Construction of Norman was completed in 2017. Photo: TAE Technologies
TAE Technologies has announced that it has produced a stable plasma of over 50 million degrees celsius inside a fusion device using a beam-driven, field-reversed configuration. “By generating such stable high-temperature plasmas, TAE has now validated that the company’s unique approach can scale to the conditions necessary for an economically viable commercial fusion power plant by the end of the decade,” the company declared in its April 8 press release. The company added that the results indicate the design’s linear configuration improves plasma confinement as temperatures rise.
In this illustration of the effects of two neutron yields (50 kt and 1 Mt) and two neutron energies (14.1 MeV and 1 MeV), the black dots represent the location of a nuclear device. Dark blue indicates where the asteroid remains solid, while all other colors show where material has been melted or vaporized. The illustration depicts asteroids with 0.8-m and 5-m diameters—much smaller than the 300-m asteroid simulated in the study—to enhance the visibility of the area of the energy deposition. Image: LLNL
A research collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and the Air Force Institute of Technology (AFIT) has investigated how the neutron energy generated by the detonation of a nuclear device could affect the path and speed of an asteroid on a collision course with Earth by melting and vaporizing a portion of the asteroid. The research, which compared the deflection caused by two different neutron energies—14.1 MeV and 1 MeV, representing fusion and fission neutrons, respectively—is described in an article published by LLNL on April 8.
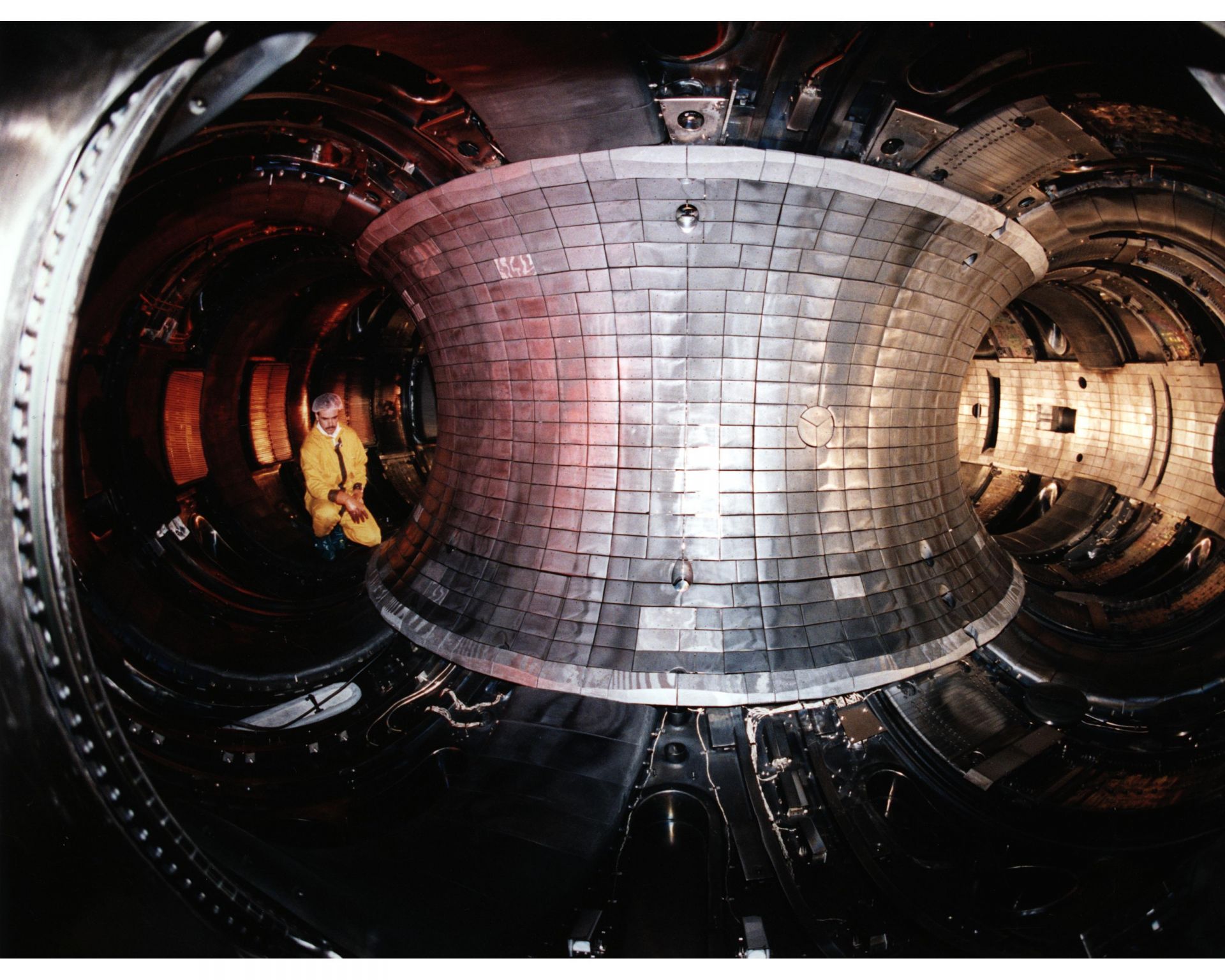
The outside of the DIII-D tokamak, where testing that supports the development of the Compact Advanced Tokamak has been performed. Photo: General Atomics
Scientists at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility have published research on a compact fusion reactor design they say could be used to develop a pilot-scale fusion power plant. According to General Atomics (GA), which operates DIII-D as a national user facility for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, the Compact Advanced Tokamak (CAT) concept uses a self-sustaining configuration that can hold energy more efficiently than in typical pulsed configurations, allowing the plant to be built at a reduced scale and cost.
Photos of physicist Alessandro Bortolon and the element boron; graph and photo showing the interior of a tokamak. Credit: Alexander Nagy and Alessandro Bortolon/Collage courtesy of Elle Starkman, PPPL
Research led by scientists at the Department of Energy's Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) provides new evidence that particles of boron, the main ingredient in Borax household cleaner, can coat internal components of doughnut-shaped plasma devices known as tokamaks and improve the efficiency of the fusion reactions, according to an article published on Phys.org on April 2.








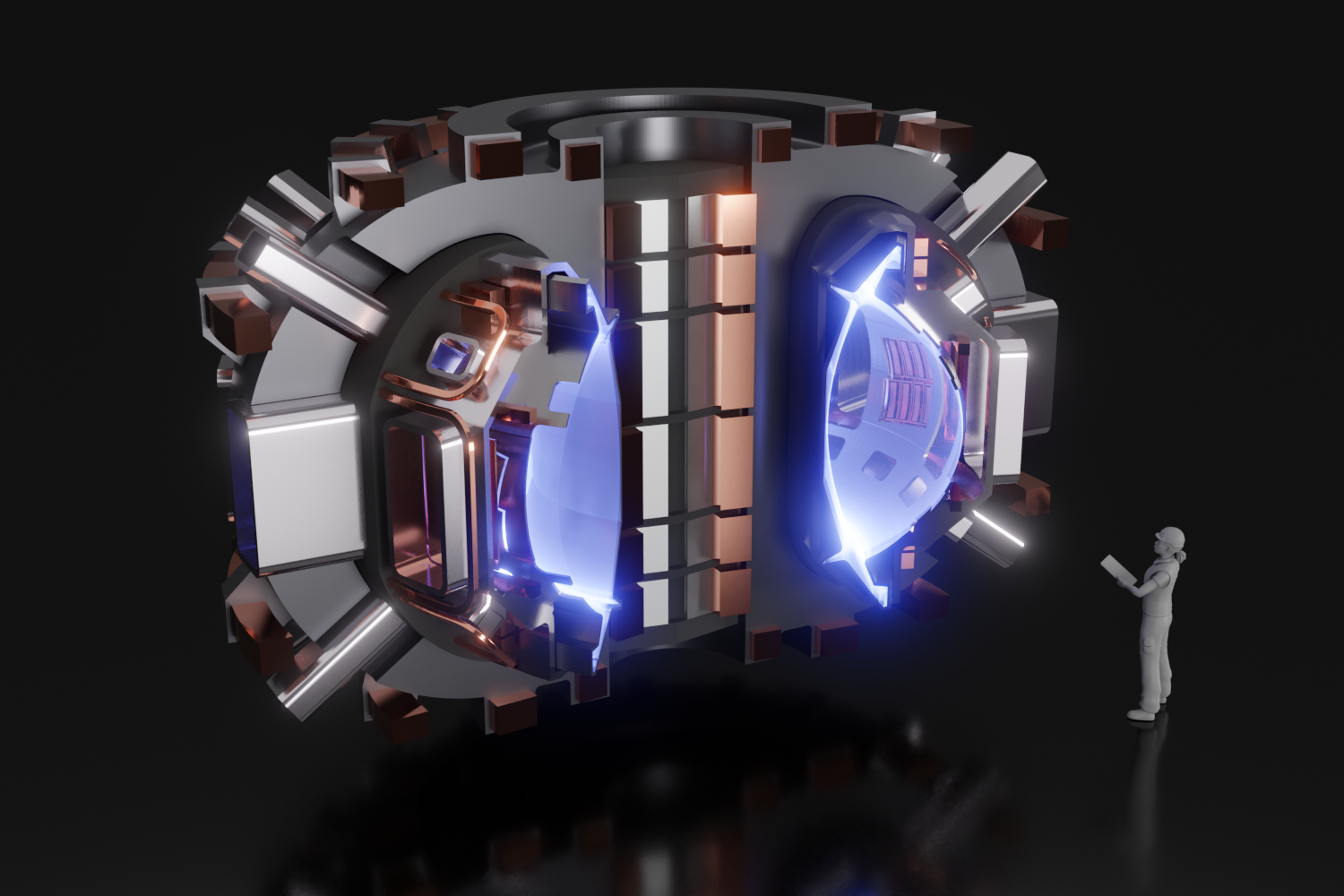
 Coordinated federal and private industry investments made now could yield an operational fusion pilot plant in the 2035–2040 time frame, according to
Coordinated federal and private industry investments made now could yield an operational fusion pilot plant in the 2035–2040 time frame, according to 


 The Fusion Energy Science Advisory Committee (FESAC), which is responsible for advising the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, on December 4 published the first public draft of
The Fusion Energy Science Advisory Committee (FESAC), which is responsible for advising the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, on December 4 published the first public draft of