The JET tokamak. (Photo: European Consortium for the Development)
Nuclear fusion “might actually be on the cusp of commercial viability” today, says a recent article in Fortune magazine. The article offers a brief review of recent technical and entrepreneurial developments in fusion energy. It also places these developments in perspective regarding the hurdles that remain before commercialization can be realized.
This still image, taken from a General Fusion video, depicts the demo plant that will be built near Oxford, U.K. (Image: General Fusion)
Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL) and General Fusion have announced a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to “develop fusion energy research capabilities within CNL, to support the goal of constructing a potential General Fusion commercial power plant in Canada before 2030.” The plant would follow on a demonstration-scale plant that General Fusion wants to have operating in the United Kingdom by 2027 to validate the performance and economics of the technology.
The U.S. ITER Project Office in Oak Ridge, Tenn. U.S. ITER has received $256 million in Inflation Reduction Act funding. (Photo: U.S. ITER)
Just days before COP27 and the U.S. midterm elections, the White House announced $1.55 billion in Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) funding for national laboratories and the launch of a Net-Zero Game Changers Initiative based on a new report, U.S. Innovation to Meet 2050 Climate Goals. Out of 37 research and development opportunities identified, fusion energy was selected as one of just five near-term priorities for the new cross-agency initiative. Together, the announcements signal policy and infrastructure support for fusion energy—the biggest chunk of Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC) IRA funding went to ITER, via Oak Ridge National Laboratory—and for advanced nuclear technologies to power the grid and provide process heat to hard-to-decarbonize industrial sectors.
A rendering of the GA fusion pilot plant. (Image: GA)
General Atomics (GA) announced on October 20 that it has developed a steady-state, compact advanced tokamak fusion pilot plant concept “where the fusion plasma is maintained for long periods of time to maximize efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and increase the lifetime of the facility.”
The Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production, shown here in an artist's rendition, is a government-backed prototype fusion energy plant planned for operation in the U.K. in the early 2040s. (Image: UKAEA)
The U.K. Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) and Tokamak Energy announced on October 10 that they signed a framework agreement to collaborate on developing spherical tokamaks for power production. This news is a complement to last week’s announcement from the U.K. government that the West Burton A coal-fired power plant site in Nottinghamshire has been selected as the future home of STEP (Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production), the U.K.’s planned prototype fusion energy plant. The government is providing £220 million (about $250 million) of funding for the first phase of STEP, which will see the UKAEA produce a concept design by 2024.
(Image: Ana Kova /USFusionEnergy.org)
The Department of Energy announced up to $50 million for a new milestone-based fusion energy development program on September 22. The funding opportunity announcement is open to for-profit companies—possibly teamed with national laboratories, universities, and others—that are prepared to meet major technical and commercialization milestones leading to a pilot fusion power plant design.
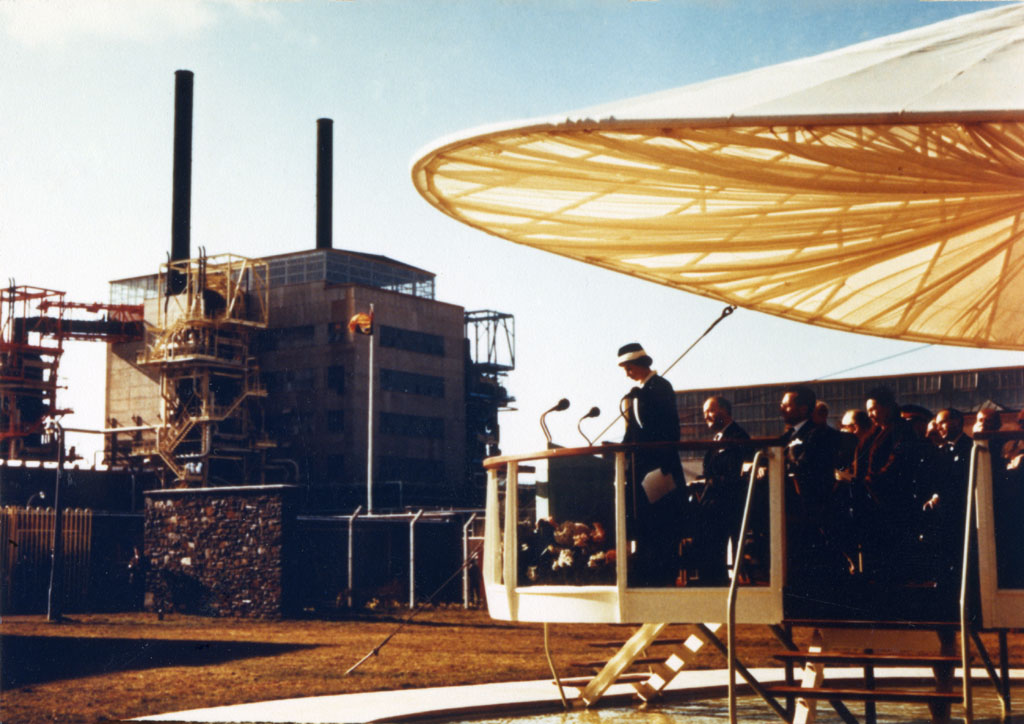
Queen Elizabeth II visits Calder Hall for its ceremonial opening in 1956. (Photo: U.K. Nuclear Decommissioning Authority)
As citizens of the United Kingdom and others around the world mourn the death of Queen Elizabeth II, many have reflected on how the world has changed during the seven decades of the queen’s reign—the same decades that saw the rise of civilian nuclear power.
Calder Hall was already under construction at the Sellafield site in West Cumbria when Princess Elizabeth became queen in 1953. Queen Elizabeth traveled to the site in October 1956 and declared, in a televised ceremony, that “It is with pride that I now open Calder Hall, Britain’s first atomic power station.” Watch the fanfare in a historical clip uploaded to YouTube by Sellafield Ltd below.
The first sector of the ITER vacuum vessel was placed in the assembly pit in May. Here, a technician positions targets on the surface of the component to be used in laser metrology. (Photo: ITER Organization)
Delivery of electricity from fusion is considered by the National Academies of Engineering to be one of the grand challenges of the 21st century. The tremendous progress in fusion science and technology is underpinning efforts by nuclear experts and advocates to tackle many of the key challenges that must be addressed to construct a fusion pilot plant and make practical fusion possible.
A stylized image of a cryogenic target used in NIF experiments. (Image: James Wickboldt/LLNL)
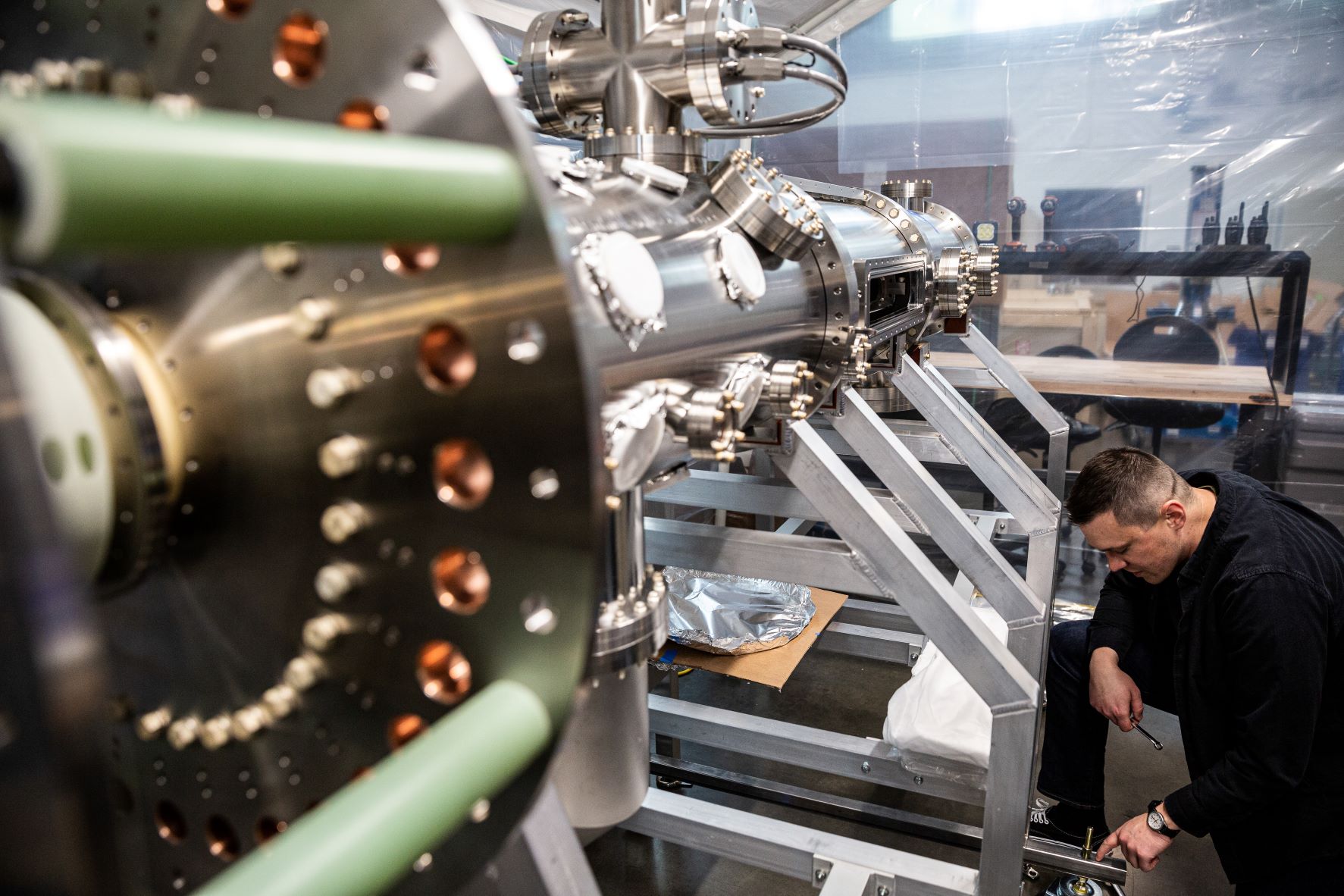
The new TRFS provides for automated adjustment of the direction of the DIII-D primary magnetic field. (Photos: GA and PPPL)
The DIII-D National Fusion Facility now boasts a unique automated system that allows for a quick reversal of the direction of its magnetic field, expanding the range of possible fusion experiments while reducing downtime. General Atomics, which operates the DIII-D for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, announced the new Toroidal Field Reversing Switch (TFRS) on July 26.
Savannah River National Laboratory (Photo: DOE)
When the Department of Energy announced Innovation Network for Fusion Energy (INFUSE) awards earlier this month, Savannah River National Laboratory was named a recipient of two of the 18 awards. SRNL released a statement on July 19 explaining how a national lab with a long history of supporting environmental management and national security missions can lend a hand in the development of future commercial fusion power.
A plaque honoring JET’s world record–setting achievement of fusion energy production of 50 megajoules in a single shot (right) and commemorating a 34-year-old bet between Goldston (top left) and Jacquinot (bottom left). (Photo: PPPL and EUROfusion consortium/collage by Kiran Sudarsanan)
A wager struck by two plasma physicists 34 years ago was finally fulfilled in June during the opening day of the 48th European Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics, when Robert Goldston, former director of the Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), virtually presented a plaque to his friend and colleague Jean Jacquinot, former director of the Joint European Torus (JET), EUROfusion's flagship fusion experiment based at the Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in the United Kingdom. Their bet, and JET’s record-breaking achievements in 2021, were celebrated in an article published by PPPL on July 8.
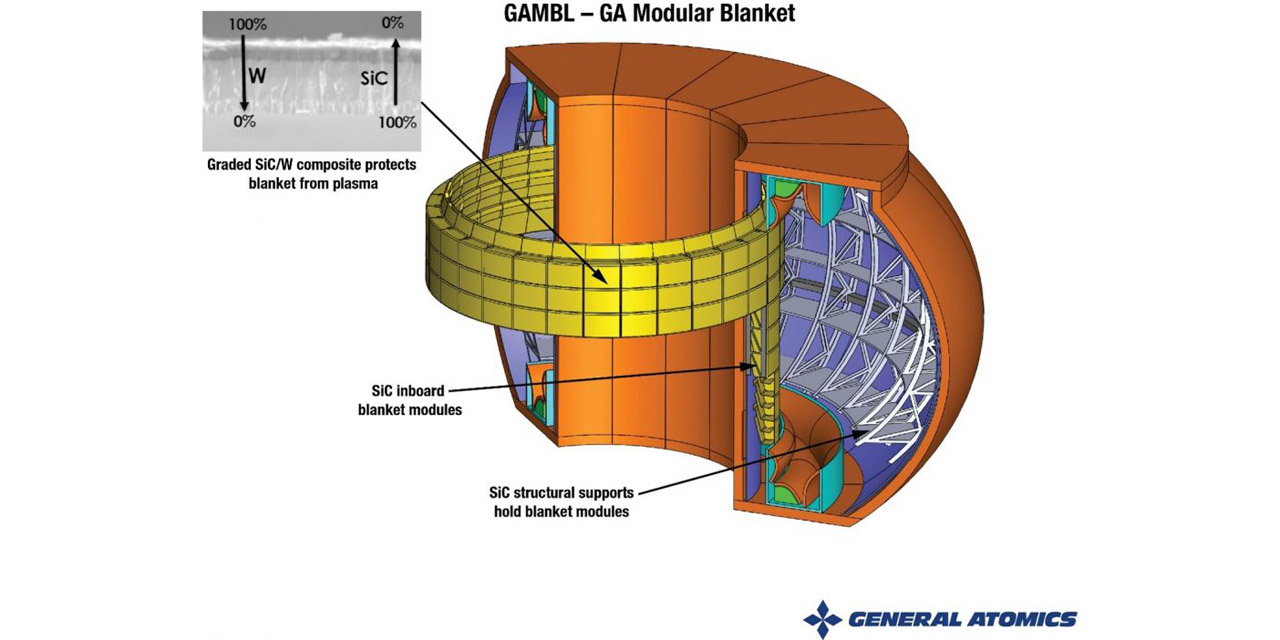
This fusion tokamak cutaway illustrates how the GAMBL concept would be incorporated into a fusion pilot plant. The SiC-tungsten composite wall provides superior heat-removal capabilities and durability, and a modular approach enables fabrication using existing technologies. (Image: GA)
Researchers at General Atomics (GA) are proposing a breeding blanket made of modular silicon carbide–based components to withstand the intense conditions in a high-power fusion power plant. The GA modular blanket (GAMBL) concept is described in an article published this month in the journal Fusion Engineering and Design, and was introduced by GA in a July 13 press release.
The first plasmas created in FuZE-Q, shown here during assembly, represent a key step towards fusion experiments with net energy output. (Photo: Zap Energy)
Zap Energy has created the first plasmas in its FuZE-Q machine—the company’s fourth prototype machine and the one it hopes will demonstrate a net energy gain from a Z-pinch fusion plasma just one millimeter in diameter and half a meter long. Zap Energy announced that engineering achievement and the close of $160 million in Series C funding in late June.
The Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP), shown here, is a government-backed prototype fusion energy plant planned for operation in the U.K. in the early 2040s. (Image: UKAEA)
Future fusion energy facilities will continue to be regulated by the Environment Agency (EA) and Health & Safety Executive (HSE), the U.K. government announced June 20, and existing law on nuclear regulations will be amended to exclude fusion energy facilities from nuclear fission regulatory and licensing requirements. The move was announced by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) with the expectation it would provide “clarity to developers of prototype/demonstration fusion facilities currently being planned to support rapid commercialization.”
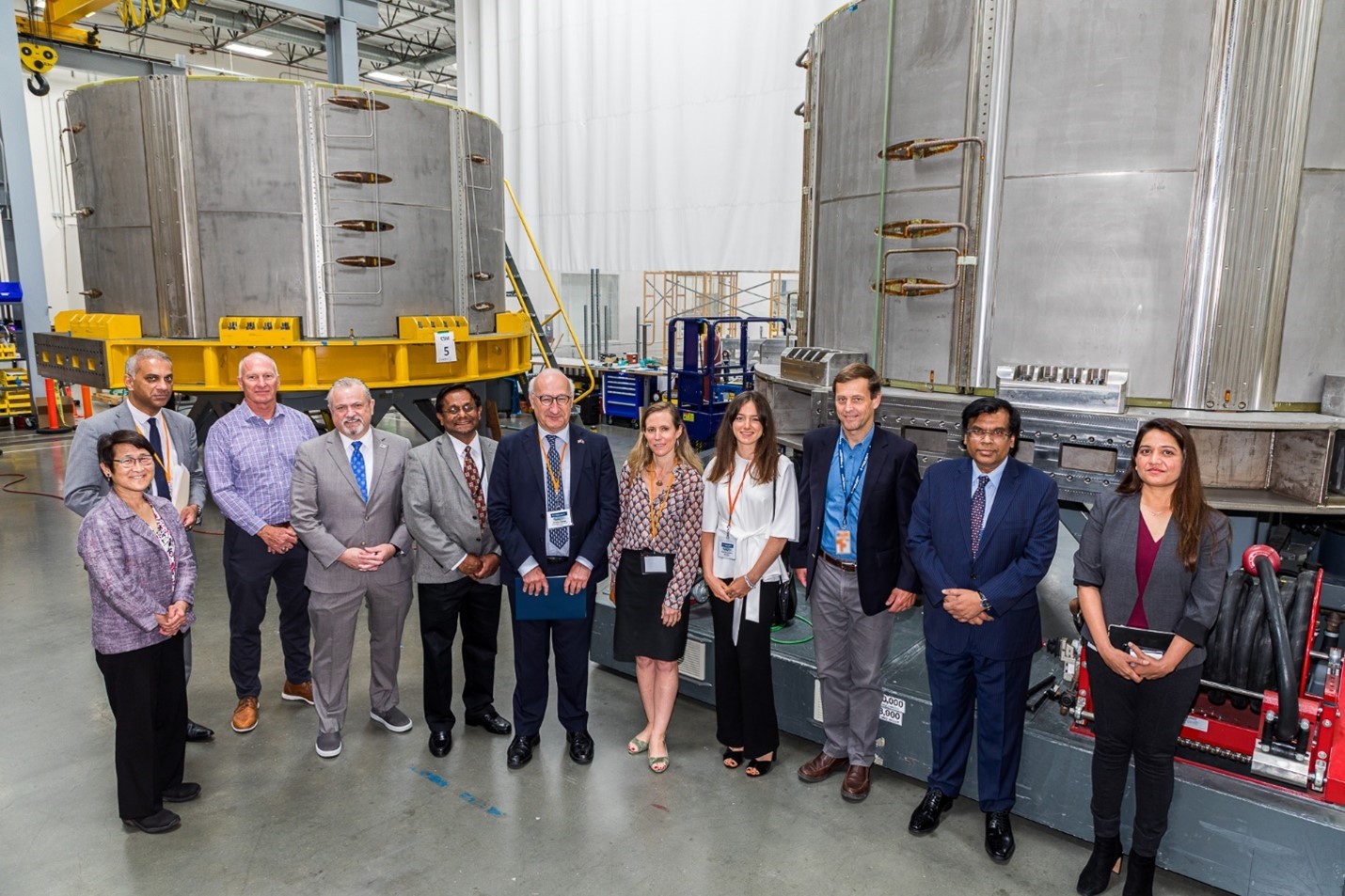
Ambassador Philippe Étienne (sixth from left) and staff from the Consulate General of France with senior leaders from General Atomics at the GA Magnet Technologies Center in Los Angeles. In the background are two partially completed ITER central solenoid modules. (Photo: GA)
General Atomics’ Magnet Technologies Center in Poway, Calif., played host last week to French ambassador Philippe Étienne, the company announced June 16. During the visit, which was hosted by Vivek Lall, chief executive of the General Atomics Global Corporation, Étienne viewed ITER central solenoid modules—all destined for shipment to France—in several stages of the fabrication process.
“General Atomics and French organizations have a strong relationship in both the defense and energy sectors, as well as in the unmanned field, that meet both France’s and the United States’ important interests,” Étienne remarked during his visit.
Session moderator Scott Hsu (left) led a discussion with (from left) Troy Carter, Kathy McCarthy, Artem Smirnov, Satoshi Konishi, and Jane Hotchkiss during an ANS Annual Meeting executive session on “The New Fusion Outlook.”
A “bold decadal plan” to accelerate fusion research, development, and demonstration in partnership with the private sector emerged from a March 2022 White House Fusion Summit and inspired the June 14 ANS Annual Meeting executive session titled “The New Fusion Outlook.” Moderator Scott Hsu, who is leaving a role as a program director for the Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy (ARPA-E) to become a senior adviser to the DOE’s undersecretary for science and innovation as well as lead fusion coordinator for the DOE, ably led a panel of fusion stakeholders representing universities, national laboratories, private fusion companies, and public policy and communication. The discussion intended to bring attendees with fission experience up to speed on the rapidly accelerating area of fusion energy and explore how the fusion energy community can work toward a unique path for fusion energy regulation and public engagement.