The U.S. Department of Energy’s Light Water Reactor Sustainability Program, led by Idaho National Laboratory, works closely with utilities to improve outage efficiencies and enable nuclear to go “toe-to-toe economically” with other energy sources.
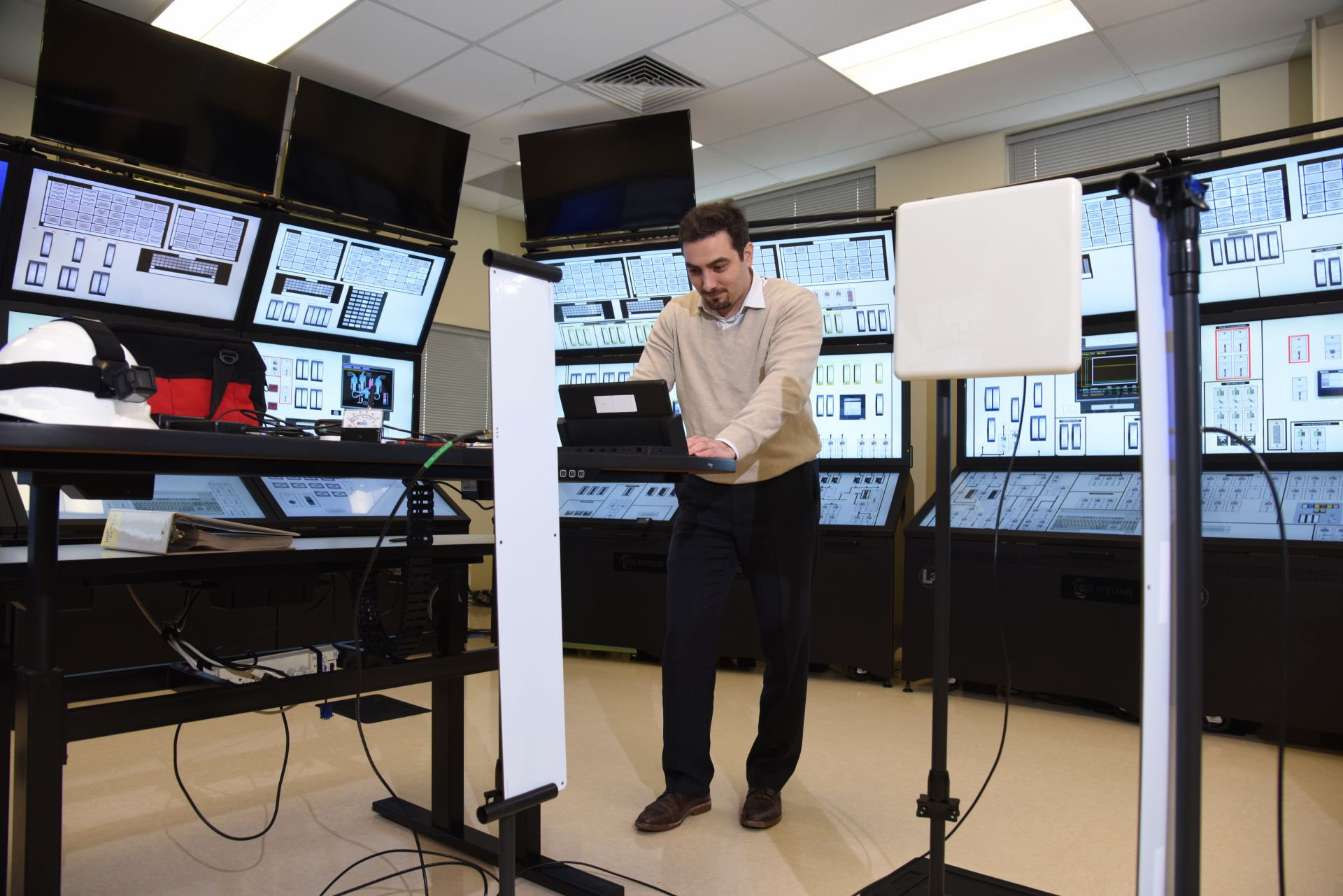

Working in INL’s Human Systems Simulation Laboratory, senior R&D scientist Ahmed Al Rashdan co-developed the Advanced Remote Monitoring project for the LWRS Program.
There are numerous similarities between auto racing pit crews and the people in the nuclear power industry who get us through outages: Pace. Efficiency. Diagnostics. Teamwork. Skill. And safety above all else.
To Paul Hunton, a research scientist at Idaho National Laboratory, the keys to successfully navigating a nuclear plant outage are planning and preparation. “When you go into an outage, you are ready,” Hunton said. “You need to manage outage time. You want to avoid adding delays to the scheduled outage work because if you do, it can add a couple million dollars to the cost.”
Hunton was the principal investigator for the September 2019 report Addressing Nuclear Instrumentation and Control (I&C) Modernization Through Application of Techniques Employed in Other Industries, produced for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Light Water Reactor Sustainability (LWRS) Program, led by INL. Hunton drew on his experience outside the nuclear industry, including a decade at Newport News Shipbuilding.
The 40-year effort to make research reactors safer and more secure has led to the conversion of 71 reactors worldwide from HEU fuel to LEU.
The Ghana Research Reactor-1, located in Accra, Ghana, was converted from HEU fuel to LEU in 2017. Photo: Argonne National Laboratory
In late 2018, Nigeria’s sole operating nuclear research reactor, NIRR-1, switched to a safer uranium fuel. Coming just 18 months on the heels of a celebrated conversion in Ghana, the NIRR-1 reboot passed without much fanfare. However, the switch marked an important global milestone: NIRR-1 was the last of Africa’s 11 operating research reactors to run on high-enriched uranium fuel.
The 40-year effort to make research reactors safer and more secure by replacing HEU fuel with low-enriched uranium is marked by a succession of quiet but immeasurably significant milestones like these. Before Africa, a team of engineers from many organizations, including the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, concluded its conversion work in South America and Australia. Worldwide, 71 reactors in nearly 40 countries have undergone conversions to LEU, defined as less than 20 percent uranium-235. Another 31 research reactors have been permanently shut down.
 The Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) is at work developing and demonstrating novel energy technologies and connecting those technologies with private-sector investors. The researchers and innovators behind ARPA-E want to tell you all about it in a series of “Energy Briefs” available through the agency’s YouTube channel.
The Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) is at work developing and demonstrating novel energy technologies and connecting those technologies with private-sector investors. The researchers and innovators behind ARPA-E want to tell you all about it in a series of “Energy Briefs” available through the agency’s YouTube channel.





