BWXT, Westinghouse partner for nuclear new builds in Canada
BWXT Canada, a subsidiary of BWX Technologies, is partnering with Westinghouse Electric Company to build new nuclear projects in Canada and globally.

A message from NV5, Inc.
Seconds Matter: Rethinking Nuclear Facility Security for the Modern Threat Landscape
BWXT Canada, a subsidiary of BWX Technologies, is partnering with Westinghouse Electric Company to build new nuclear projects in Canada and globally.
Comments on the rule are being accepted until February 28
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission will host two public meetings in early January to educate and field questions about a proposed rule to allow more flexibility in licensing nuclear plants.

Just one day after Urenco USA (UUSA) was picked by the Department of Energy as one of six contractors eligible to compete for future low-enriched uranium task orders, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission on December 11 formally approved the company’s license amendment request to boost uranium enrichment levels at its Eunice, N.M., enrichment facility to 10 percent fissile uranium-235—up from its current limit of 5.5 percent.

In a one-on-one interview with the American Nuclear Society’s chief executive officer/executive director Craig Piercy, Nuclear Regulatory Commission commissioner Annie Caputo shared her journey in the nuclear community and her vision for the future of nuclear energy.

Westinghouse Electric Company’s eVinci Advanced Logic System (ALS) Version 2 (v2) instrument and control (I&C) platform has received approval from the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission through a final safety evaluation report on two topical reports.
The eVinci is now the first and only microreactor with an I&C system approved by the NRC, which opens a path to autonomous operation. The approvals also allow the ALS v2 platform to be used by any reactor currently in the U.S. fleet.
A nuclear engineer, former reactor operator, and nuclear navy educator earned U.S. Senate approval today to take a seat on the Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
Matthew Marzano was confirmed in a 50–45 vote in the Senate and steps into an existing five-year term that will expire June 30, 2028. He joins the five-member commission, which has been without a tiebreaker vote since June 2023, when Jeff Baran’s term expired.
Marzano brings more than a decade of industry experience both working in nuclear plants and advising energy policy on Capitol Hill.
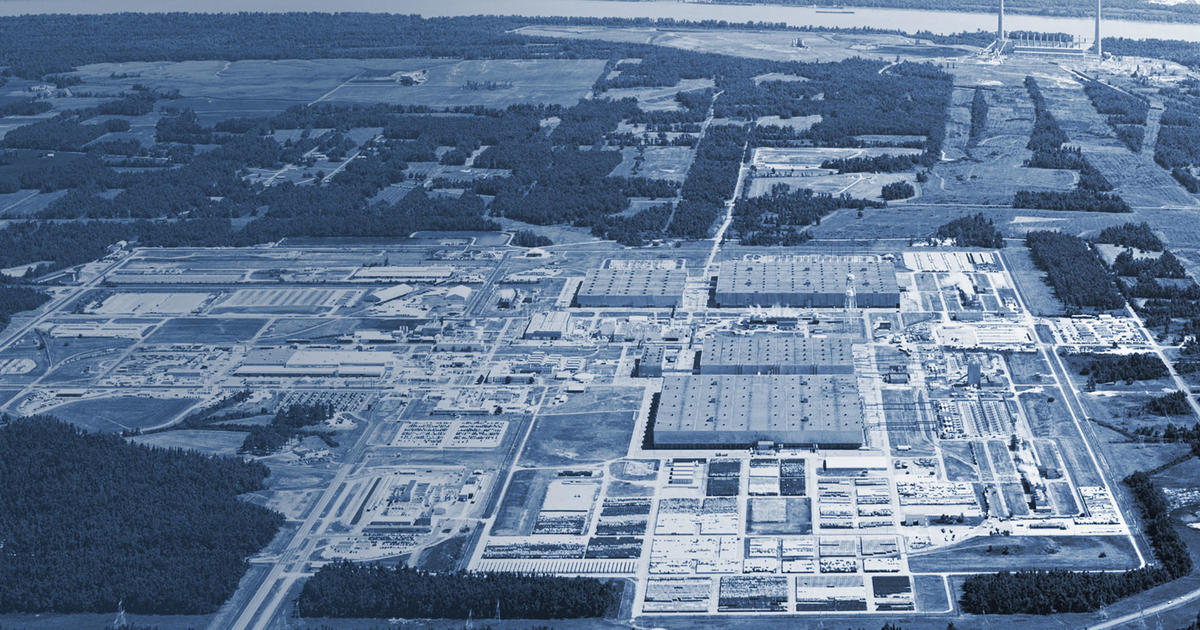
Global Laser Enrichment (GLE) has acquired a 665-acre parcel of land for its planned Paducah Laser Enrichment Facility (PLEF) in Kentucky.

Marzano
The U.S. Senate Environment and Public Works Committee voted 10–9 last week to advance the nomination of Matthew Marzano to serve on the Nuclear Regulatory Commission. It was a party-line vote, with all Democrats supporting Marzano and all Republicans voting “no.”
Marzano was nominated by President Biden in July to fill the open NRC seat, and the EPW Committee held a hearing in September on his nomination. His nomination will now go to the Senate for a vote, but it is not certain whether that will happen before the end of the year, in which case his nomination process would start over in 2025.
The five-member commission has been without a tiebreaker vote since June 2023 when Jeff Baran’s term expired.
 I like to say that I ended up at Massachusetts Institute of Technology because of my father. He saw that I seemed intimidated by the prospect of going there, so he dared me, figuring I would take the bait. And I did.
I like to say that I ended up at Massachusetts Institute of Technology because of my father. He saw that I seemed intimidated by the prospect of going there, so he dared me, figuring I would take the bait. And I did.
I graduated with a bachelor’s and master’s in physics in 1968, and two days later I married my classmate, Mike Marcus. After a summer at Ft. Monmouth, where I studied radiation damage to semiconductors, we spent the next few years back at MIT in grad school—Mike in electrical engineering and I in nuclear engineering. It was Mike who steered me toward nuclear engineering, noting that my interest was radiation damage to materials, and the nuclear engineering department was doing more of that than the physics department.

The Nuclear Regulatory Commission announced yesterday that it has directed staff to issue construction permits to Kairos Power for the company's proposed Hermes 2 nonpower test reactor facility to be built at the Heritage Center Industrial Park in Oak Ridge, Tenn. The permits authorize Kairos to build a facility with two 35-MWt test reactors that would use molten salt to cool the reactor cores.
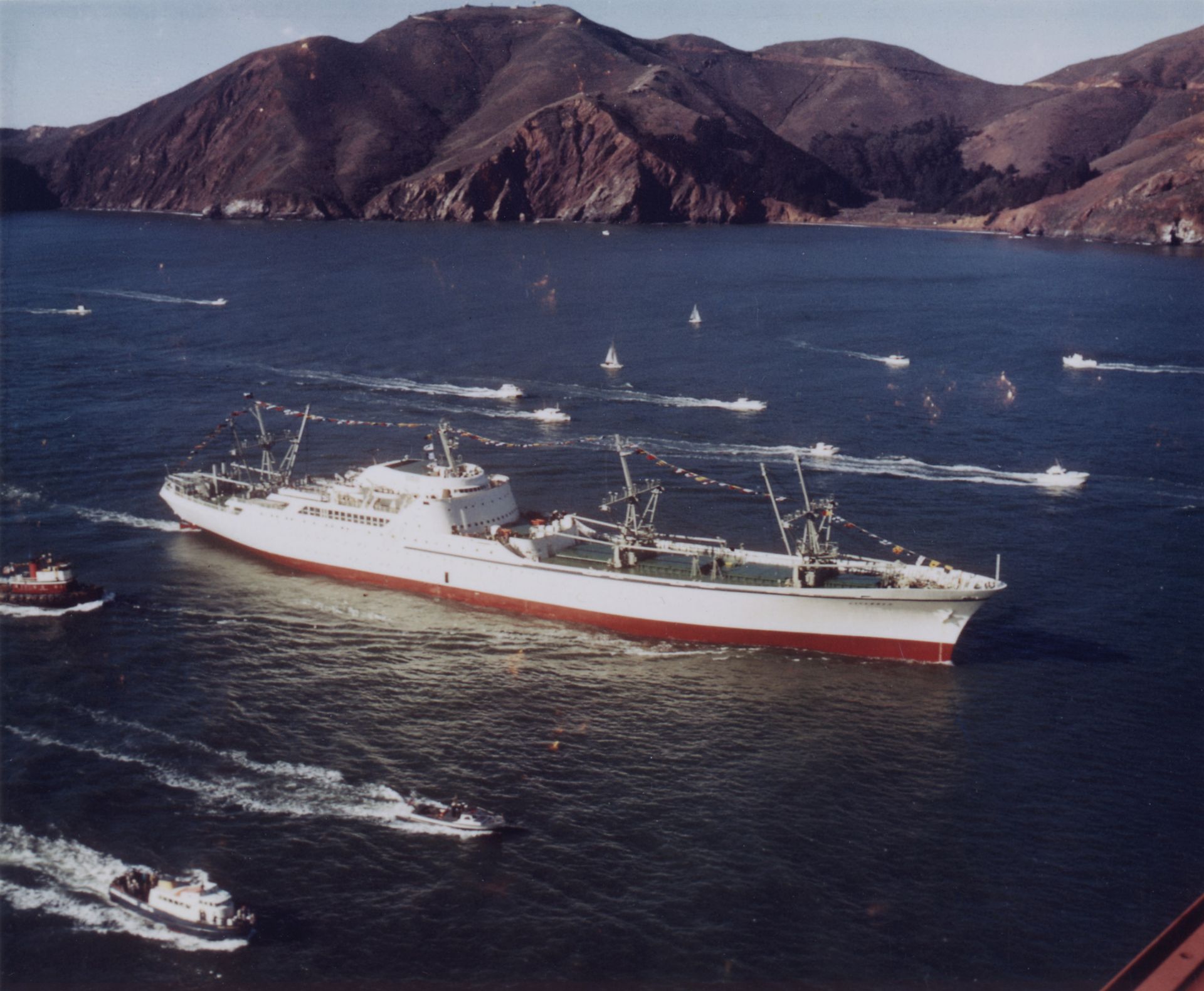

It’s safe to say that readers of Nuclear News are familiar with decommissioning. It’s even safe to assume that experienced decommissioning practitioners are familiar with the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) and how it applies to typical projects. What’s different about the N.S. Savannah is that the entire project site is a historic property—and in fact, is a federally owned National Historic Landmark (NHL), a status that confers the highest level of protection under law. Federal owners of NHLs are obligated to minimize harm in both planning and actions. Distilled to its salient point, no federal owner of an NHL should destroy it if there’s a reasonable alternative. That level of preservation is not what we normally associate with nuclear decommissioning. This perfectly summarizes the challenges, and opportunities, that decommissioning Savannah offered. The story of how the Maritime Administration (MARAD) managed these two otherwise contradictory processes showcases how historic preservation and decommissioning can positively intersect, provides a pathway for other historic facilities, and further adds to the already illustrious history of one of our nation’s significant 20th century landmarks.

Some 30 nuclear engineering departments at universities across the United States graduate more than 900 students every year. These young men and women are the present and future of the domestic nuclear industry as it seeks to develop and deploy advanced nuclear energy technologies, grow its footprint on the power grid, and penetrate new markets while continuing to run the existing fleet of reactors reliably and economically.

Holtec International announced that it has completed the campaign to transfer Diablo Canyon’s spent nuclear to dry storage ahead of its planned schedule, paving the way for the continued operation of the central California nuclear power plant.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has published a proposed rule that has been almost five years in the making: Risk-Informed, Technology-Inclusive Regulatory Framework for Advanced Reactors. The rule, which by law must take its final form before the end of 2027, would establish risk-informed, performance-based techniques the NRC can use to review and license any nuclear power reactor. This is a departure from the two licensing options with light water reactor–specific regulatory requirements that applicants can already choose.
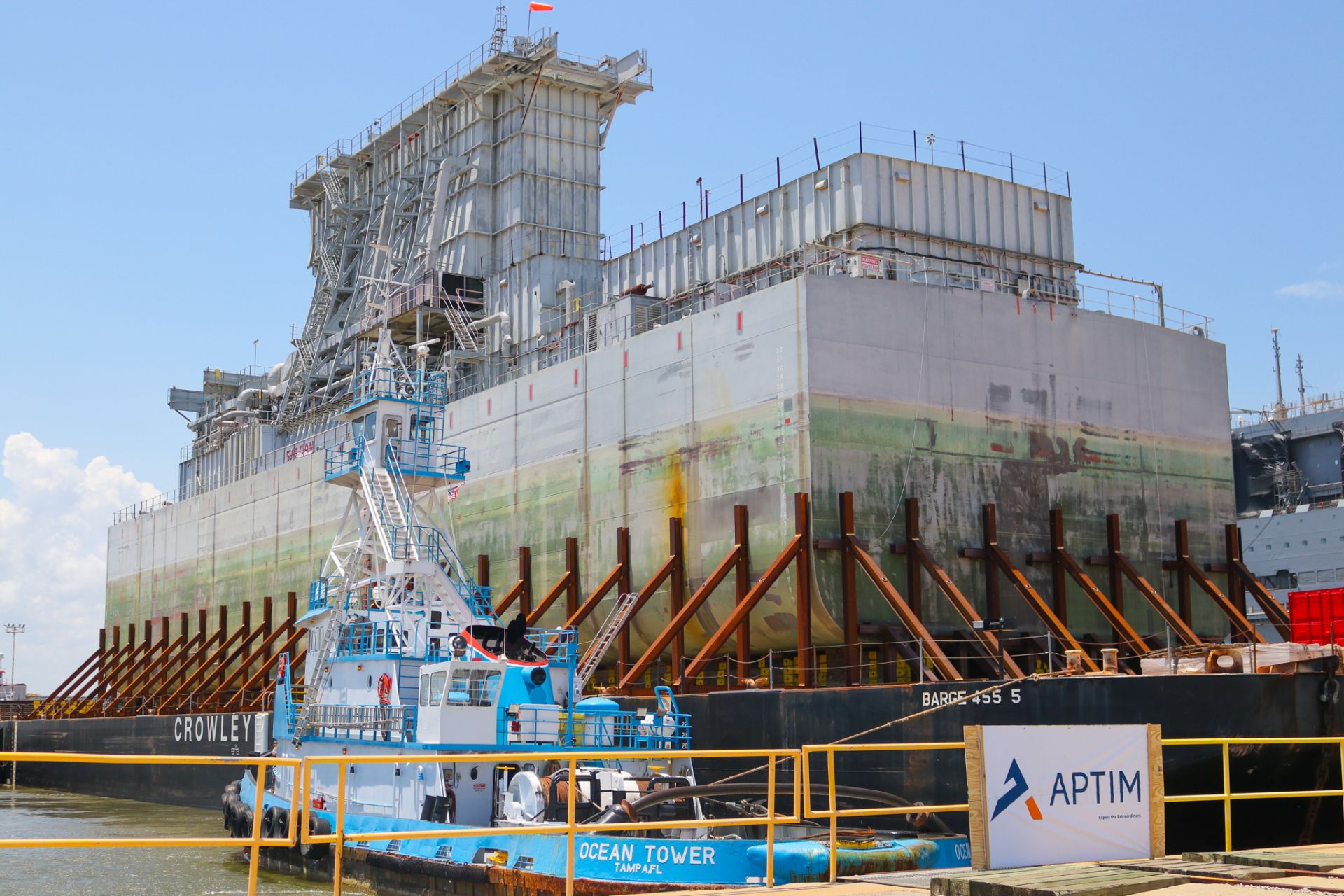

The U.S. Navy’s Surface Ship Support Barge, converted in the 1960s from a WWII T2 tanker to a support barge to accept spent nuclear fuel during the refueling of nuclear aircraft carriers, was dismantled and disposed of by the nuclear decommissioning company APTIM as a first-of-its-kind vessel dismantlement project for the Navy. The project was executed under contract with Naval Sea Systems Command; however, regulatory oversight was accomplished through an interagency framework agreement between the U.S. Navy and the Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
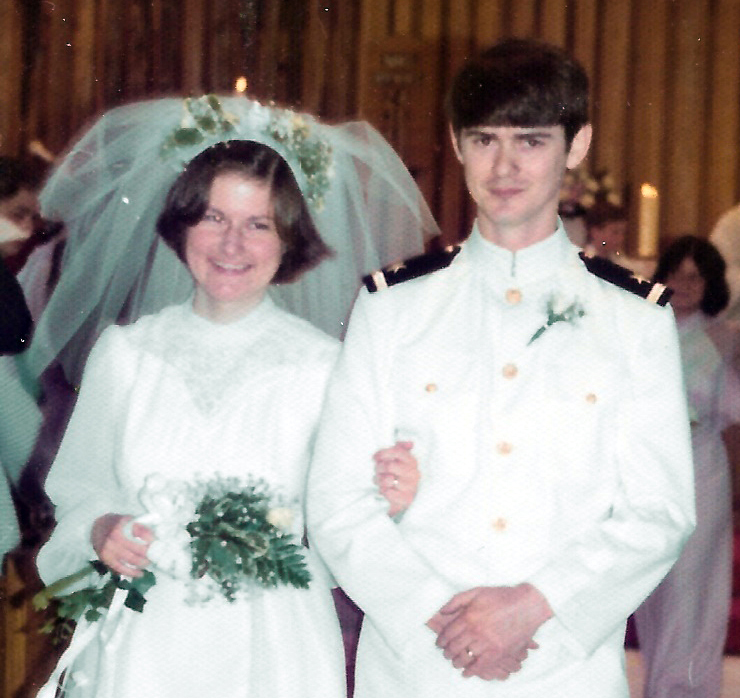

Julie and Jim Byrne on their wedding day, May 22, 1976.
As I was finishing my studies at the University of Pittsburgh and about to graduate with a degree in civil engineering, I talked to a local navy recruiter about a position with the Seabees. He told me there were no Seabee billets, but that the navy had a nuclear power program that might interest me. When I said yes, it wasn’t long before I was whisked off to Washington, D.C., to interview with someone named Admiral Hyman Rickover. The one thing they told me was to stand up to “the kindly old gentleman.”
The day started with technical interviews and then I was ushered into the admiral’s office. I was a typical college student, and I spent my money on food and beer and not on haircuts. On seeing me, Admiral Rickover told me that I looked like a girl. After a bit of back-and-forth, he asked me a couple of other questions. His last comment to me was that I must know something and to get out of his office.
Legislative proposals focused on streamlining the U.S. nuclear energy export process have circulated on Capitol Hill for several years, notably aimed at establishing a single point of contact in the government to simplify global nuclear projects.
The most recently introduced International Nuclear Energy Act (INEA) proposal (S. 826) promotes engagement with partner nations to develop a civil nuclear export strategy and to offset China’s and Russia’s growing influence on international nuclear energy development.

The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is asking for presentation proposals for a virtual workshop on the storage and transportation of TRISO and metal spent nuclear fuels for advanced reactor designs now under development.
Statement from ANS on Supreme Court’s decision to grant certiorari to NRC v. Texas
Washington, D.C. — The American Nuclear Society (ANS), a nonprofit representing over 10,000 professionals in the fields of nuclear science and technology, issued the following statement regarding the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision to grant certiorari to Nuclear Regulatory Commission v. Texas:
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is seeking comment on a proposed rule for a generic environmental impact statement for licensing new reactors. According to the NRC, the statement uses a technology-neutral framework and plant/site parameters to identify environmental issues common to new reactors as well as those issues needing project-specific analysis.