Gary Senn and Kim Mitchell assist second graders from Chukker Creek Elementary School in Aiken, S.C., with a STEM project.
For almost four decades, the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina and the Ruth Patrick Science Education Center at the University of South Carolina–Aiken (USC Aiken) have partnered to bring science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) education to the area's kindergarten through 12th grade students.
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant. (Photo: DOE)
A pair of recent reports by the U.S. Government Accountability Office and the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine highlight some of the challenges the Department of Energy faces in treating the millions of gallons of legacy radioactive waste at the Hanford Site in Washington state.
(Photo: Nielander/WikiCommons)
Westinghouse Electric Company says its eVinci microreactor technology is “100 percent factory built and assembled before it is shipped in a container to any location.” And “any location” is not restricted to planet Earth, given the company’s goal of sending a scaled-down version of eVinci to the lunar surface or on a mission to provide power in other space applications.
Announcing the funding for commercial fusion energy development were Asmeret Asefaw Berhe (top left), director of the DOE-OS; Jennifer Granholm, secretary of energy (top right); and Arati Prabhakar (bottom), director of the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy and science advisor to the president.
From a crowded field of would-be fusioneers, the Department of Energy has selected eight companies for the public-private Milestone-Based Fusion Development Program to develop fusion pilot plant designs and resolve related scientific and technological challenges within five to 10 years. The DOE announced awards totaling $46 million for an initial 18 months of work on May 31.
Jared Wicker of SRNS explains how different technologies are used to monitor the environment at SRS. (Photo: DOE)
Claflin University students recently toured the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina to learn about the facilities and occupations there.
The NWMO’s Laurie Swami (left) and the DOE’s Kathryn Huff sign a statement of intent to cooperate on used nuclear fuel management in Washington, D.C., on May 16. (Photo: CNW Group/NWMO)
The United States and Canada will cooperate on spent nuclear fuel management under a statement of intent (SOI) signed between the U.S. Department of Energy and the Nuclear Waste Management Organization, the nonprofit responsible for the management of Canada’s commercial spent fuel.
DOE-EM officials, IWTU employees, and others signed the first stainless steel canister prior to crews filling it with sodium-bearing waste and simulant. Once filled, that canister and 15 others were placed in a concrete vault for storage. (Photo: DOE)
Since the launch of operations just over a month ago, the Integrated Waste Treatment Unit (IWTU) at Idaho National Laboratory has increased sodium-bearing waste treatment fivefold. This activity is a vital step in removing the remaining liquid waste from nearby underground tanks at the site and protecting the underlying Snake River Plain Aquifer.
Energy secretary Jennifer Granholm addresses an audience of lab staff, dignitaries, and media at LLNL. (Photo: LLNL)
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory hosted current and former staff, government officials, and media on May 8 to celebrate the lab’s achievement of fusion ignition at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) on December 5, 2022. Energy secretary Jennifer Granholm and undersecretary for nuclear security and National Nuclear Security Administration administrator Jill Hruby were in attendance, and Granholm took the opportunity to announce funding of up to $45 million to support inertial fusion energy (IFE) research and development. The Department of Energy’s Office of Science (DOE-SC) wants to establish multiple IFE Science and Technology Innovation Hubs (IFE S&T hubs), with total funding for 2023 of up to $9 million for projects lasting up to four years in duration.
For the first time in 26 years, work crews performed sampling of gaseous byproducts at the MSRE. (Photo: DOE)
Crews recently replaced a motor in a crane at the SRS H Canyon for the first time in the facility’s 70-year history. (Photo: DOE)
Work crews at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina recently replaced a motor on a crane in the 70-year-old H Canyon Chemical Separations Facility. H Canyon is the only production-scale, radiologically shielded chemical separations plant in operation in the United States.
A still image from an ORNL video demonstrating the VIPER technology. (Credit: ORNL)
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a method of using augmented reality (AR) to create accurate visual representations of ionizing radiation, and that technology has just been licensed by Teletrix, a Pittsburgh, Pa.-based firm that develops simulators to train radiological workers and radiological control technicians. ORNL announced the news on May 4.
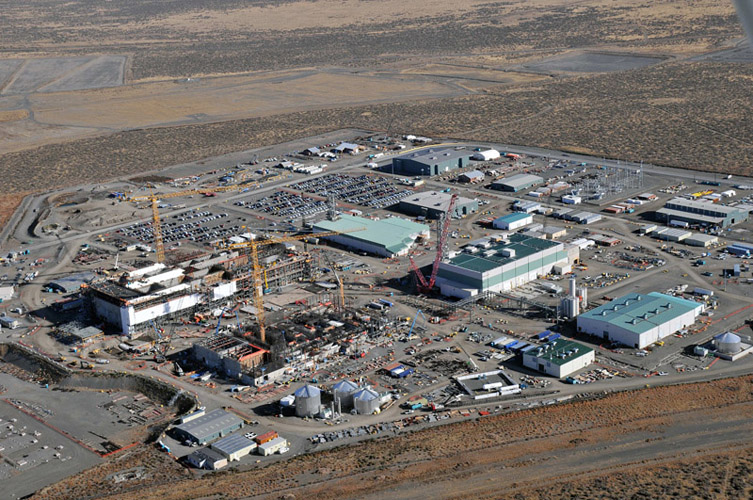
The Hanford Site’s B Complex area tank farm containing waste created during the production of plutonium at the site. (Photo: DOE)
After nearly three years of discussions and more than 60 mediation sessions, the Department of Energy, Washington State Department of Ecology, and the Environmental Protection Agency announced that they have reached a conceptual agreement on revising plans for managing millions of gallons of waste stored in tanks at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash.
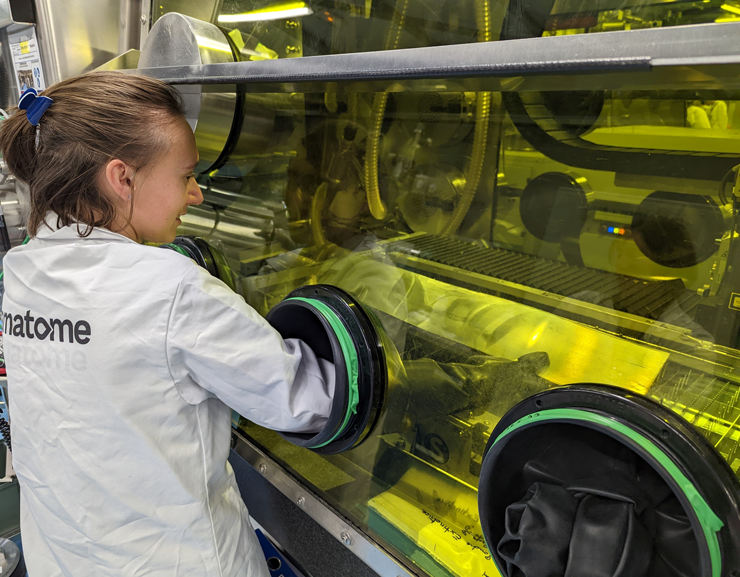
A Framatome operator fabricates U-Mo foils at CERCA. (Photo: Framatome)
Framatome is prepared to manufacture a novel molybdenum-uranium (U-Mo) fuel to extend the life and safe operation of the Forschungsreaktor München II (FRM II) research reactor in Germany. A new fuel supply—one that uses uranium enriched to less than 20 percent U-235—means the FRM II can continue to supply neutrons to industry and the scientific community. The fuel is “Europe’s low-enriched fuel with the highest density ever realized for research reactor operations,” according to Framatome’s April 27 announcement.
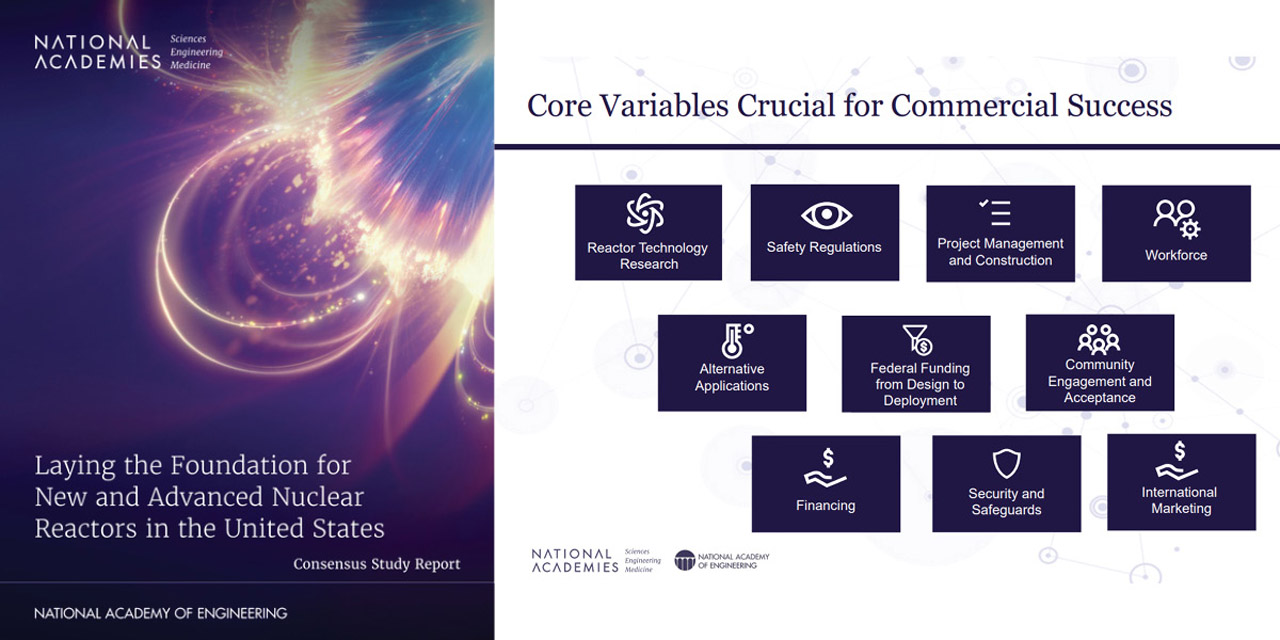
This slide on the right from the consensus committee’s public briefing identifies 10 core variables that are important to the success of advanced reactor deployments. (Image: NASEM, Laying the Foundation for New and Advanced Nuclear Reactors in the United States)