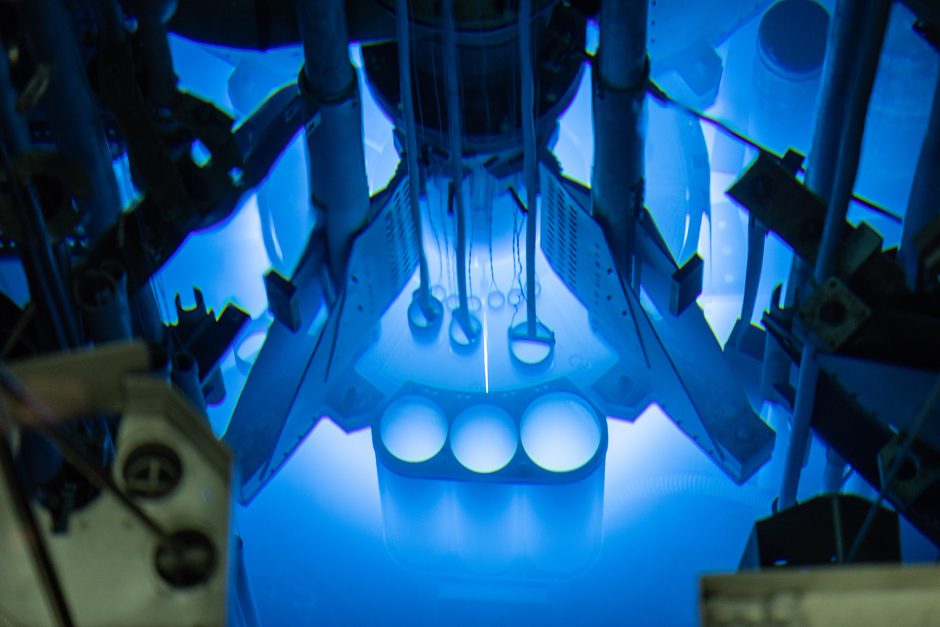
The 10 MW core of MURR contributes to the global supply of radioisotopes for medical radiopharmaceuticals and research. (Photo: MURR)
The University of Missouri Research Reactor (MURR) is the latest member of Nuclear Medicine Europe, an industry association for the radiopharmaceutical and molecular imaging industry in Europe, the University of Missouri announced July 17.
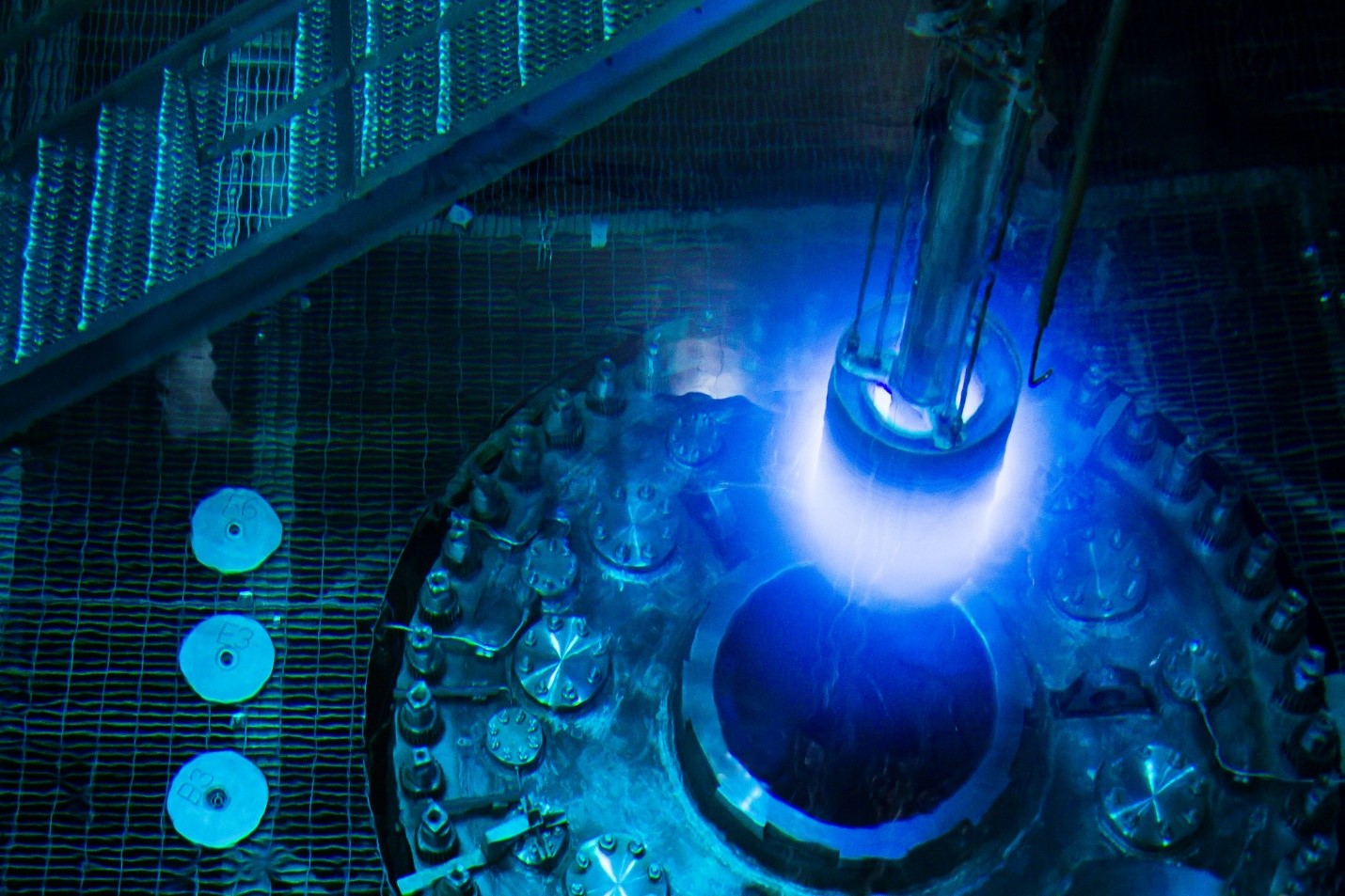
ORNL’s High Flux Isotope Reactor, where Sr-89 and other radioisotopes are produced, photographed during a 2015 refueling. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy’s Isotope Program (DOE IP) announced last week that it would end its “active standby” capability for strontium-82 production about two decades after beginning production of the isotope for cardiac diagnostic imaging. The DOE IP is celebrating commercialization of the Sr-82 supply chain as “a success story for both industry and the DOE IP.” Now that the Sr-82 market is commercially viable, the DOE IP and its National Isotope Development Center can “reassign those dedicated radioisotope production capacities to other mission needs”—including Sr-89.
A vial of Ac-225 produced by Niowave stands next to its lead shipping pig. (Photo: Niowave)
According to the Council on Radionuclides and Radiopharmaceuticals, more than 82,000 nuclear imaging procedures using nuclear medicine are performed throughout the world every day. To administer these vital medical procedures, radiopharmaceutical companies and hospitals rely on a handful of producers of medical radioisotopes.
LLNL and Penn State researchers developed a new approach to study and purify medical isotopes, including actinium. (Image: Thomas Reason/LLNL)
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and Pennsylvania State University have demonstrated that a natural protein found bonded to rare earth elements can be recovered and used as a tool to purify and effectively manage radioactive metals that show promise for cancer therapy and the detection of illicit nuclear activities.
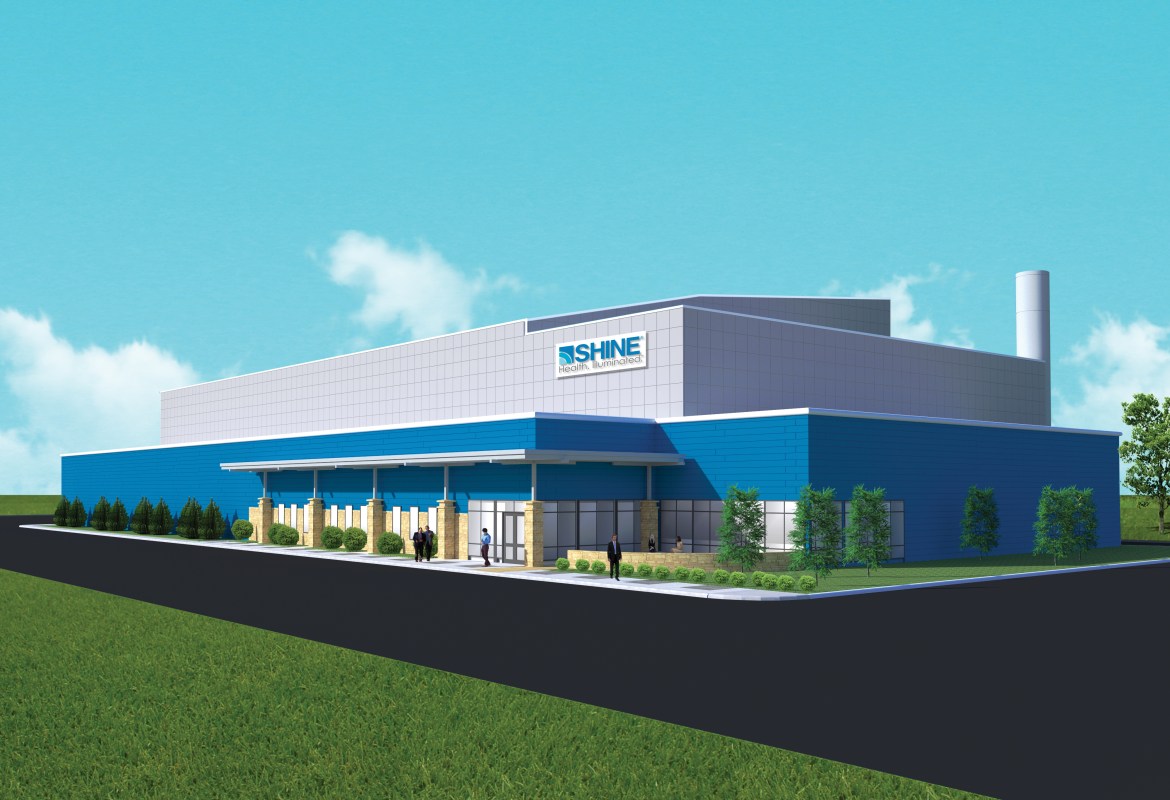
A rendering of the SHINE medical isotope production facility planned for construction in Veendam, the Netherlands. (Image: Shine)
SHINE Medical Technologies plans to locate its European medical isotope production facility in the Netherlands after a yearlong search and a review of more than 50 proposals from sites across Europe. The company announced on May 20 that construction at the site should begin in 2023 with commercial production starting in late 2025.