.
(Image: DOE)
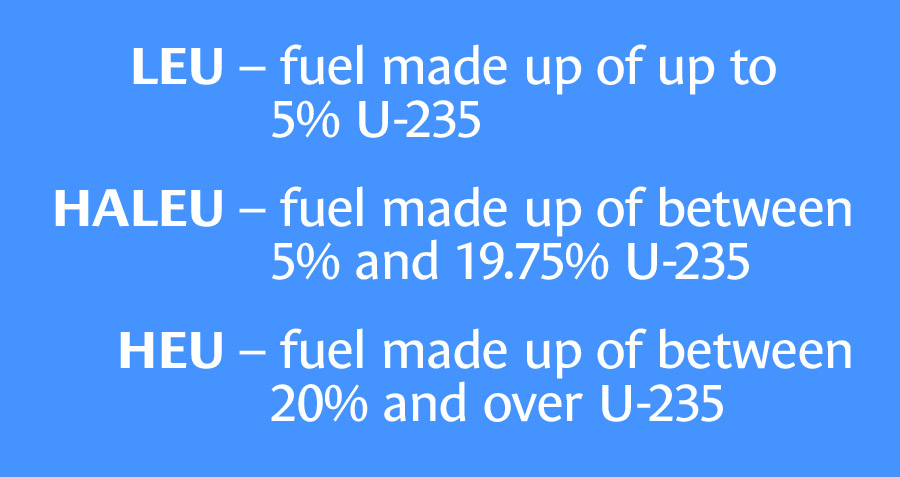
The Department of Energy reported on March 30 that the Savannah River Site’s H Canyon facility recently initiated actions to recycle a small amount of used high-enriched uranium (HEU). SRS is a 310-square-mile DOE site in South Carolina.
The HEU, which is currently stored at the site’s H Area, will be downblended in a few years into high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU), which will help to provide fuel for advanced nuclear reactors in the United States.
The DOE has a brief video available with graphic information about HALEU.
The Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site (SRS) has finalized a high-level waste tank milestones agreement with state and federal regulators that will guide the clean up of the South Carolina site.
The Defense Waste Processing Facility (DWPF) at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina has resumed operations after a completing a processing improvement that the DOE said will enable safer operations and more efficient vitrification of radioactive waste.

Work has begun to prepare the Savannah River Plutonium Processing Facility (SRPPF) at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina for its future national security mission: the manufacturing of plutonium pits for the National Nuclear Security Administration.

The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration and Office of Environmental Management have completed the first shipment of downblended surplus plutonium transuranic (TRU) material from the K Area at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico.

Another calendar year has passed. Before heading too far into 2023, let’s look back at what happened in 2022 for the American Nuclear Society and the nuclear community. In today's post that follows, we have compiled from Nuclear News and Nuclear Newswire what we feel are the top nuclear news stories from April through June 2022.
Stay tuned this week for the top stories from the rest of the past year.
But first:

Two diversion boxes were covered with concrete to permanently close them from future use. Top, one of the boxes is shown prior to it being entombed in concrete. Bottom, the diversion box after workers placed concrete over and around the structure. (Photo: DOE)
Two previously radioactive structures have been successfully entombed at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina. The DOE’s Office of Environmental Management and the Savannah River Mission Completion (SRMC), the DOE’s liquid waste contractor at SRS, placed concrete over and around two concrete structures—called diversion boxes—that contain a series of connection points that allowed high-level radioactive waste to be transferred from one tank or facility to another.
The two boxes have been out of service for more than 30 years. As part of the closure process, both structures were previously filled with grout, rendering them inoperable.
The boxes were the first ancillary structures closed in this way under SRMC’s liquid waste contract. They are located in the F Tank Farm, a grouping of large underground waste-storage tanks. The liquid waste program at SRS has closed eight of the site’s 51 massive waste tanks by filling them with cementitious grout.
Aecon-Wachs, the U.S. division of Aecon Nuclear, has been tapped to support the Department of Energy’s goal of repurposing the unfinished Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina. Known as Building 226-F, the facility is being transitioned into the Savannah River Plutonium Processing Facility (SRPPF) to produce plutonium pits for the nation’s stockpile of nuclear weapons.

Contractor employees at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina recently exceeded their plutonium downblending goal for 2022 ahead of schedule as part of the ongoing activities to remove Pu from the state, the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced.

The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced on October 18 that it has begun the process of transferring primary authority of South Carolina’s Savannah River Site (SRS) to the National Nuclear Security Administration, with the transfer expected to be completed in 2025.

The Department of Energy has extended Savannah River Nuclear Solutions’ (SRNS) management and operating contract at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina for up to an additional five years. The announcement was made recently 29 by engineering company Fluor, which leads the SRNS joint venture, along with Newport News Nuclear and Honeywell.

The first 36 students graduated this summer from Savannah River Mission Completion’s (SRMC) Nuclear Fundamentals Certificate program. SRMC is the Department of Energy’s liquid waste contractor at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina.
The program, which is a partnership between Aiken Technical College (ATC) and SRMC, is in its inaugural year.