The Palisades nuclear power plant.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has made Holtec International’s post-shutdown decommissioning activities report (PSDAR) for the closed Palisades nuclear power plant available for public comment until December 27. The NRC also plans to hold a public meeting to discuss the report on the evening of September 22 at the South Haven campus of Lake Michigan College, about 10 miles north of the Palisades site in Covert, Mich.
While many Californians are hopeful the state’s last nuclear power reactor can be saved, PG&E is actively preparing for decommissioning.
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant in San Luis Obispo County, Calif.
(Photo: Wikimedia Commons)
The reports of the death of the Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant may be greatly exaggerated. While Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) announced as early as 2016 that it would be closing California’s last operating nuclear power plant at the end of its current operating license, there has been growing political pressure to keep the plant, and its 2,200 MWe of carbon-free energy, running.
NIST's Center for Neutron Research in suburban Gaithersburg, Md. (Photo: NIST)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission announced on August 2 that it had issued a confirmatory order to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) for violating NRC requirements during a February 2021 fuel failure at the 20-MWt NIST Center for Neutron Research (NCNR) research reactor in Gaithersburg, Md. NIST committed to improving its training for fuel handing procedures and related management activities, safety culture program, reactor facility operations staff and management, corrective action program and operational procedures, and emergency response resources and procedures, among other things.
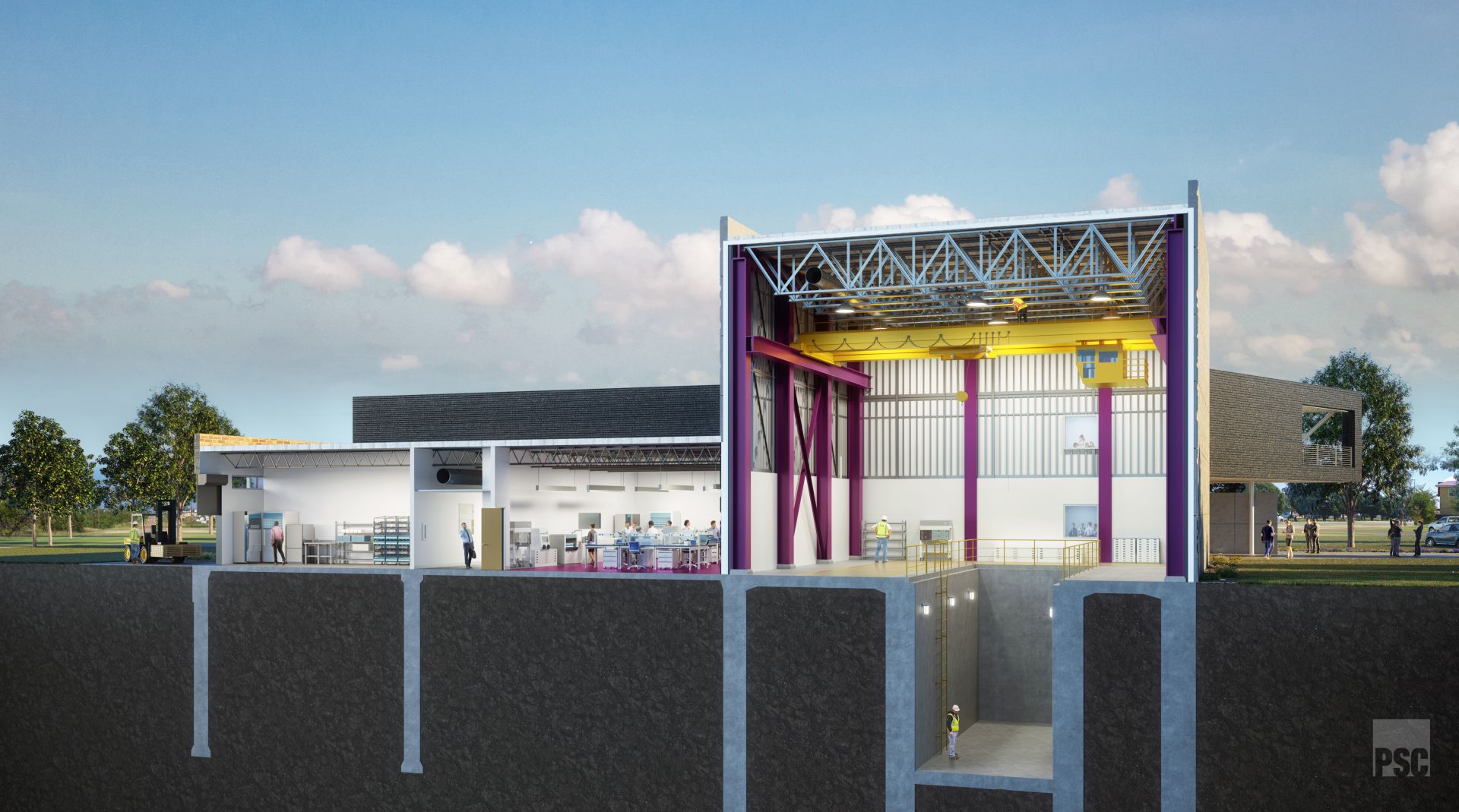
An artist rendering of the Science and Engineering Research Center under construction at Abilene Christian University. The SERC will house the NEXT Lab's new advanced university research reactor sponsored by Natura Resources.
The first university-based molten salt research reactor (MSRR) is one step closer to reality with Abilene Christian University’s Nuclear Energy eXperimental Testing (NEXT) Laboratory recently signing a contract with Teledyne Brown Engineering. After considering more than a dozen engineering firms, the NEXT Lab selected Teledyne Brown to perform the front-end engineering and design work to produce the reactor on the Abilene campus. The contract was described by NEXT Lab director Rusty Towell as “a significant step into the detailed design and construction phase of this project.” The hope is that the 1-MWt MSRR will go critical in 2025.
A rendering of Holtec’s proposed HI-STORE CISF in New Mexico. (Image: Holtec)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has published its final environmental impact statement (EIS) for Holtec International’s proposed HI-STORE consolidated interim storage facility (CISF) for spent nuclear fuel in southeastern New Mexico. Based on its environmental review, the NRC staff recommends issuing the license, subject to the findings in the staff’s ongoing safety review of the application.
Turkey Point nuclear plant. (Image: FPL)
Florida Power & Light (FPL) has submitted a supplemental environmental report to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in support of the subsequent renewed licenses for Turkey Point Units 3 and 4. According to a June 22 NRC press release, FPL’s report was submitted on June 10 to satisfy a “deficiency” in subsequent license renewal applications (SLRA) that rely on the generic environmental impact statement (GEIS) on license renewal and is being reviewed prior to docketing. William D. Maher, director of nuclear licensing projects at FPL, submitted the report, noting that “FPL’s review did not identify any information materially changing the impact assessments” in the NRC’s supplemental GEIS for the Turkey Point licenses.
The Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP), shown here, is a government-backed prototype fusion energy plant planned for operation in the U.K. in the early 2040s. (Image: UKAEA)
Future fusion energy facilities will continue to be regulated by the Environment Agency (EA) and Health & Safety Executive (HSE), the U.K. government announced June 20, and existing law on nuclear regulations will be amended to exclude fusion energy facilities from nuclear fission regulatory and licensing requirements. The move was announced by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) with the expectation it would provide “clarity to developers of prototype/demonstration fusion facilities currently being planned to support rapid commercialization.”
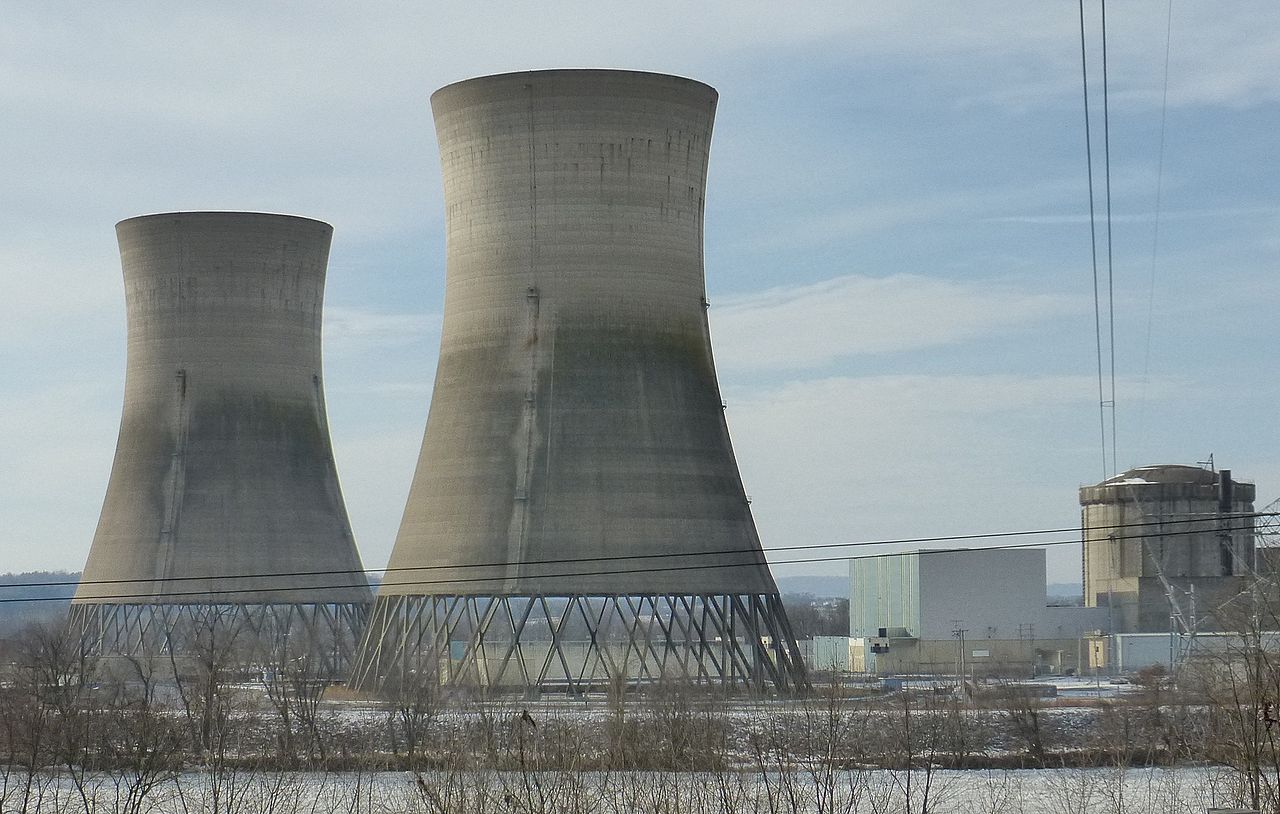
The cooling towers of Unit 2 at Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station, closed since the accident in 1979.
The Three Mile Island accident in 1979 was the most-studied nuclear reactor event in the U.S. There is a plethora of research about the accident available to the general public, including the president-appointed Kemeny Commission report and the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s Rogovin inquiry report (split into volume one, and volume two, parts one, two, and three), which are the two detailed government-sponsored investigations into the accident. There are also thousands of documents in the NRC’s ADAMS database available to the public, an excellent overview by NRC historian Samuel Walker Three Mile Island: A Nuclear Crisis in Historical Perspective, as well as the Nuclear News special report from April 1979, and articles written by ANS members like William Burchill about the accident and the many changes it forced on the industry. If the producers of Meltdown: Three Mile Island—available on Netflix—had read any of those documents instead of relying mostly on input from antinuclear activists, their “documentary” might have been presented with at least some sense of balance and credibility.
Instead, similar to a recent Science Channel documentary on the Three Mile Island accident, Meltdown focuses on drama instead of science. This four-part miniseries does not attempt to provide a balanced set of facts from the technical community and instead relies heavily on nonexpert opinions and anecdotal statements to tell a story that easily falls apart under even the faintest scrutiny.
Nuclear News reached out to multiple ANS members who were involved with either the accident response or the clean up to help provide a critical look at some of the more egregious statements made in the documentary.





.jpeg)