SHINE’s isotope production building, called the Chrysalis, under construction in October 2022. (Photo: SHINE)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has issued its final safety evaluation report (SER) related to the operating license application for SHINE Technologies' large-scale medical isotope production facility, known as The Chrysalis, in Janesville, Wis. The SER documents the results of NRC staff’s technical and safety review of SHINE’s application. SHINE announced the NRC’s decision on February 27.
A record of decision concerning the proposed issuance of the operating license will be published by the NRC at a future date.
The La Crosse site in 2019 with major decommissioning completed. The coal-fired Genoa plant is in the background. (Photo: EnergySolutions)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission announced that it has released the site of the La Crosse boiling water reactor in Wisconsin for unrestricted public use. The action comes after the NRC found that EnergySolutions subsidiary LaCrosseSolutions had met the agency’s radiation protection standards in decommissioning the nuclear power plant.
Since 1957, the Advisory Committee on Reactor Safeguards has had a continuing statutory responsibility for providing independent reviews of, and advising on, the safety of proposed or existing reactor facilities and the adequacy of proposed reactor safety standards in the United States.
The 1957 amendment to the Atomic Energy Act of 1954 established the Advisory Committee On Reactor Safeguards as a statutory committee with an independent advisory role and the responsibility to “review safety studies and facility license applications” and advise the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission “with regard to the hazards of proposed or existing reactor facilities and the adequacy of reactor safety standards.” With the enactment of the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974, the ACRS was assigned to the newly established Nuclear Regulatory Commission with its statutory requirements intact.
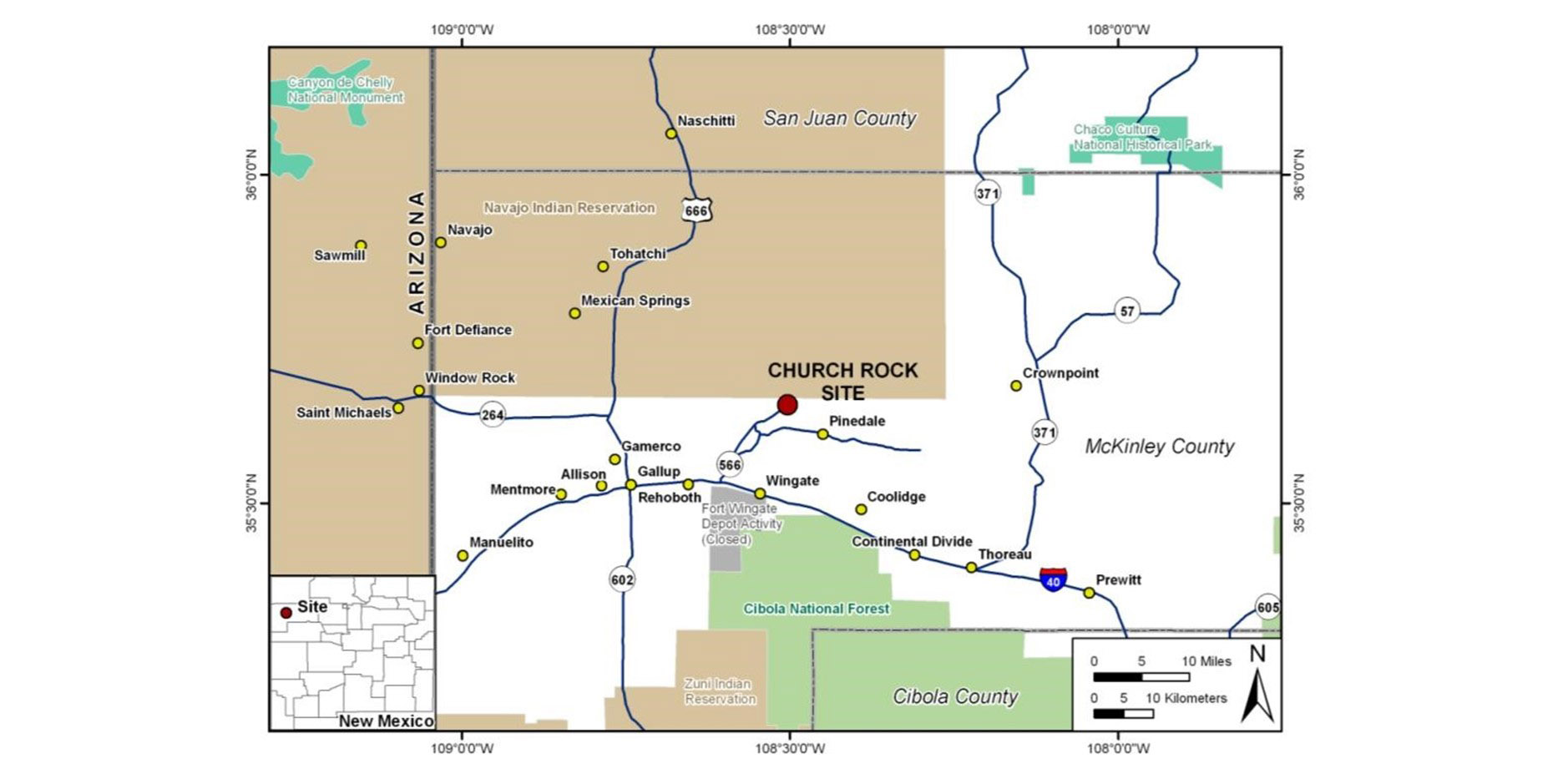
A map of the Church Rock uranium mill site location. (Image: NRC)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has approved a plan by United Nuclear Corp. (UNC) to dispose of mine waste from the Northeast Church Rock mine site in New Mexico at the company’s nearby uranium mill and tailings disposal site.
The student social media ambassadors at the IAEA Nuclear Power Ministerial in October 2022 (left to right): Sam Dotson from the University of Illinois, Madison Gitzen from Pennsylvania State University, Peter Hotvedt from the University of Michigan, Jillian Newmyer from Oregon State University, Brienna Johnson from the University of Wisconsin–Madison, and Pearle Lipinski from Ohio State University.
Pearle Lipinski is a nuclear engineering Ph.D. student in Ohio State University’s Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (MAE). In October 2022, at the International Atomic Energy Agency’s fifth International Ministerial Conference on Nuclear Power in the 21st Century (also known as the Nuclear Power Ministerial, or NPM), she acted as a student social media ambassador, where she was a “huge success in getting the word out,” according to Lei Raymond Cao, director of the OSU nuclear engineering program.
A view of the completed demo cascade. (Photo: Centrus)
Centrus Energy announced February 9 that it has finished assembling a cascade of uranium enrichment centrifuges and most of the associated support systems ahead of its contracted demonstration of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) production by the end of 2023. When the 16-machine cascade begins operating inside the Piketon, Ohio, American Centrifuge Plant, which has room for 11,520 machines, it will be the first new U.S.-technology based enrichment plant to begin production in 70 years.
A rendering of the TRISO-X fuel fabrication facility. (Image: DOE)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission recently presented its proposed 30-month licensing review timeline of TRISO-X’s planned fuel fabrication facility at the project’s first-ever public meeting in Oak Ridge, Tenn.
TRISO-X, a subsidiary of X-energy, has requested a 40-year license to possess and use special nuclear material to manufacture advanced fuel. The facility would be the first-ever commercial-scale fuel fabrication plant focused on using high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU).
SHINE’s Chrysalis production building, under construction in October 2022. (Photo: SHINE)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has issued the final supplemental environmental impact statement (EIS) for SHINE Technology’s application for a license to operate a medical isotope production facility in Janesville, Wis.
A rendering of ISP’s proposed interim storage facility in West Texas. (Image: ISP)
A federal appeals court rejected a lawsuit brought by environmental groups challenging the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s licensing of a consolidated interim storage facility (CISF) for spent nuclear fuel in Andrews County, Texas. The U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit found that the NRC reasonably applied its hearing regulations when approving Interim Storage Partners’ (ISP) license for the facility.
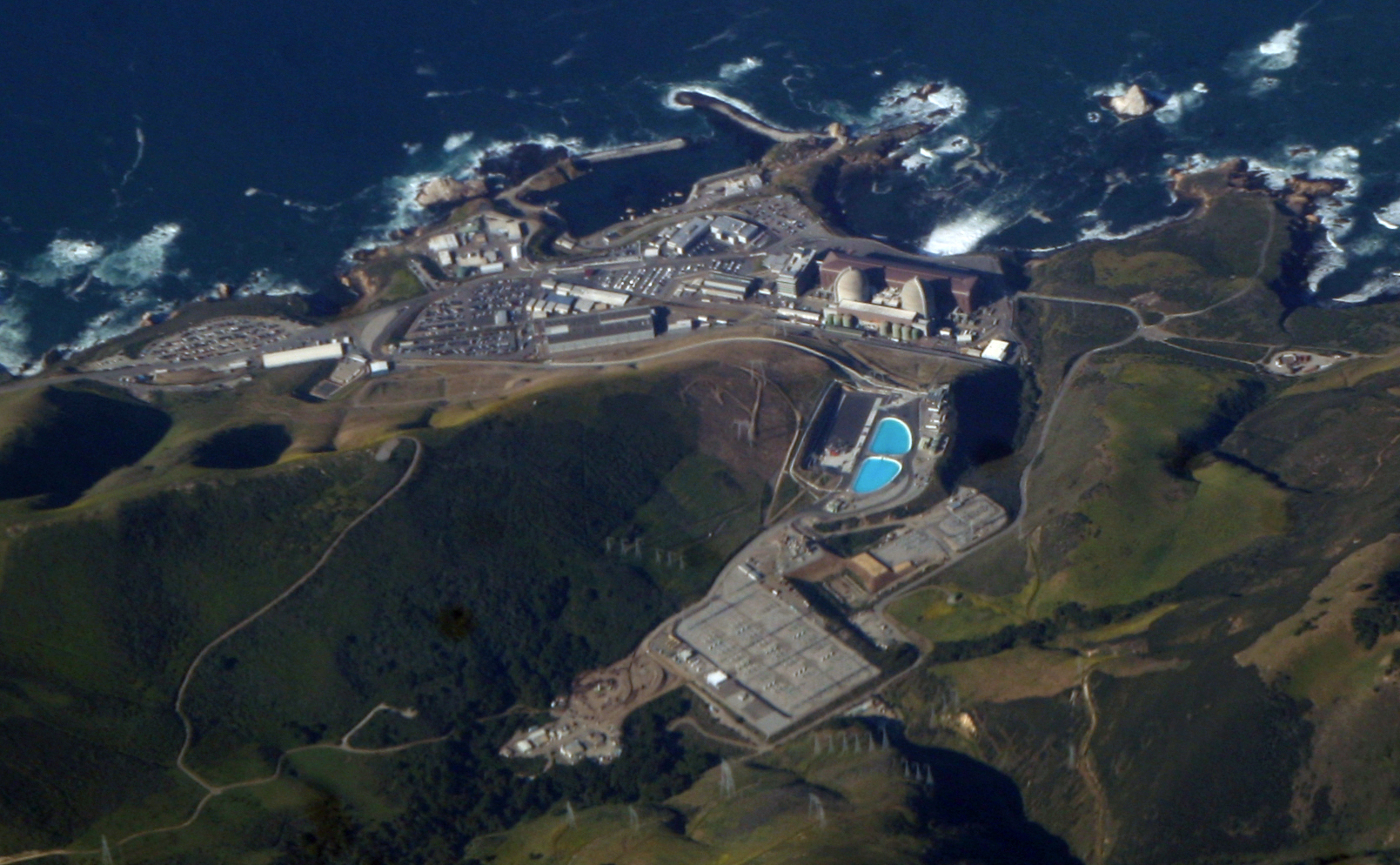
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission announced January 24 that it will not resume its review of Pacific Gas & Electric’s withdrawn Diablo Canyon license renewal application. This decision is a new setback in the long-running effort to extend the life of the plant.
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) has voted to open a rulemaking to consider extending the lifetime of the 2,289-MW two-unit Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant. The plant, which turns 50 this year, is the only remaining operational nuclear power facility in California. It generates nearly 10 percent of the state’s electricity needs.
SHINE’s isotope production building, called the Chrysalis, under construction in October 2022.
In a former farm field just outside the historic town of Janesville in south-central Wisconsin, a large concrete-and-steel building is taking shape. Dubbed the Chrysalis, the building will eventually house eight accelerator-based neutron generators, which start-up company SHINE Technologies will use to produce molybdenum-99. As the precursor to the medical radioisotope technetium-99m, Mo-99 is used in tens of millions of diagnostic procedures every year, primarily as a radioactive tracer.
At the heart of the Chrysalis will be the high-flux neutron generators, being supplied by SHINE’s sister company, Phoenix. The compact accelerators use a deuterium-tritium fusion process to produce neutrons, which in turn induce a subcritical fission reaction in an aqueous low-enriched uranium target (19.75 percent uranium-235) to produce Mo-99.