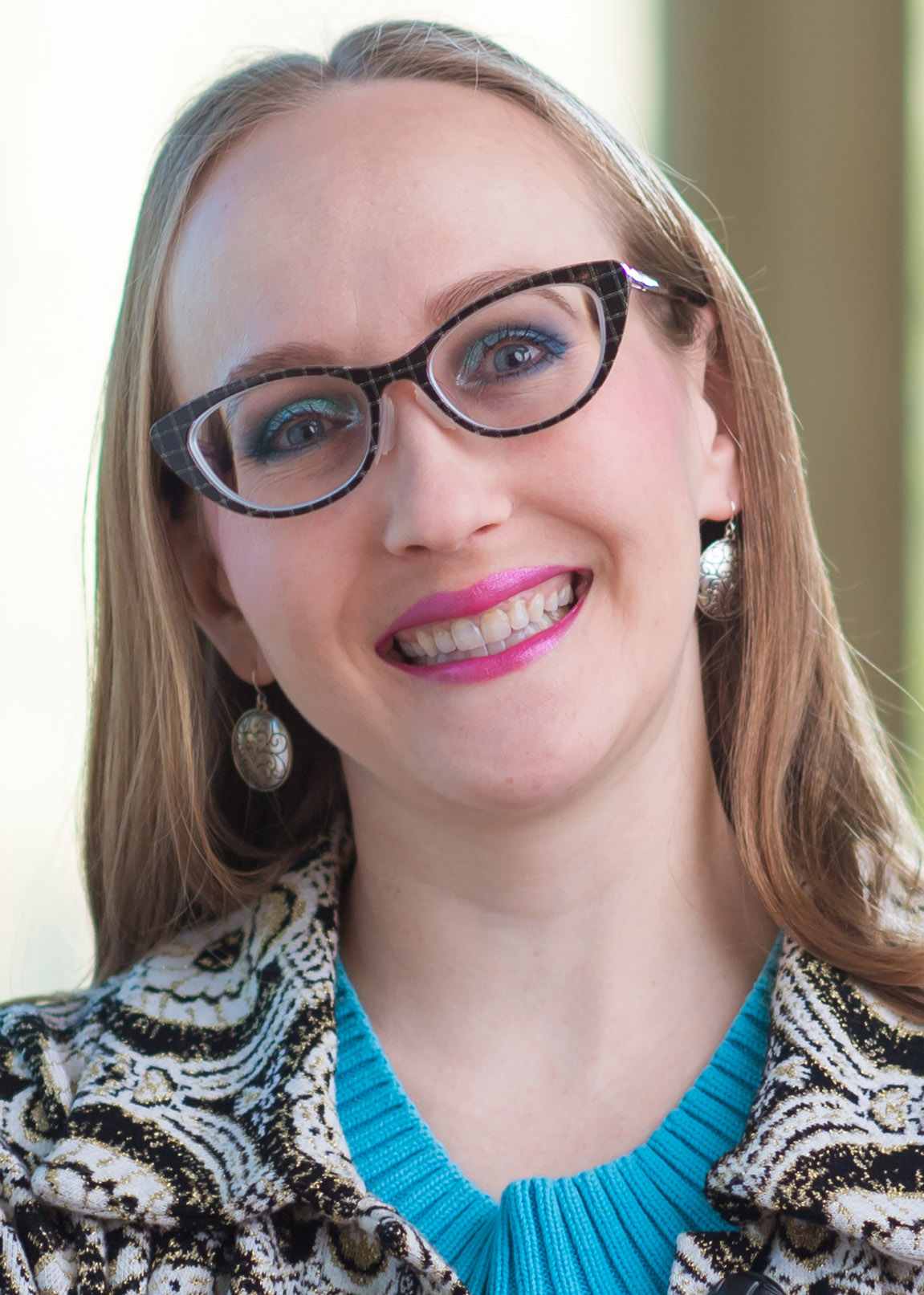
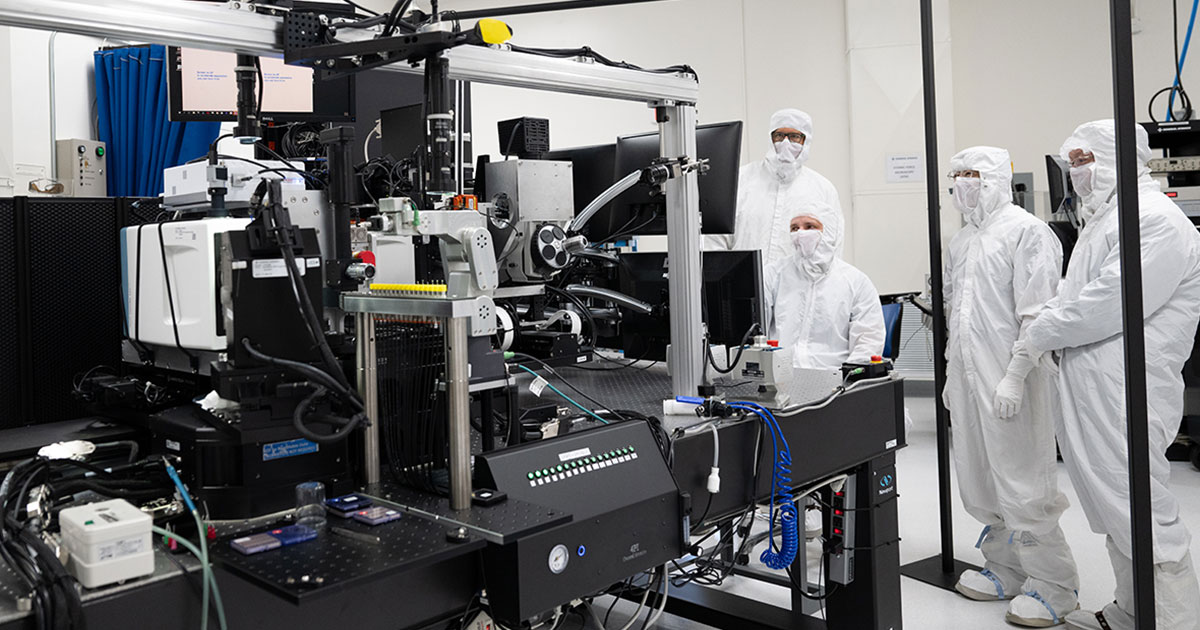
Members of the Metrology Research and Development team working with the 4Pi system in a clean room at GA headquarters. (Photo: General Atomics)
The National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has achieved fusion ignition at least five times, each time by directing its 192 high-powered lasers on a capsule containing a tiny, 2-millimeter target filled with hydrogen fuel. Not every shot achieves ignition, however. Tiny imperfections in the targets can mean fizzle, not fusion. But each of the targets used in successful experiments to date have something in common: they were characterized and selected by the 4Pi Integrated Metrology System, a new measurement system developed by General Atomics. Now, the team behind that system is being recognized.
GA announced last week that its Metrology Research and Development team had won the 2024 "Team of the Year" R&D 100 Professional Award from R&D World. The magazine that each year announces the R&D 100 awards that have been dubbed the “Oscars of Innovation” also selects just one “Team of the Year” and announces that award together with four other professional awards.
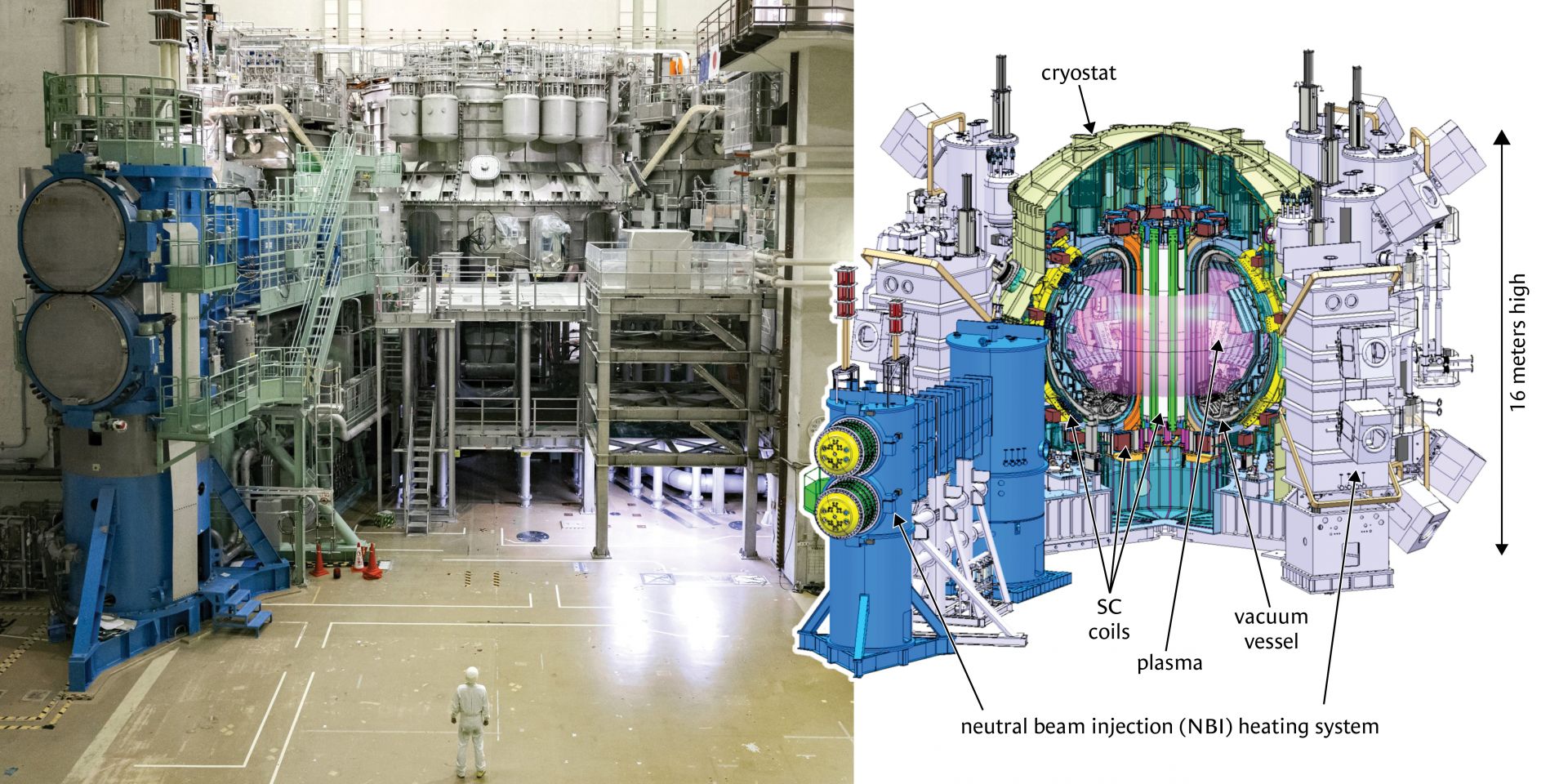
Fig. 1. A photograph (left) and schematic figure (right) of JT-60SA.
(Source: Naka Institute)
JT-60SA (Japan Torus-60 Super Advanced) is the world’s largest superconducting tokamak device. Its goal is the earlier realization of fusion energy (see Fig. 1). Fusion is the energy that powers the Sun, and just 1 gram of deuterium-tritium (D-T) fuel produces enormous energy—the equivalent of 8 tons of crude oil.
Last fall, the JT-60SA project announced an important milestone: the achievement of the tokamak’s first plasma. This article describes the objectives of the JT-60SA project, achievements in the operation campaign for the first plasma, and next steps.
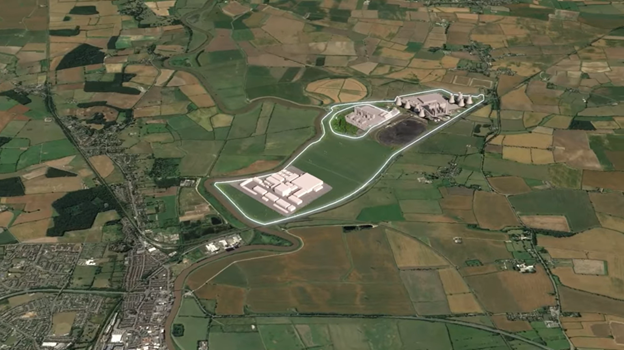
A screengrab from a video released by the STEP program on July 23 illustrating the future home of the prototype fusion power plant. (Image: UKAEA/STEP)
Japan’s recent moves to boost fusion power in the nation’s energy plan and accelerate the timeline for a prototype fusion power plant come in response to increased global attention on fusion energy. Even as ITER faces delays, more than 40 private fusion developers are pursuing different technologies and competing for attention. And so are other countries, including the United Kingdom, which announced its plans for a fusion pilot plant back in 2019. Fusion companies and nations alike are responding to a growing sense that there is a race—or at least collective momentum—to commercialize fusion energy.
Rafael Mariano Grossi, director general of the International Atomic Energy Agency. (Photo: IAEA)
The peaceful uses of nuclear science and technology today hold more promise to heal the world since Austrian Swedish physicist Lise Meitner and her colleagues discovered nuclear fission in 1938, said Rafael Mariano Grossi, director general of the International Atomic Energy Agency, in a new essay titled “Nuclear Must Be Part of The Solution” published by the magazine Foreign Affairs.
Nuclear power plants in operation or under construction as of May 2024. (Source: IAEA)
The recent article “How Innovative Is China in Nuclear Power?” published by the Information Technology and Innovation Foundation (ITIF) describes how China has become the world’s leading proponent of nuclear energy. The reason, the article maintains, is because its nuclear industry has been “supported by a whole-of-government strategy that provides extensive financing and systemic coordination.”
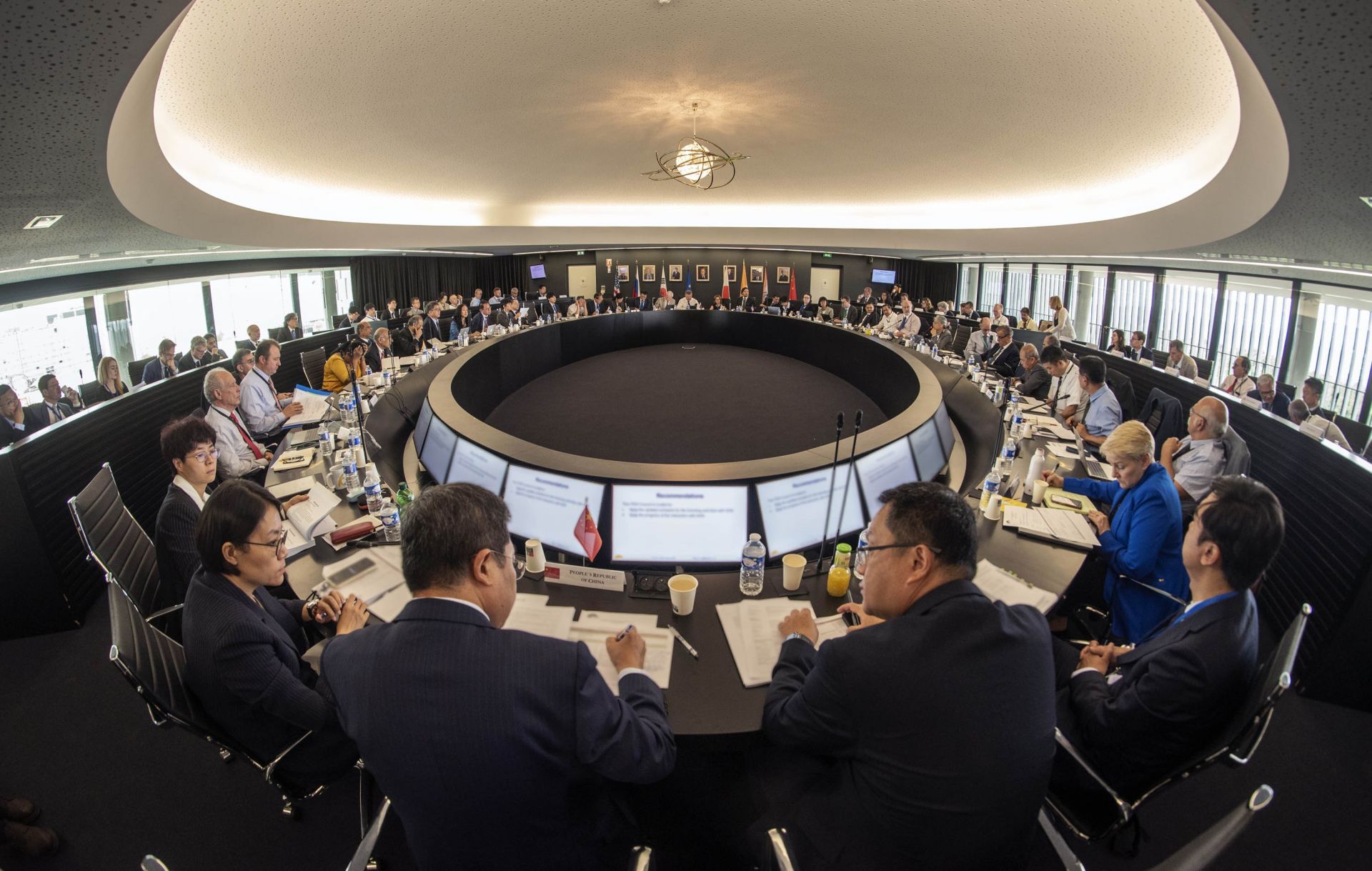
Member delegates, their experts and interpreters, and representatives of the ITER Organization and the ITER domestic agencies convened for the 34th ITER Council. (Photo: ITER)
At the 34th ITER Council Meeting, held June 19–20, ITER director general Pietro Barabaschi reported on ITER’s progress and presented an updated baseline proposal that would “prioritize the start of substantial research operations as rapidly as possible.”
Xcimer Energy’s headquarters in Denver, Colo. (Photo: Xcimer Energy)
Xcimer Energy announced June 4 that it has raised $100 million in Series A financing for a new facility in Denver, Colo., that will host a prototype laser system with “the world’s largest nonlinear optical pulse compression system.” As a private fusion developer, Xcimer wants to “extend the proven science of inertial fusion to industrial scale” with the help of that laser system and “key technologies and innovations from multiple fields.”
Image: Kyle Palmer and Michael Livingston/PPPL Communications Department
The DIII-D Superfacility team. (Photo: General Atomics)
Researchers at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility, the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), and the Energy Sciences Network (ESnet) are teaming up to make the high-performance computing (HPC) powers of NERSC available to DIII-D researchers through ESnet—a high-speed data network. Their collaboration, described in a May 29 news release, in effect boosts the computing power behind DIII-D’s diagnostic tools to make more data from fusion experiments available to researchers at DIII-D in San Diego and to the global fusion research community.
A slide on the FIRE collaboratives presented during a recent FES webinar. (Graphic: FES)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) wants Fusion Innovation Research Engine (FIRE) collaboratives to be a bridge between FES’s basic science research programs and the growing fusion industry. A funding opportunity announcement released May 22 explains that FIRE will be a “transformative initiative aimed at creating a fusion innovation ecosystem” with virtual, centrally managed collaboratives working on “end-use inspired” fusion science and technology R&D.
FFC board members (from left to right) Kiyoshi Seko (KF), Stephen Bushby (CNL), Satoshi Konishi (KF), and Ian Castillo (CNL) in Tokyo, Japan.
Japan’s Kyoto Fusioneering, a fusion startup spun out from Kyoto University, and Canadian Nuclear Laboratories have announced the formation of Fusion Fuel Cycles Inc., headquartered in Chalk River, Ontario, Canada. The joint venture extends a strategic alliance formed between the two entities in September 2023 and aims to develop and deploy deuterium-tritium (D-T) fusion fuel cycle technologies.
Ana Kova’s illustration of different types of fusion. (Image: Ana Kova/Global Fusion Forum)
An engineer adjusts mirrors while installing new diagnostic equipment inside the DIII-D tokamak. (Photo: General Atomics)
The DIII-D National Fusion Facility is starting up after an eight-month experimental hiatus, equipped with new and improved plasma control and diagnostic systems. The upgrades will help researchers from around the nation and the world resolve key physics questions to bridge the gap between current magnetic confinement fusion research and the first fusion power pilot plants. General Atomics, which operates DIII-D for the Department of Energy, announced the completion of upgrades on May 8.
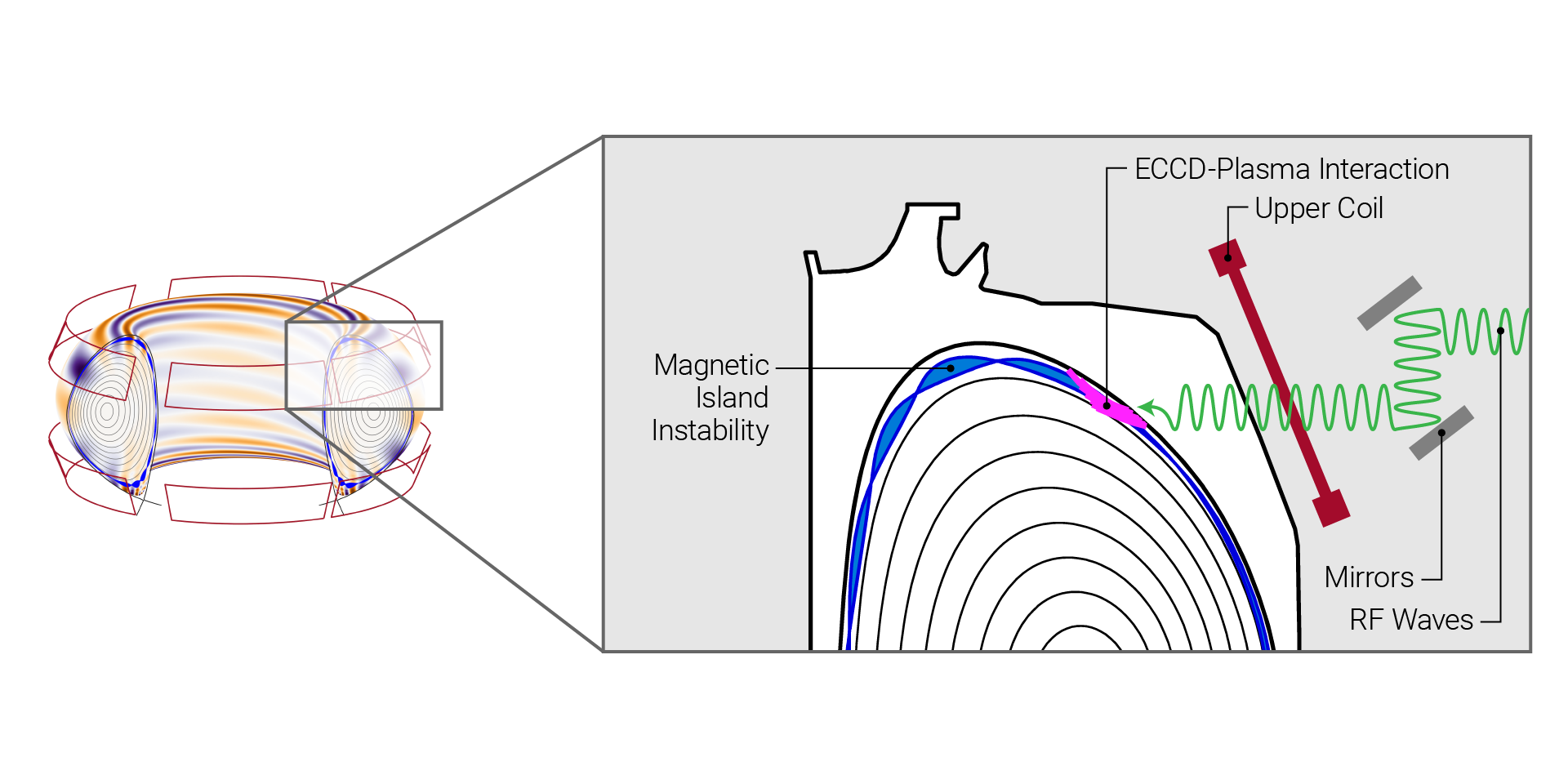
The image on the left shows the tokamak and 3D magnetic perturbation generated by 3D coils, with the purple-blue hues representing lower amplitude perturbations and the red representing higher amplitude perturbations. The image on the right is a closer view showing the top half of the tokamak and plasma. The coils are used to generate the magnetic field perturbations that produce the islands (blue). Another coil can also be found on the bottom of the machine. The injection system for the ECCD microwaves is depicted on top (red). These can be used to adjust the width of the islands. (Image: Qiming Hu / PPPL)
The combination of two previously known methods for managing plasma conditions can result in enhanced control of plasma in a fusion reactor, according to a simulation performed by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory.
The IPP’s Dirk Wünderlich and Ursel Fantz at the experimental testing facility ELISE in Germany. (Photo: MPI for Plasma Physics/Frank Fleschner)
The Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) announced that it recently has achieved a new record for ion current density for neutral particle heating at its ELISE (Extraction from a Large Ion Source Experiment) experimental testing facility in Garching, Germany. ELISE is being used to test neutral beam injection (NBI) systems that will be used to heat the plasma of the ITER fusion experiment in France.




 Following new federal funding and programs announced
Following new federal funding and programs announced