TVA's Bull Run fossil plant. (Photo: TVA)
Type One Energy Group announced plans on February 21 to relocate its headquarters from Madison, Wis., to the Tennessee Valley Authority’s (TVA) Bull Run fossil plant in Clinton, Tenn., where it will build a stellarator fusion prototype machine. According to the company, the construction of the stellarator—called Infinity One—could begin in 2025, if necessary environmental reviews, partnership agreements, permits, and operating licenses are all in hand.
The HL-2M tokamak reactor, developed by the CNNC’s Southwestern Institute of Physics. (Photo: CNNC)
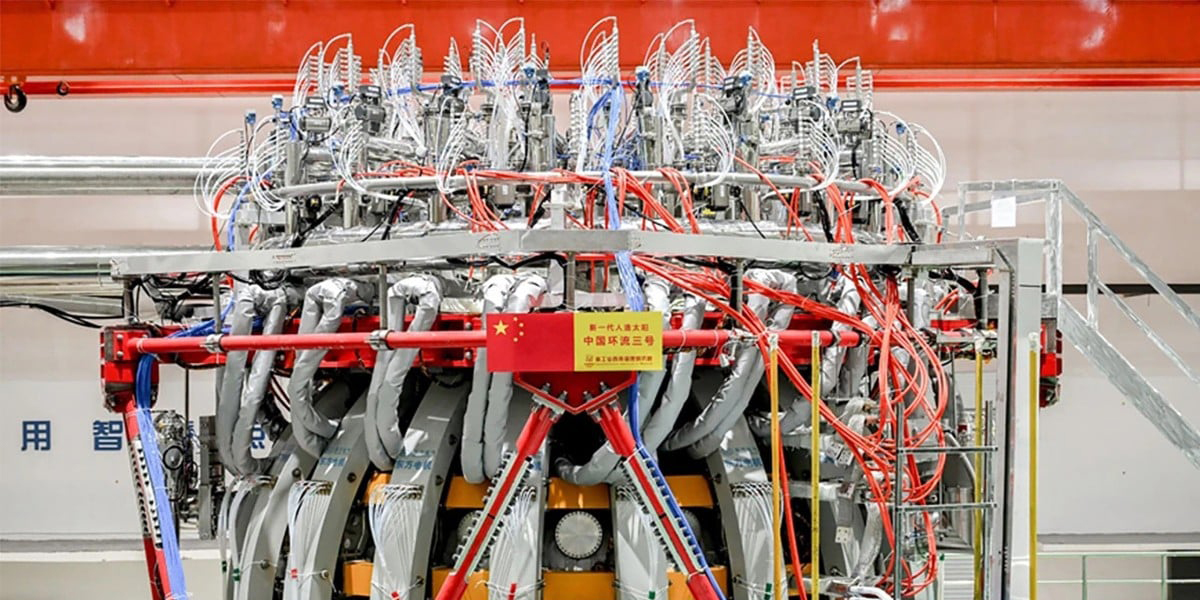
The government of China has formed a new national industrial consortium focused on the development and advancement of nuclear fusion technology, news outlets have reported.
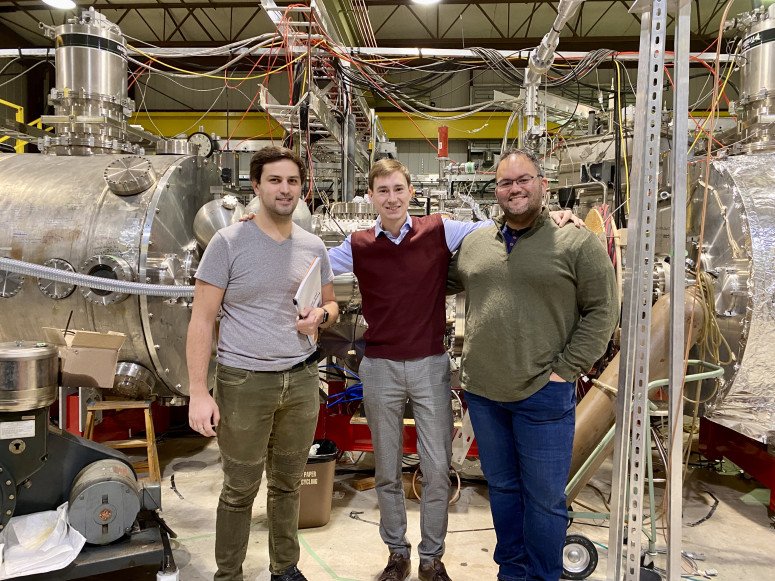
From left, engineer Jeremiah Kirch, postdoctoral researcher Mykola Ialovega, and assistant scientist Marcos Xavier Navarro-Gonzalez pose in front of the WHAM device at UW-Madison. (Photo: Mykola Ialovega)
A new type of cold spray coating, made from the metal tantalum and applied to the plasma-facing steel walls of fusion reactors, could lead to efficient, compact fusion reactors that are easy to repair and maintain, according to a study recently published in the journal Physica Scripta. The study was led by scientists and engineers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and involved researchers from South Korea, France, and Germany.
A slide from the DOE-FES’s recent presentation to the Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee. (Image: DOE)
The Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) in the Department of Energy’s Office of Science introduced a new plan—"Building Bridges: A Vision for the Office of Fusion Energy Sciences”—during a Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee (FESAC) hearing on December 13, and announced that news December 14. What’s included? A plan for the DOE to “establish the steps needed to help advance fusion energy, including addressing key science and technology gaps in the supply chain and industry.” The vision is less a guiding document than a preview of DOE-FES’s near-term intentions, which include drafting a fusion science and technology road map in 2024 to shape investments for the coming decade.
STARFIRE is the name of an inertial fusion energy hub led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory—one of three hubs announced in early December. (Image: LLNL)
The Department of Energy recently announced that it was establishing three inertial fusion energy (IFE) hubs and funding them with a total of $42 million over four years. The leaders of the three hubs selected by competitive peer review—Colorado State University, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, and the University of Rochester—all issued press releases touting the attributes and plans of their facilities and their research collaborators on the same day—December 7.
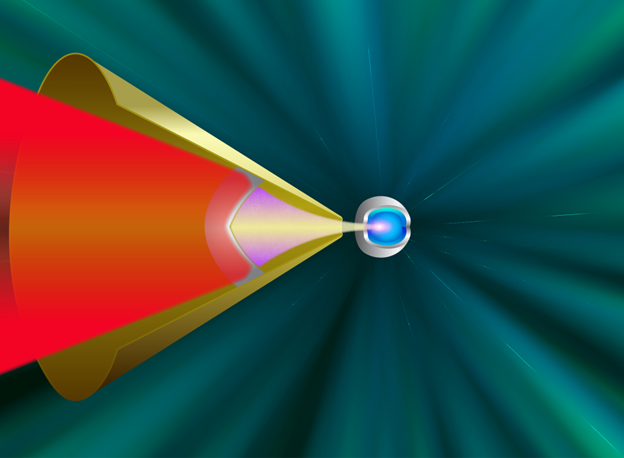
Concept art showing inertial fusion ignition. (Image: Focused Energy)
Focused Energy and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have signed a strategic partnership project agreement that will allow LLNL—home of the National Ignition Facility (NIF)—to help the company develop and assess isochoric compression target designs for inertial fusion energy. Focused Energy announced the news on November 7.
A spent nuclear fuel transportation container. (Photo: DOE)
Fusion systems company SHINE Technologies has notified the Nuclear Regulatory Commission that it intends to submit a license application to build and operate a pilot used nuclear fuel recycling facility.



 A new report,
A new report,