Concept art of a fission surface power system on the surface of the moon. (Image: Lockheed Martin)
The “space race” is once again making headlines, with technology worthy of the 21st century. Like the Cold War–era competition, this race too is about showcasing power—but this time it's nuclear power.
A new article in Power Technology examines the competing efforts of the United States, Russia, and China as they strive to be the first to put a nuclear reactor on the moon to power a lunar base, detailing the technical challenges and international rivalries.
A still image from a NASA video illustrating power needs on the lunar surface. (Image: NASA)
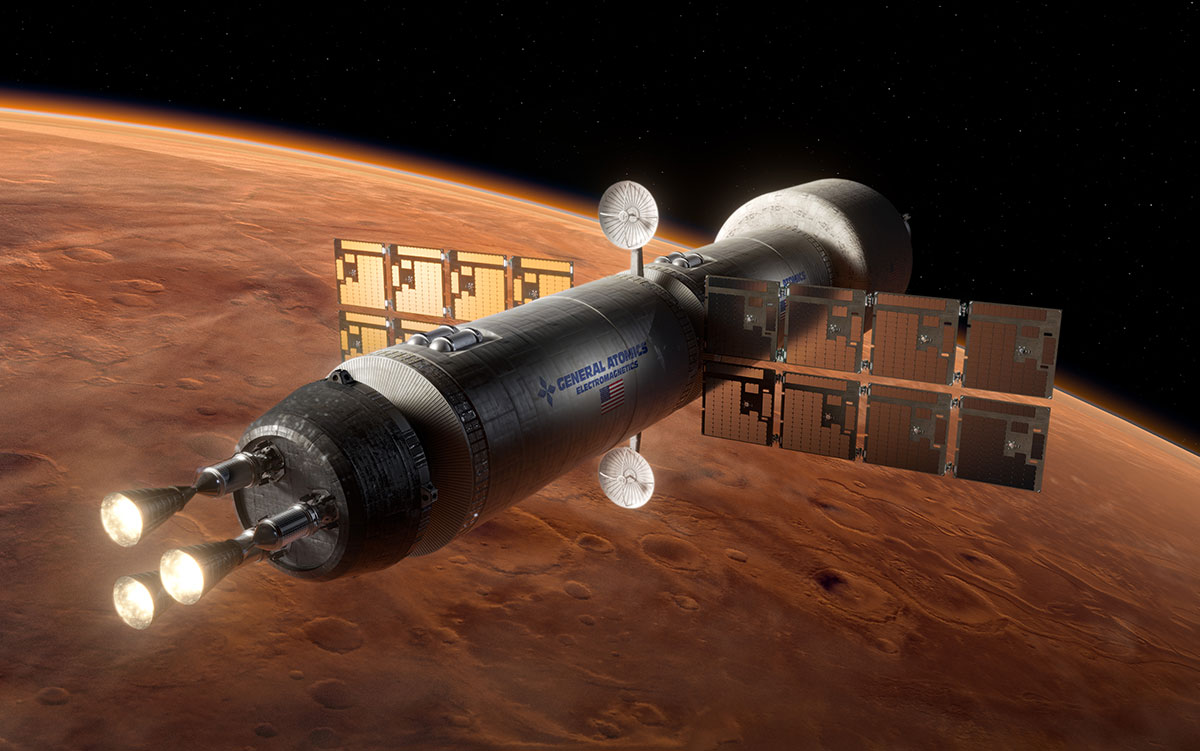
After the Trump administration’s new push to get a nuclear reactor on the moon by 2030 was first reported by Politico last month, media played up the shock value for people new to the concept. Few focused on the technical details of the new plan for lunar fission surface power (FSP), which halts and replaces a program that began under the first Trump administration with an early hope of getting a reactor on the moon by the end of 2026. Now, the focus is on streamlining NASA’s internal processes to support commercial space companies that can build a reactor with more than twice the power and mass and have it ready for launch by 2030.
In this artist’s concept, a notional spacecraft with a high-power plasma thruster is powered by kilowatt-level radiovoltaics. (Image: DARPA/Alan Clarke)
You could call it a power contest. Teams picked for a new research program from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will compete to design radiovoltaic cells that can outperform others in measured power density and endure high-flux radiation from a U.S. Army Research Lab linear accelerator. The top teams will strive to make it through a second downselect based on the performance of cells sequestered in time capsules and subjected to even more punishing high-flux radiation. Concepts that make it to the bonus period have a chance to be built into radioisotope-fueled power systems uniquely suited to high-radiation regions of space or dark, remote places on Earth.
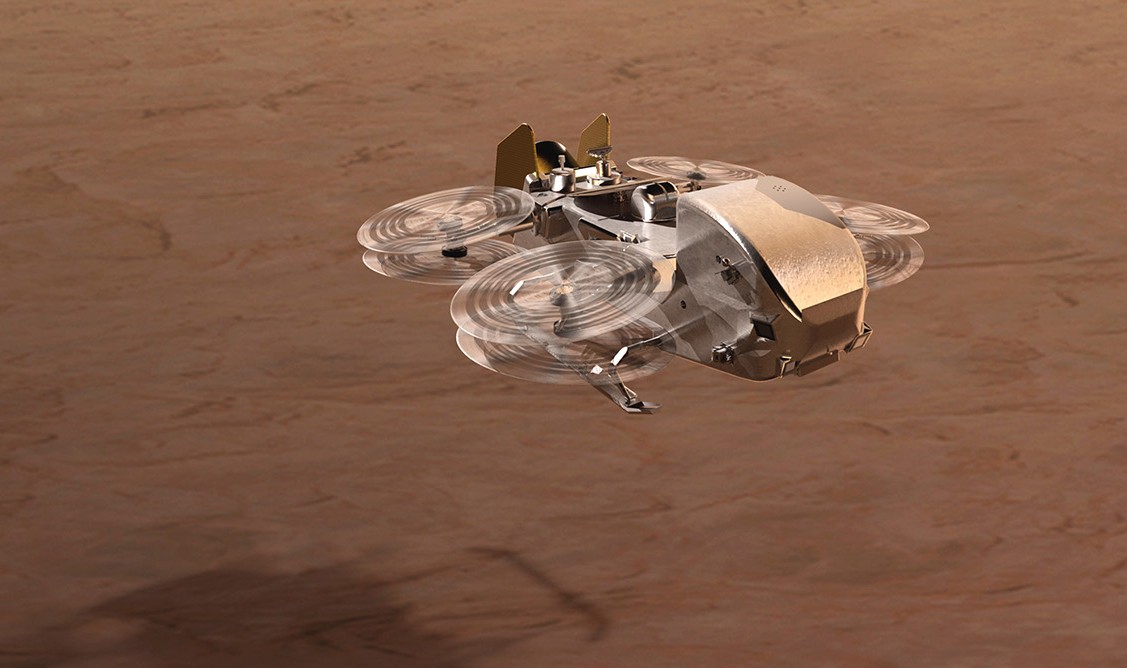
Artist’s impression of NASA’s Dragonfly approaching a landing site on Saturn’s moon Titan. Essentially a flying chemistry lab, along with cameras and other science instrumentation, Dragonfly will travel between dozens of landing sites on Titan’s surface to investigate the chemical origins of life. (Image: NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Steve Gribben)
Curiosity landed on Mars sporting a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) in 2012, and a second NASA rover, Perseverance, landed in 2021. Both are still rolling across the red planet in the name of science. Another exploratory craft with a similar plutonium-238–fueled RTG but a very different mission—to fly between multiple test sites on Titan, Saturn’s largest moon—recently got one step closer to deployment.
On April 25, NASA and the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) announced that the Dragonfly mission to Saturn’s icy moon passed its critical design review. “Passing this mission milestone means that Dragonfly’s mission design, fabrication, integration, and test plans are all approved, and the mission can now turn its attention to the construction of the spacecraft itself,” according to NASA.
The H9 Hall thruster, developed at UMich’s Plasmadynamics and Electric Propulsion Laboratory. (Image: William Hurley/University of Michigan)
Seeking spacecraft that can “maneuver without regret,” the U.S. Space Force is investing $35 million in a national research team led by the University of Michigan to develop a spacecraft with an onboard microreactor to produce electricity, with some of that electricity used for propulsion. But this spacecraft would not be solely dependent on nuclear electric propulsion—it would also feature a conventional chemical rocket to increase thrust when needed.
Understanding how several different metals—such as the contents of PNNL’s space-bound cube—react to radiation in space will help scientists understand the potential impact of radiation on space travelers. (Photo: Eddie Pablo/PNNL)
When a SpaceX rocket lifted off from Kennedy Space Center on September 10 (see video here), sending a crewed commercial mission into low Earth orbit, an experiment designed by Pacific Northwest National Laboratory was onboard. Several high-purity metal samples will orbit Earth and absorb cosmic radiation for five days—including that from the Van Allen radiation belt—to help the lab answer questions about the radiation environment for manned space missions, according to a news release from PNNL.
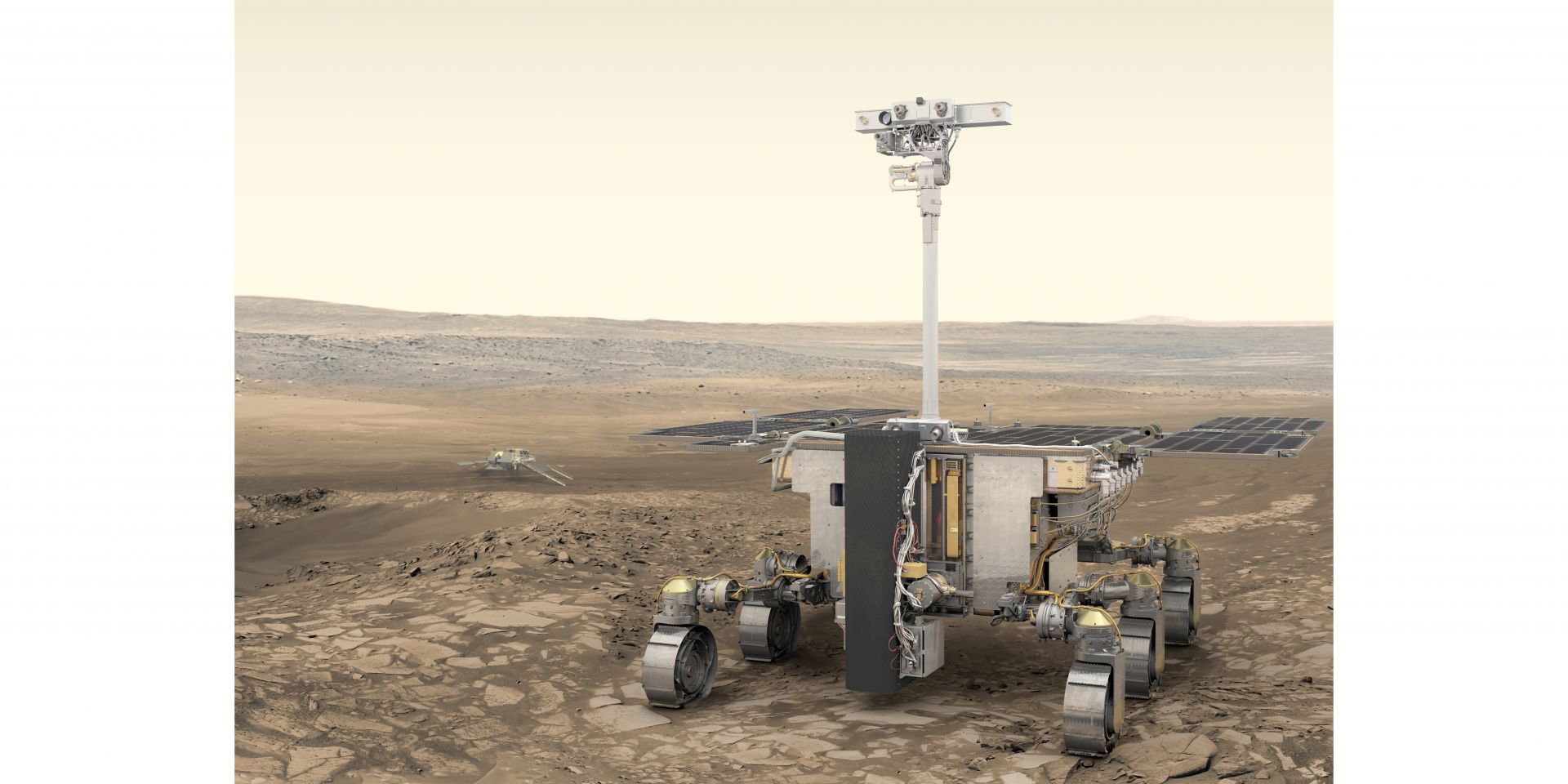
Concept art of ESA’s Rosalind Franklin rover. (Image: ESA/ATG medialab)
Europe’s first Mars rover—named Rosalind Franklin—was months away from a planned September launch when the European Space Agency (ESA) convened a meeting a few weeks after Russia’s February 2022 invasion of Ukraine. The ESA Council unanimously agreed on “the present impossibility” of working with Roscosmos as its launch partner and later decided to reboot its ExoMars mission with a new lander, new partners, and a new launch date.
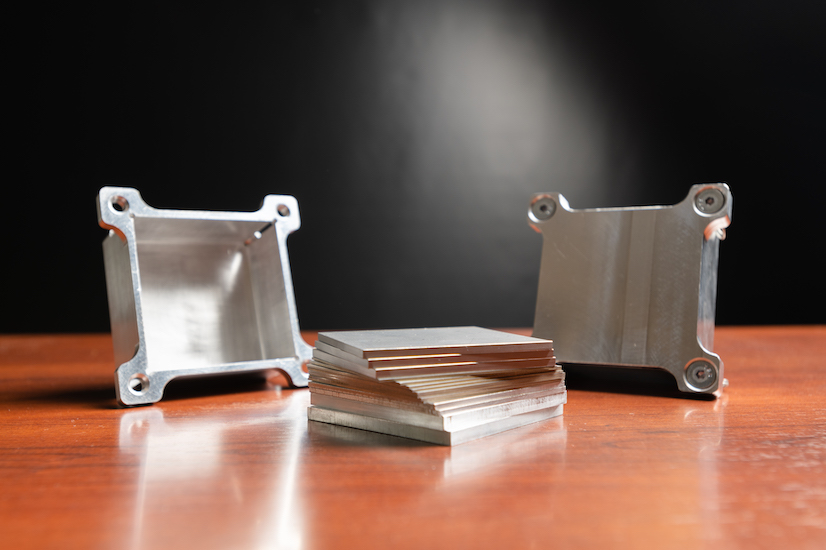
Fabricated Z1 heat source in transfer port. (Photo: Zeno Power)
Zeno Power, a developer of commercial radioisotope power systems (RPSs), announced on October 26 that it has completed the design, fabrication, and testing of its Z1 strontium-90 heat source. According to Zeno, they have tested the first commercially developed radioisotope heat source and reached a key milestone for Zeno to begin delivering RPSs to customers in 2025.
Concept art of a nuclear thermal propulsion system. (Image: USNC)
Ultra Safe Nuclear (USNC) announced on October 17 that it had been awarded a contract by NASA to develop and mature space nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) systems to advance the nation’s cislunar capabilities. Under the contract, USNC says it will manufacture and test proprietary fuel and simultaneously collaborate with its commercial partner, Blue Origin, to mature the design of an NTP engine optimized for near-term civil science and cislunar missions.
ORNL has developed an automated metrology system to produce Pu-238 pellets. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy recently shipped half a kilogram of plutonium oxide pellets from Oak Ridge National Laboratory to Los Alamos National Laboratory, the agency announced July 18, marking the largest such shipment since the DOE restarted domestic plutonium-238 production over a decade ago.
(Photo: Nielander/WikiCommons)
Westinghouse Electric Company says its eVinci microreactor technology is “100 percent factory built and assembled before it is shipped in a container to any location.” And “any location” is not restricted to planet Earth, given the company’s goal of sending a scaled-down version of eVinci to the lunar surface or on a mission to provide power in other space applications.
Rendering of a radioisotope-powered satellite. (Image: Zeno Power Systems)
Zeno Power Systems was awarded a $30 million contract to build a radioisotope-powered satellite for the U.S. Air Force by 2025. According to a SpaceNews article announcing the development and quoting company cofounder and chief executive officer Tyler Bernstein, the four-year contract is a “strategic funding increase” (STRATFI) agreement that provides $15 million in government funds, matched by $15 million from private investors.
Artist’s concept of the DRACO spacecraft, which will demonstrate a nuclear thermal rocket engine. (Image: DARPA)
NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) have announced they will collaborate on plans to launch and test DARPA’s Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations (DRACO). DARPA has already worked with private companies on the baseline design for a fission reactor and rocket engine—and the spacecraft that will serve as an in-orbit test stand—and has solicited proposals for the next phase of work. Now NASA is climbing on board, deepening its existing ties to DRACO’s work in nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) technology—an “enabling capability” required for NASA to meet its Moon to Mars Objectives and send crewed missions to Mars. NASA and DARPA representatives announced the development at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics SciTech Forum in National Harbor, Md., on January 24.
A rendering of Helga and Zohar side by side aboard the Orion spacecraft. (Image: NASA/Lockheed Martin/DLR)
NASA’s Artemis I mission, successfully launched at 1:47 a.m. EST on November 16 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, will travel 40,000 miles beyond the moon—farther from Earth than any human-crewed space mission has flown before. The historic trip was launched by the world’s largest rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS), nearly 50 years after NASA last sent humans to the moon. And while no humans are on board the Orion spacecraft, two fabricated crew members—“Luna Twins” Helga and Zohar—were assembled with thousands of sensors to obtain the best estimates yet of cosmic radiation exposure to human tissues during space travel.